Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Alcatel Call Drop Analysis
Uploaded by
tawhid_tarek_robiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Alcatel Call Drop Analysis
Uploaded by
tawhid_tarek_robiCopyright:
Available Formats
Alcatel Call Drop Analysis
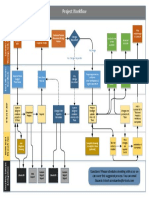
Alcatel Call Drop Reasons
Call Drop_Radio
Call Drop_BSS
Call Drop
Call Drop_HO Call Drop_Preemption
In Robi Network, Call Preemption Option is not present.
Call Drop Due to Radio Problems
This kind of call drop happens mainly of TCH drops in TCH established phase due to radio link failure per TRX. This counter takes TCH in traffic or in signaling mode into account. Typically this fault occurs with: 1) A 48.058 CONNECTION FAILURE INDICATION message with a cause value of "radio link failure" is received on Abis interface for a TCH channel (after successful seizure). 2) A 48.058 ERROR INDICATION message is received on Abis interface and leads to a loss of call. Call drop due to radio problems can be classified into: 1) Call_drop_DL_Interference 2) Call_drop_DL_Level 3) Call_drop_DL_Quality 4) Call_drop_Long_Distance 5) Call_drop_Other_Causes 6) Call_drop_Short_Distance 7) Call_drop_UL_Interference 8) Call_drop_UL_Level 9) Call_drop_UL_Quality
Call Drop Due to DL Interference
Amount of drops due to DL Interference is generally low in Network (<1%). In this case, TCH drops due to high interference level in DL. Typically the fault occurs with: 1) The same reason of call drop of radio problems. 2) The timer supervising the handover procedure expires during the intracell TCH handover.
Call Drop Due to DL Level
Amount of drops due to DL Level is generally high in Network (15-20%). In this case, number of TCH drop occurs due to low level in DL. It typically occurs with: 1) The same reason of radio problem. 2) Whenever the timer supervising the handover procedure expires during the inter-cell TCH handover. 3) Whenever the timer supervising the handover procedure on the serving cell expires during the external TCH handover. Average down link signal strength could be analyzed by MRR report. HO should have to be checked and defined properly. ( Confirm 2nd tier target cell) Unnecessary cable bending create power loss. Jumper cable should be at standard length (3m) as its high loss cable. Connectors should be Okay. (Degraded connector creates high loss) VSWR to be checked. In rural area, Submerged and forest area creates DL level drop mostly. Antenna blockage also creates DL level drop.
Call Drop Due to Call DL Quality
5-10% drop happens due to this reason. DL interference, Overshooting, missing neighbor, handover failure etc cause TCH drops due to Bad Quality DL. High count of drops in this category should be analyzed with Handover performance. Report Receive Quality Measurement per TRX will give idea on Quality distribution in cells. Frequency plan can be reviewed in MapInfo. Swapped feeder cables can be an issue relationship wise HO performance analysis or Drive test can identify the issue. Overshooting can be identified via TA analysis from measurement report.
Call Drop Due to UL Interference
Amount of drops due to UL Interference is generally very low in the network (0.02%). In this case, number of TCH drops due to high interference in UL.
Call Drop Due to UL Level
0-5% drop occurs due to that reason. In this case, number of PCH drop occurs due to low level in UL. Poor handover performance, missing neighbor will also lead to drop in UL. If a site is not serving open area but having high ratio of Low SS UL drops then report - Uplink-and-Downlink Balance Measurement per TRX can be evaluated to estimate fault with cabling.
