Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NAT Types Explained: Dynamic, Static, PAT
Uploaded by
Mohammed Musharraf MohiuddinOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NAT Types Explained: Dynamic, Static, PAT
Uploaded by
Mohammed Musharraf MohiuddinCopyright:
Available Formats
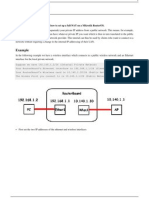
NAT (Network Address
Translation)
Natting means "Translation of
private IP address into public IP
address ".
In order to communicate with internet
we must have public IP address.
Types of NAT:-
1. Dynamic NAT
2. Static NAT
3. PAT
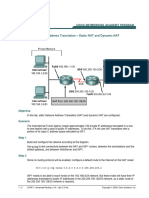
Dynamic NAT:-
Many privates IP addresses is mapped to many
of IP addresses. One to one Mapping.
Advantage is it provides only security.
Disadvantages are we need to buy many public
IP which is equal to private IP.(Expensive)
It provides only one way access.
From inside to outside access is allowed.
Outside to inside access is not allowed.
Static NAT:-
One single private IP address is mapped to single
public IP address.
It gives access to the servers from outside.
One to one mapping
It gives two way accesses.
Users from inside can access outside.
Outside users can also access inside.
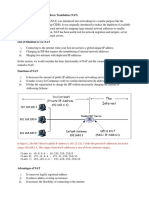
PAT (Port Address Translation)
Many private ip's is mapped to one single public
IP address.
Advantage is both save the public IP address and
security.
Disadvantage is some applications will not
support by PAT.
Also provides only one way access.
From inside to outside.
Outside to inside not allowed.
Steps to configure NAT:-
1. Define private IP address range in global
config mode using "access list"
2. Define public IP address pool in global config
mode using "ip nat pool"
3. Map private IP range with public pool in
global config mode using
ip nat inside source"
4. Apply Nat the interface mode using "ip nat
inside" and "ip nat outside".
Dynamic NAT:-Example
STEP 1:-
Define private IP address
Router(config)#access-list 1 permit 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255
STEP 2:-
Define public IP address
Router(config)#ip nat pool p1 200.1.1.1 200.1.1.100 netmask 255.255.255.0
STEP 3:-
Map private pool with public IP address
Router(config)#ip nat inside source list 1 pool p1
STEP 4:-
Apply Nat in the interface
int e0=>ip nat inside
int s0=>ip nat outside
PAT Example
STEP 1:-
Define private IP address
router(config)#access-list 1 permit 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255
STEP 2:-
Define public IP address
router(config)#ip nat pool p1 200.1.1.101 200.1.1.101 netmask 255.255.255.255
STEP 3:-
Map private pool with public IP address or interface
router(config)#ip nat inside source list 1 pool p1 overload
OR
router(config)#ip nat inside source list 1 interface s0 overload.
STEP 4:-
Apply Nat in the interface
int e0=>ip nat inside
int s0=>ip nat outside
Static Nat Example
STEP 1:-
Map private pool with public IP address or interface
router(config)#ip nat inside source static 10.1.1.1 200.1.1.101
STEP 2:-
Apply Nat in the interface
int e0=>ip nat inside
int s0=>ip nat outside
You might also like
- Wireless and Mobile Hacking and Sniffing TechniquesFrom EverandWireless and Mobile Hacking and Sniffing TechniquesNo ratings yet
- AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Exam Guide Build Your Cloud Computing Knowledge and Build Your Skills As An AWS Certified... (Rajesh Daswani)Document608 pagesAWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Exam Guide Build Your Cloud Computing Knowledge and Build Your Skills As An AWS Certified... (Rajesh Daswani)jonathan HerreraNo ratings yet
