Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drugs Used For Blood Coagulation Disorders - Katzung
Uploaded by
sarguss14Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drugs Used For Blood Coagulation Disorders - Katzung
Uploaded by
sarguss14Copyright:
Available Formats
Pharmacology
Drugs Used Coagulation D/O (katzung)
19 February 08
Chapter 34 Drugs Used in Disorders of Coagulation Endogenous anticoagulants
Outline Antithrombin
I. Blood Coagulation - SERPIN inactivates IIa, IXa, Xa. XIa, XIIa
a. Mechanism Protein C & S
b. Cascade - attenuate blood clotting cascade by proteolysis of Va & VIIIa
II. Anticoagulant Drugs
a. Indirect Thrombin Inhibitors Defects in natural anticoagulant – increased risk of venous
b. Direct Thrombin Inhibitors thrombosis
c. Warfarin & Coumarin - most common is Factor V (Leiden) defect
III. Fibrinolytic Drugs
IV. Antiplatelet Agents
a. Aspirin Fibrinolysis - Process of fibrin digestion by plasmin
b. Clopidogrel & Ticlopidine 1. In response to injury, endothelial size synthesize & release
c. GLP IIB/IIIA Receptor Blockers tPA (converting plasminogen to plasmin)
V. Drugs Used to prevent clotting 2. plasmin remodels thrombus, limits its extension by
VI. Drugs used in Bleeding Disorders proteolytic digestion of fibrin
a. Vitamin K
b. Plasma Fractions Negative regulators
c. Fibrinolytic Inhibitors: Aminocaproic Acid 1. Endothelial cells also release Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor
d. Serine Protease Inhibitors: Aprotinin – inhibits tPA
2. A2-antiplasmin – inactivate any plasmin not clot-bound
Blood Coagulation Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)
Mechanism - pathologically activated coagulation & fibrinolytic systems,
1. Vascular injury exposes reactive subendothelial matrix generalized intravascular clotting & bleeding
proteins (collagen & vWf) - may follow massive tissue injury, advanced cancers, OB
2. platelet adherence, activation, secretion and synthesis of emergencies
vasoconstrictors & platelet-recruiting & activating molecules - tx is to control the underlying disease process
(TXA2, ADP, 5HT)
3. conformational change in IIB/IIIA receptors enabling it to Activators of Fibrinolytic system (for thrombotic disease)
bind fibrinogen Tissue plasminogen activator
4. Aggregation & platelet plug formation Urokinase
Streptokinase
• Simultaneous with these events:
1. coagulation cascade activated Inhibitors of Fibrinolysis
2. thrombin generation & fibrin clot, stabilizing the platelet Aminocaproic Acid
plug
Diagnostic Significance: Anticoagulant Drugs
• Defects in primary hemostasis (formation of platelet plug) Indirect Thrombin Inhibitors
Heparin (Unfractionated, Low-Molecular-Weight, & Fondaparinux)
– bleed from mucosal sites with injury
- biologic activity dependent upon antithrombin
• Defects in secondary hemostasis (clotting) – bleed in - functions as a cofactor without being consumed
deep tissues often with no apparent inciting event, may - bind to antithrombin, cause conformational change, exposes
recur unpredictably active site to proteases, protease complex formed, heparin
is released to bind to more antithrombin
White Vs Red thrombi - Monitoring: aPTT & Protamine titration (UFH)
White – platelet-rich (arterial thrombi – limb amputation or
organ failure)
- Major ADR: bleeding (women & renal failure px more prone)
Red – fibrin-rich, contain large number of trapped RBC (venous - Other ADR: allergy (animal source), alopecia,
thrombi – pulmonary embolism) - osteoporosis, spontaneous fractures, mineralocorticoid
deficiency (long term)
- Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia (HIT) – systemic,
Cascade hypercoagulable state; tx by discontinuing heparin & direct
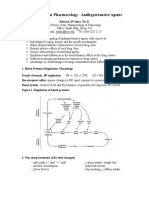
Initiation of Clotting: Tissue Factor-VIIa Complex thrombin inhibitor or fondaparinux