Call Drop Due to UL Quality
Amount of drops due to UL Quality is the highest in the network (20-25%). When drops due to this category is high in MRP network frequency & HSN plan must be checked. And, in most cases a distant interferer causes drops due to Bad Quality in UL. In SFH network, conservative MS Power control may cause high amount of Bad Quality UL drops with Traffic increase or in congestion scenario. For MRP network, report - Interference Band Measurement per TS analysis would give idea on frequency plan ratio of ICM band 3-5 (%) should be high for cells with Bad Quality UL drops. Interference from CDMA/external sources may also cause Bad Quality UL drops when no reasons can be identified external interference can be suspected. BTS alarm, TRX alarm, RX alarm should have to be checked & rectified. Antenna performance should have to be checked. Combiner performance should have to be checked. All types of physical cables & connectors should have to be checked. Antenna partial blocking should have to be removed. ( At city now bill board blockage crate it mostly) Cell and CHGR definition should have to be checked at all active TRXs
Call Drop Due to other causes
8-10% drop occurs due to that reason. A drop did not exceed thresholds of any Radio parameters (TA, Qual, SS) are categorized as other reason drops. Sudden appearance of Log normal fading may contribute drops due to other reason. In addition, counters related with Equipment faults, Abis terrestrial link failure etc can be used to identify Drops due to other reason. HW alarm, E1 SES/ES can be checked to identify drops due to other reason. If no alarm is found then replace the HW. Immediate Blockage, High raise buildings area create Sudden drop. Cell MAIO value should have to be checked. TRX configuration should have to be checked.
Call Drop Due to Long and Short Distance
These two features are not available in the network. Call drop due to short and long distance occurs due to short and long distance between MS and BS distance respectively.
Call Drop Due to BSS Problems
In this case, number of TCH drop occurs due to system problem. It can be classified into two categories: 1) Call Drop Due to Internal BSS Failure. 2) Call Drop due to Remote Transcoder Failure.
Call Drop Due to BSS Internal Failure
0-5% of drop occurs due to this reason. It typically occurs with: 1) Whenever a 48.058 ERROR REPORT message with a cause value of "OandM intervention" is received on Abis interface after TCH seizure and leads to a loss of call. 2) Whenever a 48.058 ERROR REPORT message on SAPI 0 with a cause value of "message sequence error" is received on Abis interface after TCH seizure and leads to a loss of call. 3) Whenever a LAPD failure is reported to the Layer 3 of the BSC (for an RSL supporting a TCH transaction after successful TCH seizure) and leads to a loss of call 4) Whenever a TCH call release is initiated by the BSS OandM FAULT MANAGEMENT application part or by the BSS TELECOM application part as the result of a system defense action which may be due to BSS equipment failures external to the BSC (e.g. RSL failure or CU recovery failure), or due to BSC internal hardware problems (e.g. TCU failure or DTC failure) or due to BSC internal software problems (e.g. inconsistencies detected between software modules or lack of software resources (memory, timer reference, file reference...) or communication problems between different processor boards)..
Call Drop due to Remote Transcoder Failure
10-15% of drop occurs due to this reason. In this case, number of TCH (in HR or FR usage) drops in TCH established phase due to remote transcoder failures (per TRX). The counter is incremented whenever a 48.058 CONNECTION FAILURE INDICATION message with cause "Remote Transcoder Failure" is received on Abis interface for an established TCH connection. The BSC considers a TCH connection as "established" once a 44.018 ASSIGNMENT COMPLETE message (in case of normal assignments or an internal intra-cell handovers) or a 44.018 HANDOVER COMPLETE message (in case of an internal inter-cell incoming HO or an external inter-cell incoming HO) has been received for the TCH connection.
Call Drop Due to Handover
13.76% of drop occurs due to this reason. Number of TCH drops during the execution of any TCH outgoing handover, per TRX. There are 4 types of handover: 1) Inter-cell TCH handover: whenever the timer supervising the handover procedure expires. 2) External TCH handover (2G -> 2G): whenever the timer supervising the handover procedure on the serving cell (T8) expires, except if a 48.008 CLEAR COMMAND with "normal event/call control" cause was received from the MSC, leading to a normal call release. In such a case, the handover is considered as successful. 3) Intra-cell TCH handover: whenever the timer supervising the handover procedure expires. 4) 2G -> 3G HO: whenever the timer supervising the 2G-3G handover procedure on the serving cell expires, except if a 48.008 CLEAR COMMAND with "normal event/call control" cause was received from the MSC, leading to a normal call release. In such a case, the 2G->3G handover is considered as successful.
