Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Analysis of Variance (Anova) : Heibatollah Baghi, and Mastee Badii
Uploaded by
Amit KlOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Analysis of Variance (Anova) : Heibatollah Baghi, and Mastee Badii
Uploaded by
Amit KlCopyright:
Available Formats
1
ANALYSIS OF VARIANCE
(ANOVA)
Heibatollah Baghi, and
Mastee Badii
2
Purpose of ANOVA
Use one-way Analysis of Variance to test
when the mean of a variable (Dependent
variable) differs among three or more groups
For example, compare whether systolic blood
pressure differs between a control group and two
treatment groups
3
Purpose of ANOVA
One-way ANOVA compares three or more groups defined by a
single factor.
For example, you might compare control, with drug treatment
with drug treatment plus antagonist. Or might compare control
with five different treatments.
Some experiments involve more than one factor. These data
need to be analyzed by two-way ANOVA or Factorial ANOVA.
For example, you might compare the effects of three different
drugs administered at two times. There are two factors in that
experiment: Drug treatment and time.
4
Why not do repeated t-tests?
Rather than using one-way ANOVA, you might be
tempted to use a series of t tests, comparing two
groups each time. Dont do it.
Repeated t-test increase the chances of type I error
or multiple comparison problem
If you are making comparison between 5 groups,
you will need 10 comparison of means
When the null hypothesis is true the probability that
at least 1 of the 10 observed significance levels is
less than 0.05 is about 0.29
5
Why not do repeated t-tests?
With 10 means (45 comparisons), the probability of
finding at least one significant difference is about
0.63
In other words, when level of significance is .05,
there is a 1 in 20 chance that one t-test will yield a
significant result even when the null hypothesis is
true.
The more t-test the more that probability will
increase
6
What Does ANOVA Do?
ANOVA involves the partitioning of variance of the
dependent variable into different components:
A. Between Group Variability
B. Within Group Variability
More Specifically, The Analysis of Variance is a
method for partitioning the Total Sum of Squares
into two Additive and independent parts.
7
Definition of Total Sum of
Squares or Variance
) ,......., 1 ; ,......, 1 (
) ( ) ( n ) (
2
.
2
..
2
..
p j n i
X X X X X X
n
i i
j
ij
p
i j
p
i j
ij
n
i i
ij
p
i j
= =
+ =
= = = = =
i=1 j=1 i=1 j=1 j=1
) ,......., 1 ; ,......, 1 (
) ( ) ( n ) (
2
.
2
..
2
..
p j n i
X X X X X X
n
i i
j
ij
p
i j
p
i j
ij
n
i i
ij
p
i j
= =
+ =
= = = = =
i=1 j=1 i=1 j=1 j=1
Case
Group
1
Group
2
Group
p
1 X
11
X
21
X
p1
2 X
12
X
22
X
p2
3 X
13
X
23
X
p3
..
n X
1n
X
2n
.. X
pn
Summed across
all n times p
observations
8
) ,......., 1 ; ,......, 1 (
) ( ) ( n ) (
2
.
2
..
2
..
p j n i
X X X X X X
n
i i
j
ij
p
i j
p
i j
ij
n
i i
ij
p
i j
= =
+ =
= = = = =
i=1 j=1 i=1 j=1 j=1
) ,......., 1 ; ,......, 1 (
) ( ) ( n ) (
2
.
2
..
2
..
p j n i
X X X X X X
n
i i
j
ij
p
i j
p
i j
ij
n
i i
ij
p
i j
= =
+ =
= = = = =
i=1 j=1 i=1 j=1 j=1
.j
Definition of Between Sum of
Squares
Case
Group
1
Group
2
Group
p
1 X
11
X
21
X
p1
2 X
12
X
22
X
p2
3 X
13
X
23
X
p3
..
n X
1n
X
2n
.. X
pn
Sum of squared
differences
of group means
from the grand
mean is SS
B
9
Definition of Within Sum of
Squares
) ,......., 1 ; ,......, 1 (
) ( ) ( n ) (
2
.
2
..
2
..
p j n i
X X X X X X
n
i i
j
ij
p
i j
p
i j
ij
n
i i
ij
p
i j
= =
+ =
= = = = =
i=1 j=1 i=1 j=1 j=1
) ,......., 1 ; ,......, 1 (
) ( ) ( n ) (
2
.
2
..
2
..
p j n i
X X X X X X
n
i i
j
ij
p
i j
p
i j
ij
n
i i
ij
p
i j
= =
+ =
= = = = =
i=1 j=1 i=1 j=1 j=1
Case
Group
1
Group
2
Group
p
1 X
11
X
21
X
p1
2 X
12
X
22
X
p2
3 X
13
X
23
X
p3
..
n X
1n
X
2n
.. X
pn
Sum of squared
difference
of observations
from group means
10
) ,......., 1 ; ,......, 1 (
) ( ) ( n ) (
2
.
2
..
2
..
p j n i
X X X X X X
n
i i
j
ij
p
i j
p
i j
ij
n
i i
ij
p
i j
= =
+ =
= = = = =
i=1 j=1 i=1 j=1 j=1
) ,......., 1 ; ,......, 1 (
) ( ) ( n ) (
2
.
2
..
2
..
p j n i
X X X X X X
n
i i
j
ij
p
i j
p
i j
ij
n
i i
ij
p
i j
= =
+ =
= = = = =
i=1 j=1 i=1 j=1 j=1
.j .j
) ,......., 1 ; ,......, 1 (
) ( ) ( n ) (
2
.
2
..
2
..
p j n i
X X X X X X
n
i i
j
ij
p
i j
p
i j
ij
n
i i
ij
p
i j
= =
+ =
= = = = =
i=1 j=1 i=1 j=1 j=1
) ,......., 1 ; ,......, 1 (
) ( ) ( n ) (
2
.
2
..
