Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bandwidth Management
Uploaded by
Mania PauldoeOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bandwidth Management
Uploaded by
Mania PauldoeCopyright:
Available Formats
Bandwidth management Bandwidth management is the process of measuring and controlling the communications (traffic, packets) on a network link,
to avoid filling the link to capacity or overfilling the link, which would result in network congestion and poor performance of the network.
What is Bandwidth Management? Bandwidth management is a general term given to a collection of tools and techniques that an organization can use to reduce demand on critical segments of networks. Often bandwidth management may be applied on the WAN / LAN segment that connects the organization to the greater Internet.
What Are the Issues to be addressed?
Techniques brought to bear on bandwidth management include these:
Data compression, to reduce the size of the data that must be transmitted. Local caching, to store frequently used data locally instead of transmitting it multiple times. Bandwidth prioritization, to allocate bandwidth based on the importance of the application. Distributed content, to move content from a single location to multiple locations nearer the end users. Blocking unauthorized traffic. Internet accounting packages, to track bandwidth usage and charge it back to customers (commonly used at Australian universities). User education, to educate users about the consequences of their actions and convince them to be good citizens on the network.
Bandwidth management vendors currently operating in the marketplace include: Peribit Networks SR-50 Sequence Reducer compresses data by eliminating repetitions using Molecular Sequence Reduction (MSR) technology Expand Networks ACCELERATORs combine data compression, caching, and prioritization techniques in combination Allot Communications NetEnforcer uses bandwidth prioritization, and their CacheEnforcer uses caching Packeteers PacketShaper uses bandwidth prioritization schemes to monitor, block, and throttle traffic Intelligent Compression Technologies AcceleNet and Xpress Suite use data compression Akamais EdgeSuite distributes content to a global network of servers Akonix Systems L7 Solution detects and blocks rogue protocols at the networks edge Palisade Systems PacketHound uses bandwidth prioritization schemes to monitor, block, and throttle traffic Inktomis Traffic Edge combines caching and filtering strategies Digiquants Internet Management System does Internet accounting and billing to end users
Hansen Technologies Hub does Internet accounting and billing to end users
Management Bandwidth management mechanisms may be used to further engineer performance and includes: Traffic shaping (rate limiting): TCP rate control - artificially adjusting TCP window size as well as controlling the rate of ACKs being returned to the sender
Scheduling algorithms: Weighted fair queuing (WFQ) Class based weighted fair queuing Weighted round robin (WRR) Deficit weighted round robin (DWRR) Hierarchical Fair Service Curve (HFSC) Congestion avoidance: RED, WRED - Lessens the possibility of port queue buffer tail-drops and this lowers the likelihood of TCP global synchronization Policing (marking/dropping the packet in excess of the committed traffic rate and burst size) Explicit congestion notification Buffer tuning Bandwidth reservation protocols / algorithms Resource reservation protocol (RSVP) Constraint-based Routing Label Distribution Protocol (CR-LDP) Top-nodes algorithm
Link performance Issues which may limit the performance of a given link include: TCP determines the capacity of a connection by flooding it until packets start being dropped (Slow-start) Queueing in routers results in higher latency and jitter as the network approaches (and occasionally exceeds) capacity
