Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Untitled
Uploaded by
dimpesh silarpruiyaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Untitled
Uploaded by
dimpesh silarpruiyaCopyright:
Available Formats
Lecture 1 Lecture 2 Lecture 3 Lecture 4 Lecture 5 Lecture 6 Lecture 7 Lecture 8 Lecture 9
Unit 1 Introduction of operation research Linear system and distribution models: Mathematical formulation of linear systems by LP Solution of LP for two variables only Special cases of transportation Assignment and its solution Vogel's forward looking penalty method Cell evaluation degeneracy Use of SW Lindo
Lecture 10 Tora, Excell Lecture 1 Lecture 2 Unit 2 Supply chain (SCM):Definition, importance Expenditure and opportunities in SCM,integration of inbound
Lecture 3 Outbound logistics and manufacturing to SCM,flow of material money and information Lecture 4 ion Lecture 5 Lecture 6 Lecture 7 Lecture 8 Lecture 9 Difficulties in SCM due to local v/s system wide (global) optimizat Uncertainties in demand and transportation Bull-whip effect; customer value; IT, info-sharing Strategic partnerships Plant and warehouse-network configuration Supply contracts and revenue sharing
Lecture 10 Outsourcing; transportation,cross docking and distribution Lecture 11 Forecasting models in SCM, coordination and leadership issues Lecture 12 Change of purchasing role and vendor rating,variability from multip le suppliers.
Unit 3 Lecture 1 k Lecture 2 Lecture 3 Problem of excess Inventory and cycle time (=WIP/ Throughput) Inventory models: Necessity of inventory in process and safety stoc
Lecture 4 Lecture 5 Lecture 6 Lecture 7 Lecture 8 Lecture 9
JIT/ lean mfg; basic EOQ/ EPQ models for constant Review Q-system(S,s); periodic review Base stock P-system; service level Lead time variance and safety stock ABC, VED and other analysis based on shelf life Movement, size, MRP technique and
Lecture 10 Calculations, lot sizing in MRP, linking MRP with JIT Lecture 11 Evolution of MRP to ERP to SCM and e-business Lecture 1 Lecture 2 Lecture 3 Lecture 4 Lecture 5 Lecture 6 Lecture 7 Lecture 8 Lecture 9 Unit 4 Waiting Line Models Introduction Input process, service mechanism Queue discipline single server (M/M/1) average length and times by Littl,s formula optimum service rate; basic multiple Server models (M/M/s) Competitive strategy: concept and terminology Assumptions, pure and mixed strategies Zero sum games, saddle point, dominance
Lecture 10 Graphical, algebraic and P methods for solving game theory problems Unit 5 Decision analysis: decision under certainty Risk probability and uncertainty; Hurwicz criteria AHP- assigning weight and consistency test of AHP
Lecture 1 Lecture 2 Lecture 3
Lecture 4 Meta-heuristics Definition of heuristic and meta-heuristic algorit hms; introduction to Tabu search Lecture 5 Lecture 6 Lecture 7 Simulated Annealing and Genetic algorithms Solution of traveling salesman and non linear Optimization problems.
