Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Principle of Teaching Reading
Uploaded by
Azlie IbrahimOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Principle of Teaching Reading
Uploaded by
Azlie IbrahimCopyright:
Available Formats
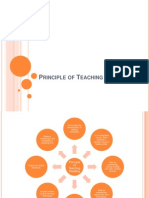
PRINCIPLE OF TEACHING READING
Encourage the development of reading strategies. Balance authenticity and readability in choosing text. In an integrated course, don't overlook a specific focus on reading skills.
Follow the SQ3R sequence.
Principle of Teaching Reading
Plan on prereading, during-reading and after reading phases
Include bottomup and top-down techniques Use technique that are intrinsically motivating.
Build as assessment aspect into your techniques.
IN AN INTEGRATED COURSE, DON'T OVERLOOK A SPECIFIC FOCUS ON READING SKILLS.
Give time for students to do silent reading that can develop a sense of fluency. Silent reading also becomes an excellent method for self-instruction on the part of learner.
USE TECHNIQUE THAT ARE INTRINSICALLY MOTIVATING.
Just focus on the goals, choose material that is relevant with the goals also the interest of students. You also can use LEA (Language Experience Approach), it is the famous one to motivating approach for reading instruction. LEA referred to where students create their own material for reading.
BALANCE AUTHENTICITY AND READABILITY IN CHOOSING TEXT.
Christine Nuttall (1996) offered three criteria for choosing reading texts: Suitability of content--> students will find interesting, enjoyable, challenging, and appropriate for their goals in learning English. Exploitability--> a text that facilitates the achievement of certain language and content goals. Readability--> a text with lexical and structural difficulty that will challenge students without overwhelming them.
ENCOURAGE THE DEVELOPMENT OF READING STRATEGIES.
To what extent are you getting your students to use all these strategies?
INCLUDE BOTTOM-UP AND TOP-DOWN TECHNIQUES
Make sure you give enough classroom time to focusing on the building blocks of written language, geared appropriately for each level.
FOLLOW THE SQ3R SEQUENCE.
SQ3R following five steps:
Survey: Skim the text to overview of the main ideas Question: Reader ask her/ his wishes to get out of the text Read: Read the text while looking for answers Recite: Write the point of the passage Review: Assess the importance of what one has just read and incorporate it into long-term associations
PLAN ON PRE-READING, DURING-READING AND
AFTER READING PHASES
Before you read: Introduce the topic, encourage your students to skimming and scanning, predicting the main idea. While you read: Giving students a sense of purpose for reading rather than just reading because your ordered it. After you read: Comprehension questions are just one form of activity appropriate for postreading.
BUILD AS ASSESSMENT ASPECT INTO YOUR TECHNIQUES.
It is important for reading to be able to accurately assess students' comprehension and development of skills. Consider some of the following overt responses that indicate comprehension:
Doing: reader respond physically command Choosing: reader select alternative posed orally or in writing Transferring: reader summarize what they have read Answering: answer the questions Considering: reader make a note or outline Extending: reader provide the end of story Duplicating: reader translate the passage into her/ his native language Modeling: for example --> reader puts together a toy after reading directions for assembly Conversing: reader engage a conversation that indicate the information
You might also like
- Classroom Interaction and Second Language AcquisitionDocument9 pagesClassroom Interaction and Second Language AcquisitionRaniena Chokyuhyun100% (1)
- How to Build Self Confidence, Happiness and Health: Part I: Self Confidence Partii: Happiness Pariii: HealthFrom EverandHow to Build Self Confidence, Happiness and Health: Part I: Self Confidence Partii: Happiness Pariii: HealthNo ratings yet
