Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Rhinitis in Domestic Animals
Uploaded by
Ali H. Sadiek أ.د. علي حسن صديق100%(2)100% found this document useful (2 votes)
610 views15 pagesIt is the inflammation of the m.ms of the nose it may be acute, chronic, croupous or follicular and is the most common cause of upper respiratory tract malfunction
Original Title
Rhinitis in domestic animals
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentIt is the inflammation of the m.ms of the nose it may be acute, chronic, croupous or follicular and is the most common cause of upper respiratory tract malfunction
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF or read online from Scribd
100%(2)100% found this document useful (2 votes)
610 views15 pagesRhinitis in Domestic Animals
Uploaded by
Ali H. Sadiek أ.د. علي حسن صديقIt is the inflammation of the m.ms of the nose it may be acute, chronic, croupous or follicular and is the most common cause of upper respiratory tract malfunction
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 15
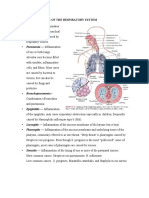
Respiratory System Diseases
• Introduction and autodefence of resp. system
• Rhinitis
• Pharyngitis , Necrobacillosis
• Laryngeo-tracheal Disorders , Gutteral
pouch myosis
• Pneumonia (Viral, bacterial, Chlamydial,
Mycotic, verminous, Aspiration, hypostatic)
• Pulmonary Emphysema
• Respiratory Diseases of Animal species
Upper respiratory tract disorders
RHINITIS, CORYZA OR NASAL CATTARAH
• It is the inflammation of the m.m of the nose
and usually involving the upper part of the
trachea,
• it may be acute, chronic, croupous or
follicular
• It is the most common cause of upper
respiratory tract malfunction,
• Rhinitis results in exudation of neutrophils,
macrophages, and fluids), or erosion and
ulceration (or both) of the nasal mucosa.
• It may be caused by viral, bacterial, fungal, or
parasitic agents, as well as by allergic
reactions.
• Atrophy of the turbinates (eg, in atrophic
rhinitis of pigs) removes a major filtration
function and exposes the lungs to much
heavier loads of dust and
microorganisms.
• Obstruction of nasal cavity may occurred
by tumors, granulomas, abscesses, or
foreign bodies.
• Sinusitis can be a complication of upper
respiratory infections or dehorning.
Rhinitis
• Inhalation of irritant vapour as ammonia or
chlorides.
• Associting upper resp. syst. Diseases or
pneumonias.
• In Cattle: Associate IBR، R.P, MHC, MD/VD
Adenovirus، Rhinosporidiosis
• In Equine: Strangles, glanders, EV Arteritis,
E. rhinooneumonitis
• In sheep: Blue tongue, Pox, Orf, Nasal Bot.
• In Camel: Pneumonia, Pox, orf, nasal pot.
Signs of Rhinitis
• Redness and swelling of mms of the nose.
• Bilateral nasal discharge which usually
begins watery then mucopurualnt &
purulent.
• Swelling of the submaxillary L.N.
• Dysphagia.
• The discharge may rises up and blocks
the nose leading to "snorting".
• When there is irritation the animal rubs its
nose against any hard objects.
• There may be lacrimation and bleeding
Rhinitis.
ORF
Pox
Pox
African horse sickness Shipping fever
Orf
Allergic rhinitis Sheep
Adenocarcinoma dog
Complications
Chronic rhinitis may extend to other parts
as nasal sinus giving rise to sinusitis.
Enlargement of submaxilary L.N.
Conjunctivitis specially in sheep.
Extension of the inflammation to the lung
Treatment of Rhinitis.
• According to the cause.
• Removal of discharge & irrigation of the
nasal cavity by N. saline.
• Nasal antiseptic & decongestant.
• Br. S. Antibiotic when necessary.
• Anti-inflammatory and anti-histaminic.
