Professional Documents
Culture Documents
D1, L8 Critical Path Analysis Early Event Time Examples
Uploaded by
mizmellOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
D1, L8 Critical Path Analysis Early Event Time Examples
Uploaded by
mizmellCopyright:
Available Formats
Analysing a network Example 1
A(3)
1
D(5)
C(6) B(4) E(1)
4 G(7) 5
F(6)
This is the network found in Example 1. We want to find the minimum duration of this project.
The first step is to find the earliest event times. This is the earliest time that an event (denoted by the numbered nodes) can occur. The event cannot occur until all activities leading into the event node have finished.
Analysing a network Example 1
2
A(3)
1 0 B(4)
D(5)
C(6) E(1)
4 G(7) 5
F(6)
Event 1 occurs at time zero.
Analysing a network Example 1
3 2 D(5)
A(3)
1 0 B(4)
C(6) E(1)
4 G(7) 5
F(6)
Event 2 cannot occur until A is finished. The earliest time for this is 3.
Analysing a network Example 1
3 2 D(5)
A(3)
1 0 B(4)
C(6) E(1)
4 G(7) 5
3
4 Event 3 cannot occur until B is finished. The earliest time for this is 4.
F(6)
Analysing a network Example 1
3 2 D(5)
A(3)
1 0 B(4)
8
C(6) E(1) 5 4 G(7)
3
4
F(6)
Event 4 cannot occur until C, D and E are all finished. The earliest C can finish is 6. The earliest D can finish is 3 + 5 = 8. The earliest E can finish is 4 + 1 = 5.
So the earliest time for event 4 is 8.
Analysing a network Example 1
3 2 D(5)
A(3)
1 0 B(4)
8
C(6) E(1) 5 4 G(7)
3
4
F(6)
15
Event 5 cannot occur until F and G are both finished. The earliest F can finish is 4 + 6 = 10. The earliest G can finish is 8 + 7 = 15.
So the earliest time for event 5 is 15.
Analysing a network Example 1
3 2 D(5)
A(3)
1 0 B(4)
8
C(6) E(1) 5 4 G(7)
3
4
F(6)
15
The next step is to find the late event times, working backwards through the network. A latest event time is the latest time that an event can occur without delaying the project. It is found by finding the latest time that each activity leading out of the event can begin the latest event time is the earliest of these.
Analysing a network Example 1
3 2 D(5)
A(3)
1 0 B(4)
8
C(6) E(1) 5 4 G(7)
3
4 Event 5 must occur by time 15, or the project will not finish in the minimum possible time.
F(6)
15
15
Analysing a network Example 1
3 2 D(5)
A(3)
1 0 B(4)
8
C(6) E(1) 4
G(7) 5
3
4
F(6)
15
15
The only activity leading from event 4 is G, which must start by time 8 if the project is not to be delayed. So event 4 must occur by time 8.
Analysing a network Example 1
3 2 D(5)
A(3)
1 0 B(4)
8
C(6) E(1) 4
G(7) 5
3
4 7
F(6)
15
15
The activities leading from event 3 are E (which must start by time 7) and F (which must start by time 9). So event 3 must occur by time 7.
Analysing a network Example 1
3 3 2 D(5)
A(3)
1 0 B(4)
8
C(6) E(1) 4
G(7) 5
3
4 7
F(6)
15
15
The only activity leading from event 2 is D, which must start by time 3. So event 2 must occur by time 3.
Analysing a network Example 1
3 3 2 D(5)
A(3)
1 0 0 B(4)
8
C(6) E(1) 4
G(7) 5
3
4 7
F(6)
15
15
Finally, event 1 must occur by time zero.
Analysing a network Example 1
3 3 2 D(5)
A(3)
1 0 0 B(4)
8
C(6) E(1) 4
G(7) 5
3
4 7
F(6)
15
15
The completed network shows that the project can be completed in 15 hours.
The critical activities are the activities (i, j) for which the LET for j the EET for i is equal to the activity duration. The critical activities are A, D and G.