- Classroom Discourse Analysis G1Document5 pagesClassroom Discourse Analysis G1Bensalem ImeneNo ratings yet
- Discourse Analysis and ReadingDocument57 pagesDiscourse Analysis and ReadingRahhal Ajbilou67% (3)
- F - CLT Definition - Weak and Strong VersionsDocument2 pagesF - CLT Definition - Weak and Strong VersionsAgustín AlemNo ratings yet
- PsycholinguisticsDocument39 pagesPsycholinguisticsAnie Nurrahmiani100% (1)
- Syllabus DesignDocument18 pagesSyllabus DesignAnonymous Wj6Bhcbw100% (1)
- Teaching by PrinciplesDocument50 pagesTeaching by PrinciplesSussanRooNo ratings yet
- Materials For Teaching GrammarDocument18 pagesMaterials For Teaching GrammarKit Oseias H. Castillo100% (1)
- Language Classroom Management HandoutsDocument102 pagesLanguage Classroom Management HandoutsHadia KhanNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Cohesion and Coherence in TextDocument17 pagesAnalysis of Cohesion and Coherence in TextMuhammad Arif Al HakimNo ratings yet
- SLA - PPT Variability in Language LearnerDocument14 pagesSLA - PPT Variability in Language LearnerRezza Anugerah100% (1)
- Transitivity System - Functional GrammarDocument20 pagesTransitivity System - Functional GrammarNguyen Quynh TrangNo ratings yet
- The Grammar of Interpersonal Meaning: MOOD: By: Avinahari Ahidatur R (2109160) LUTFI NUR AFIFAH (210916029) AmilaDocument44 pagesThe Grammar of Interpersonal Meaning: MOOD: By: Avinahari Ahidatur R (2109160) LUTFI NUR AFIFAH (210916029) Amilanur qoniahNo ratings yet
- Phrase Structure TreesDocument6 pagesPhrase Structure TreesSampath Jayakody100% (1)
- RPS ENGLISH POETRY (English)Document6 pagesRPS ENGLISH POETRY (English)Hasnah YusufNo ratings yet
- Teaching Listening To Young LearnersDocument16 pagesTeaching Listening To Young LearnersFiky AriniNo ratings yet
- Procedures in Foreign Language TeachingDocument21 pagesProcedures in Foreign Language Teachingesraerkocak100% (2)
- Unit 3. Morphology - WordsDocument3 pagesUnit 3. Morphology - WordsNyssa GNo ratings yet
- Assessing Grammar and VocabularyDocument6 pagesAssessing Grammar and VocabularyIsabel Jiménez GómezNo ratings yet
- Microsocial FactorsDocument8 pagesMicrosocial FactorsAyi Sasiah M100% (2)
- The Teaching Material Development of Problem Based Learning: Improving Student's Civic KnowledgeDocument6 pagesThe Teaching Material Development of Problem Based Learning: Improving Student's Civic KnowledgeJournal of Education and LearningNo ratings yet
- Active Speaking Task RubricDocument1 pageActive Speaking Task RubricPablo Riquelme GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Materials Development For Language Learning and TeachingDocument37 pagesMaterials Development For Language Learning and TeachingVictoria BeltránNo ratings yet
- Ell Teacher Interview EssayDocument8 pagesEll Teacher Interview Essayapi-488049837No ratings yet
- Listening Comprehension Difficulties: The Related Literature ReviewDocument7 pagesListening Comprehension Difficulties: The Related Literature ReviewDaniela ChicaNo ratings yet
- Content-Based Instruction.: Deswita Rahmadani Novi Wulandari Merianti ArdillaDocument18 pagesContent-Based Instruction.: Deswita Rahmadani Novi Wulandari Merianti ArdillaDeswitha RahmadaniNo ratings yet
- Word MeaningDocument3 pagesWord MeaningsusianakabanNo ratings yet
- Assessing GrammarDocument43 pagesAssessing GrammarLuffy RodgerNo ratings yet
- Teachers' Strategies To Improve Students' Self-Confidence in SpeakingDocument15 pagesTeachers' Strategies To Improve Students' Self-Confidence in SpeakingFaizal RisdiantoNo ratings yet
- Critical Discourse AnalysisDocument28 pagesCritical Discourse AnalysisNamisha Choudhary100% (2)
- Recent Perspectives On The Role of Previously Known (PPT Yati)Document16 pagesRecent Perspectives On The Role of Previously Known (PPT Yati)Siti Nurhayati100% (1)
- The Role of Esp TeacherDocument8 pagesThe Role of Esp TeacherIsmail Physics100% (1)
- Materials For Developing Listening and Speaking SkillsDocument2 pagesMaterials For Developing Listening and Speaking SkillsArleen J. Lim100% (1)