• For estrus ovis
7.Diluted Trichlorophan injection for nasal
pot. (Nasal drops). Ivermectin, Rafoxindie,
Ranid
You might also like
- Persuasive Speech Outline CFDocument4 pagesPersuasive Speech Outline CFThanh Trần100% (1)
- (K24) Acute & Chronic LaryngitisDocument47 pages(K24) Acute & Chronic LaryngitisSyarifah Fauziah100% (3)
- Causative Agents Causative Agents: Headache, Myalgia, & Nausea Are Added S/SX For Streptococcal PharyngitisDocument21 pagesCausative Agents Causative Agents: Headache, Myalgia, & Nausea Are Added S/SX For Streptococcal PharyngitisDon Chiaw Manongdo100% (1)
- Chapter 22 Management of Patients With Upper Respiratory Tract DisordersDocument7 pagesChapter 22 Management of Patients With Upper Respiratory Tract DisordersPeej Reyes100% (2)
- FCCS - VentilatorDocument18 pagesFCCS - VentilatorEga Jaya100% (2)
- RBANSDocument10 pagesRBANSFanel PutraNo ratings yet
- Cancer is Not a Disease - It's a Survival MechanismDocument16 pagesCancer is Not a Disease - It's a Survival MechanismPeeradej Teao100% (4)
- Psych Case StudyDocument14 pagesPsych Case Studyapi-604581864No ratings yet
- Veterinary Pathology of the Respiratory SystemDocument89 pagesVeterinary Pathology of the Respiratory SystemMuhammad HanifNo ratings yet
- VTE325 Lecture Note VIDocument60 pagesVTE325 Lecture Note VIezgiyuzbasiogluNo ratings yet
- New Castle Disease/ Ranikhet DiseaseDocument36 pagesNew Castle Disease/ Ranikhet DiseaseAnuja GhimireNo ratings yet
- 5 Sore ThroatDocument45 pages5 Sore ThroatNurul Wandasari SNo ratings yet
- Canine Distemper: Hard Pad Disease, Canine InfluenzaDocument11 pagesCanine Distemper: Hard Pad Disease, Canine InfluenzaDr-Hassan SaeedNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: Upper Respiratory Tract Lower Respiratory TractDocument40 pagesRespiratory System: Upper Respiratory Tract Lower Respiratory TractyomifNo ratings yet
- Upper Respiratory AlterationDocument34 pagesUpper Respiratory AlterationJulia ManaloNo ratings yet
- General Medicine Course-Part I&II-3rdyrDocument364 pagesGeneral Medicine Course-Part I&II-3rdyrbiography& lifestyleNo ratings yet
- Respi Patho 1Document111 pagesRespi Patho 1Quolette ConstanteNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Tenggorokan Dan Penerapan Klinisnya: Dr. Adi Arianto, M. BiomedDocument39 pagesAnatomi Tenggorokan Dan Penerapan Klinisnya: Dr. Adi Arianto, M. BiomedAl AdinNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory InfectionsDocument34 pagesAcute Respiratory InfectionssafiebuttNo ratings yet
- Upper Respiratory Tract Infections: DR John Egbagba FmcpathDocument37 pagesUpper Respiratory Tract Infections: DR John Egbagba FmcpathPrincewill SeiyefaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Disorders Respiratory in ClientDocument101 pagesChapter 6 Disorders Respiratory in Clientanisa ahmedNo ratings yet
- Ruminant AspirationDocument15 pagesRuminant AspirationMilky Jayne Pulido BulusanNo ratings yet
- Clinical RespiratoryDocument21 pagesClinical RespiratoryAhmed AbdellaNo ratings yet
- Diseases - of - The - Tonsil 2023Document41 pagesDiseases - of - The - Tonsil 2023dr MohammedNo ratings yet
- Approach To Cough and HemoptysisDocument24 pagesApproach To Cough and Hemoptysisbansaleliza26No ratings yet
- Rhinitis: AetiologyDocument13 pagesRhinitis: AetiologyAnkit RathiNo ratings yet
- GlandersDocument5 pagesGlandersAyushi YadavNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The RS 1Document157 pagesDiseases of The RS 1Alim NabekNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About RhinitisDocument40 pagesEverything You Need to Know About RhinitisayuniNo ratings yet
- Rhinitis: Submitted To: DR - Suman Submitted By: Divya MPT 2 YearDocument16 pagesRhinitis: Submitted To: DR - Suman Submitted By: Divya MPT 2 YearKeshav Singhmaar AryaNo ratings yet
