Professional Documents
Culture Documents
389H NO 5 Psychrometrics
Uploaded by
Azher MemonOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
389H NO 5 Psychrometrics
Uploaded by
Azher MemonCopyright:
Available Formats
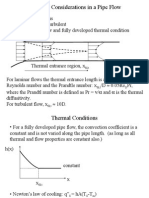
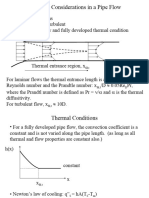
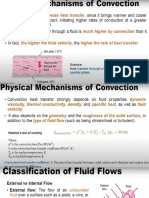
Forced Convection
External turbulent flow over a flat plate
Nu = h
m
L/k = 0.036 (Pr )
0.43
(Re
L
0.8
9200 ) (
/
w
)
0.25
External turbulent flow (40 < Re
D
<10
5
) around a single
cylinder
Nu = h
m
D/k = (0.4 Re
D
0.5
+ 0.06 Re
D
(2/3)
) (Pr )
0.4
(
/
w
)
0.25
Use with care
Re
L
= Reynolds number based on length Q = heat transfer rate (W, Btu/hr)
Re
D
= Reynolds number based on tube diameter A = area (m
2
, ft
2
)
L = tube length (m, ft) t = temperature (C, F)
k = thermal conductivity (W/m/K, Btu/hr/ft/K) Pr = Prandtl number
= dynamic viscosity in free stream( kg/m/s, lbm/ft/min)
= dynamic viscosity at wall temperature ( kg/m/s, lbm/ft/min)
h
m
= mean convection heat transfer coefficient (W/m
2
/K, Btu/hr/ft
2
/F)
Natural Convection
Common regime when buoyancy is dominant
Dimensionless parameter
Rayleigh number
Ratio of diffusive to advective time scales
Book has empirical relations for
Vertical flat plates (eqns. 2.55, 2.56)
Horizontal cylinder (eqns. 2.57, 2.58)
Spheres (eqns. 2.59)
Cavities (eqns. 2.60)
Pr
T gH T H g
Ra
/ T
2
3 3
v vo
| A
=
A
=
H = plate height (m, ft)
T = temperature (C, F)
Q = heat transfer rate (W, Btu/hr)
g = acceleration due to gravity (m/s
2
, ft/min
2
)
T = absolute temperature (K, R)
Pr = Prandtl number
= kinematic viscosity = / (m
2
/s, ft
2
/min)
= thermal diffusivity (m
2
/s)
Phase Change Boiling
What temperature does water boil under ideal
conditions?
Radiation
Transfer of energy by electromagnetic
radiation
Does not require matter (only requires that the
bodies can see each other)
100 10,000 nm (mostly IR)
Surface Radiation Issues
1) Surface properties are spectral, f()
Usually: assume integrated properties for two
beams:
Short-wave and Long-wave radiation
2) Surface properties are directional, f()
Usually assume diffuse
Radiation emission
The total energy emitted by a body,
regardless of the wavelengths, is given by:
Temperature always in K ! - absolute temperatures
c emissivity of surface = 1 for blackbody
o Stefan-Boltzmann constant
A - area
4
AT Q
emited
co =
Short-wave & long-wave radiation
Short-wave solar radiation
<3m
Glass is transparent
Does not depend on surface temperature
Long-wave surface or temperature radiation
>3m
Glass is not transparent
Depends on surface temperature
Radiation Equations
|
|
.
|
\
|
+ +
2
2
2
1
2 1 1
1
4
2
4
1 1
2 1
1 1 1
) (
c
c
c
c
o
A
A
F
T T A
Q
|
|
.
|
\
|
+ +
=
|
|
.
|
\
|
+ +
=
2
2
2
1
2 1 1
1
3
2
2
2
1
2 1 1
1
2 1
4
2
4
1
1 1 1
4
1 1 1
) (
) (
c
c
c
c
o
c
c
c
c
o
A
A
F
T
A
A
F
T T
T T
h
avg
r
t A h Q
r rad
A =
Q
1-2
= Q
rad
= heat transferred by radiation (W, BTU/hr) F
1-2
= shape factor
h
r
= radiation heat transfer coefficient (W/m
2
/K, Btu/hr/ft
2
/F) A = area (ft
2
, m
2
)
T,t = absolute temperature (R , K) , temperature (F, C)
= emissivity (surface property)
= Stephan-Boltzman constant = 5.67 10
-8
W/m
2
/K
4
= 0.1713 10
-8
BTU/hr/ft
2
/R
4
Combining Convection and Radiation
Both happen
simultaneously on a
surface
Slightly different
temperatures
Often can use h = h
c
+ h
r
Humidity Ratio, W
W = m
w
/m
a
Degree of saturation, = W/W
s
Humidity ratio is hard to measure, but very
useful in calculations
What are units?