- Nature of Learner LanguageDocument10 pagesNature of Learner LanguageSara BermúdezNo ratings yet
- FG Group Presentation Textual Metafunction and Theme SystemDocument17 pagesFG Group Presentation Textual Metafunction and Theme SystemNida Ul Husna100% (1)
- Textual Equivalence CohesionDocument35 pagesTextual Equivalence CohesionMedaReynadoNo ratings yet
- Verbs and Thematic Role GridsDocument2 pagesVerbs and Thematic Role GridsMar Crespo100% (1)
- Authentic Materials GuideDocument87 pagesAuthentic Materials GuidePramod VadlamaniNo ratings yet
- Language Policy and Planning For Developing CountriesDocument13 pagesLanguage Policy and Planning For Developing CountriesZia Mahmud Khan RatulNo ratings yet
- 8 Test Techniques and Testing Overall...Document9 pages8 Test Techniques and Testing Overall...Eric TiptonNo ratings yet
- Making Sense of Functional Grammar GerotDocument348 pagesMaking Sense of Functional Grammar GerotWITO RAHARJONo ratings yet
- Genre-Based ApproachDocument10 pagesGenre-Based ApproachAminah RosaNo ratings yet
- Makalah Discourse AnalysisDocument10 pagesMakalah Discourse AnalysisFadly Kurozaky67% (3)
- Enhancing Adult Learners Speaking Fluency Using 432 TechniqueDocument10 pagesEnhancing Adult Learners Speaking Fluency Using 432 TechniquebububugNo ratings yet
- Meaning & Characteristic of PsycholinguisticDocument3 pagesMeaning & Characteristic of Psycholinguisticdaulay siti100% (1)
- Modul Basic ReadingDocument88 pagesModul Basic ReadingJekpotni Bos Jekpotni Bos100% (1)
- Group 1 QuizDocument15 pagesGroup 1 QuizRiza ReambonanzaNo ratings yet
- NHA2 - Morphology MorphemesDocument22 pagesNHA2 - Morphology Morphemes08AV2D100% (1)
- EMS - Pertemuan 1 - Modul 1 - SMIDocument24 pagesEMS - Pertemuan 1 - Modul 1 - SMIapi-326972640No ratings yet
- Materials and Digital ResourcesDocument20 pagesMaterials and Digital ResourcesAna Marie Mestosamente100% (1)
- The Role of Extrovert and Introvert Personality in Second Language AcquisitionDocument6 pagesThe Role of Extrovert and Introvert Personality in Second Language AcquisitionInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)No ratings yet
- Assessing Speaking Group 6Document26 pagesAssessing Speaking Group 6Aufal Maram100% (1)
- Expressions of Asking And: Giving OpinionDocument12 pagesExpressions of Asking And: Giving OpinionUria HamzahNo ratings yet
- Choosing A Coursebook 1Document22 pagesChoosing A Coursebook 1Latifa RahayuNo ratings yet
- (Cognition and Literacy) Ruth Garner - Metacognition and Reading Comprehension-Ablex Publishing (1988)Document176 pages(Cognition and Literacy) Ruth Garner - Metacognition and Reading Comprehension-Ablex Publishing (1988)Chika Rizki Amaliah100% (1)
- Applying Indirect Strategies To The Four Language SkillsDocument6 pagesApplying Indirect Strategies To The Four Language SkillsWahyu AsikinNo ratings yet
- Teaching & Assessment of The Macro SkillsDocument7 pagesTeaching & Assessment of The Macro SkillsKrystel Mary SungaNo ratings yet
- KWHL Charts (Also Called "What I Know" Charts, KWL Charts, and Know-WonderDocument6 pagesKWHL Charts (Also Called "What I Know" Charts, KWL Charts, and Know-WonderBonjovi VerdejoNo ratings yet
- Week 4Document21 pagesWeek 4Ella AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Phonics Fun Day (Concept Paper)Document15 pagesPhonics Fun Day (Concept Paper)Azlie IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Hobbs 2019Document18 pagesHobbs 2019Azlie IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Stohlmann 2019Document10 pagesStohlmann 2019Azlie IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Banner Konvo LinusDocument1 pageBanner Konvo LinusAzlie IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Reading - Administering A Running RecordDocument2 pagesReading - Administering A Running RecordAzlie IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Systematic and Explicit Phonics Instruction On Linus Pupils' Reading SkillsDocument1 pageSystematic and Explicit Phonics Instruction On Linus Pupils' Reading SkillsAzlie IbrahimNo ratings yet