For analysis of the float in this example, see the Notes and Examples.
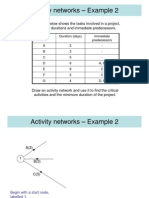
Analysing a network Example 2
2
A(2)
1 3 D(6) 5 G(4) 6
B(3)
C(5)
E(8) F(2) 4
This is the network found in Example 2. We want to find the minimum duration of this project. The first step is to find the earliest event times.
Analysing a network Example 2
2 2
A(2)
1 0 C(5) E(8) F(2) 4 3 D(6) 5 G(4) 6
B(3)
Event 1 occurs at time zero. The earliest that event 2 can occur is after A has finished, at time 2.
Analysing a network Example 2
2 2
A(2)
1 0 C(5) 3 3 E(8) F(2) 4 D(6) 5 G(4) 6
B(3)
Event 3 cannot occur until both A and B have finished, so the earliest time at which event 3 can occur is 3.
Analysing a network Example 2
2 2
A(2)
1 0 C(5) 3 3 E(8) F(2) 4 D(6) 5 G(4) 6
B(3)
Event 4 cannot occur until C has finished, so the earliest time at which event 5 can occur is 5.
Analysing a network Example 2
2 2
A(2) 13
1 0 C(5) B(3) 3 E(8) F(2) 4 3 D(6) 5 G(4) 6
The earliest that D can finish is at time 9, and the earliest that E can finish is at time 13, so the earliest that event 5 can occur is time 13.
Analysing a network Example 2
2 2
A(2) 13
1 0 C(5) B(3) 3 E(8) F(2) 4 3 D(6) 5 G(4) 6 17
The earliest that F can finish is at time 7, and the earliest that G can finish is at time 17, so the earliest that event 5 can occur is time 17.
Analysing a network Example 2
2 2
A(2) 13
1 0 C(5) B(3) 3 E(8) F(2) 4 3 D(6) 5 G(4) 6 17
The next step is to find the latest event times, starting from the sink node and working backwards.
Analysing a network Example 2
2 2
A(2) 13
1 0 C(5) B(3) 3 E(8) F(2) 4 3 D(6) 5 G(4) 6 17 17
Event 6 must not occur later than time 17, or the project will be delayed .
Analysing a network Example 2
2 2
A(2) 13
1 0 C(5) B(3) 3 E(8) F(2) 4 3 D(6)
13
5 G(4) 6 17 17
The latest G can start is at time 13, so the latest time for event 5 is 13.
Analysing a network Example 2
2 2
A(2) 13
1 0 C(5) B(3) 3 E(8) F(2) 4 3 D(6)
13
5 G(4) 6 17 17
The latest that E can start is at time 5, and the latest that F can start is at time 15, so the latest possible time for event 4 is 5.
Analysing a network Example 2
2 2
A(2) 13
1 0 C(5) B(3) 3 3 7 E(8) F(2) 4 D(6)
13
5 G(4) 6 17 17
The latest that D can start is at time 7, so the latest possible time for event 3 is 7.
Analysing a network Example 2
2 2 7
A(2) 13
1 0 C(5) B(3) 3 3 7 E(8) F(2) 4 D(6)
13
5 G(4) 6 17 17
The latest that the dummy activity (with zero duration) can start is at time 7, so the latest possible time for event 2 is 7.
Analysing a network Example 2
2 2 7
A(2) 13
1 0 0 C(5) B(3) 3 3 7 E(8) F(2) 4 D(6)
13
5 G(4) 6 17 17
The latest that event 1 can start is at time 0.
Analysing a network Example 2
2 2 7
A(2) 13
1 0 0 C(5) B(3) 3 3 7 E(8) F(2) 4 D(6)
13
5 G(4) 6 17 17
The critical activities are 5 activities for which the float is zero: i.e. the latest event time for activity j the earliest event time for activity i is equal to the activity duration.