1.exposure of TF on damaged epithelium binds TF to VIIa - Consider:
(regulated by TFPI) o Platelet counts done frequently
2.complex formed activates IX , X o Thrombocytopenia and new thrombus suspicious for
3.Xa with Va (prothrombinase complex) convert II to thrombin HIT
4.thrombin activates V, VIII, XI resulting in amplification of
thrombin generation
- Contraindication: HIT, hypersensitivity, active bleeding,
Clinical Significance: hemophilia, significant thrombocytopenia, purpura,
• Patients with Factor VIII & IX deficiency (hemophilia A & intracranial hemorrhage, severe HPN, infective endocarditis,
active TB, GIT ulcer, threatened abortion, visceral
B) have severe bleeding disorder
Elyu, Brim & Virns 1 of 3
Pharmacology – Drugs Used Coagulation Disorders by Katzung Page 2 of 3
carcinoma, advanced hepatic/renal disease, undergone Clopidogrel & Ticlopidine
surgery or lumbar puncture, anesthesia - inhibit ADP pathway of platelets
- No placental transfer but used only in pregnant women - ADR of ticlopidine – nausea, dyspepsia, diarrhea,
when clearly indicated hemorrhage, leucopenia, TTP
- ADR of clopidogrel – fewer ADR, associated with
Direct Thrombin Inhibitors neutropenia, TTP, preferred over ticlopidine
- directly binds to active site of thrombin, inhibiting its effects
- Hirudin & Bivalirudin – bivalent DTIs binding both in active & GLP IIB/IIIA Receptor Blockers
substrate recognition site - acute coronary syndromes
- Argatroban & Melagatran – active site only - inhibit platelet IIb/IIIa receptor complex
- persons lacking this receptor – Glanzmann’s
1. Hirudin thrombasthenia (platelet aggregation)
- specific, irreversible thrombin inhibitor from leech saliva - Abciximab – directed against the receptor &
- available in recombinant form – Lepirudin vibronectin receptor
- independent of antithrombin (reach & inactivate fibrin- - Eptifibatide and Tirofiban – inhibit ligand binding to
bound thrombin in thrombi) the receptor by occupancy of the receptor but not the
- aPTT monitoring vibronectin
- excreted by kidney (caution in renal insufficiency);
anaphylaxis Dipyridamole
- - Vasodilator
2. Bivalirudin – inhibits platelet activation; for percutaneous - inhibit adenosine uptake & cGMP phosphodiesterase
coronary angioplasty activity
- In combination with aspirin to prevent cerebrovascular
3. Argatroban – used in px with HIT with or without
ischemia
thrombosis; coronary angioplasty in px with HIT - With warfarin – primary prophylaxis of thromboemboli
4. Ximelagatran (prodrug of melagatran) in px with prosthetic heart valves
- predictable PK & Bioavailability (for fixed dosing &
predictable anticoag response) Cilostazol
- no need for monitoring; no interaction with P450- - newer phosphodiesterase inhibitor
interacting drugs - promotes VD and inhibition of platelet aggregation
- hepatic toxicity - treating intermittent claudication
Warfarin (Coumarin) Drugs Used to Prevent Clotting
- 100% bioavailability; as Na salt Venous Thrombosis
- block γ-carboxylation of factors II, VII, IX, X (vitamin K A. Inherited
dependent) as well as endogenous anticoagulant (protein C - tendency to form thrombi from normal anticoagulant
and S) abnormalities thrombophilia
- crosses the placenta
- should never used during pregnancy B. Acquired
- monitoring: Prothrombin time - thromboembolism associated with atrial fibrillation &
- the most serious drug interactions with warfarin – increase placement of mechanical valves, prolonged bed rest, high-
anticoagulant effect & risk of bleeding risk surgical procedures, cancer, Antiphospholipic Antibody
- interactions with pyrazolones phenylbutazone & syndrome, and drugs (synergistic risk factor)
sulfinpyrazone – hypoprothrombinemia and inhibit platelet
function, may induce PUD Prevention
- heparin & warfarin to prevent venous thrombosis