TCP global synchronization when the network reaches capacity results in waste of bandwidth Burstiness of web traffic requires spare bandwidth to rapidly accommodate the bursty traffic Lack of widespread support for explicit congestion notification and Quality of Service management on the Internet Internet Service Providers typically retain control over queue management and quality of service at their end of the link Window Shaping allows higher end products to reduce traffic flows, which reduce queue depth and allow more users to share more bandwidth fairly
Tools and techniques Packet sniffer Network traffic measurement
You might also like
- Application Delivery Controller and Virtualization (18CS7G2)Document16 pagesApplication Delivery Controller and Virtualization (18CS7G2)Ritesh HosunNo ratings yet
- Smart Traffic Management in High-Speed Networks by Fuzzy Logic ControlDocument7 pagesSmart Traffic Management in High-Speed Networks by Fuzzy Logic ControlInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- CN QuestionsDocument13 pagesCN QuestionsDhruv KumawatNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four: Network Design and Implementations ConceptsDocument21 pagesChapter Four: Network Design and Implementations ConceptsPro NebyuNo ratings yet
- Using Fuzzy Logic Control To Provide Intelligent Traffic Management Service For High-Speed NetworksDocument9 pagesUsing Fuzzy Logic Control To Provide Intelligent Traffic Management Service For High-Speed NetworksanraomcaNo ratings yet
- Traffic Regulation Mechanism Using Heecp Protocol For D.NDocument55 pagesTraffic Regulation Mechanism Using Heecp Protocol For D.NgoswamiphotostatNo ratings yet
- Combined To Many Logics: Iii. ImplementationDocument4 pagesCombined To Many Logics: Iii. ImplementationNandkishore PatilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document13 pagesChapter 1Hemn KamalNo ratings yet
- SANGFOR - WANO - v9.5.3 - Associate - 01 - Basic IntroductionDocument24 pagesSANGFOR - WANO - v9.5.3 - Associate - 01 - Basic Introductionwendy yohanesNo ratings yet
- Quality of ServicesDocument7 pagesQuality of ServicesVaishnavi TawareNo ratings yet
- HNE211 Demo QuestionsDocument4 pagesHNE211 Demo QuestionsArtwell SitholeNo ratings yet
- Agent: Refers To The Software in The Managed Element (The Router, Hub, Other Device) ThatDocument23 pagesAgent: Refers To The Software in The Managed Element (The Router, Hub, Other Device) Thatmahboobiqbal09No ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Wireless and Mobile Computing - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument10 pagesUnit 4 - Wireless and Mobile Computing - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inSana SheikhNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks 3Document10 pagesComputer Networks 3eshanpadhiar3No ratings yet
- Reference Congestion ControlDocument2 pagesReference Congestion ControlVamshi BoddulaNo ratings yet
- Qos and ModelsDocument3 pagesQos and ModelsJoseph AttardNo ratings yet
- Network Traffic Management: Angelina SunnyDocument3 pagesNetwork Traffic Management: Angelina SunnyAngelina SunnyNo ratings yet
- Missing AnswersDocument8 pagesMissing AnswersManzil TanvirNo ratings yet
- 07-03 Mini Project - Copy EditedDocument57 pages07-03 Mini Project - Copy EditedStella BathulaNo ratings yet
- Destination, Computes The Delay and Sends A Backward: Iv Snapshots SourceDocument4 pagesDestination, Computes The Delay and Sends A Backward: Iv Snapshots SourceNandkishore PatilNo ratings yet
- Tcp-Ip Unit 3Document14 pagesTcp-Ip Unit 3poojadharme16No ratings yet
- Network CongestionDocument9 pagesNetwork Congestionpy thonNo ratings yet
- Business Data Telecom Assignment 2Document14 pagesBusiness Data Telecom Assignment 2hndNo ratings yet
- BW BenchmarkDocument22 pagesBW BenchmarkCentaur ArcherNo ratings yet
- Myths of Bandwidth Optimization: White PaperDocument11 pagesMyths of Bandwidth Optimization: White Paperamos_evaNo ratings yet
- Queue Based Congestion Control Protocol On Wireless Sensor NetworksDocument6 pagesQueue Based Congestion Control Protocol On Wireless Sensor NetworksRaghav ManaiNo ratings yet
- Submission 116 vlan-D-SahaDocument6 pagesSubmission 116 vlan-D-SahaWaleed QassemNo ratings yet
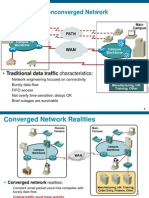
