Professional Documents
Culture Documents
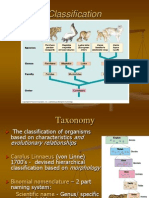
Domains & Kingdoms of Life
Uploaded by
Ram Iyer100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
173 views14 pagesn
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentn
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
173 views14 pagesDomains & Kingdoms of Life
Uploaded by
Ram Iyern
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
17.
4 Domains and Kingdoms
Do Now 4/5/12
1. Why are dichotomous keys necessary? _____________________________________________ 2. Why are evolutionary relationships more relevant than the appearance or an organism when classifying it?___________________________________________ 3. What do you think is the most diverse and abundant kind of life on earth? _____________________________________________
17.4 Domains and Kingdoms
KEY CONCEPT The current tree of life has three domains.
17.4 Domains and Kingdoms
The three domains in the tree of life are Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya.
Domains are above the kingdom level. Base on sequences from rRNA nucleotides domain model more clearly shows prokaryotic diversity
17.4 Domains and Kingdoms
Terms Systematics a method of organizing organisms based on their evolution. Phylogenetic tree A family tree that shows the evolutionary relationships thought to exist among groups of organisms.
17.4 Domains and Kingdoms
Domain Bacteria includes prokaryotes in the kingdom Eubacteria.
one of largest groups on Earth classified by shape, need for oxygen, and diseases caused
Streptococcus pyogenes
17.4 Domains and Kingdoms
Domain Archaea includes prokaryotes in the kingdom Archaea. cell walls chemically different from bacteria differences discovered by studying RNA known for living in extreme environments They are difficult to grow in the lab, therefore difficult to study. Some can produce explosive or noxious gases like methane.
17.4 Domains and Kingdoms
Bacteria and archaea can be difficult to classify. transfer genes among themselves outside of reproduction bridge to transfer DNA blurs the line between species more research needed to understand prokaryotes
17.4 Domains and Kingdoms
What makes a Eukaryote? 1. True nuclei 2. Linear chromosomes 3. Membrane bound organelles
17.4 Domains and Kingdoms
Domain Eukarya includes all eukaryotes. kingdom Protista
Euglena gracilis
17.4 Domains and Kingdoms
Domain Eukarya includes all eukaryotes. kingdom Protista kingdom Plantae
Sequoiadendron giganteum Giant Sequoia Amorphophallus titanum Corpse Flower
17.4 Domains and Kingdoms
Domain Eukarya includes all eukaryotes. kingdom Protista kingdom Plantae kingdom Fungi
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi
17.4 Domains and Kingdoms
Domain Eukarya includes all eukaryotes. kingdom Protista kingdom Plantae kingdom Fungi kingdom Animalia Draco volens
Tubastrea coccinea
17.4 Domains and Kingdoms
17.4 Domains and Kingdoms
Checkpoint 1. What are the six kingdoms in the six-kingdom system of classification? 2. What are two things that make archaebacteria difficult to study? 3. What kind of evidence indicates that organisms fall naturally into three broad domains? 4. Why do protists, fungi, plants and animals share a domain in the six-kingdom system?