Fibrinolytic Drugs - SC admin of low-dose unfractionated heparin, LMWH, or
- conversion of plasminogen to plasmin fondaparinux – prophylaxis (also warfarin but requires
monitoring of Prothrombin Time)
1. Streptokinase- protein synthesized by strep
2. Urokinase – human enzyme synthesized by kidney, directly Tx of Established Disease
converting plasminogen to plasmin - initiated with unfractionated of LMW Heparin for first 5-7
3. Anistreplase – complex of human plasminogen & bacterial days, with an overlap of warfarin
streptokinase - pregnant women – subcutaneous heparin (warfarin crosses
placenta)
4. t-PA - endogenous
5. Alteplase & Reteplase – recombinant human t-PA Arterial Thrombosis
6. Tenecteplase – mutant form of t-PA - activation of platelets considered an essential process
- TIA, strokes, unstable angina, acute MI
Indications (through IV route): o Tx: PLATELET-INHIBITING DRUGS (aspirin, clopidogrel,
- pulmonary embolism with hemodynamic instability ticlopidine)
- severe deep venous thrombosis (SVC syndrome) - In angina & infarction: used in conjunction with B-blocker,
- ascending thrombophlebitis Ca Channel Blockers, Fibrinolytic drugs
Antiplatelet Agents Drugs used in Bleeding Disorders
Aspirin Vitamin K
- inhibits synthesis of TXA2 - K2 menaquinone (found in human tissues)
- primary prophylaxis of MI - K3 menadione should never be used in therapeutics
- Vitamin K1 phytonadione (found in food)
Pharmacology – Drugs Used Coagulation Disorders by Katzung Page 3 of 3
o Available in oral or parenteral forms
o IV infusion should be slow (dyspnea, chest & back pain,
death)
o In newborns (prevent HDN associated with Vit K
deficiency)
Plasma Fractions (see table 34-3 pp 557)
Fibrinolytic Inhibitors: Aminocaproic Acid (EACA)
- Chemically similar to lysine
- synthetic inhibitor of fibrinolysis
- competitively inhibits plasminogen activation
- rapidly absorbed orally, cleared by kidney
- Tranexamic acid – analog of EACA
- Adjunct tx for hemophilia
- Tx for bleeding from fibrinolytic tx
- Prophylaxis for rebleeding from intracranial aneurysms
- ADR: intravascular thrombosis from inhibition of
plasminogen activator, Hypotension, myopathy, abdominal
discomfort, diarrhea, nasal stuffiness
- CI: DIC, upper GUT bleeding because of potential excessive
clotting
Serine Protease Inhibitors: Aprotinin
- inhibits fibrinolysis
- inhibits plasmin-streptokinase complex
- reduce bleeding by 50% (surgical)
- ADR: MI, stroke, renal damage, anaphylaxis (small test dose
done first)
Special thanks kina anne.. for sharing sa paggwa nito..
Detox corner…
Do What Heart Says . . .
Horror gripped the heart of a World War-I soldier, as he saw his lifelong
friend fall in battle. The soldier asked his Lieutenant if he could go out to
bring his fallen comrade back. "You can go," said the Lieutenant, "but
don't think it will be worth it. Your friend is probably dead and you may
throw your life away.."
The Lieutenant's words didn't matter, and the soldier went anyway.
Miraculously, he managed to reach his friend, hoisted him onto his
shoulder and brought him back to their company's trench. The officer
checked the wounded soldier , then looked kindly at his friend.
"I told you it wouldn't be worth it..," he said. "Your friend is dead and you
are mortally wounded.." " It was worth it, Sir," said the soldier..
"What do you mean by worth it?" responded the Lieutenant. " Your friend
is dead." "Yes Sir," the soldier answered, " but it was worth it because
when I got to him,he was still alive and I had the satisfaction of hearing
him say...." Jim...I knew you'd come..."
Many times in life, whether a thing is worth doing or not, really depends
on how u look at it. Take up all your courage and do something your heart
tells you to do so that you may not regret not doing it later in your life . .