2
..
p j n i
X X X X X X
n
i i
j
ij
p
i j
p
i j
ij
n
i i
ij
p
i j
= =
+ =
= = = = =
i=1 j=1 i=1 j=1 j=1
.j
) ,......., 1 ; ,......, 1 (
) ( ) ( n ) (
2
.
2
..
2
..
p j n i
X X X X X X
n
i i
j
ij
p
i j
p
i j
ij
n
i i
ij
p
i j
= =
+ =
= = = = =
i=1 j=1 i=1 j=1 j=1
) ,......., 1 ; ,......, 1 (
) ( ) ( n ) (
2
.
2
..
2
..
p j n i
X X X X X X
n
i i
j
ij
p
i j
p
i j
ij
n
i i
ij
p
i j
= =
+ =
= = = = =
i=1 j=1 i=1 j=1 j=1
.j .j
) ,......., 1 ; ,......, 1 (
) ( ) ( n ) (
2
.
2
..
2
..
p j n i
X X X X X X
n
i i
j
ij
p
i j
p
i j
ij
n
i i
ij
p
i j
= =
+ =
= = = = =
i=1 j=1 i=1 j=1 j=1
) ,......., 1 ; ,......, 1 (
) ( ) ( n ) (
2
.
2
..
2
..
p j n i
X X X X X X
n
i i
j
ij
p
i j
p
i j
ij
n
i i
ij
p
i j
= =
+ =
= = = = =
i=1 j=1 i=1 j=1 j=1
.j .j
) ,......., 1 ; ,......, 1 (
) ( ) ( n ) (
2
.
2
..
2
..
p j n i
X X X X X X
n
i i
j
ij
p
i j
p
i j
ij
n
i i
ij
p
i j
= =
+ =
= = = = =
i=1 j=1 i=1 j=1 j=1
) ,......., 1 ; ,......, 1 (
) ( ) ( n ) (
2
.
2
..
2
..
p j n i
X X X X X X
n
i i
j
ij
p
i j
p
i j
ij
n
i i
ij
p
i j
= =
+ =
= = = = =
i=1 j=1 i=1 j=1 j=1
.j
) ,......., 1 ; ,......, 1 (
) ( ) ( n ) (
2
.
2
..
2
..
p j n i
X X X X X X
n
i i
j
ij
p
i j
p
i j
ij
n
i i
ij
p
i j
= =
+ =
= = = = =
i=1 j=1 i=1 j=1 j=1
) ,......., 1 ; ,......, 1 (
) ( ) ( n ) (
2
.
2
..
2
..
p j n i
X X X X X X
n
i i
j
ij
p
i j
p
i j
ij
n
i i
ij
p
i j
= =
+ =
= = = = =
i=1 j=1 i=1 j=1 j=1
.j .j
Partitioning of Variance into
Different Components
Total sum
of squares
Between
groups
sum of
squares
Within
groups
sum of
squares
11
Test Statistic in ANOVA
Test statistic for ANOVA
is based on between &
within groups SS
) ,......., 1 ; ,......, 1 (
) ( ) ( n ) (
2
.
2
..
2
..
p j n i
X X X X X X
n
i i
j
ij
p
i j
p
i j
ij
n
i i
ij
p
i j
= =
+ =
= = = = =
i=1 j=1 i=1 j=1 j=1
) ,......., 1 ; ,......, 1 (
) ( ) ( n ) (
2
.
2
..
2
..
p j n i
X X X X X X
n
i i
j
ij
p
i j
p
i j
ij
n
i i
ij
p
i j
= =
+ =
= = = = =
i=1 j=1 i=1 j=1 j=1
.j .j
) ,......., 1 ; ,......, 1 (
) ( ) ( n ) (
2
.
2
..
2
..
p j n i
X X X X X X
n
i i
j
ij
p
i j
p
i j
ij
n
i i
ij
p
i j
= =
+ =
= = = = =
i=1 j=1 i=1 j=1 j=1
) ,......., 1 ; ,......, 1 (
) ( ) ( n ) (
2
.
2
..
2
..
p j n i
X X X X X X
n
i i
j
ij
p
i j
p
i j
ij
n
i i
ij
p
i j
= =
+ =
= = = = =
i=1 j=1 i=1 j=1 j=1
.j
) ,......., 1 ; ,......, 1 (
) ( ) ( n ) (
2
.
2
..
2
..
p j n i
X X X X X X
n
i i
j
ij
p
i j
p
i j
ij
n
i i
ij
p
i j
= =
+ =
= = = = =
i=1 j=1 i=1 j=1 j=1
) ,......., 1 ; ,......, 1 (
) ( ) ( n ) (
2
.
2
..
2
..
p j n i
X X X X X X
n
i i
j
ij
p
i j
p
i j
ij
n
i i
ij
p
i j
= =
+ =
= = = = =
i=1 j=1 i=1 j=1 j=1
.j .j
) ,......., 1 ; ,......, 1 (
) ( ) ( n ) (
2
.
2
..
2
..
p j n i
X X X X X X
n
i i
j
ij
p
i j
p
i j
ij
n
i i
ij
p
i j
= =
+ =
= = = = =
i=1 j=1 i=1 j=1 j=1
) ,......., 1 ; ,......, 1 (
) ( ) ( n ) (
2
.
2
..
2
..
p j n i
X X X X X X
n
i i
j
ij
p
i j
p
i j
ij
n
i i
ij
p
i j
= =
+ =
= = = = =
i=1 j=1 i=1 j=1 j=1
.j .j
) ,......., 1 ; ,......, 1 (
) ( ) ( n ) (
2
.
2
..
2
..
p j n i
X X X X X X
n
i i
j
ij
p
i j
p
i j
ij
n
i i
ij
p
i j
= =
+ =
= = = = =
i=1 j=1 i=1 j=1 j=1
) ,......., 1 ; ,......, 1 (
) ( ) ( n ) (
2
.