Reports required for TCH Drop RCA
Call drop measurements per cell TCH call fail per cell Uplink-and-Downlink Balance Measurement per TRX Radio Link Failure measurement per TRX Receive Quality measurement per TRX TCHF receive level measurement per TRX TCHH receive level measurement per TRX GSM Cell to Cell Incoming HO measurement GSM cell to cell Outgoing HO measurement MR measurement upon HO per cell Channel seizure measurement per TRX (Most important) Number of MR based on TA per TRX
Identifying Bad cells
KPI Load on PCH RACH Success rate MTC/MOC ratio SMS Threshold > 40% <85% >30% >5% KPI Call Drop rate ( Drop count at BH< 20) Incoming HO to Assignments Outgoing HO to Assignments HOSR HO reversion rate DL Strength HO ratio Threshold >1% >50% >50% <96% >4% >5%
Load on AGCH
SDCCH seizure for Location Update MHT of SDCCH SDCCH Congestion CSSR
>40%
>35% >10% >0.5% <96%
You might also like
- GSM Call Drop Problem AnalysisDocument66 pagesGSM Call Drop Problem AnalysisMesfin TibebeNo ratings yet
- C C CCC: OffsetêDocument17 pagesC C CCC: OffsetêDenny WijayaNo ratings yet
- CAMEL: Intelligent Networks for the GSM, GPRS and UMTS NetworkFrom EverandCAMEL: Intelligent Networks for the GSM, GPRS and UMTS NetworkRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Case AnalysisCall DropDocument76 pagesCase AnalysisCall DropKun NvtNo ratings yet
- Cross-Layer Resource Allocation in Wireless Communications: Techniques and Models from PHY and MAC Layer InteractionFrom EverandCross-Layer Resource Allocation in Wireless Communications: Techniques and Models from PHY and MAC Layer InteractionNo ratings yet
- Traffic Analysis: Security LevelDocument29 pagesTraffic Analysis: Security Levelanon_757794657No ratings yet
- Sample DiameterDocument42 pagesSample DiameterAnonymous gJHAwzENo ratings yet
- VoLTE and ViLTE: Voice and Conversational Video Services over the 4G Mobile NetworkFrom EverandVoLTE and ViLTE: Voice and Conversational Video Services over the 4G Mobile NetworkNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis Call Drop HUAWEIDocument90 pagesCase Analysis Call Drop HUAWEIfernancguillermo100% (3)
- VOIP Troubleshooting Whitepaper FinalDocument8 pagesVOIP Troubleshooting Whitepaper FinalThiago HenriqueNo ratings yet
- Q.850 ISDN Cause CodesDocument12 pagesQ.850 ISDN Cause CodesJack CastineNo ratings yet
- Diameter Result CodesDocument5 pagesDiameter Result Codeszaib29No ratings yet
- LTE Self-Organising Networks (SON): Network Management Automation for Operational EfficiencyFrom EverandLTE Self-Organising Networks (SON): Network Management Automation for Operational EfficiencySeppo HämäläinenNo ratings yet
- Gi and SGi InterfacesDocument4 pagesGi and SGi InterfacesStélio ZacariasNo ratings yet
- Dynamic DataDocument100 pagesDynamic Dataimrich horvathNo ratings yet
- Call Drop Analysis GuidelineDocument19 pagesCall Drop Analysis GuidelineFerry Alfredo HutajuluNo ratings yet
- WLAN High-Level Solution1Document24 pagesWLAN High-Level Solution1hernandez.josedomingo6804No ratings yet
- Drop Analysis in HuaweiDocument15 pagesDrop Analysis in Huaweiutkuonline100% (4)
- MOP For Bharti MGCF Codec Standardization For VoLTE in Huawei MGCFDocument10 pagesMOP For Bharti MGCF Codec Standardization For VoLTE in Huawei MGCFPartha Pratim HazraNo ratings yet
- 2G ArchitectureDocument34 pages2G ArchitectureVincent T. JosephNo ratings yet
- S3 1 3VoLTEOptimizationIEEEDocument6 pagesS3 1 3VoLTEOptimizationIEEEnewshaNo ratings yet
- (RF) Call Drops On Traffic Channel HuaweiDocument4 pages(RF) Call Drops On Traffic Channel Huaweikarthir26No ratings yet
- Presentation Mobile Data PCRF Going Live Version 02Document14 pagesPresentation Mobile Data PCRF Going Live Version 02RazaNo ratings yet