You might also like
- Basic Examination of Urine - Dr. PinedaDocument20 pagesBasic Examination of Urine - Dr. PinedaElei GarciaNo ratings yet
- Anemia and Hematologic Drugs - KatzungDocument4 pagesAnemia and Hematologic Drugs - Katzungsarguss14100% (1)
- Pharmacology of EthanolDocument5 pagesPharmacology of EthanolJoshua RemonNo ratings yet
- Pancreatic Hormones and Antidiabetic AgentsDocument3 pagesPancreatic Hormones and Antidiabetic AgentsChristian DeeNo ratings yet
- 1.05 Qualitative 0 Quantitative Platelet DisordersDocument9 pages1.05 Qualitative 0 Quantitative Platelet DisordersShiena ArchividoNo ratings yet
- Pharma Super TableDocument56 pagesPharma Super TableMarco Paulo Reyes NaoeNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Step 1 Antimicrobials ChartDocument6 pagesMicrobiology Step 1 Antimicrobials ChartM Patel100% (1)
- Cellular Adaptations and Responses to StressDocument19 pagesCellular Adaptations and Responses to StressFu Xiao ShanNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Hematologic AssessmentDocument5 pagesStudy Guide Hematologic AssessmentNancy LemusNo ratings yet
- Liver Function Tests and EnzymesDocument90 pagesLiver Function Tests and EnzymesNaji Mohamed Alfatih100% (1)
- General Pathology Lecture Group 1 HandoutDocument6 pagesGeneral Pathology Lecture Group 1 HandoutCecille AnnNo ratings yet
- Pathology Finals Reviewer on WBCs, Lymph Nodes, Spleen & ThymusDocument5 pagesPathology Finals Reviewer on WBCs, Lymph Nodes, Spleen & Thymusangel_sagun_1No ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Table BasicDocument7 pagesAntimicrobial Table BasicPAschoolstuffNo ratings yet
- Genetic and Pediatric Diseases Chapter SummaryDocument16 pagesGenetic and Pediatric Diseases Chapter SummaryJustine HungNo ratings yet
- Surgery I Block 4 Super Reviewer PDFDocument14 pagesSurgery I Block 4 Super Reviewer PDFlems9No ratings yet
- Cholinergic DrugsDocument44 pagesCholinergic Drugskhuzaima9100% (1)
- Superficial and Cutaneous Mycoses: 2. Disease CharacteristicsDocument4 pagesSuperficial and Cutaneous Mycoses: 2. Disease CharacteristicsMA. ANGELI DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Mnemonic SDocument42 pagesMnemonic SWen Jie LauNo ratings yet
- Hemophilia Nursing CareDocument10 pagesHemophilia Nursing CareEla 15No ratings yet
- Glucocorticoids & Their EffectsDocument5 pagesGlucocorticoids & Their EffectsJENICCA GONo ratings yet
- Immuno-Serology & Blood Banking Case Study: Systemic Lupus ErythematosusDocument6 pagesImmuno-Serology & Blood Banking Case Study: Systemic Lupus ErythematosusRomie SolacitoNo ratings yet
- University of Santo Tomas: Faculty of Pharmacy - Department of Medical TechnologyDocument7 pagesUniversity of Santo Tomas: Faculty of Pharmacy - Department of Medical TechnologyWynlor AbarcaNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes Haematology 1 6 PDFDocument23 pagesRevision Notes Haematology 1 6 PDFCattrainuhNo ratings yet
- Blood Gases 1Document9 pagesBlood Gases 1Osannah Irish InsongNo ratings yet
- Pharma Unit 1-2 Anti - Adrenergic DrugsDocument21 pagesPharma Unit 1-2 Anti - Adrenergic DrugsMIbrahimNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pathology ReviewDocument11 pagesClinical Pathology Reviewrob hNo ratings yet
- NCM 112: Medical Surgery CareDocument8 pagesNCM 112: Medical Surgery CareDANAH MARGARET VILLAGONZALONo ratings yet
- Genetic Disorders: A History of Key Discoveries and BreakthroughsDocument75 pagesGenetic Disorders: A History of Key Discoveries and BreakthroughscalldkNo ratings yet
- Cs 19 SolvedDocument4 pagesCs 19 SolvedgogoNo ratings yet