2
..
2
..
p j n i
X X X X X X
n
i i
j
ij
p
i j
p
i j
ij
n
i i
ij
p
i j
= =
+ =
= = = = =
i=1 j=1 i=1 j=1 j=1
.j
) ,......., 1 ; ,......, 1 (
) ( ) ( n ) (
2
.
2
..
2
..
p j n i
X X X X X X
n
i i
j
ij
p
i j
p
i j
ij
n
i i
ij
p
i j
= =
+ =
= = = = =
i=1 j=1 i=1 j=1 j=1
) ,......., 1 ; ,......, 1 (
) ( ) ( n ) (
2
.
2
..
2
..
p j n i
X X X X X X
n
i i
j
ij
p
i j
p
i j
ij
n
i i
ij
p
i j
= =
+ =
= = = = =
i=1 j=1 i=1 j=1 j=1
.j .j
12
Test Statistic in ANOVA
F = Between group variability / Within group
variability
The source of Within group variability is the individual
differences.
The source of Between group variability is effect of
independent or grouping variables.
Within group variability is sampling error across the cases
Between group variability is effect of independent groups
or variables
13
Steps in Test of Hypothesis
1. Determine the appropriate test
2. Establish the level of significance:
3. Determine whether to use a one tail or two tail test
4. Calculate the test statistic
5. Determine the degree of freedom
6. Compare computed test statistic against a
tabled/critical value
Same as Before
14
1. Determine the Appropriate Test
Independent random samples have been taken from each
population
Dependent variable population are normally distributed (ANOVA
is robust with regards to this assumption)
Population variances are equal (ANOVA is robust with regards to
this assumption)
Subjects in each group have been independently sampled
15
2. Establish Level of Significance
is a predetermined value
The convention
= .05
= .01
= .001
16
3. Use a Two Tailed Test
H
o
:
1
=
2
=
3
=
4
Where
1
= population mean for group 1
2
= population mean for group 2
3
= population mean for group 3
4
= population mean for group 4
H
1
= not H
o
17
3. Use a Two Tailed Test
H
a
= not H
o
The alternative hypothesis does not
specify whether
1
=
2
or
2
=
3
or
1
= 3
18
4. Calculating Test Statistics
F = (SS
b
/ df
B
) / (SS
w
/ df
w
)
19
4. Calculating Test Statistics
By dividing the sum of the squared deviations by
degrees of freedom, we are essentially computing
an average (or mean) amount of variation
The specific name for the numerator of the F
statistic is the mean square between (the
average amount of between-group variation
The specific name for the denominator of the F
statistic is the mean square within (the average
amount of within- group variation)
9.13
3.83
35
Within MS
MSBetween
Fc = = =
20
5. Determine Degrees of
Freedom
Degrees of freedom between
df
B
= k 1
K = number of groups
Degrees of freedom within
df
w
= N k
N = total number of subjects in the study
21
6. Compare the Computed Test
Statistic Against a Tabled Value
= .05
If F
c
> F
Reject H
0
If F
c
> F
Can not Reject H
0
22
Example
Suppose we had patients with myocardial infarction
in the following groups:
Group 1: A music therapy group
Group 2: A relaxation therapy group
Group 3: A control group
15 patients are randomly assigned to the 3 groups
and then their stress levels are measured to
determine if the interventions were effective in
minimizing stress.
23
Example
Dependent Variable
The stress scores. The ranges are from zero
(no stress) to 10 (extreme stress)
Independent Variable or Factor
Treatment Conditions(3 levels)
24
Observations
Group 1 Group 2 Group 3
0 1 5
6 4 6
2 3 10
4 2 8
3 0 6
Mean 3 2 7
25
Sum of Squares for Each Group
Group 1
0
Group 2
1
Group 3
5
6 4 6
2 3 10
4 2 8
3 0 6
SS
1
= 20 SS
2
= 10 SS
3
= 16
n1=5 n2= 5 n3 = 5
3.0 X1 = 2.0 X2 = 7.0 X3 =
26
SS Within
70 4) - 5(7 4) - 5(2 4) - 5(3 SSBetween
46 16 10 20 SSWithin
16 7) - (6 7) - (8 7) - (10 7) - (6 7) - (5
) X ( SS
10 2) - (0 2) - (2 2) - (3 2) - (4 2) - (1
) X ( SS
20 3) - (3 3) - (4 3) - (2 3) - (6 3) - (0
) ( SS
2 2 2
2 2 2 2 2
2
3
2 2 2 2 2
2
2
2 2 2 2 2
2
1
= + + =
= + + =
= + + + + =