- Topeng Mediation Product DescriptionV1.Document20 pagesTopeng Mediation Product DescriptionV1.Shonam NarayanNo ratings yet
- 244809Document106 pages244809darkkenkNo ratings yet
- AD - Guidelines On 2G - 3G - 4G Radio Link Time OutDocument11 pagesAD - Guidelines On 2G - 3G - 4G Radio Link Time OuteliaezekielNo ratings yet
- 21 27 Upc Cups Overview GuideDocument20 pages21 27 Upc Cups Overview GuideDjamel HAINENo ratings yet
- Handover Meaning in GSM and How To Optimize Handover Success RateDocument2 pagesHandover Meaning in GSM and How To Optimize Handover Success RatebrunoNo ratings yet
- Inter-PLMN Handover: The ProblemDocument2 pagesInter-PLMN Handover: The ProblemmaheshwankhedeNo ratings yet
- UMTS KPI-Optimisation & ToolsDocument41 pagesUMTS KPI-Optimisation & ToolsSukhdeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Fault Management GuideDocument3 pagesFault Management GuideBromand TurkmaniNo ratings yet
- BSC6900 UMTS Performance Counter Reference (V900R015C00 - 01) (PDF) - enDocument3,198 pagesBSC6900 UMTS Performance Counter Reference (V900R015C00 - 01) (PDF) - enoaguilar83100% (2)
- IP Multimedia Subsystem - WikipediaDocument10 pagesIP Multimedia Subsystem - Wikipediajeanne_85No ratings yet
- 4 GSM Call Drops (Influence Factors + Troubleshooting Methods and Tools + Deliverables) 20110730 (合作方版)Document96 pages4 GSM Call Drops (Influence Factors + Troubleshooting Methods and Tools + Deliverables) 20110730 (合作方版)cloudsun50% (4)
- Co-BCCH Cell (GBSS18.1 - 01)Document58 pagesCo-BCCH Cell (GBSS18.1 - 01)goutam4321No ratings yet
- Copy of HW UMTS KPIsDocument18 pagesCopy of HW UMTS KPIsMohamed MoujtabaNo ratings yet
- 2.7.4.1 Huawei UMTS Network Sharing White PaperDocument19 pages2.7.4.1 Huawei UMTS Network Sharing White PaperklajdiNo ratings yet
- JABO1 Weekly Meeting ReviewDocument24 pagesJABO1 Weekly Meeting ReviewSofian HariantoNo ratings yet
- PRS Product DescriptionDocument36 pagesPRS Product DescriptionAnonymous zyXjO6No ratings yet
- 2) LTE Air InterfaceDocument76 pages2) LTE Air Interfacegh_jazani100% (1)
- 2G KpiDocument7 pages2G KpiArpit Sharma100% (2)
- 3G DT Coverage Analysis V1.0Document19 pages3G DT Coverage Analysis V1.0Denmark WilsonNo ratings yet
- LTE BC5 - Unit 3 TRK B - 2a RF Tools - Final - Version-YajunDocument149 pagesLTE BC5 - Unit 3 TRK B - 2a RF Tools - Final - Version-YajunEng Mohamed GabalNo ratings yet
- 04.PS Precautions and Emergency Measures For Large TrafficDocument27 pages04.PS Precautions and Emergency Measures For Large TrafficYens Contreras100% (1)
- Mobile Network Core Overview: 2G/3G/4G EvolutionDocument104 pagesMobile Network Core Overview: 2G/3G/4G EvolutionHessam Alemohammad100% (1)
- Introduction To CDMA Documentation V1.2 (20100809)Document44 pagesIntroduction To CDMA Documentation V1.2 (20100809)Alaa Mahmoud Ali Al-dawoudNo ratings yet
- Lte Network ArchitectureDocument28 pagesLte Network ArchitectureJagannath ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- GSM Security (TCOM1010Document4 pagesGSM Security (TCOM1010Anonymous cQAi2l7No ratings yet
- 3G Complete KnowledgeDocument86 pages3G Complete KnowledgeArvind GuptaNo ratings yet
- CEM Solution Overview - VMB17012017 - For DRT PDFDocument70 pagesCEM Solution Overview - VMB17012017 - For DRT PDFnadhmi thabetNo ratings yet
- 01 - CloudEPC V100R019 Alarm Monitoring Introduction ISSUE1.00Document96 pages01 - CloudEPC V100R019 Alarm Monitoring Introduction ISSUE1.00BarziNo ratings yet
- HCIP-LTE-RNP - RNO V1.0 Exam OutlineDocument6 pagesHCIP-LTE-RNP - RNO V1.0 Exam OutlineSemirNo ratings yet
- Tems Log-File AnalysisDocument36 pagesTems Log-File AnalysisasadNo ratings yet
- CS KPIs and PS KPIs for Bangladesh Telecom NetworkDocument2 pagesCS KPIs and PS KPIs for Bangladesh Telecom Networktawhid_tarek_robiNo ratings yet