- Dell EMC 2000 Networking 2020Document30 pagesDell EMC 2000 Networking 2020abdulmuizzNo ratings yet
- Abt-Ccp143-Tsm 2012-08Document376 pagesAbt-Ccp143-Tsm 2012-08Juan Diego BahamonNo ratings yet
- Network Security All-in-one: ASA Firepower WSA Umbrella VPN ISE Layer 2 SecurityFrom EverandNetwork Security All-in-one: ASA Firepower WSA Umbrella VPN ISE Layer 2 SecurityNo ratings yet
- MikroTik AP SetupDocument23 pagesMikroTik AP SetupuntungpriyantoNo ratings yet
- Class B Subnetting Using CIDR WorksheetDocument2 pagesClass B Subnetting Using CIDR WorksheetTrung NguyenNo ratings yet
- LISP Network Deployment and Troubleshooting - The Complete Guide To LISP Implementation On IOS-XE, IOS-XR, and NX-OS PDFDocument1,412 pagesLISP Network Deployment and Troubleshooting - The Complete Guide To LISP Implementation On IOS-XE, IOS-XR, and NX-OS PDFLan Hương Phan0% (1)
- ERICSSON Node B Commissioning and IntegrationDocument34 pagesERICSSON Node B Commissioning and Integrationzakirmmughal75% (8)
- Ccnax 021913 Cag PDFDocument108 pagesCcnax 021913 Cag PDFkarkac brico to100% (2)
- How Student Writing on Race is Affected by ContextDocument5 pagesHow Student Writing on Race is Affected by ContextMohammed Musharraf MohiuddinNo ratings yet
- 11.5.1.2 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration Challenge - ILMDocument6 pages11.5.1.2 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration Challenge - ILMkds20850No ratings yet
- Aws Csaa Exam CramDocument253 pagesAws Csaa Exam CramCarlos Enrique Ureta Casas-corderoNo ratings yet
- Network Address Translation NAT TutorialDocument4 pagesNetwork Address Translation NAT Tutorialjorge jaramillo coronellNo ratings yet
- s7-1200 Opc Simatic-Net Tia-Portal e PDFDocument71 pagess7-1200 Opc Simatic-Net Tia-Portal e PDFMahadzir Bin Mat Rabi'No ratings yet
- Data Communications Summary Forouzan PDFDocument27 pagesData Communications Summary Forouzan PDFerwin rosumanNo ratings yet
- How Configure NatDocument5 pagesHow Configure NatAbhinav MishraNo ratings yet
- Nat 2Document3 pagesNat 2Abhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Lab - 9 - NATDocument5 pagesLab - 9 - NATFarukIslamNo ratings yet
- Fatima Jinnah Women University: Items DescriptionDocument5 pagesFatima Jinnah Women University: Items DescriptionfaizaNo ratings yet
- CCNA NAT essentialsDocument3 pagesCCNA NAT essentialsjordano1No ratings yet
- NAT TutorialDocument8 pagesNAT TutorialJuan Matias DamelioNo ratings yet
- NAT 10 Lab TasksDocument4 pagesNAT 10 Lab Tasksmuhammad.mursleen025No ratings yet
- Lab 2 10 4aDocument3 pagesLab 2 10 4asilindeanNo ratings yet
- Understanding Network Address Translation (NATDocument55 pagesUnderstanding Network Address Translation (NATSanjana BakshiNo ratings yet
- CN - 1 Sample Lab ProgramsDocument20 pagesCN - 1 Sample Lab Programskannanperu123No ratings yet
- Lab Report - 7 - EditedDocument5 pagesLab Report - 7 - EditedAbdullah bin zahirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - NATDocument32 pagesChapter 6 - NATRoberthNo ratings yet
- CCNP Tshoot Ch10 IP Services TroubleshootingDocument7 pagesCCNP Tshoot Ch10 IP Services TroubleshootingAbdelrahim Hussam MoubayedNo ratings yet
- Static NAT Configuration in CiscoDocument11 pagesStatic NAT Configuration in CiscotalldesalegnNo ratings yet
- Network Address Translation: Example: NAT Address TypesDocument7 pagesNetwork Address Translation: Example: NAT Address TypesstNo ratings yet
- Natting in depth guideDocument31 pagesNatting in depth guideJunior foxNo ratings yet
- ASA Firewall Configuration GuideDocument34 pagesASA Firewall Configuration GuideKarthickNo ratings yet