You might also like
- Presentation 1Document13 pagesPresentation 1dimpesh silarpruiyaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Failure of Materials 9789814560375-c2Document23 pagesMechanical Failure of Materials 9789814560375-c2Recep Vatansever0% (1)
- Mechanical Failure of Materials 9789814560375-c2Document23 pagesMechanical Failure of Materials 9789814560375-c2Recep Vatansever0% (1)
- Electric WeldingDocument7 pagesElectric Weldingdimpesh silarpruiyaNo ratings yet
- Assignment-I ME-704 Automobile EngineeringDocument1 pageAssignment-I ME-704 Automobile Engineeringdimpesh silarpruiyaNo ratings yet
- Design and Calculation For KersDocument5 pagesDesign and Calculation For Kersdimpesh silarpruiyaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.4 AutomobileDocument4 pagesExperiment No.4 Automobiledimpesh silarpruiyaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 1 AutomobileDocument4 pagesExperiment No 1 Automobiledimpesh silarpruiyaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument3 pagesUntitleddimpesh silarpruiyaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument6 pagesUntitleddimpesh silarpruiyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 AvailabilityDocument6 pagesChapter 6 Availabilitygovind4ever5No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitleddimpesh silarpruiyaNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5784)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Grade 12 Data Management NotesDocument2 pagesGrade 12 Data Management Noteskayj090% (1)
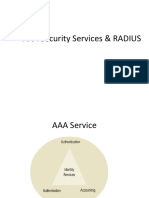
- AAA Security Services & RADIUS AuthenticationDocument20 pagesAAA Security Services & RADIUS AuthenticationYandra Permi PutraNo ratings yet
- STC 4G1 Configuration 20120414Document227 pagesSTC 4G1 Configuration 20120414anon_170666234No ratings yet
- YouTube Brand Channel RedesignDocument60 pagesYouTube Brand Channel Redesignchuck_nottisNo ratings yet
- Digital Comms Course OutlineDocument12 pagesDigital Comms Course OutlineHamid RazzaqNo ratings yet
- Prime Factorization 2-1000Document5 pagesPrime Factorization 2-1000NewTriMNo ratings yet
- United Arab Emirates: Cybersecurity PolicyDocument3 pagesUnited Arab Emirates: Cybersecurity Policymmh771No ratings yet
- Arieli and Avron - Reasoning With Logica BillaticesDocument40 pagesArieli and Avron - Reasoning With Logica BillaticesMorganNo ratings yet
- Assignment Set-1: MB0048 - Operation ResearchDocument13 pagesAssignment Set-1: MB0048 - Operation ResearchKumar GauravNo ratings yet
- Ijbb V5 I3Document65 pagesIjbb V5 I3AI Coordinator - CSC JournalsNo ratings yet
- OBJECTS in Oracle R12Document8 pagesOBJECTS in Oracle R12Siddiqa AyeshaNo ratings yet
- 20773A ENU TrainerHandbook PDFDocument340 pages20773A ENU TrainerHandbook PDFRicardo AraujoNo ratings yet
- DB Link CreationDocument4 pagesDB Link CreationRamesh GurumoorthyNo ratings yet
- XML ImplementationDocument10 pagesXML ImplementationPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Olympic Message System Usability: Early Testing Reveals 57 IssuesDocument16 pagesOlympic Message System Usability: Early Testing Reveals 57 Issuestrevor randyNo ratings yet
- Ajax CheatSheetDocument7 pagesAjax CheatSheetdrypzNo ratings yet
- Javascript Html5 CanavasDocument13 pagesJavascript Html5 CanavasmihailuNo ratings yet
- Binary LocksDocument4 pagesBinary LocksShelvin EchoNo ratings yet
- Cad Desk Student Fee's ReceiptDocument2 pagesCad Desk Student Fee's ReceiptPushpendra LodhiNo ratings yet
- WWW - Goair.In: Go Airlines (India) LTDDocument2 pagesWWW - Goair.In: Go Airlines (India) LTDdhavalesh1No ratings yet
- Check Point and Restart LogicDocument4 pagesCheck Point and Restart LogicPankaj Kumar100% (1)
- Advanced DTrace Tips, Tricks and GotchasDocument56 pagesAdvanced DTrace Tips, Tricks and Gotchaswanna_acNo ratings yet
- GUI Payroll SystemDocument4 pagesGUI Payroll Systemfeezy1No ratings yet
- As 9103 o ReviewDocument28 pagesAs 9103 o ReviewAnonymous Wi2Pd2UgPINo ratings yet
- ArchiCAD 16 and COBieDocument22 pagesArchiCAD 16 and COBieUntal AparicioNo ratings yet
- Ipc/jedec 9703Document46 pagesIpc/jedec 9703metaballinNo ratings yet
- Business PartnerDocument12 pagesBusiness PartnerNatraj Rangoju100% (1)
- Top USB Tools for creating, formatting and securing bootable USB drivesDocument9 pagesTop USB Tools for creating, formatting and securing bootable USB drivesjeanNo ratings yet
- XLR UserDemoDocument27 pagesXLR UserDemoSobhy GendykhelaNo ratings yet