- Final PresentationDocument7 pagesFinal Presentationtawhid_tarek_robiNo ratings yet
- Converting Excel To MapInfoDocument6 pagesConverting Excel To MapInfotawhid_tarek_robiNo ratings yet
- AMR WB Enabled HandsetsDocument6 pagesAMR WB Enabled Handsetstawhid_tarek_robiNo ratings yet
- Huawei WCDMA CountersDocument616 pagesHuawei WCDMA Counterstawhid_tarek_robiNo ratings yet
- Cgskd21wa Alarm LogDocument37 pagesCgskd21wa Alarm Logtawhid_tarek_robi0% (1)
- Bgoura 3G Neighbor PlanDocument22 pagesBgoura 3G Neighbor Plantawhid_tarek_robiNo ratings yet
- APQRC Brochure v3Document2 pagesAPQRC Brochure v3tawhid_tarek_robiNo ratings yet
- Huawei PCHRDocument6 pagesHuawei PCHRtawhid_tarek_robi100% (2)
- Registration Form (Adults)Document2 pagesRegistration Form (Adults)tawhid_tarek_robiNo ratings yet
- CMBRR12Document96 pagesCMBRR12tawhid_tarek_robiNo ratings yet
- Proposed Inventory Process FlowDocument1 pageProposed Inventory Process Flowtawhid_tarek_robiNo ratings yet
- IManger Client Installation BSS M2000Document10 pagesIManger Client Installation BSS M2000tawhid_tarek_robiNo ratings yet
- Registration Form (Adults)Document2 pagesRegistration Form (Adults)tawhid_tarek_robiNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Proposed Inventory Process FlowDocument1 pageProposed Inventory Process Flowtawhid_tarek_robiNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Additional Reselect Parameter IndicationDocument18 pagesAdditional Reselect Parameter Indicationtawhid_tarek_robiNo ratings yet
- Drive Test 2G Vs 3GDocument11 pagesDrive Test 2G Vs 3GBayu100% (2)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- List of Govt. Holidays For 2014Document2 pagesList of Govt. Holidays For 2014tawhid_tarek_robiNo ratings yet
- Group 8 - Study On Customer Perception On Current Brands in Home Furniture Industry in Dhaka Metropolitan CityDocument29 pagesGroup 8 - Study On Customer Perception On Current Brands in Home Furniture Industry in Dhaka Metropolitan Citytawhid_tarek_robiNo ratings yet
- Enterprise Specific Strategic Analysis Robi Axiata LimitedDocument30 pagesEnterprise Specific Strategic Analysis Robi Axiata Limitedtawhid_tarek_robi75% (4)
- DBS3900 Installation GuideDocument47 pagesDBS3900 Installation Guidetawhid_tarek_robiNo ratings yet
- 5.1.2.8 Lab - Viewing Network Device MAC AddressesDocument8 pages5.1.2.8 Lab - Viewing Network Device MAC AddressesFREDERICK QUISPE HIPOLITONo ratings yet
- Data Warehouse NotesDocument14 pagesData Warehouse NotesMuhammad Hamza AzamNo ratings yet
- Qualcomm Snapdragon 660 Mobile Platform Product Brief PDFDocument2 pagesQualcomm Snapdragon 660 Mobile Platform Product Brief PDFWellington BarbosaNo ratings yet
- Create and View LOG Using SLG0 and SLG1 TransactionDocument3 pagesCreate and View LOG Using SLG0 and SLG1 TransactionRAMNo ratings yet
- Diagrama Sony Wega de CursoDocument4 pagesDiagrama Sony Wega de CursoWellington PrevistoNo ratings yet
- Simatic S7-200 Micro PLC: Ordering Information DescriptionDocument13 pagesSimatic S7-200 Micro PLC: Ordering Information DescriptionVinicius ViniNo ratings yet
- Mark Zovne ResumeDocument1 pageMark Zovne Resumeapi-238819482No ratings yet
- Defensive ProgrammingDocument24 pagesDefensive ProgramminglmohandaNo ratings yet
- Gaming Content Picture Settings and Tips For: Samsung Nu7100 Nuxxxx TV Series (European)Document7 pagesGaming Content Picture Settings and Tips For: Samsung Nu7100 Nuxxxx TV Series (European)Lougan LuzNo ratings yet
- Industrial Training Presentation On: Study and Upgradation of Drona Architecture at DesidocDocument15 pagesIndustrial Training Presentation On: Study and Upgradation of Drona Architecture at DesidocAishaaniMaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Clearscada Getting StartedDocument28 pagesClearscada Getting StartedErhan KırcımanoğluNo ratings yet