E =
= + + + + =
E =
= + + + + =
E =
X
X
X X
3j
2j
1j 1
2
3j
3
70 4) - 5(7 4) - 5(2 4) - 5(3 SSBetween
46 16 10 20 SSWithin
16 7) - (6 7) - (8 7) - (10 7) - (6 7) - (5
) X ( SS
10 2) - (0 2) - (2 2) - (3 2) - (4 2) - (1
) X ( SS
20 3) - (3 3) - (4 3) - (2 3) - (6 3) - (0
) ( SS
2 2 2
2 2 2 2 2
2
3
2 2 2 2 2
2
2
2 2 2 2 2
2
1
= + + =
= + + =
= + + + + =
E =
= + + + + =
E =
= + + + + =
E =
X
X
X X
3j
2j
1j
70 4) - 5(7 4) - 5(2 4) - 5(3 SSBetween
46 16 10 20 SSWithin
16 7) - (6 7) - (8 7) - (10 7) - (6 7) - (5
) X ( SS
10 2) - (0 2) - (2 2) - (3 2) - (4 2) - (1
) X ( SS
20 3) - (3 3) - (4 3) - (2 3) - (6 3) - (0
) ( SS
2 2 2
2 2 2 2 2
2
3
2 2 2 2 2
2
2
2 2 2 2 2
2
1
= + + =
= + + =
= + + + + =
E =
= + + + + =
E =
= + + + + =
E =
X
X
X X
3j
2j
70 4) - 5(7 4) - 5(2 4) - 5(3 SSBetween
46 16 10 20 SSWithin
16 7) - (6 7) - (8 7) - (10 7) - (6 7) - (5
) X ( SS
10 2) - (0 2) - (2 2) - (3 2) - (4 2) - (1
) X ( SS
20 3) - (3 3) - (4 3) - (2 3) - (6 3) - (0
) ( SS
2 2 2
2 2 2 2 2
2
3
2 2 2 2 2
2
2
2 2 2 2 2
2
1
= + + =
= + + =
= + + + + =
E =
= + + + + =
E =
= + + + + =
E =
X
X
X X
3j
70 4) - 5(7 4) - 5(2 4) - 5(3 SSBetween
46 16 10 20 SSWithin
16 7) - (6 7) - (8 7) - (10 7) - (6 7) - (5
) X ( SS
10 2) - (0 2) - (2 2) - (3 2) - (4 2) - (1
) X ( SS
20 3) - (3 3) - (4 3) - (2 3) - (6 3) - (0
) ( SS
2 2 2
2 2 2 2 2
2
3
2 2 2 2 2
2
2
2 2 2 2 2
2
1
= + + =
= + + =
= + + + + =
E =
= + + + + =
E =
= + + + + =
E =
X
X
X X
3j
2j
1j 1
2
3j
3
27
70 4) - 5(7 4) - 5(2 4) - 5(3 SSBetween
46 16 10 20 SSWithin
16 7) - (6 7) - (8 7) - (10 7) - (6 7) - (5
) X ( SS
10 2) - (0 2) - (2 2) - (3 2) - (4 2) - (1
) X ( SS
20 3) - (3 3) - (4 3) - (2 3) - (6 3) - (0
) ( SS
2 2 2
2 2 2 2 2
2
3
2 2 2 2 2
2
2
2 2 2 2 2
2
1
= + + =
= + + =
= + + + + =
E =
= + + + + =
E =
= + + + + =
E =
X
X
X X
3j
2j
1j 1
2
3j
3
70 4) - 5(7 4) - 5(2 4) - 5(3 SSBetween
46 16 10 20 SSWithin
16 7) - (6 7) - (8 7) - (10 7) - (6 7) - (5
) X ( SS
10 2) - (0 2) - (2 2) - (3 2) - (4 2) - (1
) X ( SS
20 3) - (3 3) - (4 3) - (2 3) - (6 3) - (0
) ( SS
2 2 2
2 2 2 2 2
2
3
2 2 2 2 2
2
2
2 2 2 2 2
2
1
= + + =
= + + =
= + + + + =
E =
= + + + + =
E =
= + + + + =
E =
X
X
X X
3j
2j
1j
70 4) - 5(7 4) - 5(2 4) - 5(3 SSBetween
46 16 10 20 SSWithin
16 7) - (6 7) - (8 7) - (10 7) - (6 7) - (5
) X ( SS
10 2) - (0 2) - (2 2) - (3 2) - (4 2) - (1
) X ( SS
20 3) - (3 3) - (4 3) - (2 3) - (6 3) - (0
) ( SS
2 2 2
2 2 2 2 2
2
3
2 2 2 2 2
2
2
2 2 2 2 2
2
1
= + + =
= + + =
= + + + + =
E =
= + + + + =
E =
= + + + + =
E =
X
X
X X
3j
2j
70 4) - 5(7 4) - 5(2 4) - 5(3 SSBetween
46 16 10 20 SSWithin
16 7) - (6 7) - (8 7) - (10 7) - (6 7) - (5
) X ( SS
10 2) - (0 2) - (2 2) - (3 2) - (4 2) - (1
) X ( SS
20 3) - (3 3) - (4 3) - (2 3) - (6 3) - (0
) ( SS
2 2 2
2 2 2 2 2
2
3
2 2 2 2 2
2
2
2 2 2 2 2
2
1
= + + =
= + + =
= + + + + =
E =
= + + + + =
E =
= + + + + =
E =
X
X
X X
3j
70 4) - 5(7 4) - 5(2 4) - 5(3 SSBetween
46 16 10 20 SSWithin
16 7) - (6 7) - (8 7) - (10 7) - (6 7) - (5
) X ( SS
10 2) - (0 2) - (2 2) - (3 2) - (4 2) - (1
) X ( SS
20 3) - (3 3) - (4 3) - (2 3) - (6 3) - (0
) ( SS
2 2 2
2 2 2 2 2
2
3
2 2 2 2 2
2
2
2 2 2 2 2
2
1
= + + =
= + + =
= + + + + =
E =
= + + + + =
E =
= + + + + =
E =
X
X
X X
3j
2j
1j 1
2
3j
3
Number
of cases
SS Between
Group 2
average
Group 1
average
Group 3
average
Grand
average
28
Sum of Squares Total
116 4) - (6 4) - (8 4) - (10
4) - (6 4) - (5 4) - (0 4) - (2
4) - (3 4) - (4 4) - (1 4) - (3
4) - (4 4) - (2 4) - (6 4) - (0 SSTotal
2 2 2
2 2 2 2
2 2 2 2
2 2 2 2
= + +
+ + + +
+ + + +
+ + + + =
29
Components of Variance
SS
Total
= SS
Between
+ SS
Within
116 = 70 + 46
) ,......., 1 ; ,......, 1 (
) ( ) ( n ) (
2
.
2
..
2
..
p j n i
X X X X X X
n
i i
j
ij
p
i j
p
i j
ij
n
i i
ij
p
i j
= =
+ =
= = = = =
i=1 j=1 i=1 j=1 j=1
) ,......., 1 ; ,......, 1 (
) ( ) ( n ) (
2
.