- Protozoan and Helminth Infections: Types, Transmission, and Clinical ManifestationsDocument2 pagesProtozoan and Helminth Infections: Types, Transmission, and Clinical Manifestationsgnb2104No ratings yet
- HIV Transmission, Pathophysiology, Clinical Manifestations and TreatmentDocument4 pagesHIV Transmission, Pathophysiology, Clinical Manifestations and TreatmentBatch V Med 2 SY 21-22No ratings yet
- Delayed Hypersensitivity and Type IV ReactionsDocument12 pagesDelayed Hypersensitivity and Type IV Reactionsella Sy100% (1)
- Cellular Injury and AdaptationsDocument145 pagesCellular Injury and AdaptationsAjmal RockzzNo ratings yet
- 1 PATHO 2a - Inflammation - Dr. BailonDocument12 pages1 PATHO 2a - Inflammation - Dr. BailontonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 27 GuytonDocument6 pagesChapter 27 GuytonGabriella ChafrinaNo ratings yet
- Gram Positive: NotesDocument37 pagesGram Positive: Notesgabb bbNo ratings yet
- Diseases of ImmunityDocument13 pagesDiseases of ImmunityRose AnnNo ratings yet
- Liver Pathology PDFDocument7 pagesLiver Pathology PDFjohn smithNo ratings yet
- Clinpath - : Red Blood CellsDocument14 pagesClinpath - : Red Blood CellsYolanda Primrosa NurhanNo ratings yet
- Micro-Para Practical Exam ReviewerDocument8 pagesMicro-Para Practical Exam ReviewerRA TranceNo ratings yet
- Hematology 1 PrelimsDocument19 pagesHematology 1 Prelimsella SyNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis of Painful Genital LesionsDocument7 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of Painful Genital LesionsKyra KhalidNo ratings yet
- ImmunologyDocument29 pagesImmunologyBis 秉禾 Box100% (4)
- PHM - Endocrine DrugsDocument3 pagesPHM - Endocrine DrugsJeanne RodiñoNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Pharmacology - Antihypertensive AgentsCardiovascular Pharmacology - Antihypertensive AgentsDocument14 pagesCardiovascular Pharmacology - Antihypertensive AgentsCardiovascular Pharmacology - Antihypertensive AgentsAndySatrioTipunkNo ratings yet
- HematologyDocument5 pagesHematologyIvy Jan OcateNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Trans 1Document4 pagesPharmacology Trans 1GLOMARIE DE GUZMANNo ratings yet
- Patho4-6 - Liver (Dr. Dy)Document13 pagesPatho4-6 - Liver (Dr. Dy)miguel cuevas100% (1)
- CANCER CHEMOTHERAPY REGIMENS AND THEIR TOXICITIESDocument13 pagesCANCER CHEMOTHERAPY REGIMENS AND THEIR TOXICITIESVaibhav Bharat100% (1)
- Lab ValuesDocument5 pagesLab Valuespragya_devkotaNo ratings yet
- Sources of Parasitic InfectionDocument74 pagesSources of Parasitic InfectionCristy Jean100% (1)
- Fluids and Electrolytes Management in Surgical PatientsDocument4 pagesFluids and Electrolytes Management in Surgical PatientsJanine Maita BalicaoNo ratings yet
- Determining The Cause: AnemiaDocument9 pagesDetermining The Cause: AnemiaSelina SubiasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Blood Vessel DiseasesDocument20 pagesChapter 11 Blood Vessel Diseasesmiguel cuevas100% (1)
- ReviewerDocument12 pagesReviewermkct111No ratings yet
- Characteristics and Treatment of Hypertension in PheochromocytomaDocument17 pagesCharacteristics and Treatment of Hypertension in PheochromocytomaJunior TorresNo ratings yet
- Immuno-Pharmacology: Dr. Harshika Patel Pharmacology and Therapeutics II Date:23/05/2018 Time: 11am - 1pmDocument90 pagesImmuno-Pharmacology: Dr. Harshika Patel Pharmacology and Therapeutics II Date:23/05/2018 Time: 11am - 1pmBob MuneneNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Inducers and Inhibitors TransDocument6 pagesEnzyme Inducers and Inhibitors TransLeonallee MayorNo ratings yet
