Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug List Psych Optho Neuro
Uploaded by
Ashley BarrileCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug List Psych Optho Neuro
Uploaded by
Ashley BarrileCopyright:
Available Formats
Common Name
Sub Category
Mechanism of Action Increased presynaptic NE vesicular release
Clinical Use/Indications ADHD Meds 1st line for ADHD - good for attentional symptoms
Adverse Effects 1. Can be abused and cause psychological and physical dependence
Methylphenidate (Ritalin) Amphetaminetype stimulants Dexmethylphenidate (Focalin) Mixed amphetamine salts (Adderall) Atomoxetine Nonamphetamine stimulant Clonidine Alpha-2 Adrenergic Guanfacine Agonist
2nd line for ADHD = helps with inattention, overactivity Increase noradrenergic tone in inhibitory synapses 3rd line for ADHD - helps with hyperactivity, motor symptoms (tics)
Buproprion Venlafaxine TCAs
Antidepressants Dopamine reuptake inhibitors and dual-reuptake inhibitors (NE/5-HT)
3rd line for ADHD Not used in kids because of cardio
Typical Antipsychotic Agents Chlorpromazine* Thioridazine* Mezoridazine Prochlorperazine Fluphenazine* Trifluoperazine* Haloperidol (Haldol)* Droperidol Thithixene Butyrophenone derivatives Thioxanthene derivative Phenothiazine derivatives 1. Competitively blocking dopamine receptors (D2/D3 ratio = 10-50) 2. Inhibit activation of adenyl cyclase and shuts down the mesolimbic system 3. D2 receptors located in limbic, extrapyramidal, endocrine structures 1. Treatment of psychosis - Schizo -> positive symptoms - Bipolar - Delirium - Depression w/ psychosis 2. Off-label uses - Depression - Aggression - Personality disorders - Eating disorders - Impulse control disorders 1. Anticholinergic - dryness 2. Extrapyramidal (EPS) - Parkinsonian syndrome - Acute dystornia - spasm of nexk muscles - tx w/ benztropine - Tardive dyskinesia - involuntary movement 3. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS) - blockage of D2 in hypothalamus - hyperthermia, hypertension, dyskinesia - tx w/ dantrolene/bromocriptine 4. Sedation 5. Cardiovascular - prolonged QT, ECG change 6. Endocrine --> galactorrhea, amenorrhea Atypicals have better side effect profiles
Atypical Antipsychotic Agents Serotonin/dopa 1. Competitively block serotonin receptors (5mine HT2), which inhibits dopamine release in frontal lobes Risperidone (Risperdal)* antagonists 2. Higher degree of binding/blocking D4/D3 3. Improves negative symptoms of schizo, reduces Olanzapine* EPS side effect, improves positive symptoms Quetiapine* Clozapine* Ziptrasidone* 1. Dop antag in high (mesolimbic) and agonist in Apripiprazole (Abilify)* Dopamine agonist/antagoni low dopamine (frontal lobes) st See above, except can also treat negative symptoms - Olanzapine for OCD, anxiety, depression, mania, Tourrette's
Common Name
Sub Category
Mechanism of Action
Clinical Use/Indications ADHD Meds Mood Stabilizers
Adverse Effects
Lithium*
Classic
1. Possibly inhibits phosphoinositol cascade
1. 1st line for acute bipolar depression prophylaxes depression 2. Blocks relapse and acute manic events
Lamotrigine
Anticonvulsants Interferes w. Na channels and reduces excitation
1. Prophylax depression - Bipolar depression (treatment and maintenance) 1. Acute mania and in rapid cycling bipolar/mixed episodes
Valproic Acid (Depakote)
Interferes w/ Ca/Na channels, enhances GABA, inhibits glutamate
Carbamazepine
Acts on Na/K channels to enhance GABA
Only use if Lithium or Valproic acid fail
1. LMNOP - Lithium - Movement (tremor) - Nephrogenic DI - hypOthyroidism - Pregnancy problems 2. Need to monitor closely - toxicity seen at 1.5-2 mEq/L 1. Dizziness, sedation, diplopia, ataxia 2. Pregnancy issue 3. Severe rash/Steven Johnson syndrom 1. Pregnancy Issue (D) 2. Sedation, dizziness 3. Can induce Hepatitis/hepatic fail, pancreatitis, abnormal bleeding 1. Pregnancy Issue (D) - spina bifida 2. GI, dizziness, Agranulocytosis 4. Hepatitis/cholestatic jaundice 5. Steven Johnson
Oxcarbazepine Gabapentin Symbyax Antipsychotics Benzodiazepines Other mood stabilizers
Similar to Carbamazepine, with better side effects
Antitussives and Mucokinetic Agents (Coughing) Codeine Hydrocodone Dextromethorphan Centrally acting 1. Non-specifically reduce excitability of cough antitussives center (anodynes) 1. Non-productive cough 1. Resp depression - caution in < 2 - when cough results in sleep loss 2. Constipation, miosis, sedate, addict - to prevent herniation, spread of infection Fewer side effects - Confusion, excitation, nervous, resp depression in high dose - high abusive potential