2
..
2
..
p j n i
X X X X X X
n
i i
j
ij
p
i j
p
i j
ij
n
i i
ij
p
i j
= =
+ =
= = = = =
i=1 j=1 i=1 j=1 j=1
.j .j
) ,......., 1 ; ,......, 1 (
) ( ) ( n ) (
2
.
2
..
2
..
p j n i
X X X X X X
n
i i
j
ij
p
i j
p
i j
ij
n
i i
ij
p
i j
= =
+ =
= = = = =
i=1 j=1 i=1 j=1 j=1
) ,......., 1 ; ,......, 1 (
) ( ) ( n ) (
2
.
2
..
2
..
p j n i
X X X X X X
n
i i
j
ij
p
i j
p
i j
ij
n
i i
ij
p
i j
= =
+ =
= = = = =
i=1 j=1 i=1 j=1 j=1
.j
) ,......., 1 ; ,......, 1 (
) ( ) ( n ) (
2
.
2
..
2
..
p j n i
X X X X X X
n
i i
j
ij
p
i j
p
i j
ij
n
i i
ij
p
i j
= =
+ =
= = = = =
i=1 j=1 i=1 j=1 j=1
) ,......., 1 ; ,......, 1 (
) ( ) ( n ) (
2
.
2
..
2
..
p j n i
X X X X X X
n
i i
j
ij
p
i j
p
i j
ij
n
i i
ij
p
i j
= =
+ =
= = = = =
i=1 j=1 i=1 j=1 j=1
.j .j
) ,......., 1 ; ,......, 1 (
) ( ) ( n ) (
2
.
2
..
2
..
p j n i
X X X X X X
n
i i
j
ij
p
i j
p
i j
ij
n
i i
ij
p
i j
= =
+ =
= = = = =
i=1 j=1 i=1 j=1 j=1
) ,......., 1 ; ,......, 1 (
) ( ) ( n ) (
2
.
2
..
2
..
p j n i
X X X X X X
n
i i
j
ij
p
i j
p
i j
ij
n
i i
ij
p
i j
= =
+ =
= = = = =
i=1 j=1 i=1 j=1 j=1
.j .j
) ,......., 1 ; ,......, 1 (
) ( ) ( n ) (
2
.
2
..
2
..
p j n i
X X X X X X
n
i i
j
ij
p
i j
p
i j
ij
n
i i
ij
p
i j
= =
+ =
= = = = =
i=1 j=1 i=1 j=1 j=1
) ,......., 1 ; ,......, 1 (
) ( ) ( n ) (
2
.
2
..
2
..
p j n i
X X X X X X
n
i i
j
ij
p
i j
p
i j
ij
n
i i
ij
p
i j
= =
+ =
= = = = =
i=1 j=1 i=1 j=1 j=1
.j
) ,......., 1 ; ,......, 1 (
) ( ) ( n ) (
2
.
2
..
2
..
p j n i
X X X X X X
n
i i
j
ij
p
i j
p
i j
ij
n
i i
ij
p
i j
= =
+ =
= = = = =
i=1 j=1 i=1 j=1 j=1
) ,......., 1 ; ,......, 1 (
) ( ) ( n ) (
2
.
2
..
2
..
p j n i
X X X X X X
n
i i
j
ij
p
i j
p
i j
ij
n
i i
ij
p
i j
= =
+ =
= = = = =
i=1 j=1 i=1 j=1 j=1
.j .j
30
Degrees of Freedom
Df
between
= 3 -1
Df
within
= 15 - 3
df
B
= k 1
df
w
= N k
31
Test Statistic
MS
Between
= 70 / 2 = 35
MS
Within
= 46 / 12 = 3.83
F
c
= MS
Between
/ MS
Within
F
c
= 35 / 3.83 = 9.13
32
Lookup Critical Value
F
= 3.88
33
Conclusions
F
c
= 9.13 > F
= 3.88
F
c
> F
Therefore Reject H
0
34
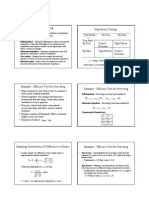
One-way ANOVA Summary
Source SS DF MS F
c
F
-------------- ------ ------ -------- ------ ------
Between 70 2 35 9.13 3.88
Within 46 12 3.83
------- ------ ---- ----- ----- -------
Total 116 14
35
Multiple Comparison
Groups
F test does not tell which pair are
not equal
Additional analysis is necessary to
answer which pair are not equal
36
Fishers LSD Test
These are the null and alternative hypothesis
being tested
H
o1
: 1 = 2 H
a1
: 1 = 2
H
o2
: 1 = 3
Ha2
: 1 = 3
H
o3
: 2 = 3 H
a3
: 2 = 3
37
Fishers LSD Test
Known as the protected t-test
The least difference between means needed for
significance
Df = N K
Use the following formula:
) / 2 ( 05 . n MSw t LSD=
) / 2 ( 05 . n MSw t LSD=
) / 2 ( 05 . n MSw t LSD=
38
Calculation of LSD
All pairs for means differing by at least 2.70
points on the stress scale would be
significantly different from on another.
70 . 2 ) 40 (. 83 . 3 18 . 2 = = LSD
39
Application to Three
Samples
Mean 1 Mean 2 = 1
Mean 3 Mean 1 = 4
Mean 3 Mean 2 = 5
Alternative Hypotheses:
H
o1
:1 = 2 Not Rejected
H
o2
:1 = 3 Rejected
H
o3
:2 = 3 Rejected
40
Use of SPSS in ANOVA
41
Data in SPSS
Input Format
Stress Score Groups
0 1
6 1
2 1
4 1
3 1
1 2
4 2
3 2
2 2
0 2
5 3
6 3
10 3
8 3
6 3
42
SPSS Output for ANOVA
Descriptives
Stress Levels
Music Therapy
5
3.00
2.236
1.000
.22
5.78
0
6
Relaxation
Therapy
5
2.00
1.581
.707
.04
3.96
0
4
Control Group
5
7.00
2.000
.894
4.52
9.48
5
10
N
Mean
Std. Deviation
Std. Error
95% Confidence Interval
for Mean
Minimum
Maximum
Lower
Bound
Upper
Bound
Total
15
4.00
2.878
.743
2.41
5.59
0
10
43
SPSS Output for ANOVA
Test of Homogeneity of Variances
Stress Levels.