- Author A DVD MPEG Using TMPGEnc DVD AuthorDocument5 pagesAuthor A DVD MPEG Using TMPGEnc DVD AuthorAndrew Lee ChardNo ratings yet
- Spartan Family of One-Time Programmable Configuration Proms (Xc17S00)Document9 pagesSpartan Family of One-Time Programmable Configuration Proms (Xc17S00)saikumarNo ratings yet
- RS485 PDFDocument3 pagesRS485 PDFLaurentiu Iacob100% (2)
- Computer Networking TermsDocument11 pagesComputer Networking TermsroyNo ratings yet
- Research Article: FPGA Implementation of Digital Images Watermarking System Based On Discrete Haar Wavelet TransformDocument18 pagesResearch Article: FPGA Implementation of Digital Images Watermarking System Based On Discrete Haar Wavelet TransformSanjana M PNo ratings yet
- LTE CA: Carrier Aggregation TutorialDocument18 pagesLTE CA: Carrier Aggregation TutorialManan AroraNo ratings yet
- KS-18 Sap ScriptsDocument23 pagesKS-18 Sap Scriptsవంశీ యుNo ratings yet
- Digital Input / Output: F2833x Block DiagramDocument32 pagesDigital Input / Output: F2833x Block DiagramMaria MEKLINo ratings yet
- Powervault-Tl2000 Reference Guide2 En-UsDocument16 pagesPowervault-Tl2000 Reference Guide2 En-UsNguyen Cong ThangNo ratings yet
- Suggested Company Workflow 1Document1 pageSuggested Company Workflow 1Paolo FarinelliNo ratings yet
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux-7-High Availability Add-On Overview-en-USDocument18 pagesRed Hat Enterprise Linux-7-High Availability Add-On Overview-en-USaeldeeb7No ratings yet
- ODICUDocument230 pagesODICUyojo76No ratings yet
- Mock Cutoff Mtech PDFDocument25 pagesMock Cutoff Mtech PDFAbhishekNo ratings yet
- Nokia Live PresentationDocument27 pagesNokia Live PresentationwasiffarooquiNo ratings yet
- PIC16F887Document338 pagesPIC16F887David BaronNo ratings yet
- Managing User Accounts in LinuxDocument5 pagesManaging User Accounts in LinuxErwinMacaraigNo ratings yet
- 195740Hik-Connect For PC - Windows 7, 8, 10, MacDocument2 pages195740Hik-Connect For PC - Windows 7, 8, 10, Macd4pagyc782No ratings yet
- AELogDocument6 pagesAELogJean Kendy AlmonordNo ratings yet
- Solution Brief - FortiMail For Service ProvidersDocument31 pagesSolution Brief - FortiMail For Service ProvidersabaheabaheabaheNo ratings yet
- Ultimate Guide to YouTube for BusinessFrom EverandUltimate Guide to YouTube for BusinessRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Photographic Rendering with VRay for SketchUpFrom EverandPhotographic Rendering with VRay for SketchUpRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- How to Do Nothing: Resisting the Attention EconomyFrom EverandHow to Do Nothing: Resisting the Attention EconomyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (421)
- Ten Arguments for Deleting Your Social Media Accounts Right NowFrom EverandTen Arguments for Deleting Your Social Media Accounts Right NowRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (388)
- Get Into UX: A foolproof guide to getting your first user experience jobFrom EverandGet Into UX: A foolproof guide to getting your first user experience jobRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Monitored: Business and Surveillance in a Time of Big DataFrom EverandMonitored: Business and Surveillance in a Time of Big DataRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Ultimate Guide to LinkedIn for Business: Access more than 500 million people in 10 minutesFrom EverandUltimate Guide to LinkedIn for Business: Access more than 500 million people in 10 minutesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- The Social Media Bible: Tactics, Tools, and Strategies for Business SuccessFrom EverandThe Social Media Bible: Tactics, Tools, and Strategies for Business SuccessRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (19)