You might also like
- Science Strategies to Increase Student Learning and Motivation in Biology and Life Science Grades 7 Through 12From EverandScience Strategies to Increase Student Learning and Motivation in Biology and Life Science Grades 7 Through 12No ratings yet
- Domains Kingdoms and ClassificationDocument3 pagesDomains Kingdoms and ClassificationsenjicsNo ratings yet
- Domains and Kingdoms Spring Break ProjectDocument2 pagesDomains and Kingdoms Spring Break Projectapi-368559350No ratings yet
- The Characteristics of Living ThingsDocument8 pagesThe Characteristics of Living ThingsMiy El NinoNo ratings yet
- Earth Scie 22Document26 pagesEarth Scie 22HayaradjNo ratings yet
- Cladogram WsDocument4 pagesCladogram Wsjeffery thomasNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 12 Science CurrDocument264 pagesGrade 11 12 Science Currapi-301141568No ratings yet
- Food Chain GangDocument115 pagesFood Chain GangJoy FernandezNo ratings yet
- Biological Organization LevelsDocument12 pagesBiological Organization LevelsAlrei D MeaNo ratings yet
- Living Things PPT For Class FiveDocument14 pagesLiving Things PPT For Class Fivestudnt07No ratings yet
- Classification of Animals ChartDocument1 pageClassification of Animals CharthaslimiNo ratings yet
- Animal DiversityDocument10 pagesAnimal DiversityjenforrestNo ratings yet
- Scientific Method Powerpoint PHP 2Document21 pagesScientific Method Powerpoint PHP 2api-251215724No ratings yet
- Characteristics of Living ThingsDocument25 pagesCharacteristics of Living Thingsdbhatt55No ratings yet
- General BiologyDocument189 pagesGeneral BiologySamantha AgustinNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology Course PlanDocument7 pagesIGCSE Biology Course PlaneeappleNo ratings yet
- Basicscience PDFDocument133 pagesBasicscience PDFMohammed KaleemNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - Zoology (Honours & General)Document18 pagesSyllabus - Zoology (Honours & General)api-19803189No ratings yet
- AP Biology Syllabus 2009-2010Document10 pagesAP Biology Syllabus 2009-2010yulianaholicNo ratings yet
- General Biology: 1-3 (Second Grading)Document8 pagesGeneral Biology: 1-3 (Second Grading)Dhexter Masungsong MirandaNo ratings yet
- InvertebratesDocument61 pagesInvertebratesJoyce Ann RamirezNo ratings yet
- New Virutal Lab Vascular and Nonvascular PlantsDocument24 pagesNew Virutal Lab Vascular and Nonvascular PlantsLindsey0% (1)
- Hand-Outs Biology 2014Document38 pagesHand-Outs Biology 2014ISCCNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 PDFDocument34 pagesChapter 2 PDFZzaraa99No ratings yet
- Sbi3u Microscopy Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesSbi3u Microscopy Lesson Planapi-504985945No ratings yet
- The Nature of CurriculumDocument44 pagesThe Nature of CurriculumRoan ArnegaNo ratings yet
- Classification of Organisms-VMDocument67 pagesClassification of Organisms-VMLee-Anne Lutchman100% (1)
- Basic Structure of A CellDocument51 pagesBasic Structure of A Cellsi_miaomiaoNo ratings yet
- Scientific Method WorksheetDocument2 pagesScientific Method WorksheetTamara Vanessa Báez-Flores0% (1)
- Plant Reproduction: Seed Dispersal and Germination ExplainedDocument3 pagesPlant Reproduction: Seed Dispersal and Germination ExplainedSunil Nagar100% (1)
- Dichotomous Key ProjectDocument8 pagesDichotomous Key Projectapi-292905822No ratings yet
- AP Biology Lab 9Document35 pagesAP Biology Lab 9WutWut0% (1)
- Chemistry Exam Slides (Simplified)Document380 pagesChemistry Exam Slides (Simplified)nayef aNo ratings yet
- Patterns and Mechanisms WorksheetDocument7 pagesPatterns and Mechanisms Worksheetmichelle_phillips_jhs3020100% (1)