Promethazine/phenerga Diphenhydramine (Benadryl) Benzonatate
Guaifenesin Robitussin/Humibid N-Acetylcysteine
Peripheral acting antitussive Mucokinetic Expectorants Mucokinetic Mucolytics
Reduce afferent inputs to the cough center - on stretch receptors in the respiratory passage Stimulate/modify mucous production in bronchi stomach irritant that causes bronchial secretion Break down sputum aggregates to smaller parts splits disulfide bonds - Nebulize 1. Productive coughs - Expectorants - thick/tenacious cough secretions - Mucolytics - cystic fibrosis, antidote to acetaminophen poisoning
1. Can cause hypersensitivity rxn procain/tetracaine 2. DON'T CHEW - anesthesia GI tract issues
Common Name Demulcents
Sub Category Mucokinetic Demulcents
Mechanism of Action Sticky substances that protect lining of resp tract
secretions - Mucolytics - cystic fibrosis, antidote to Clinical Use/Indications acetaminophen poisoning ADHD Meds
Adverse Effects
Common Name
Sub Category
Mechanism of Action
Clinical Use/Indications ADHD (vomiting) Anti-EmeticsMeds
Adverse Effects
Chlorpromazine Prochlorperzine Promethazine Thiethylperazine Droperidol Scopolamine Diphenhydramine Dimenhydrinate Hydroxyzine Meclizine Promethazine (phenergan) Ondansetron Granisetron Dolasetron Polonosetron Trimethobenzamide Metoclopramide
Antipsych
1. Depresses excitability of the CTZ by blocking D2 receptors and transmission 2. Also peripherally blocks D2 in GI
1. Radiation/drug induced vomiting 2. Thiethylperazine used for post-op 3. Doperidol has tranquilizing effects
1. Sedation 2. EPS 3. Allergic
Anticholinergic Blocks Ach receptors in CTZ, vest nuclei and GI tract Antihistamines - Blocks Ach receptors in vest nuclei and CTZ Ethanolamine Antihistamine1st gen pipera Antihistamine phenothiazine Serotonin Selectively blocks serotonin receptors (5-HT3) in blockers GI and CTZ
Motion sickness Motion sickness Vertigo, motion sickness
Sedation, blurred vision, reduced GI/bladder tone Sedation, blurred vision, dry mouth 1. Pregnancy issue 1. Contraindicate in children
1. Post-op n/v following highly emetogenic surgery 2. drug-induced n/v (antineoplastics) 3. Radiation therapy n/v 4. NO motion sickness 1. Post-op n/v and coughing 1. GE reflux 2. Daibetic gastric stasis 3. N/v assoc w/ cisplatin, radiation N/v due to antineoplastics Anorexia w/ weight loss in AIDS
1. No EPS 2. Headache, diarrhea, constipation, phlebitis
Benzamide derivatives
Antiemetic - depresses CTZ (D2) Antitussive - suppresses laryngeal reflex 1. Prokinetic 2. Anti-emetic - antagonism of dopamine Vestibular Potent CYP3A4 inhibitor
1. CNS depression 2. EPS, Reye's syndrome 1. CNS depression 2. EPS Impairs cognitive and motor fx
Dronabinol Aprepitant Aplprazolam Triazolam* Lorazepam* Oxazepam Flurazepam Prazepam Diazepam* Pehnobarbital Mephobarbital Pentobarbital Secobarbital
Other - nausea vomiting
Sedative-Hypnotic Drugs Benzodiazepein 1. Binds to site on GABA A receptor, which es (short acting) enhances GABA's effect 2. Mediates both sedation and memory effects 3. Benzo + GABA = increased freq of channelopening events (Cl-) Benzodiazepein es (long acting) 1. Anxiety 2. Spasticity 3. Status epilepticus (lorazepam, diazepam) 4. Detox 5. Night terrors, sleepwalking 6. Insomnia (estazolam, fluraz, quaz, tema, triazolem) - bind 3 alpha-1 sybtype 1. Anticonvulsant - seizures 2. Basal anesthesia 3. Narco-analysis 4. Decreases respiration neurogenic/chemical/hypoxic drives 1. Potential abuse - lethal:effective dose = 200:1 2. Withdrawal 3. Daytime drowsiness 4. Respiratory impairment
Barbiturate Sedativehypnotics
1. Barbiturates + GABA = increased duration of channel-opening events (Cl-) -> decreased neuron firing
1. Contraindicate in porphyria 2. Dependence 3. Lethal, especially with alcohol
hypnotics Common Name Thiopental Chloral hydrate Diphenhydramine (Benadryl) Trazodone Ramelteon Zolpidem (Ambien) Zaleplon (Sonata) Eszopiclone (Lunesta) Historical Antihistamines Antidepressan Sub Category
firing Mechanism of Action
3. Narco-analysis 4. Decreases respiration Clinical Use/Indications neurogenic/chemical/hypoxic drives ADHD Meds
3. Lethal, especially with alcohol Adverse Effects
Hepatic injury Sedating antihistamine
Melatonin agonist Imidazopyridine Act on alpha subunit of GABA A - selectively bind Insomnia derivative to receptor to produce hypnotic effects Pyrazolopyrimid ine class Antidepressants
Fluoxetine (Prozac) Sertraline (Zoloft) Paroxetine (Paxil) Citalopram (Celexa) Escitalopram (Lexapro) Fluvoxamine Imipramine Desipramine Amitripltyline Nortriptyline Venlafaxine (Effexor)