Analysing a network Example 2
2 2 7
A(2) 13
1 0 0 C(5) B(3) 3 3 7 E(8) F(2) 4 D(6)
13
5 G(4) 6 17 17
The critical activities are C, E and G.
The project can be completed in 17 days.
For analysis of the float in this example, see Example 2 in the Notes and Examples.
Analysing a network Example 3
C(5)
3 4
A(2)
1
E(6)
F(3) H(2)
6
B(4) G(8) 2 5
D(3) This is the network found in Example 3. We want to find the minimum duration of this project.
The first step is to find the early event times.
Analysing a network Example 3
C(5)
3 4
A(2)
1
E(6)
F(3) H(2)
6
0 B(4) G(8) 2 5
D(3) Event 1 occurs at time zero.
Analysing a network Example 3
C(5)
3 4
A(2)
1
E(6)
F(3) H(2)
6
0 B(4) G(8) 2 5
D(3)
4
Event 2 cannot occur until B has finished, so the earliest time for event 2 is 4.
Analysing a network Example 3
4
C(5)
3 4
A(2)
1
E(6)
F(3) H(2)
6
0 B(4) G(8) 2 5
D(3)
4
Event 3 cannot occur until both A and B have finished, so the earliest time for event 3 is 4.
Analysing a network Example 3
4
C(5)
3 4 F(3)
A(2)
1
E(6)
H(2)
6
0 B(4) G(8) 2 5
D(3)
4
Event 4 cannot occur until C has finished, so the earliest time for event 4 is 4 + 5 = 9.
Analysing a network Example 3
4
C(5)
3 4 F(3)
A(2)
1
E(6)
H(2)
6
0 B(4) G(8) 2 5
D(3)
4 7
Event 5 cannot occur until D has finished, so the earliest time for event 5 is 4 + 3 = 7.
Analysing a network Example 3
4
C(5)
3 4 F(3)
A(2)
1 0 B(4)
E(6)
H(2) 12
G(8) 2 5
D(3)
4 7
Event 6 cannot occur until both D and F have finished. The earliest time that D can finish is 7, and the earliest time that F can finish is 9 + 3 = 12, so the earliest time for event 6 is 12.
Analysing a network Example 3
4
C(5)
3 4 F(3)
A(2)
1 0 B(4)
E(6)
H(2) 12
7
15 G(8)
D(3)
4 7
Event 7 cannot occur until E, G and H have all finished. The earliest time that E can finish is 9 + 6 = 15, the earliest time that G can finish is 7 + 8 = 15, and the earliest time that H can finish is 12 + 2 = 14, so the earliest time for event 7 is 15.
Analysing a network Example 3
4
C(5)
3 4 F(3)
A(2)
1 0 B(4)
E(6)
H(2) 12
7
15 G(8)
D(3)
4 7
The next step is to find the late event times, working backwards through the network.
Analysing a network Example 3
4
C(5)
3 4 F(3)
A(2)
1 0 B(4)
E(6)
H(2) 12
7
15 15 G(8)
D(3)
4 7
The latest time that event 7 can occur without delaying the project is 15.
Analysing a network Example 3
4
C(5)
3 4 F(3)
A(2)
1 0 B(4)
E(6)
H(2) 12 13
7
15 15 G(8)
D(3)
4 7
The latest time that activity H can start is 13, so the latest time for event 6 is 13.
Analysing a network Example 3
4
C(5)
3 4 F(3)
A(2)
1 0 B(4)
E(6)
H(2) 12 13
7
15 15 G(8)
D(3)
4 7 7
Activity G and a dummy activity both lead out of event 5. The latest time that activity G can start is 7, and the latest time that the dummy activity can start is 13, so the latest time for event 5 is 7.
Analysing a network Example 3
4
C(5)
3 4 F(3)
A(2)
1 0 B(4)
E(6)
H(2) 12 13
7
15 15 G(8)
D(3)
4 7 7
Activities E and F both lead out of event 4. The latest time that activity E can start is 9, and the latest time that activity F can start is 9, so the latest time for event 4 is 9.