- (Models and Modeling in Science Education 4) John K. Gilbert, David F. Treagust (Auth.), Prof. John K. Gilbert, Prof. David Treagust (Eds.)-Multiple Representations in Chemical Education-Springer Neth (Recovered)Document369 pages(Models and Modeling in Science Education 4) John K. Gilbert, David F. Treagust (Auth.), Prof. John K. Gilbert, Prof. David Treagust (Eds.)-Multiple Representations in Chemical Education-Springer Neth (Recovered)NestiNo ratings yet
- Behavioral EcologyDocument16 pagesBehavioral EcologyrvshnNo ratings yet
- Biology Grade 7Document5 pagesBiology Grade 7Gunawan MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Instructional Strategies ActivitiesDocument33 pagesInstructional Strategies Activitiesaliro205No ratings yet
- BIOSCI030 Biological ScienceDocument80 pagesBIOSCI030 Biological ScienceJay Anne Marie MontalesNo ratings yet
- Invertebrates G7Document65 pagesInvertebrates G7Julia MeirellesNo ratings yet
- General Science ReviewerDocument1 pageGeneral Science ReviewerTin AcidreNo ratings yet
- EarthDocument80 pagesEarthDaisy100% (1)
- Macmillan Science 5 PB U1Document14 pagesMacmillan Science 5 PB U1AnaKareninaMartinez100% (1)
- Biology and Chemistry: The BasicsDocument79 pagesBiology and Chemistry: The BasicsKENT GARCIA100% (2)
- Micro-Invertebrates As Bio-Indicators in The Lake Fred Stream SystemDocument13 pagesMicro-Invertebrates As Bio-Indicators in The Lake Fred Stream SystemAlex ListNo ratings yet
- AQA Practical Handbook FinalDocument35 pagesAQA Practical Handbook FinaljannyankiriNo ratings yet
- SioppppppDocument2 pagesSioppppppapi-262633772No ratings yet
- Activity 5 Science Educ in The PhilippinesDocument4 pagesActivity 5 Science Educ in The Philippinesgerald rupidoNo ratings yet
- GENERAL BIOLOGY 4th Quarter - ACTIVITY #1-5Document7 pagesGENERAL BIOLOGY 4th Quarter - ACTIVITY #1-5Kimberly AyusoNo ratings yet
- BIO 103 Lecture 1Document25 pagesBIO 103 Lecture 1Samiul Hasan Pranto100% (1)
- Teaching & Learning BiologyDocument178 pagesTeaching & Learning BiologyobsrvrNo ratings yet
- 1008458-Chapter 7 - Ecosystem DynamicDocument12 pages1008458-Chapter 7 - Ecosystem DynamicrhimalinyNo ratings yet
- Classfication Study GuideDocument2 pagesClassfication Study Guideapi-293263627No ratings yet
- Classification Study Guide Answer KeyDocument2 pagesClassification Study Guide Answer Keyhop2starNo ratings yet
- ECO WorkbookDocument17 pagesECO Workbookdaniwilson245No ratings yet
- TaxonomyDocument56 pagesTaxonomyKrezia Mae SolomonNo ratings yet
- Classification of Living ThingsDocument4 pagesClassification of Living ThingsmceldowneaNo ratings yet
- Full Download Biology Organisms and Adaptations Media Update Enhanced Edition 1st Edition Noyd Solutions ManualDocument27 pagesFull Download Biology Organisms and Adaptations Media Update Enhanced Edition 1st Edition Noyd Solutions Manualantonynolleus2645100% (39)
- Systematics L9Document35 pagesSystematics L9ledesma avelinoNo ratings yet
- Nepal Deforestation Harms Environment and EconomyDocument2 pagesNepal Deforestation Harms Environment and EconomyRam IyerNo ratings yet
- ReadmeDocument3 pagesReadmeMax YevonNo ratings yet
- Taste of the Suburbs Food and Wine FestivalDocument1 pageTaste of the Suburbs Food and Wine FestivalRam IyerNo ratings yet
- ClassificationDocument15 pagesClassificationRam IyerNo ratings yet
- Pa OnlyDocument73 pagesPa OnlyRam IyerNo ratings yet
- ConfigDocument18 pagesConfigLuis Manuel Cárcamo MoralesNo ratings yet