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)
1. Selectively block uptake of serotonin 2. Advantages - more benign than TCAs, no quinidine action on heart, no significant weight gain 3. High safety margin
1. Depression 2. OCD, panic disorders, PRSD 3. Eating disorders, GAD 4. PMS
1. Transient - nervousness, insomnia, nausea, diarrhea 2. Persistent - sexual dysfx 3. Serotonin syndrome - confusion, fever, altered consciousness, myoclonus 4. Inhibits p450
Tricyclic 1. Block active reuptake of norep and serotonin antidepressants higher levels in synaptic cleft (TCA) 2. Original gold standard
1. Resistant depression 2. Enuresis in childhood (Imipramine) 3. Chronic pain, neuralgias, miagraine, diabetic neuropathy 1. Depression, GAD, Panic 2. PTSD, PMS
1. Sedation, anticholinergic 2. ECG change 3. Weight gain, impotence 4. Can precipitate mania Similar to SSRIs
Duloxetine
Serotonin + Reuptake inhibitor of serotonin, norep, and some Norep reuptake dopamine inhibitors (SNRI)
Phenelzine
MAO inhibitors Inhibits MAO A and B non-selectively, which result in higher norep and serotonin release
Tranylcypromine Buproprion (Wellbutrin, Zyban) Norep + Blocks reuptake of norep and dop dopamine reuptake inhib (NDRI) Noradrenaline + serotonin (NaSSA) Serotonin antag reuptake inhibitors (SARI)
1. Better for bipolar/atypical depression 2. Phobias 3. Migraines 4. Neurodermatitis 1. Depression (fewer sex side effects) 2. Smoking cessation - Zyban 3. ADHD
1. Weight gain, sexual dysfx 2. Hepatotoxic 3. Slower onset Sexual dysfunction Faster onset 1. Agitation, insomnia, seizures 2. Inhibits 2D6
Mirtazapine Nefazodone
Common Name Trazodone
Sub Category reuptake inhibitors (SARI) Serotonin antag Mechanism of Action
Clinical Use/Indications ADHD Meds
Adverse Effects
Common Name
Sub Category
Mechanism of Action
Clinical Use/Indications ADHD Meds General Anesthetics
Adverse Effects
Nitrous Oxide (N2O) Halothane Enflurane Isoflurane Desflurane Sevoflurane Ketamine Propofol Etomidate
Gases
CNS depressants - blood soluble = rapid induction/recovery - lipid soluble = potency = 1/MAC - ventilation + concentration = more rapid uptake
Must combine w. IV narcotics, barbiturate 1. Bone marrow suppression in high conc and relaxants 2. Neuropathy 1. Massive hepatic necrosis (halothane hepatitis) in 1/35,000, less in children 2. slows HR, decreases MAP/CO 1. Free F- released = renal fail (preexist) 2. Increases HR, decreases MAP/CO 1. No renal dysfx, minimal metab 2. Increases HR, decreases MAP/CO + SVR 1. Minimal liver biotransform 2. Increases HR, decreases MAP 1. Same as enflurane - disolve in soda lime 2. Little heart effect
IV agents
Muscarinic receptor antagonist Opiate receptor agonist Produces dissociated anethesia
1. Myocardial depressant 2. Depresses respiration
Local Anesthetics Bupivacaine Ropivacaine Lidocaine Tetracaine Cocaine Procaine Benzocaine Intraocular Pressure (IOP) Lowering Agents - Ocular Hypertensives Brimonidine Timolol Dorzolamide hydrochloride Acetazolamide Mannitol Glycerin Isosorbide Pilocarpine Echothiophate iodide Latanoprost Prostaglandins Miotics Direct - stimulate muscarinic receptors to cause constriction and increase flow Indirect - blocks Ach-esterase F2 - increase matrix turnover = increased flow Alpha agonists Beta blockers Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Hyperosmolar agents Activates alpha 2 - inhibits aqueous secretion Blocks beta receptors - decrease aqueous secre Inhibits CA, which decreases aqueous production 1. Open angle glaucoma 2. Ocular hypertension dry mouth, hypotension, lethargy Bradycardia, bronchospasms, fatigue, worse myasthenia gravis Drops - bitter taste, diuresis, fatigue, StevensJohnson Oral/IV - hypokalemia, renal stones, aplastic anemia, Stevens-Johnson CHF, urinary retention, back acne, MI vomiting, less CHF, similar to mannitol same as glycerin, but safer in DM Angle closure, breakdown of barrier, retinal tears - don't use in young patients Retinal detachment, myopia, angle closure Increase melanin, blurred vision, URI symptoms, myalgia Esters Amides 1. Blocks voltage dependent Na channels - block AP 2. Absorption - short = limited, need vasoconstrictor 3. Vasodilate except for cocaine 4. Esters metab by pseudocholinesterases, Amides by hepatic microsomal enzymes 1. Minor surgery 2. Spinal anesthesia 3. Regional anesthesia 4. Infiltration anesthesia 5. Post-op analgesia 1. CNS - lightheaded, restless, tonic-clonic 2. CV - cocaine = htn, mi, cerebral hemorrhage 3. Allergy - esters 4. Treat convulsions w/ diazepam or barbiturates