Analysing a network Example 3
4 4
C(5)
3 4 F(3)
A(2)
1 0 B(4)
E(6)
H(2) 12 13
7
15 15 G(8)
D(3)
4 7 7
The latest time that activity C can start is 4, so the latest time for event 3 is 4.
Analysing a network Example 3
4 4
C(5)
3 4 F(3)
A(2)
1 0 B(4)
E(6)
H(2) 12 13
7
15 15 G(8)
D(3)
4 4 7 7
Activity D and a dummy activity both lead out of event 2. The latest time that activity D can start is 6, and the latest time that the dummy activity can start is 4, so the latest time for event 2 is 4.
Analysing a network Example 3
4 4
C(5)
3 4 F(3)
A(2)
1 0 0 B(4)
E(6)
H(2) 12 13
7
15 15 G(8)
D(3)
4 4 7 7
Finally, the latest time for event 1 is zero.
Analysing a network Example 3
4 4
C(5)
3 4 F(3)
A(2)
1 0 0 B(4)
E(6)
H(2) 12 13
7
15 15 G(8)
D(3)
4 4 7 7 The float in this example is analysed in the Notes and Examples.
The minimum duration of the project is 15 days. The critical activities are B, C, D, E and G.
Notice that there are two critical paths: BCE and BDG.
You might also like
- Weekly Home Learning Plans for Empowerment TechnologiesDocument3 pagesWeekly Home Learning Plans for Empowerment TechnologiesCharlon Mamacos100% (9)
- Probability and Combinatorics Word ProblemsDocument5 pagesProbability and Combinatorics Word ProblemsGhulam FareedNo ratings yet
- Commercial Building Maintenance and External Cleaning CompanyDocument8 pagesCommercial Building Maintenance and External Cleaning Companybisankhe2No ratings yet
- ISO 27001-2022 Transition BookDocument20 pagesISO 27001-2022 Transition BookzghibNo ratings yet
- Ce182P-2 Ce Project 1 1 QTR SY2019-2020 July 2019 Structural Engineering Cluster F.A.A.UyDocument4 pagesCe182P-2 Ce Project 1 1 QTR SY2019-2020 July 2019 Structural Engineering Cluster F.A.A.UyemmaNo ratings yet
- 3 - Multiple Choice Questions in Engineering MathematicsDocument159 pages3 - Multiple Choice Questions in Engineering MathematicsPJBautistaMaddumaNo ratings yet
- Summary Report of Republic Act No. 544Document7 pagesSummary Report of Republic Act No. 544JannenNo ratings yet
- Ce134p SyllabusDocument7 pagesCe134p SyllabuskelvinNo ratings yet
- Engenvi NotesDocument12 pagesEngenvi NotesMariaNo ratings yet
- 11 17 2014 Differential CalculusDocument1 page11 17 2014 Differential CalculusEj ApeloNo ratings yet
- 03 Chapter 2 Review of Related LiteratureDocument8 pages03 Chapter 2 Review of Related LiteratureJon JoviNo ratings yet
- Consistency of cement pasteDocument5 pagesConsistency of cement pasteEngel De VillaNo ratings yet
- EM 7 - EDA - Problem Set 1Document2 pagesEM 7 - EDA - Problem Set 1Ron Michael Dave Cezar0% (1)
- Batangas Polytechnic College faces faculty shortageDocument1 pageBatangas Polytechnic College faces faculty shortageAngelica Jolie P BarbonNo ratings yet
- Project 1st Proposal - ESE144Document17 pagesProject 1st Proposal - ESE144Hamee GomezNo ratings yet
- Worksheetmat GensciDocument12 pagesWorksheetmat GensciMaeChenSarabiaInfanteNo ratings yet
- Luffa Acutangula (Sponge Gourd) FiberDocument15 pagesLuffa Acutangula (Sponge Gourd) FiberShiela SorinoNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Hydraulics Lab OverviewDocument2 pagesCivil Engineering Hydraulics Lab OverviewgpowerpNo ratings yet
