Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Divisions of Biology and Biologists
Uploaded by
liklik_phCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Divisions of Biology and Biologists
Uploaded by
liklik_phCopyright:
Available Formats
Angelique P.
Hibaya II- Amethyst Zamboanga del Norte National High School Activity 2 Divisions of Biology and Biologists
Aerobiology: organic particles, such as bacteria Agriculture: farming Anatomy: internal structures of living things Astrobiology: living things within the universe Biochemistry: use of chemistry in living things Bioengineering: use in engineering of biological organisms Bioinformatics: information technology to life sciences Biomathematics: use of mathematics in living things Biomechanics: mechanical principles to living organisms Biomedical research: human body in health and disease Biophysics: use of physics in living things Biotechnology: manipulation of living matter Building biology: indoor living environment Botany: plants Cell biology: cell as a complete unit Conservation Biology: habitat preservation and protection Cryobiology: effects of organisms at low temperatures Developmental Biology: development of an organism Ecology: relationships of organisms and their environment Embryology: development of embryos Entomology: insects Environmental Biology: natural world, as a whole Epidemiology: spread and control of diseases Ethology: animal behavior Evolutionary Biology: evolution of species over time Genetics: genes and heredity Herpetology: reptiles and amphibians Histology: cells and tissues Ichthyology: fish Integrative biology: whole organisms Limnology: inland waters Mammalogy: mammals Marine Biology: ocean ecosystems and organisms Microbiology: microorganisms and their interactions Molecular Biology: molecular basis of biological activity Mycology: fungi Neurobiology: cells of the nervous system Oceanography: ocean Oncology: cancer processes Ornithology: birds Population biology: the populations of organisms Paleontology: fossils Pathology: diseases Parasitology: parasites and parasitism Pharmacology: drugs Physiology: function of living systems Phytopathology: plant diseases Psychobiology: biological bases of psychology Sociobiology: biological bases of sociology Structural biology: molecular structure of biological macromolecules Virology: viruses Zoology: animal Atony Van Leeuwenhoek (1632-1723) - invented a simple microscope and studied living cells August Weismann (1834-1914) - introduced Germ plasm theory in 1892 Alexander Fleming (1881-1955) - discovered Penicillin Carolus Linnaeus (1707-1778) - introduced Binomial Nomenclature for naming plants and animals Charles Robert Darwin (1809-1882) - proposed the theory of Pangenesis - proposed Origin of species Empedocles (495-425 BC) - stated source of body temperature was blood - proposed concept of evolution Gregor Johann Mendel (1822-1884) - discovered principles of inheritance Georges Leopold Cuvier (1769-1832) - founded Paleontology and comparative anatomy Hans Krebs (1900-1981) - discovered the "trycarboxilic acids cycle", also named "Krebs cycle" Jean Baptiste De Lamarck (1744-1829) - proposed inheritance of acquired characters - discarded the idea of fixity of species Louis Pasteur (1822-1895) - proposed 'Germ theory of disease' - discovered vaccine against 'Anthrax' - proposed pasteurization for sterilization Robert Hooke (1935-1945) - assembled a compound microscope - discovered cells in cork Rita Levi-Montalcini (1909) - discovered nerve-growth factor (NGF), the first cell-growth factor discovered Theodor Schwann (1810-1882) - proposed cell theory in 1839 by his study on animal tissue William Harvey (1578-1657) - discovered blood circulation Thomas Hunt Morgan (1866-1945) - discovered sex linked inheritance - laid foundation of gene theory
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5784)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Biliary Atresia Copy LNGDocument10 pagesBiliary Atresia Copy LNGlloraoNo ratings yet
- Surgery Papillary Thyroid CADocument15 pagesSurgery Papillary Thyroid CAMelissa LabadorNo ratings yet
- Phase 1 Mixed - MCQDocument74 pagesPhase 1 Mixed - MCQLee June LyngNo ratings yet