- What To ReadDocument1 pageWhat To ReadRam IyerNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Microbiology: Mary Lou Dullona-BasaDocument68 pagesIntroduction To Microbiology: Mary Lou Dullona-BasaChloe TangonanNo ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy of The Prokaryotic CellDocument22 pagesFunctional Anatomy of The Prokaryotic Cellm umair zahirNo ratings yet
- Soil BiotaDocument10 pagesSoil BiotaSi CNo ratings yet
- Prescotts Microbiology 8th Edition Willey Test BankDocument25 pagesPrescotts Microbiology 8th Edition Willey Test BankDavidDavisxmny100% (39)
- Chapters Summary (Biology by Solomon)Document10 pagesChapters Summary (Biology by Solomon)edomin00No ratings yet
- Introduction To Biological Evolution (Table of Contents)Document10 pagesIntroduction To Biological Evolution (Table of Contents)Mitch Forbes100% (1)
- Biology Chapter 1 Notes (Grade 11)Document4 pagesBiology Chapter 1 Notes (Grade 11)Tammy Lam100% (11)
- Bacteria Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesBacteria Lesson PlanJenesis MirandaNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEM Mid - Short QuestionsDocument13 pagesBIOCHEM Mid - Short QuestionsMazhar FarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 An Invisible WorldDocument28 pagesChapter 1 An Invisible WorldDia KhamelNo ratings yet
- Classifying of MicroorganismsDocument26 pagesClassifying of MicroorganismsDaman Huri WibowoNo ratings yet
- Microbiology and Parasitology - Prelim CAMPOS ELLADocument47 pagesMicrobiology and Parasitology - Prelim CAMPOS ELLAClarice EllaNo ratings yet
- Brief History of MicrobiologyDocument62 pagesBrief History of MicrobiologySamuel AlakeNo ratings yet
- BacteriaDocument22 pagesBacteriajenelynNo ratings yet
- C18 Biodiversity, Classification & Conservation PDFDocument95 pagesC18 Biodiversity, Classification & Conservation PDFKazi Yousra MomrezNo ratings yet
- Sabree Rondon Handelsman MetagenomicsDocument11 pagesSabree Rondon Handelsman MetagenomicsChaitanya SampatNo ratings yet
- Diverse Uncultivated Ultra-Small Bacterial Cells in GroundwaterDocument8 pagesDiverse Uncultivated Ultra-Small Bacterial Cells in GroundwaterAruaco AruacoNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry The Chemical Reactions of Living Cells 2d Ed Vols 1 2 David E. MetzlerDocument1,977 pagesBiochemistry The Chemical Reactions of Living Cells 2d Ed Vols 1 2 David E. MetzlerEvelyn Biscari100% (7)
- Micropara ReviewerDocument21 pagesMicropara Reviewerririkamobami259No ratings yet
- Microbiology PDFDocument26 pagesMicrobiology PDFAladin herzALLAHNo ratings yet
- Role of taxonomy in diagnostic microbiologyDocument2 pagesRole of taxonomy in diagnostic microbiologyAlex LiganNo ratings yet
- Archaebacteria vs Eubacteria ComparisonDocument38 pagesArchaebacteria vs Eubacteria ComparisonNur AfiahNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology Lectures Reading Guide and Key ConceptsDocument39 pagesCell Biology Lectures Reading Guide and Key ConceptswaimoeNo ratings yet
- Review of 16S Primers for Bacterial and Archaeal DetectionDocument15 pagesReview of 16S Primers for Bacterial and Archaeal DetectionahmicphdNo ratings yet
- The Three Domains and Six Kingdoms of LifeDocument14 pagesThe Three Domains and Six Kingdoms of LifeRowena NimNo ratings yet
- Manual 1102L Fall22Document96 pagesManual 1102L Fall22Sir JoshNo ratings yet
- Endosymbiotic TheoriesDocument18 pagesEndosymbiotic TheoriesleztlyNo ratings yet
- Microbiology OPDocument1,309 pagesMicrobiology OPThư Phạm100% (2)
- Archaebacteria 12847268357901 Phpapp01Document42 pagesArchaebacteria 12847268357901 Phpapp01Rudi Tabuti Bahar AlexaNo ratings yet
- Methanogenic ArchaebacteriADocument49 pagesMethanogenic ArchaebacteriASabyasachi DasguptaNo ratings yet