- Laringitis Akut Dan KronisDocument37 pagesLaringitis Akut Dan KronisMonika AyuningrumNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Diseases of Horses GuideDocument5 pagesRespiratory Diseases of Horses GuideDonnabelContignoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The NoseDocument17 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The NoseDomz LunaNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary PathologyDocument134 pagesPulmonary PathologyFor ChristNo ratings yet
- E6.anatomy of The PharynxDocument24 pagesE6.anatomy of The PharynxOmar mohamedNo ratings yet
- Peste Des Petits Ruminants in GoatDocument24 pagesPeste Des Petits Ruminants in Goatkarki Keadr Dr100% (2)
- Upper Respiratory Infections: Symptoms and TreatmentsDocument45 pagesUpper Respiratory Infections: Symptoms and TreatmentsNatasha Abdulla100% (2)
- Ovine RinderpestPPRDocument23 pagesOvine RinderpestPPRDr.Kedar Karki ,M.V.Sc.Preventive Vet.Medicine CLSU Philippines100% (2)
- Respiratory Parasitic Infections UpdatedDocument11 pagesRespiratory Parasitic Infections Updatedmus zaharaNo ratings yet
- Upper Airway ObsDocument23 pagesUpper Airway ObsCk TwuNo ratings yet
- Acute and Chronic PharyngitisDocument10 pagesAcute and Chronic PharyngitisUjjawalShriwastavNo ratings yet
- AdenotonsilitisDocument42 pagesAdenotonsilitisELIA RICHARDNo ratings yet
- PPR oral lesions, epidemiologyDocument3 pagesPPR oral lesions, epidemiologyaramhorseNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The Oropharynx & NasopharynxDocument38 pagesDiseases of The Oropharynx & Nasopharynxalmazmulu76No ratings yet
- Ent Infection: Ridha Wahyutomo, SP - MK Clinical Microbiologist-Infection PreventionistDocument28 pagesEnt Infection: Ridha Wahyutomo, SP - MK Clinical Microbiologist-Infection PreventionistAnonymous 1GSeSV0No ratings yet
- Respiratory DiseaseDocument206 pagesRespiratory Diseasemulugetaketema394No ratings yet
- Respiratory & Gastrointestinal Infections GuideDocument2 pagesRespiratory & Gastrointestinal Infections GuideKate LagundiNo ratings yet
- Respiratory-Renal System Diseases GuideDocument96 pagesRespiratory-Renal System Diseases Guidemina mounirNo ratings yet
- Morbid Viral DiseasesDocument31 pagesMorbid Viral DiseasesWael Magdi MohammedNo ratings yet
- URT PathologiesDocument58 pagesURT PathologiesFira'ol GabayoNo ratings yet
- Adeno Tonsillitis: Dr. A. Karunagaran, M.S. D.L.ODocument148 pagesAdeno Tonsillitis: Dr. A. Karunagaran, M.S. D.L.ODrravikumar BhandariNo ratings yet
- GS Bronchial Asthma Bronchiectasis EmphysemaDocument68 pagesGS Bronchial Asthma Bronchiectasis EmphysemaBibika MallaNo ratings yet
- 4 - Pulmonary PathophysiologyDocument56 pages4 - Pulmonary PathophysiologyReynandriel100% (1)
- Swollen Head Syndrome in Poultry Caused by Avian MetapneumovirusDocument27 pagesSwollen Head Syndrome in Poultry Caused by Avian MetapneumovirusRayza LubisNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATORY INFECTION TREATMENTDocument57 pagesRESPIRATORY INFECTION TREATMENTHandi KrisnawanNo ratings yet
- Otitis ExternaDocument14 pagesOtitis ExternaRizkaGayoNo ratings yet
- Upper Respiratory Disorders: Rhinitis and SinusitisDocument113 pagesUpper Respiratory Disorders: Rhinitis and SinusitisVictor StevenNo ratings yet
- Submitted by - Shikhar Karan Verma B.V.SC & A.H.3 YearDocument24 pagesSubmitted by - Shikhar Karan Verma B.V.SC & A.H.3 YearRahul RdvNo ratings yet
- Granulo 3Document94 pagesGranulo 3Sathvika BNo ratings yet
- 754 Respiratory Tract InfectionsDocument33 pages754 Respiratory Tract Infectionszia ziaNo ratings yet
- Adeno TonsillitisDocument65 pagesAdeno TonsillitisdrtpkNo ratings yet
- 3-4-5 Larynx Pharynx EsophagusDocument25 pages3-4-5 Larynx Pharynx Esophagustaliya. shvetzNo ratings yet
- Upper Respiratory Tract InfectionsDocument17 pagesUpper Respiratory Tract Infectionsfrankozed1No ratings yet