- Neuropsych Lec 5 Mental Status ExamDocument2 pagesNeuropsych Lec 5 Mental Status ExamnkivcNo ratings yet
- CysticfibrosisDocument6 pagesCysticfibrosisSghir SghirNo ratings yet
- Hematopoiesis (Occurs in The Liver) Is Considered As The Counterpart in Fetal DevelopmentDocument17 pagesHematopoiesis (Occurs in The Liver) Is Considered As The Counterpart in Fetal DevelopmentEG Ongteco Gonzaga OngtecoNo ratings yet
- DermatologyDocument121 pagesDermatologyjimisurgon83100% (4)
- 705 FullDocument11 pages705 FullNguyễn HùngNo ratings yet
- MP 0035 BulDocument3 pagesMP 0035 BulRayane Teles de FreitasNo ratings yet
- Training On Molecular Biology, Biotechnology, DNA Fingerprinting and DNA Barcoding Organized by Genomics Research Labs New Delhi India-110092Document9 pagesTraining On Molecular Biology, Biotechnology, DNA Fingerprinting and DNA Barcoding Organized by Genomics Research Labs New Delhi India-110092Escherichia GenomicsNo ratings yet
- UNIT 3.0 Medical Technology CurriculumDocument12 pagesUNIT 3.0 Medical Technology CurriculumJean Carmelette BalalloNo ratings yet
- Rare Case of Malignant Phylloides Cystosarcoma in PregnancyDocument29 pagesRare Case of Malignant Phylloides Cystosarcoma in PregnancyRod Rafael De LeonNo ratings yet
- Prenatal Diagnosis: Asheber Gaym M.D. January 2009Document7 pagesPrenatal Diagnosis: Asheber Gaym M.D. January 2009Israel WoseneNo ratings yet
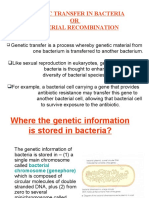
- Bacteria-Genetic TransferDocument57 pagesBacteria-Genetic TransferKA AngappanNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Microbiology An Introduction 13th Edition Gerard J Tortora Berdell R Funke Christine L Case Derek Weber Warner BairDocument35 pagesTest Bank For Microbiology An Introduction 13th Edition Gerard J Tortora Berdell R Funke Christine L Case Derek Weber Warner Bairshriekacericg31u3100% (37)
- Nt-Probnp: The Gold Standard Biomarker in Heart FailureDocument3 pagesNt-Probnp: The Gold Standard Biomarker in Heart FailureRiuin23No ratings yet
- Basal Ganglia Physiological AspectsDocument54 pagesBasal Ganglia Physiological AspectsPhysiology by Dr Raghuveer100% (1)
- Method Development and Validation For The Simultaneous Estimation of Sitagliptin and Metformin by HPLC and Uv-Spectroscopy MethodsDocument116 pagesMethod Development and Validation For The Simultaneous Estimation of Sitagliptin and Metformin by HPLC and Uv-Spectroscopy MethodsNaveen MadirajuNo ratings yet
- Directions: Each Question Below Contains Five Suggested Answers. Choose The One Best Response ToDocument3 pagesDirections: Each Question Below Contains Five Suggested Answers. Choose The One Best Response ToTrottTamilNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The Endocrine SystemDocument4 pagesDiseases of The Endocrine SystemJerahmeel Sombilon Genilla100% (1)
- JytjtyjDocument262 pagesJytjtyjarkaprava paulNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Tumor Rongga MulutDocument36 pagesKuliah Tumor Rongga MulutIceBearNo ratings yet
- Bacteriophages - Biology and Applns - E. Kutter, A. Sulakvelidze (CRC, 2005) WW PDFDocument485 pagesBacteriophages - Biology and Applns - E. Kutter, A. Sulakvelidze (CRC, 2005) WW PDFMădă Iorga100% (2)
- Quantitative Analysis of The Substrate Specificity of Human Rhinovirus 3C Protease and Exploration of Its Substrate Recognition MechanismsDocument14 pagesQuantitative Analysis of The Substrate Specificity of Human Rhinovirus 3C Protease and Exploration of Its Substrate Recognition MechanismsLuís MiguelNo ratings yet
- Dendrimers: Synthesis, Applications, and Properties: Nanoreview Open AccessDocument10 pagesDendrimers: Synthesis, Applications, and Properties: Nanoreview Open AccessIonut StirbescuNo ratings yet
- Newborn Pulmonary Hypertension Causes and TreatmentDocument10 pagesNewborn Pulmonary Hypertension Causes and TreatmentWali MoralesNo ratings yet
- Introduction of MicrobiologyDocument9 pagesIntroduction of MicrobiologyRahul PalsNo ratings yet
- Argumentative Essay 1Document5 pagesArgumentative Essay 1api-451529335No ratings yet
- Bio Control LectureDocument8 pagesBio Control Lecturedars23No ratings yet
- AQA B Psychology-Anxiety Disorders - An Introduction To Phobias & ExplanationsDocument5 pagesAQA B Psychology-Anxiety Disorders - An Introduction To Phobias & Explanationswarsan bidarNo ratings yet