- Configure Network Address Translation - CiscoDocument13 pagesConfigure Network Address Translation - CiscoFederacion Hip Hop DominicanaNo ratings yet
- NAT (Network Address Translation) : Defining NAT Inside and Outside InterfacesDocument6 pagesNAT (Network Address Translation) : Defining NAT Inside and Outside Interfacesimb2No ratings yet
- NAT ConfigurationDocument4 pagesNAT Configurationabalo afiNo ratings yet
- 04.NGFW Firewall FeatureDocument32 pages04.NGFW Firewall FeaturedikaNo ratings yet
- NAT Explained: Network Address Translation Configuration and Case StudyDocument19 pagesNAT Explained: Network Address Translation Configuration and Case StudyBohubrihi TutorialNo ratings yet
- DHCP and NAT - Knowledge BaseDocument6 pagesDHCP and NAT - Knowledge BaseHasib Hamidul HaqueNo ratings yet
- NetEngine AR600 AR6000 Series Routers NAT Feature DescriptionDocument44 pagesNetEngine AR600 AR6000 Series Routers NAT Feature DescriptionEDWIN GREGORIO MARIN VARGASNo ratings yet
- Configure IP Routing Using RIP and RIPv2Document19 pagesConfigure IP Routing Using RIP and RIPv2Kajal GoudNo ratings yet
- MikroTik Step-by-Step Router Configuration GuideDocument15 pagesMikroTik Step-by-Step Router Configuration GuideBujangKereNo ratings yet
- What is NAT? Explained with ExamplesDocument4 pagesWhat is NAT? Explained with ExamplesmanjitNo ratings yet
- New Network ProjectDocument13 pagesNew Network ProjectSubham PandeyNo ratings yet
- 52 Nat PatDocument5 pages52 Nat PatBHARYNo ratings yet
- Lab7 DNAT To A Single IPDocument9 pagesLab7 DNAT To A Single IPsaravanasanthosh_uNo ratings yet
- How To Make Securing Your Router MikrotikDocument43 pagesHow To Make Securing Your Router MikrotikAhmad Fahmi AnwariNo ratings yet
- Configure Network Address TranslationDocument10 pagesConfigure Network Address Translationunidad patrimonialNo ratings yet
- Sybex CCNA 640-802 Chapter 13Document15 pagesSybex CCNA 640-802 Chapter 13xkerberosxNo ratings yet
- LABSEC-2020 ASA 8.3 (Or Higher) Lab Guide PDFDocument11 pagesLABSEC-2020 ASA 8.3 (Or Higher) Lab Guide PDFRiadh MadhourNo ratings yet
- Network Address Translation (NAT) Commands and ConfigurationsDocument4 pagesNetwork Address Translation (NAT) Commands and ConfigurationsNaseer IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Great Great Soniwall NattingDocument8 pagesGreat Great Soniwall NattingfqtsysNo ratings yet
- 24 Network Address TranslationDocument20 pages24 Network Address TranslationRakesh CharyNo ratings yet
- Troubleshoot Firewall and IDS IssuesDocument26 pagesTroubleshoot Firewall and IDS IssuesNirabhra RayNo ratings yet
- Redes de ComputadorasDocument5 pagesRedes de ComputadorasGonzalo ViñamaguaNo ratings yet
- CCNA Assigment Aditya SahaDocument33 pagesCCNA Assigment Aditya SahaSUBHAM HAZRANo ratings yet
- What Is NATDocument9 pagesWhat Is NATBelete TilahunNo ratings yet
- Key Points: Private IP Address Public IP AddressDocument3 pagesKey Points: Private IP Address Public IP Addressbekalu amenuNo ratings yet
- Key Points: Private IP Address Public IP AddressDocument3 pagesKey Points: Private IP Address Public IP Addressbekalu amenuNo ratings yet
- CPE 528 Lab Six Introduction to Network Address Translation (NATDocument11 pagesCPE 528 Lab Six Introduction to Network Address Translation (NATCharles CarpenterNo ratings yet
- DCN Project ReportDocument18 pagesDCN Project ReportPragati PawarNo ratings yet
- CCNA NAT SIM Question 2: Go To CommentsDocument2 pagesCCNA NAT SIM Question 2: Go To CommentsReinor JuniorNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document4 pagesLab 1zakariaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal NAT OverloadingDocument7 pagesJurnal NAT OverloadingMohammad NowafNo ratings yet