- 1120314晨會 Miller Ch50. Patient Blood Management CoagulationDocument56 pages1120314晨會 Miller Ch50. Patient Blood Management Coagulationw8412358No ratings yet
- Blok 5 Hemostatic DrugDocument39 pagesBlok 5 Hemostatic DrugPutri HusnanNo ratings yet
- World Gastroenterology Organization Global GuidelineDocument29 pagesWorld Gastroenterology Organization Global GuidelineRizky Rachmania AmandaNo ratings yet
- Preoperative EvaluationDocument25 pagesPreoperative Evaluationsarguss14No ratings yet
- Epidural and Spinal AnesthesiaDocument86 pagesEpidural and Spinal Anesthesiasarguss1471% (7)
- Axial Arthritis: Degenerative Annular DiseaseDocument18 pagesAxial Arthritis: Degenerative Annular Diseasesarguss14100% (1)
- Introduction To RadiologyDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Radiologysarguss14No ratings yet
- Stage 1: Dorsal Induction: Pediatric NeuroradiologyDocument8 pagesStage 1: Dorsal Induction: Pediatric Neuroradiologysarguss14100% (1)
- NeuroradiologyDocument11 pagesNeuroradiologysarguss14100% (2)
- Inhalational Anesthetics: Patigas, Requinta, ResuelloDocument88 pagesInhalational Anesthetics: Patigas, Requinta, Resuellosarguss140% (1)
- Small BowelDocument4 pagesSmall Bowelsarguss14100% (1)
- Cyanotic Congenital Heart Diseases, Etc.Document12 pagesCyanotic Congenital Heart Diseases, Etc.sarguss14100% (2)
- Kidney, Ureter, BladderDocument12 pagesKidney, Ureter, Bladdersarguss14100% (1)
- From Doc Bandong's Own Words:: Shar 1 of 20Document20 pagesFrom Doc Bandong's Own Words:: Shar 1 of 20sarguss14100% (1)
- Male PelvisDocument8 pagesMale Pelvissarguss14100% (1)
- Male Genital TractDocument7 pagesMale Genital Tractsarguss14No ratings yet
- Pediatric GI RadiologyDocument6 pagesPediatric GI Radiologysarguss14No ratings yet
- Gallbladder, Liver, Pancreas and SpleenDocument19 pagesGallbladder, Liver, Pancreas and Spleensarguss14100% (3)
- CNS Tumors and Infections Part3Document6 pagesCNS Tumors and Infections Part3sarguss14100% (1)
- Genitourinary SystemDocument8 pagesGenitourinary Systemsarguss14100% (1)
- Extracerebral Hemorrhage, Etc.Document14 pagesExtracerebral Hemorrhage, Etc.sarguss14No ratings yet
- Cardiac ImagingDocument7 pagesCardiac Imagingsarguss14No ratings yet
- Chest RadiologyDocument3 pagesChest Radiologysarguss14No ratings yet
- CNS Tumors and Infections Part2Document2 pagesCNS Tumors and Infections Part2sarguss14No ratings yet
- Bone TumorsDocument15 pagesBone Tumorssarguss1450% (2)
- CNS Tumors and Infections Part1Document2 pagesCNS Tumors and Infections Part1sarguss14100% (1)
- NeuroradiologyDocument25 pagesNeuroradiologysarguss14100% (2)
- Congenital Cystic Adenomatoid Malformation (CCAM)Document7 pagesCongenital Cystic Adenomatoid Malformation (CCAM)sarguss14No ratings yet
- ArthritisDocument9 pagesArthritissarguss14100% (1)
- Pleura and MediastinumDocument16 pagesPleura and Mediastinumsarguss14100% (1)
- Genitourinary SystemDocument8 pagesGenitourinary Systemsarguss14100% (1)
- Introduction To RadiologyDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Radiologysarguss14No ratings yet
- Dracaena Cinnabari Research PaperDocument6 pagesDracaena Cinnabari Research Paperapi-272090995No ratings yet
- Rshakmgp-011r Glp-1 (Active) Elisa Kit Eng.001Document18 pagesRshakmgp-011r Glp-1 (Active) Elisa Kit Eng.001scribdNo ratings yet
- Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Origin, Function, Imaging, and TherapeuticDocument33 pagesCancer-Associated Fibroblasts Origin, Function, Imaging, and TherapeuticANA PAULANo ratings yet
