Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Concept Map - Abby !
Uploaded by
Abegail AbaygarOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Concept Map - Abby !
Uploaded by
Abegail AbaygarCopyright:
Available Formats
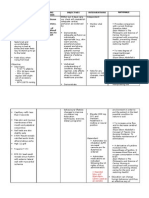
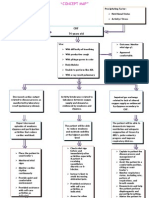
CONCEPT MAP
Predisposing Factor: Age Gender Genetics Precipitating Factor: Nutritional Status Activity / Stress Lifestyle
CHF 74 years old
S/sx: With difficulty of breathing With productive cough With phlegm green in color Body Malaise Unable to perform like ADL With x-ray result pulmonary edema.
Outcome: Monitor vital sign q1. Appeared comfortable. Assume the pt. In semi-fowlers position. Monitor the respiratory rate and pulse rate.
Decreased cardiac output related to disease process as manifested by laboratory result (pulmonary edema).
Activity Intolerance related to imbalance between oxygen supply and demand as evidenced by weakness and dyspnea.
Impaired gas exchange related to lack of altered oxygen supply as evidenced by dyspnea secondary to CHF.
Report decreased episodes of weakness dyspnea and participation activities that reduce cardiac workload.
The patient will be able to reduce weakness and maintain mobility at the highest possible level.
The patient will be able to demonstrate improve ventilation and adequate oxygenation of tissues by ABGs, pulse oximetry progress and improve respiratory distress.
Place the patient in semi-fowlers Monitored vital signs Monitor cardiac rhythm continuously Provide quiet and comfortable environment Provided assistance with self-care activities as indicated.
Check vital sign before and immediately after activities especially if patient is receiving vasodilators diuretics or bblocker. Instruct client to avoid increasing abdominal pain. Provided assistance with self-care activities as indicated. Assess for other precipitators/ causes of fatigue.
Explain to patient the disease process and management of symptoms Assist the patient in a comfortable position, sitting or semifowlers Monitor respiratory status, including rate, pattern of respirations, and breath sounds Demonstrate and help the patient perform diaphragmatic and pursed lip breathing. Advise the patient to allow the patient to rest and limit activities. The patient will be able to demonstrate improve ventilation and adequate oxygenation of tissues by ABGs, pulse oximetry progress and improve respiratory distress.
Report decreased episodes of weakness dyspnea and participation activities that reduce cardiac workload.
The patient was able to reduce weakness and maintain mobility at the highest possible level.
You might also like
- Nursing Care Plan: Date/ Time Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluatio NDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Date/ Time Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluatio NnananaNo ratings yet
- Rufino, Leslie Kriztel S. BSN 3-2 Group 1Document6 pagesRufino, Leslie Kriztel S. BSN 3-2 Group 1Deinielle Magdangal RomeroNo ratings yet
- NCP PTBDocument6 pagesNCP PTBJay Dela VegaNo ratings yet
- SLCN Gazette Magazine, Volume 1, Issue 1, 2019Document20 pagesSLCN Gazette Magazine, Volume 1, Issue 1, 2019Mayzelle RizNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective DataDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Subjective DataAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesTissue PerfusionMichael John LeandichoNo ratings yet
- Compartment Syndrome NCP (PAIN)Document2 pagesCompartment Syndrome NCP (PAIN)eunica16No ratings yet
- NCP BMDocument1 pageNCP BMSourabh MehraNo ratings yet
- San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesDocument3 pagesSan Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, Philippineskuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesNursing Care PlanPaola Marie VenusNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPneumoniaPia MedinaNo ratings yet
- MGH 8 - Ihd - NCPDocument12 pagesMGH 8 - Ihd - NCPSesinando Niez Quilao Jr.100% (1)
- Impaired Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesImpaired Tissue PerfusionLyka Mae Imbat - PacnisNo ratings yet
- NCP Acitivity IntoleranceDocument3 pagesNCP Acitivity IntolerancegizelleNo ratings yet
- Word Ncp.......... TetanusDocument6 pagesWord Ncp.......... TetanusaianrNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance Nursing Care Planrois romaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan. HypertensionDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan. HypertensionKiara Shanelle Posadas AbrioNo ratings yet
- NCP For CTTDocument1 pageNCP For CTTJen Rhae LimNo ratings yet
- Healthcare - Nursing Care Plan - Excess Fluid VolumeDocument4 pagesHealthcare - Nursing Care Plan - Excess Fluid VolumeBenjamin CañalitaNo ratings yet
- NCP For StokeDocument5 pagesNCP For StokeMemedNo ratings yet
- Decrease Cardiac OutputDocument6 pagesDecrease Cardiac OutputGerardeanne ReposarNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument13 pagesNursing Care PlanCris Solis33% (3)
- NCP Acute Pain FractureDocument1 pageNCP Acute Pain FractureAi RouNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Group 4-Open Wound Head Injury After Debris FallDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Group 4-Open Wound Head Injury After Debris FallNicole Villanueva, BSN - Level 3ANo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationjennelyn losantaNo ratings yet
- Course in The WardDocument1 pageCourse in The WardGeevee Naganag VentulaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans For Activity IntoleranceDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plans For Activity IntolerancethebigtwirpNo ratings yet