Dehydrates vitreous and draw fluid into intravascular space
Common Name Dipivefrin
Sub Category
Mechanism of Action
Clinical Use/Indications ADHD Meds
Adverse Effects Cystoid macular edema, mydriasis, blurred vision, tachycardia, htn, headache
Sympathomimet Beta stimulation in trabecular network = increased ic flow
Common Name
Sub Category
Mechanism of Action
Clinical Use/Indications ADHD Meds Other Eye Drugs
Adverse Effects
Penicillin, etc Non-steroidals/ Corticosteroids Tropicamide Atropine sulfate Phenylephrine Macugen Lucentis Avastin Acetaminophen Aspirin Naproxen Isometheptene (Midrin) Metoclopramide Sumatriptan Zolmitriptan Naratriptan Rizatriptan Almotriptan Frovatriptan Eletriptan Ergaotamine Dihydroergatamine Chlorpromazine Propranolol Timolol Divalproex Topiramate Verapamil Flunarizine TCAs
Antibacterials
Self-explanatory
Antiinflammator y Dilating drops Parasympatholytic - block Ach receptors in iris ciliary body - mydriasis and cycloplegia Sympathomimetic - stimular dilator muscle Anti-VEGF
Eye drops
Mydriasis and cycloplegia (paralysis)
Pegylated oligonucleotide binds to VEGF 165 and Stops angiogenesis/neovascular in: prevents ability to bind to receptor 1. macular degen (wet), DM retino 2. Neovascular glaucoma, retinal vein Recombinant fragment that ragets VEGF-A occlusion Parent of Lucentis Migraine Drugs Mild-moderate migraines Just helps with the pain
1. Blurred vision, pain, redness of eye, increased IOP, retinal detachment 2. Dizziness, headache, nausea, diarrhea 3. Beware hypersensitivity rxn
Analgesic NSAIDs
Ideal for pregnant - contra in severe kidney/liver disease, G6PD
Combine to prevent migraine Good for nausea and vomiting Triptans 1. 5-HT1B/D agonists, some 1F (1B = bv, 1D/F = neurons) 2. Selectively constrict cranial vessels and reduce inflammation 3. Block pain transmission from CN V to trigeminal nucleus caudalis 4. All except sumatriptan are more centrally penetrant Abort Moderate-Severe migraines If doesn't abort in 2-4 then medication won't help 1. Contraindications - Heart disease/MI - Angina, HTN - basilar migraine 2. Triptans can't be used w/ other triptans or ergot or MAOIs 3. Too much ergot = poisoning
Ergot alkaloids 1. 5-HT1B/D agonists 2. Additional receptor affinities Neuroleptics Opioids Beta blockers Anti-epileptic Ca blockers Antidepressants Without sympathomimetic activity GABA agonists Prolonged migraine + signif n/v Don't respond to normal tx Migraine prevention Safe for pregnant when limited 1. Decreased sexual activity, bradycardia, lethargy Pregnancy group D, liver issues Significant cardiac (Class 4 antiarrhy) Severe cardiac effects, orthostatic hypotension
Common Name
Sub Category
Mechanism of Action
Clinical Use/Indications Parkinson's ADHD-Meds Drugs Dopamine agents
Adverse Effects
Levodopa
Levodopa
Trihexyphenidyl Benztropine Bromocriptine Pergolide Pramipexole Ropinirole Apomorphine Entacapone Tolcapone Selegiline Rasagiline Amantadine Antipsychotics Reserpine Tetrabenazine Botulinum toxin
Dopamine replacement - absorbed in SB through LNAA - converted to dopamine + O-methyl dopa by DDC Anticholinergic Blocks central muscarinic receptors Dopamine agonist Stimulate dopamine receptor directly
Most effective for treating Parkinson's tremor, rigidity, bradykinesia
Nausea, hypotension, hallucinations - Must be administered w/ carbidopa, a DDC inhibitor Mild tx for Parkinson's - tremor + rigidity dry mouth, sedation, blurry vision, urinary retention Moderate tx for Parkinson's - tremor, rigidity, bradykinesia PUD, vasoconstrictive, pulm fibrosis, hallucination, valve disease (pergolide) Somnolence, leg edema, compulsive behavior
COMT inhibitors MAO-B Inhibitors Other Dopamine Receptor Blockers and Depleters Poison
Inhibit breakdown of dopamine by COMT Inhibit breakdown of dopamine by MAO Dopaminergic, anticholinergic, NMDA antag
Adjunct w/ L-dopa - increases ON time Mild tx - tremor, rigid, bradykinesia, potentially neuroprotective Mild tx - tremor, rigid, bradykinesia
Orange discoloration of urine, diarrhea Fatal hepatitis Serotonin syndrome w/ SSRIs Peripheral edema, hallucinations
Inhibits release of Ach at the NMJ
Focal dystonia - cervical dystonia, blepharospasm, hemifacial spasm Antiepileptic drugs Tx of choice for acute seizures Refractory status epilepticus Partial seizures
Lasts 3-6 months - could overweaken muscles Sedation, resp depression bad side effects- only use in infant, poor Can cause absence epilepticus, sedation Thrombophlebitis, sedation, dizziness, diplopia, hepatotoxicity, myelosuppression