- Traditional Nonconverged Network: Traditional Data Traffic CharacteristicsDocument40 pagesTraditional Nonconverged Network: Traditional Data Traffic CharacteristicsCesar CriolloNo ratings yet
- Optimizing Congestion Control by Using Devices Authentication in Software-Defined NetworksDocument15 pagesOptimizing Congestion Control by Using Devices Authentication in Software-Defined NetworksAIRCC - IJNSANo ratings yet
- Managing Network BandwidthDocument6 pagesManaging Network Bandwidthamos_eva100% (1)
- Extending San Connectivity For Engenio Arrays: Sanbox 6142 Intelligent Storage RouterDocument14 pagesExtending San Connectivity For Engenio Arrays: Sanbox 6142 Intelligent Storage RoutertatallorNo ratings yet
- Best Practices For WAN Design and Capacity PlanningDocument10 pagesBest Practices For WAN Design and Capacity PlanningsuhailkapoorNo ratings yet
- Using Fuzzy Logic Control To Provide Intelligent Traffic Management Service For High Speed NetworksDocument4 pagesUsing Fuzzy Logic Control To Provide Intelligent Traffic Management Service For High Speed NetworksNandkishore PatilNo ratings yet
- Congestion Control Algorithm33Document5 pagesCongestion Control Algorithm334nn21is019No ratings yet
- Ubicc Paper 33 33Document11 pagesUbicc Paper 33 33Usman TariqNo ratings yet
- STN QB Unit 2Document18 pagesSTN QB Unit 2Mahima mpNo ratings yet
- Data Center NetworkingDocument5 pagesData Center NetworkingIvan CappilloNo ratings yet
- Fast-Response Dynamic RoutingDocument9 pagesFast-Response Dynamic RoutingChirag SachdevaNo ratings yet
- Over ProvisioningDocument3 pagesOver ProvisioningscribdslaskNo ratings yet
- Topology Architectures and Network ComponentsDocument51 pagesTopology Architectures and Network ComponentsNgọc HuyNo ratings yet
- Fast Ip Recovery 2Document13 pagesFast Ip Recovery 2Murali DaranNo ratings yet
- Combined To Many Logics: Iii. ImplementationDocument4 pagesCombined To Many Logics: Iii. ImplementationNandkishore PatilNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Choosing The Right Bus Technology: Lan, Usb, Gpib, Pci/PxiDocument12 pages3.1 Choosing The Right Bus Technology: Lan, Usb, Gpib, Pci/PxiAnsar MNo ratings yet
- Network Traffic Management: By: Kareena PatelDocument25 pagesNetwork Traffic Management: By: Kareena Patel47-kareena patelNo ratings yet
- Part 5: Transport Protocols For Wireless Mobile Networks: Sequence NumbersDocument6 pagesPart 5: Transport Protocols For Wireless Mobile Networks: Sequence NumbersKani MozhiNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning Prediction Approach To Enhance Congestion Control in 5G IoT EnvironmentDocument10 pagesMachine Learning Prediction Approach To Enhance Congestion Control in 5G IoT EnvironmentRashika KhannaNo ratings yet
- Plan If 2000Document5 pagesPlan If 2000kajfahmNo ratings yet
- TCP ACC Simulation Enhanced Congestion Window Increment and Adaptive Fast Recovery Congestion Control Algorithm in Wired Network Scenario19!1!18Document13 pagesTCP ACC Simulation Enhanced Congestion Window Increment and Adaptive Fast Recovery Congestion Control Algorithm in Wired Network Scenario19!1!18GirishPaliwalNo ratings yet
- Network Planning PrinciplesDocument42 pagesNetwork Planning Principleszbekele100% (1)
- Client Server Network DCCDocument4 pagesClient Server Network DCCbhattanushka60No ratings yet
- Fuzzy RED To Reduce Packet Loss in Computer NetworkDocument8 pagesFuzzy RED To Reduce Packet Loss in Computer Networkkhald4233No ratings yet
- Faster Transimission of DataDocument7 pagesFaster Transimission of DataPruthvi PrakashaNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Multimedia Future NetworkingDocument9 pagesUnit 7 Multimedia Future Networkingnirjan ghimireNo ratings yet
- Routing AlgorithmsDocument2 pagesRouting Algorithmsaadi1988No ratings yet
- Local Area NetworkDocument83 pagesLocal Area Networknegikshitij3No ratings yet
- Traffic Isolation and Network Resource Sharing For Performance Control in GridsDocument6 pagesTraffic Isolation and Network Resource Sharing For Performance Control in Gridsmax37No ratings yet