- Diseases of the Horse - With Information on Diagnosis and TreatmentFrom EverandDiseases of the Horse - With Information on Diagnosis and TreatmentNo ratings yet
- 911 Pigeon Disease & Treatment Protocols!From Everand911 Pigeon Disease & Treatment Protocols!Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Internal Vet. Med. Exam April 2010Document3 pagesInternal Vet. Med. Exam April 2010Ali H. Sadiek أ.د. علي حسن صديقNo ratings yet
- Role of Cryptosporidial Infection F. Osman and Ali SadiekDocument10 pagesRole of Cryptosporidial Infection F. Osman and Ali SadiekAli H. Sadiek أ.د. علي حسن صديق100% (4)
- Follow Up Exam April 2009Document12 pagesFollow Up Exam April 2009Ali H. Sadiek أ.د. علي حسن صديق100% (1)
- Follow Up Exam April 2009Document12 pagesFollow Up Exam April 2009Ali H. Sadiek أ.د. علي حسن صديق100% (1)
- Diseases of The Intestine of Farm Animals by Ali Sadiek Vet. Med. AssiutDocument47 pagesDiseases of The Intestine of Farm Animals by Ali Sadiek Vet. Med. AssiutAli H. Sadiek أ.د. علي حسن صديق100% (9)
- Postparturient Hypomagnesemia, Grass TetanyDocument21 pagesPostparturient Hypomagnesemia, Grass TetanyAli H. Sadiek أ.د. علي حسن صديق50% (2)
- Water and Electrolyte Homeostasis For Vet. StudentsDocument45 pagesWater and Electrolyte Homeostasis For Vet. StudentsAli H. Sadiek أ.د. علي حسن صديق100% (2)
- Acid Base Disorders For Vet. StudentsDocument43 pagesAcid Base Disorders For Vet. StudentsAli H. Sadiek أ.د. علي حسن صديق100% (2)
- Final Term Exam For 5th Year Student (Internal Vet. Med. Part II.Document3 pagesFinal Term Exam For 5th Year Student (Internal Vet. Med. Part II.Ali H. Sadiek أ.د. علي حسن صديق100% (1)
- Metabolic Diseases, Milk Fever by Ali SadiekDocument30 pagesMetabolic Diseases, Milk Fever by Ali SadiekAli H. Sadiek أ.د. علي حسن صديق100% (3)
- Azoturia, Paralytic Myoglobinuria of EquineDocument16 pagesAzoturia, Paralytic Myoglobinuria of EquineAli H. Sadiek أ.د. علي حسن صديق100% (1)
- Gastritis, Gastric Ulcer and Gastric Rupture in Monogastric Animals by Ali SadiekDocument27 pagesGastritis, Gastric Ulcer and Gastric Rupture in Monogastric Animals by Ali SadiekAli H. Sadiek أ.د. علي حسن صديق100% (6)
- Downer Cow Syndrome, Creeper Cows.Document8 pagesDowner Cow Syndrome, Creeper Cows.Ali H. Sadiek أ.د. علي حسن صديق100% (1)
- Post Parturient HemoglobinuriaDocument12 pagesPost Parturient HemoglobinuriaAli H. Sadiek أ.د. علي حسن صديق67% (3)
- Buffalo Health and Disease For AVSSADocument51 pagesBuffalo Health and Disease For AVSSAAli H. Sadiek أ.د. علي حسن صديق100% (5)
- ELISA in Comparison With Conventional Methods For Detection ofDocument9 pagesELISA in Comparison With Conventional Methods For Detection ofAli H. Sadiek أ.د. علي حسن صديق100% (1)
- Hepatic Problems in Farm Animal by Prof. Ali SadiekDocument23 pagesHepatic Problems in Farm Animal by Prof. Ali SadiekAli H. Sadiek أ.د. علي حسن صديقNo ratings yet
- Gastric Dilatation in Monogastric Animals by Ali SadiekDocument8 pagesGastric Dilatation in Monogastric Animals by Ali SadiekAli H. Sadiek أ.د. علي حسن صديقNo ratings yet
- Peritonitis in farm animals by Ali Sadiek الالتهاب البريتوني في حيوانات المزرعةDocument27 pagesPeritonitis in farm animals by Ali Sadiek الالتهاب البريتوني في حيوانات المزرعةAli H. Sadiek أ.د. علي حسن صديق100% (2)
- Diseases of The Abomasum For Vet. Student by Ali SadiekDocument36 pagesDiseases of The Abomasum For Vet. Student by Ali SadiekAli H. Sadiek أ.د. علي حسن صديق100% (1)
- Respiratory System Disease RSDDocument19 pagesRespiratory System Disease RSDAli H. Sadiek أ.د. علي حسن صديق100% (1)
- Diseases of Pahyrinx and Esophagus in Farm Animals by Ali SadiekDocument39 pagesDiseases of Pahyrinx and Esophagus in Farm Animals by Ali SadiekAli H. Sadiek أ.د. علي حسن صديق100% (4)