Benzodiazepines Barbiturates Tiagabine Phenytoin Carbamazepine Oxcarbazepine Lamotrigine Lacosamide Ethosuximide Valproate Topiramate Zonisamide Levetiracetam Gabapentin/Pregabalin
GABA affecting GABA-A - Cl channel opens more GABA-A - Cl channel opens longer Selective GABA reuptake inhibitor Na channel effecting
Voltage/Frequency dependent block of Na channel Partial and GTC seizures
Enhances the slow inactivated state of channel Enhances slow inactivation of the channel Ca channel Blocks T-type Ca channels in thalamus - stops affecting abnormal thalamic excitability Multiple MOAs 1. synaptic GABA, 2. NMDA excite 1. Cl events, 2. glutamate, Ca channels 1. Na channels, 2. Ca channels, 3. CA inhib Unique MOAs Binds vesicle protein SV2A - unknown a2 subunit of Ca channels
Good for all seizures Only absence seizures Good for all seizures All except absence seizures Good for all seizures Good for all seizures Partial seizures - pain
Headache, insomnia, rash Sedation, dizziness, headache, behavioral, myelosuppression Cog impairment, weight gain, hair loss, tremor, bad for pregnant Very safe - paresthesias, cog impair, weight loss Typical side effects, decreased appetite Safe - sedation, irritability Mild - sedation, weight gain
Common Name
Sub Category
Mechanism of Action
Clinical Use/Indications Drugs ofADHD and Addiction Abuse Meds
Adverse Effects
Alcohol
Metabolized via dehydrogenase system
Binds GABA, dilates bvs, decreases glutamate, reduces ADH secretion CNS/resp depression, miosis 1. CNS/resp depression, lethargy, coma 2. GHB - agitation, seizure, brady, amnesia 3. Chloral - dysrthmias 4. Withdrawal - insomnia, n/v, sweat, tachy 1. HR/BP, euphoria, strokes, rhabdomyolysis, seizures, renal fail Euphoria, hallucin, tense jaw, bruxism Euphoria, panic attacks, paranoia Tachy, htn, ataxia, seizure, coma drowsiness, euphora, paranoia Euphoria, dysrythmias, met acid transient euphoria, CNS depress Treats diarrhea/intestinal colic Neonatal opioid dependency Analgesic, dyspnea due to PE Mild/moderate pain, antitussive Schedule 1, 3x more than morphine Parkinsons oral analgesic moderate/severe pain
Heroin/Morphine Barbiturates Benzodiazepines Chloral hydrate GHB Cocaine Ecstasy LSD Phencyclidine (PCP) Marijuana Hydrocarbons Nitrous Oxide (N2O) Paregoric Morphine Codeine Heroin Apomorphine Oxycodone Hydromorphone Meperidine Fentanyl Diphenoxylate Loperamide Methadone Darvocet Pentazocine Nalbuphine Naloxone Naltrexone Buprenorphine
Opioids Sedativehypnotics
Binds to mu receptors 1. Enhance GABA 2. GHB - odorless, colorless 3. Chloral hydrate - pear-like odor
Wenicke, Korsakoff, cirrhosis, PUD, fetal alcohol syndrome, pancreatitis - BAD w/ acetaminophen Tx: ABCs, Narcan for acute, supportive Treatment: 1. Supportive care 2. Phenobarb - urine alkalinization 3. Chloral - beta blokcers 4. Benz - Flumazenil Treatment: supportive Hyperthermia - ice, Seizures - Benzo, phenobarb HTN - sodium nitroprusside, phentolamine Treatment - supportive
Stimulants
1. Block presynaptic reuptake of dopa, norep, serotonin 2. Produces vasoconstrict and local anesthetic Interacts with serotonin receptors Related to ketamine - CNS depressant
Hallucinogens
Inhalants
CNS depressants
Chronic: met acidosis, hypokal Chronic: polyneuro, mega anemia 1. Seizures (Meperidine) 2. Depress resp 3. Emetic effect - n/v 4. Miosis (morphine) 5. Antitussive - lower dose than analgesic 6. Bowel dysfx/constipation 7. CV - hypotension/brady 8. Euphoria, sedation 9. Dependence
Naturally 1. Inhibit firing of neurons in dorsal horn, limbic occuring opioid structures and cerebral cortex agonist 2. adenylyl cyclase -> cAMP -> Ca influx or K efflux -> neurotransmitter release 3. Targets mu receptors Semi-synthetic agonist
Synthetic agonists
Not antitussive, local anesthetic Post-op/chronic pain, anesthesia Diarrhea acute, non-specific diarrhea mod/severe pain, opioid dependency No clinical usefulness
agonist/antagoni Agonists at kappa receptor, antagonists at mu st receptor
Moderate pain due to kappa receptor
Potential abuse, psychotomimetic, hallucinatory and dysphoric effects Need to assist resp depression w/ vent Liver toxicity Reduction in bowel dysfunction, constipation
Pure antagonists Binds all opioid receptors with higher affinity than Antagonize opioid effects agonist and reverse effects of agonists Treat opioid dep, alcohol, detox Partial agonist Mu Agonist to a ceiling, submaximal response PAMOR antagonists Analgesic effect