- A Great Online Dating Profile: 30 Tips to Get Noticed and Get More ResponsesFrom EverandA Great Online Dating Profile: 30 Tips to Get Noticed and Get More ResponsesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Web Copy That Sells: The Revolutionary Formula for Creating Killer Copy That Grabs Their Attention and Compels Them to BuyFrom EverandWeb Copy That Sells: The Revolutionary Formula for Creating Killer Copy That Grabs Their Attention and Compels Them to BuyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (13)
- The Ultimate LinkedIn Sales Guide: How to Use Digital and Social Selling to Turn LinkedIn into a Lead, Sales and Revenue Generating MachineFrom EverandThe Ultimate LinkedIn Sales Guide: How to Use Digital and Social Selling to Turn LinkedIn into a Lead, Sales and Revenue Generating MachineNo ratings yet
- The Internet Con: How to Seize the Means of ComputationFrom EverandThe Internet Con: How to Seize the Means of ComputationRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (6)
- TikTok Algorithms 2024 $15,000/Month Guide To Escape Your Job And Build an Successful Social Media Marketing Business From Home Using Your Personal Account, Branding, SEO, InfluencerFrom EverandTikTok Algorithms 2024 $15,000/Month Guide To Escape Your Job And Build an Successful Social Media Marketing Business From Home Using Your Personal Account, Branding, SEO, InfluencerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Music Production for Beginners: How to Make Professional Electronic Dance Music, The Ultimate 3 in 1 Bundle for Producers (Synthesizer Explained, The Ultimate Melody Guide & Mixing EDM Music)From EverandMusic Production for Beginners: How to Make Professional Electronic Dance Music, The Ultimate 3 in 1 Bundle for Producers (Synthesizer Explained, The Ultimate Melody Guide & Mixing EDM Music)No ratings yet
- The No-Code Startup: The complete guide to building apps without codeFrom EverandThe No-Code Startup: The complete guide to building apps without codeNo ratings yet
- Branding: What You Need to Know About Building a Personal Brand and Growing Your Small Business Using Social Media Marketing and Offline Guerrilla TacticsFrom EverandBranding: What You Need to Know About Building a Personal Brand and Growing Your Small Business Using Social Media Marketing and Offline Guerrilla TacticsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (32)
- How to Create Cpn Numbers the Right way: A Step by Step Guide to Creating cpn Numbers LegallyFrom EverandHow to Create Cpn Numbers the Right way: A Step by Step Guide to Creating cpn Numbers LegallyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (27)
- Your Network Is Your Net Worth: Unlock the Hidden Power of Connections for Wealth, Success, and Happiness in the Digital AgeFrom EverandYour Network Is Your Net Worth: Unlock the Hidden Power of Connections for Wealth, Success, and Happiness in the Digital AgeRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (43)
- A History of Video Games in 64 ObjectsFrom EverandA History of Video Games in 64 ObjectsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (26)
- Kill All Normies: Online Culture Wars From 4Chan And Tumblr To Trump And The Alt-RightFrom EverandKill All Normies: Online Culture Wars From 4Chan And Tumblr To Trump And The Alt-RightRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (126)
- iPhone Photography: A Ridiculously Simple Guide To Taking Photos With Your iPhoneFrom EverandiPhone Photography: A Ridiculously Simple Guide To Taking Photos With Your iPhoneNo ratings yet
- Mastering YouTube Automation: The Ultimate Guide to Creating a Successful Faceless ChannelFrom EverandMastering YouTube Automation: The Ultimate Guide to Creating a Successful Faceless ChannelNo ratings yet