- WorksheetDocument1 pageWorksheetAzlie IbrahimNo ratings yet
- A ChickenDocument6 pagesA ChickenAzlie IbrahimNo ratings yet
- What Does It Take To Be A Good ParentDocument7 pagesWhat Does It Take To Be A Good ParentAzlie IbrahimNo ratings yet
- What Does It Take To Be A Good ParentDocument7 pagesWhat Does It Take To Be A Good ParentAzlie IbrahimNo ratings yet
- What Does It Take To Be A Good ParentDocument7 pagesWhat Does It Take To Be A Good ParentAzlie IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Principle of Teaching ReadingDocument10 pagesPrinciple of Teaching ReadingAzlie IbrahimNo ratings yet
- A Greedy HippoDocument1 pageA Greedy HippoAzlie IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Alat Muzik TraditionalDocument6 pagesAlat Muzik TraditionalAzlie IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Garden ToolsDocument7 pagesGarden ToolsAzlie IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Out Campus Learning Mode of StudyDocument3 pagesOut Campus Learning Mode of StudyAzlie IbrahimNo ratings yet
- 1.session 1,2&3 QMSDocument152 pages1.session 1,2&3 QMSRomnick PortillanoNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Learning SyllabusDocument4 pagesBlockchain Learning SyllabusHimanshu TomarNo ratings yet
- GDDXGBCFDDocument202 pagesGDDXGBCFDAna ArsicNo ratings yet
- Self Reflection 1Document2 pagesSelf Reflection 1api-282229828No ratings yet
- Oleksiak Curriculum VitaeDocument6 pagesOleksiak Curriculum VitaeTimothyPatrickNo ratings yet
- Teaching Portfolio ResumeDocument3 pagesTeaching Portfolio Resumeapi-455800090No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document15 pagesChapter 2Milbert Loyloy SalmasanNo ratings yet
- CADD ClassDocument2 pagesCADD ClassajeethNo ratings yet
- Examples of Abdellah's Publications: TestabilityDocument3 pagesExamples of Abdellah's Publications: TestabilityleewfNo ratings yet
- What Is A Professional Learning CommunityDocument13 pagesWhat Is A Professional Learning Communityrida74100% (1)
- Upbeat 2Document2 pagesUpbeat 2jessie44No ratings yet
- Phonics Trainer Notes Remedial Y1 2015Document3 pagesPhonics Trainer Notes Remedial Y1 2015Saiful Azuar Bin IdrisNo ratings yet
- August 2012 NewsletterDocument27 pagesAugust 2012 NewsletterBiewBiewNo ratings yet
- Relatorio Exemplo 1 PDFDocument8 pagesRelatorio Exemplo 1 PDFMarta CancelaNo ratings yet
- CSE 241 Database Systems and Applications Spring 2014 (Jan 8, 2014)Document9 pagesCSE 241 Database Systems and Applications Spring 2014 (Jan 8, 2014)iad215No ratings yet
- Edid6503 - Assignment 2Document12 pagesEdid6503 - Assignment 2api-374444760No ratings yet
- Taa04 1Document701 pagesTaa04 1wawan_prasNo ratings yet
- Edtech 270 Course SummaryDocument3 pagesEdtech 270 Course SummaryGrace MartinezNo ratings yet
- Critical Reading SkillsDocument1 pageCritical Reading SkillsAnonymous E3Jd3DNo ratings yet
- Mindfulness Workshop Ravi PradhanDocument44 pagesMindfulness Workshop Ravi Pradhanapi-250421371No ratings yet
- Linus ModuleDocument14 pagesLinus Module悟真佛No ratings yet
- DLP Cot 2Document2 pagesDLP Cot 2Shila Pelegrino de Pinho100% (1)
- Curriculum Vitae: Adama JallowDocument3 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Adama Jallowanon_147691525No ratings yet
- Jessica Arnoldi Resume 2014-2015Document2 pagesJessica Arnoldi Resume 2014-2015api-192521921No ratings yet
- Undergraduate LO RubricsDocument5 pagesUndergraduate LO RubricsSafaruddin Al AfganiNo ratings yet
- WikipediaDocument3 pagesWikipediaChew Lee YunNo ratings yet
- Assignment-1: Creating A Board GameDocument2 pagesAssignment-1: Creating A Board GameAmrith FlyzNo ratings yet
- Cashier CurriculumDocument224 pagesCashier CurriculumHervin CalabiaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Applied LinguisticsDocument38 pagesUnderstanding Applied LinguisticsLiLaNo ratings yet
- The Once and Future King Book 1Document32 pagesThe Once and Future King Book 1api-255939949No ratings yet