- Aboleth Guide to Deadly Deep Sea CreatureDocument1 pageAboleth Guide to Deadly Deep Sea CreatureYugi Oh0% (1)
- Astral Dynamics Learning Astral Projection With The Brainwave GeneratorDocument7 pagesAstral Dynamics Learning Astral Projection With The Brainwave GeneratorDi Patrizio SaraNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0923181121000840 MainDocument16 pages1 s2.0 S0923181121000840 Mainleon4009No ratings yet
- Antenna of Chalcidoidea and Its Significance 22Document17 pagesAntenna of Chalcidoidea and Its Significance 22kalaielakkiya98No ratings yet
- NS Conduction and NeurotransmissionDocument23 pagesNS Conduction and Neurotransmissionbav92100% (1)
- USMLE Flashcards: Behavioral Science - Side by SideDocument96 pagesUSMLE Flashcards: Behavioral Science - Side by SideMedSchoolStuffNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Sex HormonesDocument6 pagesPharmacology of Sex Hormonesarnold23456100% (4)
- Cell Adhesion Molecules 300107Document32 pagesCell Adhesion Molecules 300107V Lee 'Nozhat'100% (1)
- Interpreting Blood Gases Easy As Abc PDFDocument6 pagesInterpreting Blood Gases Easy As Abc PDFmuhammad hidayahNo ratings yet
- JCD - Vol - 4 - No - 1 - Vitamins and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Dr. ABM Kamrul Hasana Dr. AKM Aminul Islam Dr. Moinul Islam Dr. Shahjada Selim PDFDocument8 pagesJCD - Vol - 4 - No - 1 - Vitamins and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Dr. ABM Kamrul Hasana Dr. AKM Aminul Islam Dr. Moinul Islam Dr. Shahjada Selim PDFFiona Marie Berlon DyangkoNo ratings yet
- FlatwormsDocument19 pagesFlatwormsanon :)No ratings yet
- Introduction To Biochemistry: Ms. Jirehkriza G. Suganob General Biology 1Document27 pagesIntroduction To Biochemistry: Ms. Jirehkriza G. Suganob General Biology 1Jcob SntosNo ratings yet
- Screen Sleep Disorders QuestionnaireDocument2 pagesScreen Sleep Disorders QuestionnaireMarivic Sonido100% (1)
- Branford High SchoolDocument1 pageBranford High SchoolHelen BennettNo ratings yet
- Wanted: On The Organelle TrailDocument5 pagesWanted: On The Organelle TrailMOISES DEANDANo ratings yet
- The Effect of The Methanol Extract of Haloxylon Salicornicum (Moq.) Bunge Ex Bioss. On Alleviating in AmmationsDocument8 pagesThe Effect of The Methanol Extract of Haloxylon Salicornicum (Moq.) Bunge Ex Bioss. On Alleviating in AmmationszzakieNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic and Cholinergic (2017 - 11 - 01 22 - 03 - 49 UTC)Document2 pagesAdrenergic and Cholinergic (2017 - 11 - 01 22 - 03 - 49 UTC)Kimberly WhitesideNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMDocument14 pagesBIOCHEMLyhNo ratings yet
- General - GITDocument90 pagesGeneral - GITAbdallah GamalNo ratings yet
- Catalase AEBIDocument6 pagesCatalase AEBIGabriel CamarenaNo ratings yet
- Encyclopedia of Biological Chemistry - Vol - 1Document895 pagesEncyclopedia of Biological Chemistry - Vol - 1aishbiyaNo ratings yet
- NehaDocument7 pagesNehaJisha Mohd Athar QureshiNo ratings yet
- Human Male Reproductive SystemDocument45 pagesHuman Male Reproductive Systemcyber secNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2: 2 Quarter - Module 2Document2 pagesGeneral Biology 2: 2 Quarter - Module 2Veronica RojasNo ratings yet
- FULLY REVISED EDITION: NEET RANK EDGE SERIES BIOLOGYDocument111 pagesFULLY REVISED EDITION: NEET RANK EDGE SERIES BIOLOGYSam MishraNo ratings yet
- Post-Operative Care, DSTC Online, Jun.2021Document38 pagesPost-Operative Care, DSTC Online, Jun.2021tepat rshsNo ratings yet
- Enteral Feeding GuidelinesDocument15 pagesEnteral Feeding GuidelinesAnonymous rDD9I2No ratings yet