Levene
Statistic
df1
df2
Sig level
or p-
value
.242
2
12
.788
Stress Levels
Between Groups
70.000
2
35.000
9.130
.004
Within Groups
46.000
12
3.833
Sum of
Squares
df
Mean
Square
F
Sig.level
or p-
value
Total
116.000
14
P<.05, therefore, we reject the Null Hypothesis and continue with Multiple Comparison Table
P > .05, therefore, th assumption of Homogeneity of Variance is met.
ANOVA
44
SPSS Output for ANOVA
Multiple Comparisons
Dependent Variable: Stress Levels
LSD
Music Therapy
Relaxation
Therapy
1.000
1.238
.435
-1.70
3.70
Control Group
-4.000(*)
1.238
.007
-6.70
-1.30
Relaxation
Therapy
Music Therapy
-1.000
1.238
.435
-3.70
1.70
Control Group
-5.000(*)
1.238
.002
-7.70
-2.30
Control Group
Music Therapy
4.000(*)
1.238
.007
1.30
6.70
Relaxation
Therapy
5.000(*)
1.238
.002
2.30
7.70
(I) Groups
(J) Groups
Mean
Difference
(I-J)
Std. Error
Sig.
Level
95% Confidence Interval
* The mean difference is significant at the .05 level.
45
Take home lesson
How to compare means of three or
more samples
You might also like
- A Multivariate Weibull DistributionDocument12 pagesA Multivariate Weibull DistributionJean ReneNo ratings yet
- 21mab204t - PQT - Unit 2, 3Document23 pages21mab204t - PQT - Unit 2, 3Avinash ReddyNo ratings yet
- Solutions Exercises Chapter 2: Dependence)Document3 pagesSolutions Exercises Chapter 2: Dependence)DanyValentinNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - DISCRETE AND CONTINOUS PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS PDFDocument37 pagesUnit 3 - DISCRETE AND CONTINOUS PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS PDFnganduNo ratings yet
- Boundary Value Problem and Its Application in I-Function of MultivariableDocument7 pagesBoundary Value Problem and Its Application in I-Function of MultivariableAlexander DeckerNo ratings yet
- MATLAB FormulasDocument3 pagesMATLAB FormulasRoberto Alessandro IonescuNo ratings yet
- Recursion Formula For The Probability Distribution of Sum of (Vu+Document9 pagesRecursion Formula For The Probability Distribution of Sum of (Vu+Chukwuebuka EgbunaNo ratings yet
- Chap 14Document58 pagesChap 14Vinayaga VigneshNo ratings yet
- Root Finding:: X X D D X X D X XDocument3 pagesRoot Finding:: X X D D X X D X Xyana22No ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document28 pagesChapter 6Sahand NoorizadehNo ratings yet
- 3a PPS Sampling With ReplacementDocument10 pages3a PPS Sampling With ReplacementKEEME MOTSWAKAENo ratings yet
- Chpt05-FEM For 2D SolidsnewDocument56 pagesChpt05-FEM For 2D SolidsnewKrishna MyakalaNo ratings yet
- Properties of Complex Numbers (Contd) : NPTEL - Physics - Mathematical Physics - 1Document8 pagesProperties of Complex Numbers (Contd) : NPTEL - Physics - Mathematical Physics - 1vkphyNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Several Multivariate MeansDocument103 pagesComparison of Several Multivariate MeansBrian Cr50% (2)
- FormulaSheet Test 1Document6 pagesFormulaSheet Test 1bestreview7No ratings yet
- Stat 130n Answers To The LAs in Lessons 3.1-3.3Document18 pagesStat 130n Answers To The LAs in Lessons 3.1-3.3Faith GarfinNo ratings yet
- Notes On Non-Cooperative Game Theory Econ 8103, Spring 2009, Aldo RustichiniDocument30 pagesNotes On Non-Cooperative Game Theory Econ 8103, Spring 2009, Aldo RustichiniMegan JohnstonNo ratings yet
- Duoc1AB 2Document3 pagesDuoc1AB 2Lê Nguyễn Hoàng AnhNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document5 pagesLecture 5alcinialbob1234No ratings yet
- Name of The Student: Branch:: Engineering Mathematics Material 2010Document13 pagesName of The Student: Branch:: Engineering Mathematics Material 2010krrmallikaNo ratings yet
- Booklet 19.downloadDocument3 pagesBooklet 19.downloadHila Neuberger RiterNo ratings yet
- Characterising and Displaying Multivariate DataDocument15 pagesCharacterising and Displaying Multivariate DataR. Shyaam PrasadhNo ratings yet
- CVEN2002 Week5Document43 pagesCVEN2002 Week5Kai LiuNo ratings yet
- Rumus Double Sampling and Three StageDocument1 pageRumus Double Sampling and Three StageAhmad JailaniNo ratings yet
- Ha 9Document5 pagesHa 9Аружан ЖадырасынNo ratings yet
- Show All Solutions and Enclose All Final Answers.: T T T XT T TDocument1 pageShow All Solutions and Enclose All Final Answers.: T T T XT T TAnna Karissa PerezNo ratings yet
- Lecture-5-6 Moment, Skewness and KurtosisDocument5 pagesLecture-5-6 Moment, Skewness and KurtosisNafiul Alam SnigdhoNo ratings yet
- Topic11.Hypothesis Testing. One-Way ANOVADocument3 pagesTopic11.Hypothesis Testing. One-Way ANOVAKyrby CabalquintoNo ratings yet
- 2.ANOVA-solution - Solution LaboratoryDocument13 pages2.ANOVA-solution - Solution LaboratoryAriadna AbadNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Mathematics and Statistics Invention (IJMSI)Document6 pagesInternational Journal of Mathematics and Statistics Invention (IJMSI)inventionjournalsNo ratings yet