Prevent opioid withdrawal, so good for opioid dependence
Alvimopan/Methynaltrexo Restricted ne antagonists
Other
Low potency - low incidence of EPS, high sedating/CV effects
High potency - low sedating/CV effects, higher incidence of EPS
May cause agranulocytosis
Metabolic syndrome No weight gain
Other
Drug interact: - DAMN (Dehydrate, AceI, Metro, NSAID) - COAST (CA inhib, Osmotic, Antacid, Salt, Caffeine)
Drug interact - aspirin, felbamate - Rifampin Induces own metabolism watch hepatic enzyme Be careful of asians
Opioids - doses < for cough vs analgesia Non-opioid - d-isomer of codeine - don't use with MAOIs
NOT 1st line antitussive
Smells bad, tastes horrible
Other
Other
Pentothiazine derivatives
Butyro derivative Derm patch aka Benadryl aka Dramamine
Also binds H1 histamine receptors
1. Antacids decrease absorp 2. Antihist/barbit/ETOH increase depression 3. CYP450 except loraz, oxaze, temaz
Lots of interactions because of P450
Other
25-50 mg hs
Rapid acting, short halflife Useful for middle of night insomnia
Takes a long time to reach steady state Shorter half life, better More sedating, better for anxiety
If overdosed (cardiac monitoring) use gastric lavage, NaHCO3, Lidocaine or Phenytoin 1. Liver metabolized 2. Dose dependent HTN Less risk of liver issue, can treat Diabetic neuropathy 1. Tyramine food, amphetamines -> HTN crisis
Other
Other
Nonvolatile 1. Depressed heart contractility 2. Decreased smooth muscle tone, PVR, TV 3. Blocks vent response to hypoxia
More rapid recovery than barbiturates Minimal CV effects Long acting Medium Acting Long duration Medium + surface Short duration Surface Don't use in kids Don't use w/ sulfa allergy, hyponatremia/kalemia, thiazides or digitalis
worse myasthenia gravis
tinal tears - don't use in young
ure
ymptoms, myalgia
Other
red vision, tachycardia, htn,
Other
ney/liver disease, G6PD
Oral, subQ, nasal liver/renal Oral, nasal - liver Oral - renal Oral- no renal/liver Oral - liver Oral - renal Oral - liver Oral - only 2x/wk IV/nasal - avoid preg
High efficacy, mild/moderate adverse effects
Not in US
Other
Ergot derivatives Nonergot derivative w/ specificity for the D3 receptor
Non-selective MAO I's = tyrosine effect
Lorazepam/Diazepam Phenobarbitol (IV) Nonlinear pharmaco SJ syndrome, asians Not as bad Good for Preg women New drug
Hepatic failure, polycystic ovary ight loss Works fast Short half-life
Other
Tx: supply thiamine, benzos, disulfiram
henobarb mine
Tx: supportive, betablockers for dysryth
Dilaudid - good renal
Schedule IV drugs
You might also like
- ANTIDEPRESSANT DRUGS: Types, Mechanisms and Side EffectsDocument21 pagesANTIDEPRESSANT DRUGS: Types, Mechanisms and Side EffectsKashis SharmaNo ratings yet
- Psycho PharmaDocument8 pagesPsycho PharmaMark JosephNo ratings yet
- Drug List PsychopharmDocument23 pagesDrug List PsychopharmGeorge HananiaNo ratings yet
- Medication Fact Book for Psychiatric Practice, Fifth EditionFrom EverandMedication Fact Book for Psychiatric Practice, Fifth EditionNo ratings yet
- Antipsychotic Medication: Generic Name Trade Name Indications Contraindications Drug Interaction Side Effects Nursing ImplicationDocument6 pagesAntipsychotic Medication: Generic Name Trade Name Indications Contraindications Drug Interaction Side Effects Nursing ImplicationJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Geriatric Giants - DR SeymourDocument108 pagesGeriatric Giants - DR SeymourSharon Mallia100% (1)
- Antipsychotics Guide for Nursing Intervention and Patient EducationDocument10 pagesAntipsychotics Guide for Nursing Intervention and Patient Educationwawing16No ratings yet
- Bipolar DisorderDocument1 pageBipolar DisorderNur BalqisNo ratings yet
- Common Psychiatric TermsDocument6 pagesCommon Psychiatric TermsKatrina Heart Rauto AvilaNo ratings yet
- Mental Status Exam of Patient with Psychiatric HoldDocument4 pagesMental Status Exam of Patient with Psychiatric HoldJoan ChoiNo ratings yet
- Algorithm for Treating DepressionDocument12 pagesAlgorithm for Treating Depressioniwul kiwul KriwulNo ratings yet
- Sudden Onset (Within 2 Weeks) of at Least One of TheDocument2 pagesSudden Onset (Within 2 Weeks) of at Least One of TheNeicole BandalaNo ratings yet
- Psychiatry Notes Psychiatry Notes: Medicine (Queen Mary University of London) Medicine (Queen Mary University of London)Document28 pagesPsychiatry Notes Psychiatry Notes: Medicine (Queen Mary University of London) Medicine (Queen Mary University of London)Noman ButtNo ratings yet