Is W a function of temperature? What about
W
s
?
W
s
= humidity ratio at saturation
m
a
= mass of dry air
m
w
= mass of water vapor
Relative Humidity
= x
w
/x
w,s
= P
w
/P
ws
Function of T
Easy to measure and useful in some contexts, but
often need to know temperature as well
W
W
s
+
+
= u
622 . 0
622 . 0
x = mole fraction
P = pressure
= degree of saturation
W = humidity ratio
Dew-point temperature, t
d
Temperature at which condensation will form
Under appropriate surface conditions
Vapor is saturated
= ?
W
s
(P, t
d
) = W
Wet-bulb temperature, VBT (t*)
Temperature of wet surface or
Temperature at which water, by evaporating into the
air, will bring air to saturation adiabatically
* superscript is designation that variable is evaluated
at the wet-bulb temperature
Note, distinct from that measured by a sling
psychrometer
Section 9.5
Tables for Moist Air (P = 1 atm)
Tables A.4 in your text
Ability to get W
s
for calculations
Subscripts:
a = dry air, s = saturated air
v = v
a
+v
as
h = h
a
+h
as
s = s
a
+s
as
Psychrometric Chart
Need two quantities for a state point
Can get all other quantities from a state point
Can do all calculations without a chart
Often require iteration
Many digital psychrometric charts available
Can make your own
Best source is ASHRAE fundamentals (Chapter 6)
Also in your text (back cover fold-out)
Ref: Tao and Janis (2001)
Ref: Tao and Janis (2001)
Ref: Tao and Janis (2001)
Ref: Tao and Janis (2001)
Examples
What is enthalpy of air in the classroom right
now?
Condensation on windows when taking a
shower
How cold does it have to be outside for condensation to
form on windows?
Assumption is that windows are the same temperature as
outside air
80 F, RH = 80%
Alternate calculation for W
PV = mRT (IGL)
What do we know about R ratio?
P = P
w
+ P
a
w
a
a
w
T R
V P
T R
V P
a
w
R
R
P
P
m
m
W
a
a
w
w
=
|
.
|
\
|
|
.
|
\
|
= =
w
w
P P
P
W
= 622 . 0
R = gas constant
P = pressure
V = volume
T = absolute temperature
W = humidity ratio
Subscripts: w is water
vapor, a is dry air
Calculation of psychometric quantities
For an ideal gas,
h
da
= c
pa
dT, h
w
= c
pw
dT
So, h
da
= c
p,da
t which assumes a reference state of 0
F or 0 C Tables A4
Note different reference
h
w
= c
pw
t + h
g0
h = c
p,da
t + W(c
pw
t + h
g0
)
Or you can use:
h = c
p
t + Wh
g0
, c
p
= c
p,da
+ Wc
pw
c
p
= specific heat
h = enthalpy
T = absolute temperature
t = temperature
W = humidity ratio
Subscripts: w is water
vapor, a is dry air, g is
saturated water vapor
Adiabatic mixing
Governing equation
h m Q h m
out in
= +
External heat
Sensible heating
t c m Q
p
A =
Dehumidification by Cooling
Real Dehumidification Process
Mold in a duct
Transport of saturated air
tsurface < tdp Condensation
Humidification
h
w
Specific enthalpy
of water added to
system
h
g
Specific enthalpy
of saturated water
vapor
Summary
Describe psychrometric quantities
Given any two psychrometric quantities,
calculate any other quantity
Use Tables A4 or psychrometric charts to look
up psychrometric quantities
Calculate psychrometric quantities at non-
standard conditions
You might also like
- Service Manual Kaeser SK 19Document75 pagesService Manual Kaeser SK 19Joe100% (8)
- Heat Transfer (Ramos)Document54 pagesHeat Transfer (Ramos)jester navarquez75% (4)
- Spur Gear DesignDocument15 pagesSpur Gear DesignMaharaja KanthasamyNo ratings yet
- Homework Assignment 1: - Review Material From Chapter 2 - Mostly Thermodynamics and Heat TransferDocument43 pagesHomework Assignment 1: - Review Material From Chapter 2 - Mostly Thermodynamics and Heat TransferIppiNo ratings yet
- Application - Problems PP PDocument230 pagesApplication - Problems PP PAanand Rishabh DagaNo ratings yet