- As Needed.: Environmental Stimuli 6Document4 pagesAs Needed.: Environmental Stimuli 6Nicole GumolonNo ratings yet
- NCP and DStudyDocument8 pagesNCP and DStudyJessica Rosan Hewald ManapatNo ratings yet
- Student Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan AmputationDocument3 pagesStudent Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan AmputationNur faizah bt azmiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care Planapi-309251523No ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument14 pagesNursing Care PlanVin Landicho100% (1)
- Risk For InfectionDocument1 pageRisk For InfectionEuanne OrellanoNo ratings yet
- Risk For Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument4 pagesRisk For Decreased Cardiac Outputapi-283482759No ratings yet
- NCP CKDDocument3 pagesNCP CKDRiel TumandaNo ratings yet
- NCP BronchopneumoniaDocument8 pagesNCP BronchopneumoniaCrisantaCasliNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument1 pageIneffective Airway ClearanceChristineAlaNo ratings yet
- SNU49Document2 pagesSNU49Nora BacolNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance CareplanDocument6 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance CareplanderreshaNo ratings yet
- NCP HyperthermiaDocument1 pageNCP HyperthermiaPastor James PacadaljenNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care PlanMarielle SorianoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument1 pageNursing Care PlanMikki lor PuaganNo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas Exchange NCPDocument3 pagesImpaired Gas Exchange NCPRomel BaliliNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals & Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals & Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationMiggy SikatNo ratings yet
- NCP - Activity Intolerance & Excess Fluid VolumeDocument2 pagesNCP - Activity Intolerance & Excess Fluid VolumeCindy MariscotesNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objective Interventions Rationale Expected Outcome Short Term: Short TermDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objective Interventions Rationale Expected Outcome Short Term: Short TermGensen Cu RoxasNo ratings yet
- Medication ThalassemiaDocument3 pagesMedication ThalassemiaDivya ToppoNo ratings yet
- Scribd 020922 Case Study-Oncology A&kDocument2 pagesScribd 020922 Case Study-Oncology A&kKellie DNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain SCMCDocument2 pagesAcute Pain SCMCWik Wik PantuaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Measures To Maintain Normal Respiratory Function and OxygenationDocument2 pagesNursing Measures To Maintain Normal Respiratory Function and Oxygenationlodeth100% (2)
- NCA2 PosttestsDocument20 pagesNCA2 PosttestsCzarena Ysabelle PayotNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Peripheral Tissue Perfusion Related To Vasoconstriction Secondary To High Glucose Level.Document6 pagesIneffective Peripheral Tissue Perfusion Related To Vasoconstriction Secondary To High Glucose Level.SAROL, RYAN CHRISTIAN B.No ratings yet
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY of RabiesDocument5 pagesANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY of RabiesDavid CalaloNo ratings yet
- Case No 45: of Intermittent Abdominal Pain Abdominal Bloating and Nausea and Vomiting (NVDocument17 pagesCase No 45: of Intermittent Abdominal Pain Abdominal Bloating and Nausea and Vomiting (NVPremiums of the RoseNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 1: Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions RationaleDocument8 pagesNursing Care Plan 1: Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions RationaleTrysna Ayu SukardiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan FinalDocument16 pagesNursing Care Plan FinalErickson OcialNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Studies: The Forced Expiratory Volume Over 1 Second (FEVDocument7 pagesDiagnostic Studies: The Forced Expiratory Volume Over 1 Second (FEVKushan SenanayakaNo ratings yet
- Nursing DiagnosisDocument7 pagesNursing DiagnosisMariya Mikaela Garcia SoledadNo ratings yet
- Nursing DiagnosisDocument16 pagesNursing DiagnosisSi Bunga JonquilleNo ratings yet
- Cardiac ComplicationDocument12 pagesCardiac ComplicationResa ShotsNo ratings yet
- Chest PhysiotherapyDocument88 pagesChest Physiotherapy私 シャーロットNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary EdemaDocument14 pagesPulmonary EdemaRizzamwah Catague100% (1)
- Concept Map - Abby !Document2 pagesConcept Map - Abby !Abegail Abaygar100% (3)
- New York Heart Association (NYHA) Functional ClassificationDocument1 pageNew York Heart Association (NYHA) Functional ClassificationEjanZulqadMaulanaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Stimulants, Expectorants and Anti-TussivesDocument16 pagesRespiratory Stimulants, Expectorants and Anti-TussivesAshish Mittal0% (3)
- Birth AsphyxiaDocument2 pagesBirth AsphyxiaTeslim Raji100% (3)
- Essentials of Internal MedicineDocument832 pagesEssentials of Internal MedicineEmanuelMC100% (75)
- Decrease Cardiac Output Related To Altered Stroke VolumeDocument3 pagesDecrease Cardiac Output Related To Altered Stroke VolumeRalph PelegrinoNo ratings yet
- First Tutorial: Brain StormingDocument3 pagesFirst Tutorial: Brain Stormingsemicircularis0% (1)
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument3 pagesImpaired Gas ExchangePaul VincentNo ratings yet
- Review of Systems FDDocument1 pageReview of Systems FDchronicidalNo ratings yet
- Shortness of Breath: Checklist PMPF Checklist PMPFDocument1 pageShortness of Breath: Checklist PMPF Checklist PMPFanz_4191No ratings yet
- Amlodipine Drug StudyDocument8 pagesAmlodipine Drug StudyChamCham Aquino75% (4)