- 6 - Nat - PatDocument2 pages6 - Nat - PatDarlin DountsNo ratings yet
- CCNA Chapter 11Document4 pagesCCNA Chapter 11moves819No ratings yet
- FIT327 03 - Tutorial - Real LAN ConfigurationDocument9 pagesFIT327 03 - Tutorial - Real LAN ConfigurationLê Quốc Đức 7C-20ACNNo ratings yet
- Engr. Bhai Nhuraisha I. DeplomoDocument42 pagesEngr. Bhai Nhuraisha I. DeplomoJhoyce Ann AcostaNo ratings yet
- Access The Public Internet Via Network Address Translation (NAT)Document7 pagesAccess The Public Internet Via Network Address Translation (NAT)Hotico CatalinNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Network Address Translation (NAT)Document4 pagesIntroduction To Network Address Translation (NAT)Firemandeheavenly InamenNo ratings yet
- How to Filter a Website in RouterOSDocument15 pagesHow to Filter a Website in RouterOSWandi BudianaNo ratings yet
- SwnatDocument4 pagesSwnatririnarsy15No ratings yet
- Huawei Ar1200 Nat Configuration PDFDocument4 pagesHuawei Ar1200 Nat Configuration PDFHussein Dhafan100% (1)
- Large List of Interview QuestionsDocument11 pagesLarge List of Interview QuestionsMohammed Musharraf MohiuddinNo ratings yet
- Telephone Directory 2011 of HyderabadDocument43 pagesTelephone Directory 2011 of HyderabadMohammed Musharraf MohiuddinNo ratings yet
- A Statistical Monitoring of Overall Network Performance WithDocument8 pagesA Statistical Monitoring of Overall Network Performance WithMohammed Musharraf MohiuddinNo ratings yet
- PBR Check PointDocument5 pagesPBR Check PointXavier AguilaNo ratings yet
- FusionSolar Smart PV Solution-Device Replacement Commissioning GuideDocument40 pagesFusionSolar Smart PV Solution-Device Replacement Commissioning GuideFred GarsideNo ratings yet
- CCNA 200-125 Certification Practice Exam AnswersDocument49 pagesCCNA 200-125 Certification Practice Exam Answerssiddig02No ratings yet
- How To Connect Two Computers (Via A Switch) - WikiHowDocument6 pagesHow To Connect Two Computers (Via A Switch) - WikiHowkriskl03100% (1)
- CCNA BOOTCAMP - ActivityDocument41 pagesCCNA BOOTCAMP - ActivityEric ResuelloNo ratings yet
- IPv6 SubnettingDocument3 pagesIPv6 SubnettingSaturnoNo ratings yet
- Lab 7Document14 pagesLab 7stiviNo ratings yet
- Amp Editor: Owner's ManualDocument214 pagesAmp Editor: Owner's ManualAnonymous EkXNA0Dg9No ratings yet
- BACnet Connecting To BBMD DeviceDocument3 pagesBACnet Connecting To BBMD DeviceOrangeTuxNo ratings yet
- Subnet MasksDocument5 pagesSubnet MasksDomsNo ratings yet
- Cisco - Aci - White Paper c11 740861Document67 pagesCisco - Aci - White Paper c11 740861PrasannaNo ratings yet
- OMU Windows OSDocument5 pagesOMU Windows OSsamNo ratings yet
- 7.3.2.5 Packet Tracer - Verifying IPv4 and IPv6 AddressingDocument3 pages7.3.2.5 Packet Tracer - Verifying IPv4 and IPv6 AddressingEd McCawleyNo ratings yet
- Alain University TCP/IP Chapter 05 ExerciseDocument9 pagesAlain University TCP/IP Chapter 05 ExerciseAnas JrabNo ratings yet
- Manual ISCANcfg v1-7Document14 pagesManual ISCANcfg v1-7nsfNo ratings yet
- DATA ONTAP Simulate 8.1.1 C-Mode Installation (NetappU Labs)Document45 pagesDATA ONTAP Simulate 8.1.1 C-Mode Installation (NetappU Labs)Gaurav SachanNo ratings yet
- Toi Ohomai Institute of Technology COMP.6201 Routing and Switching ProjectDocument12 pagesToi Ohomai Institute of Technology COMP.6201 Routing and Switching Projectnathan fitnessNo ratings yet
- Packet Tracer 3 Lab - VLSM 2: ObjectiveDocument6 pagesPacket Tracer 3 Lab - VLSM 2: ObjectiveAli N ChoumanNo ratings yet