- Forced Convection (Heat)Document13 pagesForced Convection (Heat)hishamNo ratings yet
- Two Phase FlowDocument43 pagesTwo Phase FlowVineet K. MishraNo ratings yet
- Humidification and Cooling Towers - 2nd 2011Document46 pagesHumidification and Cooling Towers - 2nd 2011Vona Sophia MalvarNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer FundamentalsDocument6 pagesHeat Transfer FundamentalsMuhammad FahadNo ratings yet
- 15forced Convection, External Flow Over CylindersDocument17 pages15forced Convection, External Flow Over Cylindersananth2012No ratings yet
- Experiment No 7 Pin Fin ApparatusDocument5 pagesExperiment No 7 Pin Fin Apparatusgaur123450% (2)
- University of Tennessee - ChattanoogaDocument49 pagesUniversity of Tennessee - ChattanoogaMALIK ZARYABBABARNo ratings yet
- Natural Convection Lab ManualDocument12 pagesNatural Convection Lab Manualjohn paul.jaisonNo ratings yet
- Heat Lab Exp 1 PDFDocument12 pagesHeat Lab Exp 1 PDFjohn paul.jaisonNo ratings yet
- Thermal Considerations in Pipe FlowsDocument11 pagesThermal Considerations in Pipe FlowsWaqas AhmadNo ratings yet
- Convection Heat Transfer: Reading ProblemsDocument16 pagesConvection Heat Transfer: Reading ProblemspcelumalaiNo ratings yet
- TEST ON A PIN - FIN APPATATUS BY FORCED CONVECTION - Pin Fin New-2Document5 pagesTEST ON A PIN - FIN APPATATUS BY FORCED CONVECTION - Pin Fin New-2Jady chess24No ratings yet
- 07 - Convective Heat TransferDocument75 pages07 - Convective Heat TransferMerazka FaroukNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger LectureDocument22 pagesHeat Exchanger LectureThulasi Ram100% (1)
- Class V - Forced Convection - External Flow - Cylinders & Spheres - Formulae & ProblemsDocument17 pagesClass V - Forced Convection - External Flow - Cylinders & Spheres - Formulae & ProblemsSai Ashok Kumar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Hydrology WSE 3 2008Document22 pagesHydrology WSE 3 2008Jorge ZafraNo ratings yet
- Thermal Considerations in Pipe FlowsDocument11 pagesThermal Considerations in Pipe FlowsjayNo ratings yet
- Pin FinDocument8 pagesPin FinmuralidharanNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept ThermodynamicsDocument62 pagesBasic Concept Thermodynamicscjdbbt1No ratings yet
- Nazaruddin Sinaga: Laboratorium Efisiensi Dan Konservasi Energi Fakultas Teknik Universitas DiponegoroDocument39 pagesNazaruddin Sinaga: Laboratorium Efisiensi Dan Konservasi Energi Fakultas Teknik Universitas DiponegoroAgung Tri WidodoNo ratings yet
- Basic Revision of Overall Heat-Transfer Calculations: HT2Document39 pagesBasic Revision of Overall Heat-Transfer Calculations: HT2Naveen ShettyNo ratings yet
- Manual For Experimental Water Cooling TowerDocument7 pagesManual For Experimental Water Cooling TowerBalRam Dhiman100% (1)
- Thermal Considerations in Pipe FlowsDocument11 pagesThermal Considerations in Pipe FlowsHimank JainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1, A, Introduction To Heat TransferDocument49 pagesChapter 1, A, Introduction To Heat Transfer01094255175 01094255175No ratings yet
- Heat Exchangers: DR Ali JawarnehDocument46 pagesHeat Exchangers: DR Ali Jawarnehprasanthi100% (1)
- STUDENT Chapter V - DRYINGDocument37 pagesSTUDENT Chapter V - DRYINGAmyNo ratings yet
- Ch4 PsychrometricsDocument102 pagesCh4 PsychrometricsJayant SisodiaNo ratings yet
- Constant Area Fin: Q=Ua ΔtDocument11 pagesConstant Area Fin: Q=Ua ΔtMuyambo SàmsøñNo ratings yet
- Thermal Considerations in Pipe FlowsDocument11 pagesThermal Considerations in Pipe FlowsOlusegun OyebanjiNo ratings yet
- Sect 2 Eqns of StateDocument35 pagesSect 2 Eqns of State조기현/초빙교수/스마트소재부품공학No ratings yet