- DEI Technical College Applied Mechanics Question BankDocument10 pagesDEI Technical College Applied Mechanics Question BankRaNo ratings yet
- Tunay Na InaDocument4 pagesTunay Na InaWayneNoveraNo ratings yet
- CEHR0313-Mod2 3 2Document27 pagesCEHR0313-Mod2 3 2Kei KagayakiNo ratings yet
- Benefit Cost Ratio, FWADocument27 pagesBenefit Cost Ratio, FWANur Irfana Mardiyah Diyahlikebarcelona100% (1)
- ch02 2Document4 pagesch02 2yi LeeNo ratings yet
- Module 3. Construction Project RequirementsDocument4 pagesModule 3. Construction Project RequirementsIvyJoama Batin-Barnachea Priolo0% (1)
- Case Study: RE Construction: It's Now or NeverDocument11 pagesCase Study: RE Construction: It's Now or NeverJomarie AlcanoNo ratings yet
- Schedule, Ratings, Results, RosterDocument7 pagesSchedule, Ratings, Results, RosterJekkuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Kinetics of Particles Energy and Momentum MethodsDocument32 pagesLecture 3 - Kinetics of Particles Energy and Momentum MethodsKeu JiannRong0% (2)
- Foundation Engineering: Module 2: Geotechnical Properties of SoilDocument4 pagesFoundation Engineering: Module 2: Geotechnical Properties of SoilAljon AvilaNo ratings yet
- Amortization Equivalent Annual Cost-UploadDocument6 pagesAmortization Equivalent Annual Cost-Uploadniaz kilamNo ratings yet
- Determining the Center of Gravity of a Floating BodyDocument6 pagesDetermining the Center of Gravity of a Floating BodyDarlin Cara TurquezaNo ratings yet
- Intro 2nd EditionDocument594 pagesIntro 2nd EditionDDINo ratings yet
- 2 Moisture Content of Aggregates - MIOTENDocument7 pages2 Moisture Content of Aggregates - MIOTENAirielle MIotenNo ratings yet
- Molasses As Retarding Admixture For Concrete in Road Construction PDFDocument11 pagesMolasses As Retarding Admixture For Concrete in Road Construction PDFSha SibayanNo ratings yet
- Ch01 Units Quantities VectorsDocument35 pagesCh01 Units Quantities VectorsNatasha RochaNo ratings yet
- Money-Time Relationships and Equivalence in Engineering EconomicsDocument14 pagesMoney-Time Relationships and Equivalence in Engineering EconomicsleojhunNo ratings yet
- THE STRUGGLES OF ENGINEERING STUDENTS IN CTU-MCDocument45 pagesTHE STRUGGLES OF ENGINEERING STUDENTS IN CTU-MCDavid Paul Talisic RomeroNo ratings yet
- Technopreneurship: Asingan CampusDocument18 pagesTechnopreneurship: Asingan CampusThentadashiNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Report 1.1 Determination of Water Content, Unit Weight, Void Ratio and Degree of Saturation of SoilDocument5 pagesLaboratory Report 1.1 Determination of Water Content, Unit Weight, Void Ratio and Degree of Saturation of SoilM MNo ratings yet
- Department of Education Schools Division of Zamboanga Del NorteDocument3 pagesDepartment of Education Schools Division of Zamboanga Del Nortearjo17122No ratings yet
- 6.surface TensionDocument14 pages6.surface Tensionnicky1213aNo ratings yet
- Problem 1Document10 pagesProblem 1BeverlyNo ratings yet
- Classification of Engineering Services: Section 2Document15 pagesClassification of Engineering Services: Section 2Ravie Del PilarNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Quiz Solution PDFDocument4 pagesModule 1 Quiz Solution PDFBanana QNo ratings yet