- Treatment Modalities For Mood DisordersDocument55 pagesTreatment Modalities For Mood DisordersGlory MimiNo ratings yet
- Antidepressants and Mood StabilizersDocument4 pagesAntidepressants and Mood Stabilizers우정은No ratings yet
- Psychopharmacology in PsychiatryDocument94 pagesPsychopharmacology in PsychiatryOslo SaputraNo ratings yet
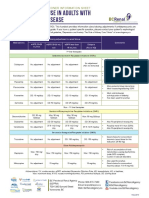
- Antidepressant Use in Adults With Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument1 pageAntidepressant Use in Adults With Chronic Kidney DiseaseAzhar Ali100% (1)
- Shortened REM Latency and Increased REM: Previous AttemptDocument19 pagesShortened REM Latency and Increased REM: Previous AttemptActeen MyoseenNo ratings yet
- 504 - Pediatric Psychopharmacology - General PrinciplesDocument54 pages504 - Pediatric Psychopharmacology - General PrinciplesAlvaro HuidobroNo ratings yet
- Just Getting The Main RX Names Down : Antidepressants Mood StabilizersDocument1 pageJust Getting The Main RX Names Down : Antidepressants Mood StabilizersCarlos Eduardo LinaresNo ratings yet
- Drugs For NeurolepticsDocument1 pageDrugs For Neurolepticssyamil_daudNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy in PschiatryDocument8 pagesPharmacotherapy in PschiatryygfhdgNo ratings yet
- Test 2 222Document12 pagesTest 2 222Ken Carter0% (1)
- PA 644 - M2 LecturesDocument412 pagesPA 644 - M2 LectureskatNo ratings yet
- Psychopharma 1Document7 pagesPsychopharma 1Mitchee Zialcita100% (1)
- Adhd Toolkit MedicationsDocument1 pageAdhd Toolkit MedicationsreneezNo ratings yet
- Depression Medications ExplainedDocument5 pagesDepression Medications ExplainedxyzNo ratings yet
- Psychopharmacology in Medically Ill PatientsDocument21 pagesPsychopharmacology in Medically Ill PatientsAklile TsegaNo ratings yet
- Quiz PsychopharmacologyDocument1 pageQuiz PsychopharmacologySolsona Natl HS MaanantengNo ratings yet
- MENTAL HEALTH ACTDocument178 pagesMENTAL HEALTH ACTGarry GuiteNo ratings yet
- Introduction To NeuropharmacologyDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Neuropharmacologyammarhafez78100% (1)
- Generics Antidepressants Comparison Chart PDFDocument2 pagesGenerics Antidepressants Comparison Chart PDFYazirNo ratings yet
- CEP BPSD Discussion Guide ENG RFCG Updated2019 PDFDocument8 pagesCEP BPSD Discussion Guide ENG RFCG Updated2019 PDFM.DalaniNo ratings yet
- Psychotropic Drugs.Document15 pagesPsychotropic Drugs.Xiaoqing SongNo ratings yet
- SSRI (Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor)Document1 pageSSRI (Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor)Mike EveretteNo ratings yet
- Handy Summary Chart Comparing The Main Medications For DepressionDocument2 pagesHandy Summary Chart Comparing The Main Medications For Depressionrowanpurdy100% (4)
- Pharmacology Review For FinalsDocument9 pagesPharmacology Review For FinalsJaya ReyesNo ratings yet
- SCTL NeurotransmitterDocument32 pagesSCTL Neurotransmitternur qistina humaira zulkarshamsiNo ratings yet
- Mental Health and Psychiatric Nursing: Vernalin B. Terrado, RNDocument35 pagesMental Health and Psychiatric Nursing: Vernalin B. Terrado, RNverna100% (1)
- Psychiatric history assessment guideDocument4 pagesPsychiatric history assessment guideChloe GoteraNo ratings yet
- Antidepressant Therapy AlgorithmDocument12 pagesAntidepressant Therapy AlgorithmZubair Mahmood KamalNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Testing in PsychiatryDocument29 pagesLaboratory Testing in PsychiatrySera ChunNo ratings yet
- SeroquelDocument1 pageSeroquelE100% (1)
- Anxiety Disorders Treatment OptionsDocument5 pagesAnxiety Disorders Treatment OptionsJohn HolmesNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology (1) - 104-122Document19 pagesPharmacology (1) - 104-122Dental LecturesMMQNo ratings yet
- K P Differential Diagnosis Pyramid: OPMAPS: Sychiatry EvisionDocument36 pagesK P Differential Diagnosis Pyramid: OPMAPS: Sychiatry EvisionArama CristiNo ratings yet
- Psychopharmacology 1Document7 pagesPsychopharmacology 1RajP01No ratings yet
- Biological Aspects of OCD SeminarDocument60 pagesBiological Aspects of OCD Seminarneha mattikoppaNo ratings yet
- B2B Psychopharmacology 2015Document128 pagesB2B Psychopharmacology 2015Soleil DaddouNo ratings yet
- Neurotransmitter Pathway in PsychiatryDocument22 pagesNeurotransmitter Pathway in PsychiatryameerNo ratings yet
- Session 7 Psychiatric AssessmentDocument54 pagesSession 7 Psychiatric AssessmentPetroNo ratings yet