- Basics of Heat-Exchangers Design by N. SinagaDocument81 pagesBasics of Heat-Exchangers Design by N. SinagaİBRAHİM HAZAR AYTULUNNo ratings yet
- Forced Convection Heat TransferDocument6 pagesForced Convection Heat TransferHani BanatNo ratings yet
- Additional Notes For Energy BalancesDocument6 pagesAdditional Notes For Energy BalancesJoseph Neil TacataniNo ratings yet
- Heat ExchangersDocument29 pagesHeat Exchangersprotoscope photographyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document36 pagesChapter 4siva sachaphibulkijNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Heat TransferDocument14 pagesChapter 10 Heat TransferaimanrslnNo ratings yet
- Department of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering The National University of SingaporeDocument6 pagesDepartment of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering The National University of SingaporeHaha WoNgNo ratings yet
- Drying Technology - An Overview - For ME5202Document134 pagesDrying Technology - An Overview - For ME5202mahe_sce4702No ratings yet
- HJD Institute of Tech Edu & Research Mechanical Engg DeptDocument6 pagesHJD Institute of Tech Edu & Research Mechanical Engg DeptM Hamza NadeemNo ratings yet
- HMT KKK Unit 1, 2Document73 pagesHMT KKK Unit 1, 2Siddharth GarkhailNo ratings yet
- PRGRN603: Module 5: Stationary CollectorsDocument18 pagesPRGRN603: Module 5: Stationary CollectorsRony Bou cheblNo ratings yet
- Numerical Solution of A Cylindrical Heat Conduction Problem Using A Model TechniqueDocument16 pagesNumerical Solution of A Cylindrical Heat Conduction Problem Using A Model TechniqueGabriel SaavedraNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 8 Heat TransferDocument22 pagesCHAPTER 8 Heat Transferaimanrsln0% (1)
- P2Document55 pagesP2Abdulla BaderNo ratings yet
- Forced Convection by Rahul MondalDocument25 pagesForced Convection by Rahul MondalRahul Mondal100% (1)
- 3-One-Dimensional Steady-State Conduction PDFDocument18 pages3-One-Dimensional Steady-State Conduction PDFAaron Qin Yuan WongNo ratings yet
- Forced and Free Conv - PDFDocument11 pagesForced and Free Conv - PDFEkrema DasanNo ratings yet
- 08B - Chapter 8, Sec 8.4 - 8.8 BlackDocument18 pages08B - Chapter 8, Sec 8.4 - 8.8 BlackAli HazratNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1, B, Introduction To Heat TransferDocument68 pagesChapter 1, B, Introduction To Heat Transfer01094255175 01094255175No ratings yet
- Forced Convection Lab ManualDocument10 pagesForced Convection Lab Manualjohn paul.jaisonNo ratings yet
- Thermo-Fluid Engineering: Prof. XI Guannan (喜冠南)Document34 pagesThermo-Fluid Engineering: Prof. XI Guannan (喜冠南)noyakhalibivagh chaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Forced Convectionxexternal FlowDocument19 pagesChapter 7 Forced Convectionxexternal FlowDazuky UkyNo ratings yet
- Treatise on Irreversible and Statistical Thermodynamics: An Introduction to Nonclassical ThermodynamicsFrom EverandTreatise on Irreversible and Statistical Thermodynamics: An Introduction to Nonclassical ThermodynamicsRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1From EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1No ratings yet
- ISCL Strainer PressureDropCalc BrochureDocument1 pageISCL Strainer PressureDropCalc BrochuregopinathsampathNo ratings yet
- Load Calculation PresentationDocument32 pagesLoad Calculation PresentationAzher MemonNo ratings yet
- R&AC Lecture 40Document13 pagesR&AC Lecture 40Mohammed SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Load CalcculationDocument46 pagesLoad CalcculationAzher MemonNo ratings yet