- Script Confidence Intervals PDFDocument16 pagesScript Confidence Intervals PDFRojan PradhanNo ratings yet
- Probability DistributionDocument11 pagesProbability Distributionshakil ahmedNo ratings yet
- 2006 AJC H2 MY SolnDocument9 pages2006 AJC H2 MY Solnjunie9201No ratings yet
- MHPM SfieskDocument10 pagesMHPM SfieskKawa Mustafa AzizNo ratings yet
- Probability Theory and Mathematical Statistics: Homework 2, Vitaliy PozdnyakovDocument13 pagesProbability Theory and Mathematical Statistics: Homework 2, Vitaliy PozdnyakovGarakhan TalibovNo ratings yet
- P and S - Unit 2Document44 pagesP and S - Unit 2Nandha KashwaranNo ratings yet
- Q. 1: For The Rectangular Element Shown in The Figure Obtain The Coefficient MatrixDocument6 pagesQ. 1: For The Rectangular Element Shown in The Figure Obtain The Coefficient MatrixVivek HarrisNo ratings yet
- All Solutions For YangDocument48 pagesAll Solutions For YangSdpp SudheerNo ratings yet
- ANOVA With Summary Statistics A STATA MaDocument6 pagesANOVA With Summary Statistics A STATA MaRock Hall Primary SchoolNo ratings yet
- I. Newton-Raphson Method - 2 Dim Case: X X X X FDocument9 pagesI. Newton-Raphson Method - 2 Dim Case: X X X X FsayedmhNo ratings yet
- Probability & Random Process: FormulasDocument10 pagesProbability & Random Process: FormulasvrsafeNo ratings yet
- Z Transform and It's ApplicationsDocument11 pagesZ Transform and It's Applicationsলাজ মাহমুদNo ratings yet
- 2006 2 SolutionsDocument13 pages2006 2 Solutionshoangthai2971990No ratings yet
- 18MAB204T - PQT - UNIT 2, 3 - Cycle Test II - March 2023Document29 pages18MAB204T - PQT - UNIT 2, 3 - Cycle Test II - March 2023JEMINA J (RA2011037010010)No ratings yet
- Formuli NumerickaMatematikaDocument8 pagesFormuli NumerickaMatematikaGoshev BlagojchoNo ratings yet
- Probability & Queuing Theory FormulasDocument13 pagesProbability & Queuing Theory Formulasrahul.n90No ratings yet
- OUTLINE and REVIEW PROBLEMS FOR TEST ON PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONSDocument4 pagesOUTLINE and REVIEW PROBLEMS FOR TEST ON PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONSPffflyers KurnawanNo ratings yet
- ModuleDocument25 pagesModuleYogix ThetroubleshooterNo ratings yet
- HW 3 Mechanics of Materials 2 (1-4)Document6 pagesHW 3 Mechanics of Materials 2 (1-4)AdzimNo ratings yet
- Sampling Theory: Double Sampling (Two Phase Sampling)Document12 pagesSampling Theory: Double Sampling (Two Phase Sampling)andriyesNo ratings yet
- Unit IX - Session 22Document10 pagesUnit IX - Session 22e16125No ratings yet
- Notes 2 - Module 2Document7 pagesNotes 2 - Module 2bandi nagavindhyaNo ratings yet
- Num SheetDocument1 pageNum SheetedexcelpastpapersNo ratings yet
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandInverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Applications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandApplications of Derivatives Errors and Approximation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Differentiation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDifferentiation (Calculus) Mathematics Question BankRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Logical progression of twelve double binary tables of physical-mathematical elements correlated with scientific-philosophical as well as metaphysical key concepts evidencing the dually four-dimensional basic structure of the universeFrom EverandLogical progression of twelve double binary tables of physical-mathematical elements correlated with scientific-philosophical as well as metaphysical key concepts evidencing the dually four-dimensional basic structure of the universeNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Cardiac MonitoringDocument5 pagesCardiac MonitoringAmit Kl100% (1)
- Management Theories PDFDocument27 pagesManagement Theories PDFRaja RamanNo ratings yet
- Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument22 pagesDiabetic KetoacidosispoktaviantiNo ratings yet
- 11g GeneralDocument33 pages11g GeneralsvuhariNo ratings yet
- Equipment Procedure:: Assisting The Patient Undergoing ThoracentesisDocument4 pagesEquipment Procedure:: Assisting The Patient Undergoing ThoracentesisAmit KlNo ratings yet
- CCN StaffingDocument16 pagesCCN StaffingAmit KlNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 - Cardiac EmergenciesDocument96 pagesChapter 20 - Cardiac EmergenciesAmit KlNo ratings yet
- ArdsDocument81 pagesArdsAmit KlNo ratings yet
- Chap 39 Infectious-Communicable DiseasesDocument129 pagesChap 39 Infectious-Communicable DiseasesAmit KlNo ratings yet
- Path o PhysiologyDocument122 pagesPath o PhysiologyAmit KlNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Patients Receiving Chemotherapy Ranjita Rajesh Lecturer People's College of Nursing BhopalDocument55 pagesNursing Care of Patients Receiving Chemotherapy Ranjita Rajesh Lecturer People's College of Nursing BhopalFayizatul AkmarNo ratings yet