- Diseases of Nervous System of Farm Animals by Ali SadiekDocument65 pagesDiseases of Nervous System of Farm Animals by Ali SadiekAli H. Sadiek أ.د. علي حسن صديق100% (7)
- Simple Indigestion in RuminantsDocument11 pagesSimple Indigestion in RuminantsAli H. Sadiek أ.د. علي حسن صديق75% (4)
- Tympany in Ruminants by Ali Sadiek Assiut Univ.Document27 pagesTympany in Ruminants by Ali Sadiek Assiut Univ.Ali H. Sadiek أ.د. علي حسن صديق100% (9)
- Vagus Indigestionعسر الهضم المسبب باصابة العصب الحائرDocument27 pagesVagus Indigestionعسر الهضم المسبب باصابة العصب الحائرAli H. Sadiek أ.د. علي حسن صديق100% (3)
- Traumatic Reticuloperitonitis by Ali SadiekDocument32 pagesTraumatic Reticuloperitonitis by Ali SadiekAli H. Sadiek أ.د. علي حسن صديق100% (7)
- Omasoabomasal Impaction in A Gersy CowDocument6 pagesOmasoabomasal Impaction in A Gersy CowAli H. Sadiek أ.د. علي حسن صديق100% (1)
- Ruminal Acidosis/Rumen Overload For Vet. Students /ali SadiekDocument25 pagesRuminal Acidosis/Rumen Overload For Vet. Students /ali SadiekAli H. Sadiek أ.د. علي حسن صديق100% (2)
- Morning Neurology Report August 2016Document19 pagesMorning Neurology Report August 2016Deasy Arindi PutriNo ratings yet
- Blood and Tissue ParasitesDocument62 pagesBlood and Tissue Parasitesapi-3856362No ratings yet
- Malaria Combat in ItalyDocument3 pagesMalaria Combat in ItalyBinh Pham ThanhNo ratings yet
- Tugas 1 Reading IIIDocument7 pagesTugas 1 Reading IIIeva desmaliaNo ratings yet
- Non-Invasive Ventilation 2Document25 pagesNon-Invasive Ventilation 2Ramanesh DNo ratings yet
- ASA 2011 by DR - Hesham AzzaziDocument10 pagesASA 2011 by DR - Hesham AzzaziSayed NourNo ratings yet
- ENT Anatomy of NoseDocument10 pagesENT Anatomy of NoseMahesh ShresthaNo ratings yet
- BORLAND D. M., Pneumonias (Bl4)Document54 pagesBORLAND D. M., Pneumonias (Bl4)asyabatool100% (5)
- Dah011 BFD Livestock Diseases (PPP Sept 2021)Document672 pagesDah011 BFD Livestock Diseases (PPP Sept 2021)Kevin KagambiNo ratings yet
- Small Script: Tittle: Ulcer Preceptor: Fransina Mayabubun, S.PD Name: Saniyyah Maharani Class: XII IPA 5Document8 pagesSmall Script: Tittle: Ulcer Preceptor: Fransina Mayabubun, S.PD Name: Saniyyah Maharani Class: XII IPA 5kiralawliet17No ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway ClearanceMaria ArregoitiaNo ratings yet
- CHN Board Review: IMCI Guidelines for Child HealthDocument39 pagesCHN Board Review: IMCI Guidelines for Child Healthsue_cideNo ratings yet
- Tension Type HeadacheDocument30 pagesTension Type HeadacheIndraYudhi100% (2)
- Covid 19 Lab TestDocument3 pagesCovid 19 Lab TestSNo ratings yet
- Thyroidinum for Metabolic ImbalancesDocument4 pagesThyroidinum for Metabolic ImbalancesSuriya OsmanNo ratings yet
- Arterial Blood Gas (ABG) Analysis: Normal ValuesDocument3 pagesArterial Blood Gas (ABG) Analysis: Normal ValuesNayem Hossain HemuNo ratings yet
- Assessment Exam in Cc2and3Document7 pagesAssessment Exam in Cc2and3mika de guzmanNo ratings yet
- Saudi ENT MCQ Exam 2010Document162 pagesSaudi ENT MCQ Exam 2010Hamada Hassan Alloq100% (1)
- Cvs FFVDocument10 pagesCvs FFVapi-448659779No ratings yet
- A CASE STUDY ON Chronic Renal FailureDocument2 pagesA CASE STUDY ON Chronic Renal FailureJake Yvan DizonNo ratings yet
- AP Prefixes Suffixes Ebook 2016Document22 pagesAP Prefixes Suffixes Ebook 2016Jorge MarroneNo ratings yet
- Risk Factors of Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome in ChildrenDocument7 pagesRisk Factors of Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome in ChildrenkasandraharahapNo ratings yet
- The Negative Effects of Overconsumption of SugarDocument11 pagesThe Negative Effects of Overconsumption of SugarHermilinda Orenze100% (5)
- Imaging in Otosclerosis: A Pictorial ReviewDocument8 pagesImaging in Otosclerosis: A Pictorial ReviewChlo14No ratings yet
- SpirometryDocument63 pagesSpirometryAries DocNo ratings yet