- (Basic Electrical Theory 1) : ACE 11 (Engineering Utilities 1)Document25 pages(Basic Electrical Theory 1) : ACE 11 (Engineering Utilities 1)MARK JOSHUA CONDEZA GARCIANo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument9 pagesPhysicsAngelica Sibayan QuinionesNo ratings yet
- Slidex - Tips - Elementary Surveying by Juny Pilapil La Putt Free Download 5029 PDFDocument2 pagesSlidex - Tips - Elementary Surveying by Juny Pilapil La Putt Free Download 5029 PDFLia LBNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Design Constraints, Tradeoffs and Standards 3.1 Design ConstraintsDocument21 pagesChapter 3 - Design Constraints, Tradeoffs and Standards 3.1 Design ConstraintsJeric EliveraNo ratings yet
- Geological and Geophysical Investigation in Civil EngineeringDocument5 pagesGeological and Geophysical Investigation in Civil EngineeringLyka Jane Tapia Opeña100% (1)
- CE 3151 Numerical SolutionsDocument75 pagesCE 3151 Numerical SolutionsAsus LaptopNo ratings yet
- Ce Laws The Seven Canons of Ethics With Assessment CtuDocument19 pagesCe Laws The Seven Canons of Ethics With Assessment CtuCharlie OnlyNo ratings yet
- HAU Civil Engineering Arch AnalysisDocument6 pagesHAU Civil Engineering Arch Analysiscutie4everrNo ratings yet
- Detailed road inventory and traffic analysis of an intersection in Bantay, Ilocos SurDocument4 pagesDetailed road inventory and traffic analysis of an intersection in Bantay, Ilocos SurVinz GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Hydrology: Puan Saedatulfirdaus BT Sa'AraniDocument26 pagesEngineering Hydrology: Puan Saedatulfirdaus BT Sa'AraniHasmittha100% (1)
- Pili Nut Cracking MachineDocument5 pagesPili Nut Cracking MachineJefferNo ratings yet
- Short Bond Paper Landscape: Score Statics-Rb RubricDocument6 pagesShort Bond Paper Landscape: Score Statics-Rb RubricxVlad LedesmaNo ratings yet
- CEBU INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY BACHELOR OF SCIENCE IN CIVIL ENGINEERINGDocument2 pagesCEBU INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY BACHELOR OF SCIENCE IN CIVIL ENGINEERINGMae Antonette TabanaoNo ratings yet
- Example 4 1 Circuits IntroductionDocument4 pagesExample 4 1 Circuits IntroductionDiego Escobar MoncadaNo ratings yet
- Network Diagram Project PlanningDocument8 pagesNetwork Diagram Project PlanningKlent Evran JalecoNo ratings yet
- Compiled Lecture in Engineering Economy PDFDocument78 pagesCompiled Lecture in Engineering Economy PDFLJ dela PazNo ratings yet
- Activity networks critical path exampleDocument21 pagesActivity networks critical path examplemizmellNo ratings yet
- Activity Networks Example 3Document24 pagesActivity Networks Example 3mizmellNo ratings yet
- Activity networks – Example 1Document20 pagesActivity networks – Example 1mizmellNo ratings yet
- A Ules For Network ConstructionDocument53 pagesA Ules For Network Constructionlimulsa78No ratings yet
- Activity Networks Example 3Document24 pagesActivity Networks Example 3mizmellNo ratings yet
- 4 1Document10 pages4 1mizmellNo ratings yet
- D1, L9 Solving Linear Programming ProblemsDocument16 pagesD1, L9 Solving Linear Programming ProblemsmizmellNo ratings yet