- Adm Ash AddmDocument50 pagesAdm Ash AddmpkextrasNo ratings yet
- HyptestDocument4 pagesHyptestsandy1001No ratings yet
- Chi-Square: Heibatollah Baghi, and Mastee BadiiDocument37 pagesChi-Square: Heibatollah Baghi, and Mastee BadiiAnand RajputNo ratings yet
- Upgrading From Oracle 9i To Oracle Database 11g:: A Real World Customer ExperienceDocument41 pagesUpgrading From Oracle 9i To Oracle Database 11g:: A Real World Customer ExperienceEmerson Rodrigo OrciNo ratings yet
- Chap 23 BurnsDocument79 pagesChap 23 BurnsAmit KlNo ratings yet
- 11gR2 Physical Data Guard Setup Project, With Active Data Guard OptionDocument26 pages11gR2 Physical Data Guard Setup Project, With Active Data Guard Optionjlc1967No ratings yet
- InstallDocument176 pagesInstallAmit KlNo ratings yet
- Oracle RDBMS & SQL Tutorial (Very Good)Document66 pagesOracle RDBMS & SQL Tutorial (Very Good)api-3717772100% (7)
- Oracle RAC Design Techniques: Book Excerpt Oracle 10g Grid & Real Application ClustersDocument19 pagesOracle RAC Design Techniques: Book Excerpt Oracle 10g Grid & Real Application ClustersgauravkumarsinhaNo ratings yet
- Final Exam MAT1004 Summer Code 1Document3 pagesFinal Exam MAT1004 Summer Code 1Anh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Disiplin, Etos Kerja, Dan Budaya Organisasi Terhadap Pegawai Administrator Pelabuhan Tanjung PriokDocument10 pagesPengaruh Disiplin, Etos Kerja, Dan Budaya Organisasi Terhadap Pegawai Administrator Pelabuhan Tanjung PriokGud SangadNo ratings yet
- 405 Econometrics: by Domodar N. GujaratiDocument47 pages405 Econometrics: by Domodar N. Gujaratimuhendis_8900No ratings yet
- Weibull Normal Lognormal Galton Exponential Pearsoniii Logpearsoniii Gumbel Max Gumbel Min Weibull L-Moments Gev-Max (K. Spec.)Document1 pageWeibull Normal Lognormal Galton Exponential Pearsoniii Logpearsoniii Gumbel Max Gumbel Min Weibull L-Moments Gev-Max (K. Spec.)Adrian MirandaNo ratings yet
- Business Analytics: Advance: Logistic RegressionDocument26 pagesBusiness Analytics: Advance: Logistic RegressionKetan Bhalerao100% (1)
- Central Tendency Variability and Sampling Distribution PNCHDocument6 pagesCentral Tendency Variability and Sampling Distribution PNCHJASTHER LLOYD TOMANENGNo ratings yet
- 6.4 Process CapabilityDocument13 pages6.4 Process CapabilitychuszNo ratings yet
- Statistics - Dispersion - Week 4Document4 pagesStatistics - Dispersion - Week 4Austin Capal Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- NATG6 Stratified Sampling TemplateDocument154 pagesNATG6 Stratified Sampling Templatemichelle.bulfaNo ratings yet
- Multiple Linear Regression (Continue) Example:: CO Product Y Solvent Total X Hydrogen Consumption X Y X Y X Y X XDocument4 pagesMultiple Linear Regression (Continue) Example:: CO Product Y Solvent Total X Hydrogen Consumption X Y X Y X Y X XMuhammad BilalNo ratings yet
- Statistics For BiologyDocument18 pagesStatistics For Biologyidawayu100% (1)
- ECON3206 - Tutorial 4 - FelipeDocument19 pagesECON3206 - Tutorial 4 - FelipeAntonio DwNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Econometrics (3 Updated Edition) : (This Version July 20, 2014)Document7 pagesIntroduction To Econometrics (3 Updated Edition) : (This Version July 20, 2014)Sanjna ChimnaniNo ratings yet
- AP STAT Midterm ReviewDocument8 pagesAP STAT Midterm ReviewGan PentonNo ratings yet
- MCQ 12765 KDocument21 pagesMCQ 12765 Kcool_spNo ratings yet
- Control Chart ConceptsDocument32 pagesControl Chart ConceptsNur FarhinNo ratings yet
- StatDocument70 pagesStatcj_anero67% (3)
- PR2 Module 9Document41 pagesPR2 Module 9Earl Laurence PlatinoNo ratings yet
- Tugas SPSSDocument2 pagesTugas SPSSIlyasa YusufNo ratings yet
- True ExperimentDocument8 pagesTrue Experimentkeira nizaNo ratings yet
- Material To Lecture 3Document6 pagesMaterial To Lecture 3Данила ДенисовNo ratings yet
- EFA GuideDocument28 pagesEFA GuideSoni RathiNo ratings yet
- Question 1 (Chp.2) : Mid 1 July 22nd, 2021, STAT 245, U of Sask Exam Period: 3 HoursDocument12 pagesQuestion 1 (Chp.2) : Mid 1 July 22nd, 2021, STAT 245, U of Sask Exam Period: 3 HoursJaheda SultanaNo ratings yet
- Sop TableDocument3 pagesSop TableCleofe SobiacoNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 2Document2 pagesProblem Set 2SOPHIA BEATRIZ UYNo ratings yet
- Homework Problems - Paired Samples T-TestDocument48 pagesHomework Problems - Paired Samples T-TestDevan BhallaNo ratings yet
- Statistics Formula Sheet and Tables 2020Document6 pagesStatistics Formula Sheet and Tables 2020bella lubbockNo ratings yet
- Estructuras Hidraulicas HyfranDocument34 pagesEstructuras Hidraulicas HyfranFavio Espinoza PariNo ratings yet
- Arma 1Document4 pagesArma 1Lâm Anh VũNo ratings yet