- Handy Hints When Prescribing Antidepressants: Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (Ssris)Document3 pagesHandy Hints When Prescribing Antidepressants: Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (Ssris)Mariya ZhekovaNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - D - Antipsychotics For Bipolar DisorderDocument19 pagesModule 3 - D - Antipsychotics For Bipolar Disorderpsychopharmacology100% (2)
- Antipsychotic DrugsDocument47 pagesAntipsychotic DrugsIkram UddinNo ratings yet
- Psychotropic Drugs Used in Psychiatry: An OverviewDocument32 pagesPsychotropic Drugs Used in Psychiatry: An OverviewAmar Nur Arif ZazuliNo ratings yet
- Psychotropics NotesDocument5 pagesPsychotropics NotesJulianna Rheaven JoreNo ratings yet
- Black Box WarningDocument17 pagesBlack Box WarningSantosh AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Neuro Psych - Antiepileptic Drug ChartDocument5 pagesNeuro Psych - Antiepileptic Drug ChartMonica J Ortiz Pereira100% (1)
- Table 1: Substrates of Cytochrome P450 (CYP) EnzymesDocument6 pagesTable 1: Substrates of Cytochrome P450 (CYP) EnzymesNurul Kamilah SadliNo ratings yet
- ABAP Program Types and System FieldsDocument9 pagesABAP Program Types and System FieldsJo MallickNo ratings yet
- Chippernac: Vacuum Snout Attachment (Part Number 1901113)Document2 pagesChippernac: Vacuum Snout Attachment (Part Number 1901113)GeorgeNo ratings yet
- CSEC English SBA GuideDocument5 pagesCSEC English SBA GuideElijah Kevy DavidNo ratings yet
- Sosai Masutatsu Oyama - Founder of Kyokushin KarateDocument9 pagesSosai Masutatsu Oyama - Founder of Kyokushin KarateAdriano HernandezNo ratings yet
- Anschutz Nautopilot 5000Document4 pagesAnschutz Nautopilot 5000Văn Phú PhạmNo ratings yet
- Karnataka Email Id DataDocument5,173 pagesKarnataka Email Id DataSumalatha Venkataswamy100% (6)
- Deforestation Contributes To Global Warming: Bruno GERVETDocument11 pagesDeforestation Contributes To Global Warming: Bruno GERVETMajid JatoiNo ratings yet
- 52 Codes For Conscious Self EvolutionDocument35 pages52 Codes For Conscious Self EvolutionSorina LutasNo ratings yet
- Script For The FiestaDocument3 pagesScript For The FiestaPaul Romano Benavides Royo95% (21)
- Midterm Exam ADM3350 Summer 2022 PDFDocument7 pagesMidterm Exam ADM3350 Summer 2022 PDFHan ZhongNo ratings yet
- Lean Foundation TrainingDocument9 pagesLean Foundation TrainingSaja Unķnøwñ ĞirłNo ratings yet
- Issues and Concerns Related To Assessment in MalaysianDocument22 pagesIssues and Concerns Related To Assessment in MalaysianHarrish ZainurinNo ratings yet
- Doulci Activator For IOS 9Document2 pagesDoulci Activator For IOS 9Syafiq Aiman100% (2)
- Lantern October 2012Document36 pagesLantern October 2012Jovel JosephNo ratings yet
- HiaceDocument1 pageHiaceburjmalabarautoNo ratings yet
- The Alkazi Collection of Photography Vis PDFDocument68 pagesThe Alkazi Collection of Photography Vis PDFMochamadRizkyNoorNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ResearchDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Researchapi-385504653No ratings yet
- Lecture Notes - Design of RC Structure - Day 5Document6 pagesLecture Notes - Design of RC Structure - Day 5Tapabrata2013No ratings yet
- Intern - Annapolis PharmaceuticalsDocument34 pagesIntern - Annapolis Pharmaceuticalsjoycecruz095No ratings yet
- 4 FIN555 Chap 4 Prings Typical Parameters For Intermediate Trend (Recovered)Document16 pages4 FIN555 Chap 4 Prings Typical Parameters For Intermediate Trend (Recovered)Najwa SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Revision and Second Term TestDocument15 pagesRevision and Second Term TestThu HươngNo ratings yet
- Quatuor Pour SaxophonesDocument16 pagesQuatuor Pour Saxophoneslaura lopezNo ratings yet
- Keppel's lease rights and option to purchase land upheldDocument6 pagesKeppel's lease rights and option to purchase land upheldkdcandariNo ratings yet
- Destiny by T.D. JakesDocument17 pagesDestiny by T.D. JakesHBG Nashville89% (9)
- Real Vs Nominal Values (Blank)Document4 pagesReal Vs Nominal Values (Blank)Prineet AnandNo ratings yet
- IT WorkShop Lab ManualDocument74 pagesIT WorkShop Lab ManualcomputerstudentNo ratings yet
- Reaction PaperDocument1 pageReaction Papermarvin125No ratings yet
- Susan Oyama The Ontogeny of Information Developmental Systems and Evolution Science and Cultural Theory 2000Document297 pagesSusan Oyama The Ontogeny of Information Developmental Systems and Evolution Science and Cultural Theory 2000Marelin Hernández SaNo ratings yet
- AdmitCard 1688037Document1 pageAdmitCard 1688037P.Supreeth ReddyNo ratings yet
- PCC ConfigDocument345 pagesPCC ConfigVamsi SuriNo ratings yet