- Decision Maths: Chapter 4: Route InspectionDocument13 pagesDecision Maths: Chapter 4: Route InspectionmizmellNo ratings yet
- Activity Networks Example 3Document24 pagesActivity Networks Example 3mizmellNo ratings yet
- D1, L9 Solving Linear Programming ProblemsDocument16 pagesD1, L9 Solving Linear Programming ProblemsmizmellNo ratings yet
- D1 2011-01Document24 pagesD1 2011-01mizmellNo ratings yet
- Numbers Activity - Critical Path SolutionsDocument2 pagesNumbers Activity - Critical Path SolutionsmizmellNo ratings yet
- Task-Numbers Activity - Critical PathDocument3 pagesTask-Numbers Activity - Critical PathmizmellNo ratings yet
- D1 Exercise 1fDocument1 pageD1 Exercise 1fmizmellNo ratings yet
- D1, L8 Critical Path AnalysisDocument25 pagesD1, L8 Critical Path AnalysismizmellNo ratings yet
- D1, L5 1 Kruskal's and Prim's AlgorithmsDocument18 pagesD1, L5 1 Kruskal's and Prim's AlgorithmsmizmellNo ratings yet
- D1, L9 Solving Linear Programming ProblemsDocument16 pagesD1, L9 Solving Linear Programming ProblemsmizmellNo ratings yet
- D1, L8 Critical Path Gantt DiagramsDocument25 pagesD1, L8 Critical Path Gantt DiagramsmizmellNo ratings yet
- Edexcel GCE: Wednesday 18 January 2006 Time: 1 Hour 30 MinutesDocument7 pagesEdexcel GCE: Wednesday 18 January 2006 Time: 1 Hour 30 MinutesmizmellNo ratings yet
- Edexcel GCE: Thursday 16 June 2005 Time: 1 Hour 30 MinutesDocument8 pagesEdexcel GCE: Thursday 16 June 2005 Time: 1 Hour 30 MinutesmizmellNo ratings yet
- June 2006 6689 Decision Maths D1 Mark Scheme: Page 1 / 14Document13 pagesJune 2006 6689 Decision Maths D1 Mark Scheme: Page 1 / 14mizmellNo ratings yet
- Edexcel GCE: Tuesday 2 November 2004 Time: 1 Hour 30 MinutesDocument12 pagesEdexcel GCE: Tuesday 2 November 2004 Time: 1 Hour 30 MinutesmizmellNo ratings yet
- Edexcel GCE: Wednesday 24 May 2006 Time: 1 Hour 30 MinutesDocument7 pagesEdexcel GCE: Wednesday 24 May 2006 Time: 1 Hour 30 MinutesmizmellNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2007: GCE Mathematics Decision Mathematics D1 (6689)Document7 pagesMark Scheme (Results) January 2007: GCE Mathematics Decision Mathematics D1 (6689)mizmellNo ratings yet
- D1 June 2007Document12 pagesD1 June 2007RoNi Jason James StinsonNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2007: GCE Mathematics Decision Mathematics D1 (6689)Document6 pagesMark Scheme (Results) Summer 2007: GCE Mathematics Decision Mathematics D1 (6689)mizmellNo ratings yet
- 2008 June MSDocument12 pages2008 June MSmeirttNo ratings yet
- Edexcel GCE: Tuesday 2 November 2004 Time: 1 Hour 30 MinutesDocument12 pagesEdexcel GCE: Tuesday 2 November 2004 Time: 1 Hour 30 MinutesmizmellNo ratings yet
- Edexcel GCE: Decision Mathematics D1 Advanced/Advanced SubsidiaryDocument12 pagesEdexcel GCE: Decision Mathematics D1 Advanced/Advanced SubsidiarymizmellNo ratings yet
- Edexcel GCE: Decision Mathematics D1 Advanced/Advanced SubsidiaryDocument24 pagesEdexcel GCE: Decision Mathematics D1 Advanced/Advanced SubsidiarymizmellNo ratings yet
- Edexcel GCE: Thursday 16 June 2005 Time: 1 Hour 30 MinutesDocument8 pagesEdexcel GCE: Thursday 16 June 2005 Time: 1 Hour 30 MinutesmizmellNo ratings yet