- COEN 3193 (Data Communications) - Chapter 3Document80 pagesCOEN 3193 (Data Communications) - Chapter 3Joel ManacmulNo ratings yet
- DESIGNING AND SUPPORTING COMPUTER NETWORK FileDocument28 pagesDESIGNING AND SUPPORTING COMPUTER NETWORK FileKarandeep Singh100% (4)
- Packet Loss Control Using STLCC MechanismDocument4 pagesPacket Loss Control Using STLCC MechanismseventhsensegroupNo ratings yet
- Call Direct Cellular Solutions CD Series Cellular Router AT (V.250) Command ManualDocument33 pagesCall Direct Cellular Solutions CD Series Cellular Router AT (V.250) Command Manualdjnhh0anNo ratings yet
- ZigbeeDocument38 pagesZigbeePrabhat SharmaNo ratings yet
- Computer Communication & Networks COMP 3112: Lecture # 01Document23 pagesComputer Communication & Networks COMP 3112: Lecture # 01Iqra zaibNo ratings yet
- Final ReportDocument8 pagesFinal ReportolcenasNo ratings yet
- Bank Payment Integration in Using H2H ConnectivityDocument10 pagesBank Payment Integration in Using H2H Connectivitysudhirpatil15No ratings yet
- Fortigate Cli Ref 54Document438 pagesFortigate Cli Ref 54Seshi KanthNo ratings yet
- Nokia MSAN Project Integration Proposal (17 Sites)Document8 pagesNokia MSAN Project Integration Proposal (17 Sites)amde tessemaNo ratings yet
- The Berkeley Sockets API: Networked Systems Architecture 3Document25 pagesThe Berkeley Sockets API: Networked Systems Architecture 3Sowmya MadhavanNo ratings yet
- DS-2CD6424FWD-10'20'30'40 2MP Covert Network Camera: Key FeaturesDocument3 pagesDS-2CD6424FWD-10'20'30'40 2MP Covert Network Camera: Key FeaturesneoalexaNo ratings yet
- Windows Networking Interview QuestionsDocument10 pagesWindows Networking Interview QuestionsSupriyo SahaNo ratings yet
- TestDocument16 pagesTestabdullah asshidiqNo ratings yet
- IJTC201512002-Comparative Study and Evaluation of AODV, DSR and OLSR ProtocolsDocument8 pagesIJTC201512002-Comparative Study and Evaluation of AODV, DSR and OLSR ProtocolsInternational Journal of Technology and Computing (IJTC)No ratings yet
- SD WAN TopologiesDocument21 pagesSD WAN Topologieschriscaldas5No ratings yet
- 3GPP TS 38.340Document22 pages3GPP TS 38.340holapaquitoNo ratings yet
- Duplex Config FlagsDocument5 pagesDuplex Config FlagsEddy GuttyNo ratings yet
- MdrsDocument36 pagesMdrsDeepakdarsan MoharanaNo ratings yet
- 01 02 Ethernet. Cables de Conexion EthernetpdfDocument9 pages01 02 Ethernet. Cables de Conexion EthernetpdfdimarclNo ratings yet
- AX86U WAN LinkAggregation Mode0 Possible QuestionDocument1 pageAX86U WAN LinkAggregation Mode0 Possible QuestionRafael KnabenNo ratings yet
- Be Winter 2022Document1 pageBe Winter 2022Jenish LathiyaNo ratings yet
- Tellabs 8110 Network Terminating Unit (CTU-R) Managed Broadband DSL Router FP1.3Document3 pagesTellabs 8110 Network Terminating Unit (CTU-R) Managed Broadband DSL Router FP1.3MauricioNo ratings yet
- Equivalencias Comandos Huawei Vs Cisco14Document94 pagesEquivalencias Comandos Huawei Vs Cisco14David BenavidesNo ratings yet
- Multicast ConsiderationsDocument19 pagesMulticast Considerationsjorigoni2013No ratings yet
- Modular Qos Configuration Guide For Cisco Ncs 540 Series Routers, Cisco Ios XR Release 7.4.XDocument114 pagesModular Qos Configuration Guide For Cisco Ncs 540 Series Routers, Cisco Ios XR Release 7.4.XCCIE RocksNo ratings yet
- Network Organization Concepts: Understanding Operating Systems, Fourth EditionDocument73 pagesNetwork Organization Concepts: Understanding Operating Systems, Fourth EditionrekxyNo ratings yet
- Data Network Design Technical Training CourseDocument1 pageData Network Design Technical Training Courseshriniwas ghadyaljiNo ratings yet
- Satellite Communication - 7Document47 pagesSatellite Communication - 7Ramesh KonakallaNo ratings yet
- The Internet: Chapter 1 Lesson 1Document28 pagesThe Internet: Chapter 1 Lesson 1Ray TuayonNo ratings yet
- Architecture QoS - Partie 07 ModeÌ Le DiffServ PDFDocument15 pagesArchitecture QoS - Partie 07 ModeÌ Le DiffServ PDFMo SalahNo ratings yet
- BRCD Edge Loop Detection DPDocument20 pagesBRCD Edge Loop Detection DPHam ZaNo ratings yet
- Chap 3 CNDocument25 pagesChap 3 CN48Nara Amit GopalNo ratings yet