- Heating Load-Solar RadiationDocument19 pagesHeating Load-Solar RadiationkakoullisgNo ratings yet
- Cooling and Heating Load Calculations - Heat Transfer Through Buildings - Fabric Heat Gain/LossDocument28 pagesCooling and Heating Load Calculations - Heat Transfer Through Buildings - Fabric Heat Gain/LosscaptainhassNo ratings yet
- Variable Volume, Constant Temperature SystemDocument6 pagesVariable Volume, Constant Temperature SystemAzher MemonNo ratings yet
- Dual DuctDocument9 pagesDual DuctAzher MemonNo ratings yet
- Solar Heat Gain Thru Glass-HVACDocument18 pagesSolar Heat Gain Thru Glass-HVACAzher MemonNo ratings yet
- HRV SizingDocument1 pageHRV SizingAzher MemonNo ratings yet
- E 126 - 92 R98 Rteyng - PDFDocument6 pagesE 126 - 92 R98 Rteyng - PDFLuis Alberto Cristo GallegoNo ratings yet
- PhotogrammetryDocument45 pagesPhotogrammetryValerie VictoriaNo ratings yet
- 17 Capacitors and Inductors in AC CircuitsDocument12 pages17 Capacitors and Inductors in AC CircuitsAbhijit PattnaikNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Quiz Chapter 4 Form 4 @Document3 pagesChemistry Quiz Chapter 4 Form 4 @Mohd Norihwan100% (1)
- Physics ExerciseDocument6 pagesPhysics ExerciseLaw Jing SeeNo ratings yet
- D 6988 - 03 Medicion de CalibreDocument7 pagesD 6988 - 03 Medicion de CalibreMiguelAngelPerezEsparzaNo ratings yet
- EO Using Small Satellites CapabilitiesDocument36 pagesEO Using Small Satellites CapabilitiesМРязанскийNo ratings yet
- AyanamsaDocument30 pagesAyanamsahari1833% (6)
- HCLDocument8 pagesHCLlalit shakhaNo ratings yet
- FluidMechanicsI HW01Document1 pageFluidMechanicsI HW01AzlNo ratings yet
- Mollier Diagram BeginDocument3 pagesMollier Diagram BeginKalu BhaiNo ratings yet
- Multi Meter Triplett 630-NA Tested by ZS1JHGDocument2 pagesMulti Meter Triplett 630-NA Tested by ZS1JHGJohn Howard GreenNo ratings yet
- Practical Flow EssentialsDocument8 pagesPractical Flow EssentialsAyman TermaniniNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1sanjana.gummuluruNo ratings yet
- Experiment No - 1 Flow Through A Sluice GateDocument11 pagesExperiment No - 1 Flow Through A Sluice Gatesalman40% (5)
- Arc Detection in Electro-Discharge MachiningDocument16 pagesArc Detection in Electro-Discharge MachiningMitu Leonard-GabrielNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: OpticsDocument3 pagesDepartment of Education: Opticsronald100% (1)
- NOTES Genchem 2 Lesson 6 Phase Diagram of Water and Carbon DioxideDocument8 pagesNOTES Genchem 2 Lesson 6 Phase Diagram of Water and Carbon DioxidestephniedayaoNo ratings yet
- Claim The Sky Preview 2021-10-04 G9r9eoDocument16 pagesClaim The Sky Preview 2021-10-04 G9r9eoAlexandre AmorimNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument10 pagesChemistryMaame Ama FrempongNo ratings yet
- 000 ProntoSIL CatalogDocument12 pages000 ProntoSIL CatalogAbhijeet SangwanNo ratings yet
- TRUMPF Technical Data Sheet TruDiskDocument9 pagesTRUMPF Technical Data Sheet TruDiskHLNo ratings yet
- Bearings Exam Question HomeworkDocument3 pagesBearings Exam Question Homeworkabbey4623No ratings yet
- Comparison of Heald Frame Motion Generated by Rotary Dobby and Crank & Cam Shedding MotionsDocument6 pagesComparison of Heald Frame Motion Generated by Rotary Dobby and Crank & Cam Shedding MotionsKannan KumarNo ratings yet
- Regular Solution TheoryDocument4 pagesRegular Solution TheoryLouie G NavaltaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 02 - Acoustics + Psychoacoustics PDFDocument115 pagesLecture 02 - Acoustics + Psychoacoustics PDFpaolokboardNo ratings yet
- 05 PDFDocument1 page05 PDFdruwid6No ratings yet
- Physics Enrich Test STPM Sem 1Document17 pagesPhysics Enrich Test STPM Sem 1雷顺开No ratings yet