- Edexcel GCE: Decision Mathematics D1 Advanced/Advanced SubsidiaryDocument12 pagesEdexcel GCE: Decision Mathematics D1 Advanced/Advanced SubsidiarymizmellNo ratings yet
- 2008 June MSDocument12 pages2008 June MSmeirttNo ratings yet
- How To Recover MSSQL From Suspect Mode Emergency Mode Error 1813Document3 pagesHow To Recover MSSQL From Suspect Mode Emergency Mode Error 1813Scott NeubauerNo ratings yet
- FoxMeyer's ERP Implementation Failure Case StudyDocument30 pagesFoxMeyer's ERP Implementation Failure Case StudyNeo LiveNo ratings yet
- Pervasive Healthcare Computing: EMR/EHR, Wireless and Health MonitoringDocument3 pagesPervasive Healthcare Computing: EMR/EHR, Wireless and Health MonitoringPajak RedikonNo ratings yet
- Courant Friedrichs LewyDocument20 pagesCourant Friedrichs LewyEv OzcanNo ratings yet
- Performance Evaluation of BPSK Modulation With Error Control CodingDocument6 pagesPerformance Evaluation of BPSK Modulation With Error Control CodingSaketh RaviralaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Operational AmplifierDocument31 pagesChapter 2 - Operational AmplifierElie AyoubNo ratings yet
- Samaresh Das: Education SkillsDocument1 pageSamaresh Das: Education SkillsSamaresh DasNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7Document42 pagesLesson 7Nithya NairNo ratings yet
- Relay Circuit PDFDocument8 pagesRelay Circuit PDFGuru Mishra100% (1)
- End of Chapter 8 (p.606) Questions 1,2,4,8,14.: Short AnswerDocument4 pagesEnd of Chapter 8 (p.606) Questions 1,2,4,8,14.: Short AnswerTung VanNo ratings yet
- Apollo247 247201631 Labinvoice CompleteDocument1 pageApollo247 247201631 Labinvoice CompleteAjay VanaparthiNo ratings yet
- Singh G. CompTIA Network+ N10-008 Certification Guide... N10-008 Exam 2ed 2022Document692 pagesSingh G. CompTIA Network+ N10-008 Certification Guide... N10-008 Exam 2ed 2022hazzardousmonk100% (1)
- Langdo Led Lighting Co.,LimitedDocument24 pagesLangdo Led Lighting Co.,LimitedRudi CressaNo ratings yet
- Modulo 4Document2 pagesModulo 4Monii TranquinoNo ratings yet
- Raspberry Pi Projects Book PDFDocument204 pagesRaspberry Pi Projects Book PDFstanchan82100% (1)
- 2021 Anna University RegulationsDocument415 pages2021 Anna University RegulationsThamarai KannanNo ratings yet
- Chaderton Barbara AS400Document3 pagesChaderton Barbara AS400Sivakumar RajuNo ratings yet
- C5G - R1C - Roboshop Program 2.0.0Document82 pagesC5G - R1C - Roboshop Program 2.0.0kukaNo ratings yet
- Scripting Language - WikipediaDocument9 pagesScripting Language - WikipediaGilbertNo ratings yet
- G120X Op Instr 0319 en-USDocument966 pagesG120X Op Instr 0319 en-USABI RAJESH GANESHA RAJANo ratings yet
- DVD615 PDFDocument228 pagesDVD615 PDFFreddy FerrerNo ratings yet
- Oed 2,0 2022Document139 pagesOed 2,0 2022Ellish ErisNo ratings yet
- Đề Chuyên (Chính Thức) 2017Document10 pagesĐề Chuyên (Chính Thức) 2017Nguyễn Minh ThưNo ratings yet
- 21 Primavera Tips and ShortcutsDocument30 pages21 Primavera Tips and ShortcutsMarioNo ratings yet
- Oracle Financial FaqDocument259 pagesOracle Financial FaqAndrea NguyenNo ratings yet
- FLS DemonstrationDocument30 pagesFLS DemonstrationLeah UljerNo ratings yet
- V11 What's New and Changes PDFDocument98 pagesV11 What's New and Changes PDFGNo ratings yet