Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Marketing Class1
Uploaded by
Piyush ChaturvediCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Marketing Class1
Uploaded by
Piyush ChaturvediCopyright:
Available Formats
INTRODUCTION TO MARKETING
WHAT IS MARKETING?
Simple definition:
Marketing is the management process responsible for
identifying, anticipating, and satisfying customer
requirements profitably. (CIM,2001)
Goals:
1. Attract new customers by promising superior value.
2. Keep and grow current customers by delivering
satisfaction.
MARKETING DEFINED
Marketing is the activity, set of instructions, and
processes for creating, communicating,
delivering, and exchanging offerings that have
value for customers, clients, partners, and
society at large.
OLD view of
marketing:
Making a sale
telling and selling
NEW view of
marketing:
Satisfying
customer needs
WHY IS MARKETING IMPORTANT?
Shifting Business Paradigms
Sellers markets
Buyers markets
THE MARKETING PROCESS
A simple model of the marketing process:
Understand the marketplace and customer
needs and wants.
Design a customer-driven marketing strategy.
Construct an integrated marketing program that
delivers superior value.
Build profitable relationships and create
customer delight.
Capture value from customers to create profits
and customer quality.
NEEDS, WANTS, AND DEMANDS
Need: State of felt deprivation including physical, social,
and individual needs.
Physical needs: Food, clothing, shelter, safety
Social needs: Belonging, affection
Individual needs: Learning, knowledge, self-expression
Want: Form that a human need takes, as shaped
by culture and individual personality.
Wants + Buying Power = Demand
NEED/ WANT FULFILLMENT
Needs & wants are fulfilled through a Marketing
Offering:
Products:
Persons, places, organizations, information, ideas.
Services:
Activity or benefit offered for sale that is essentially
intangible and does not result in ownership.
Experiences:
Consumers live the offering.
CUSTOMER VALUE AND SATISFACTION
Dependent on the products perceived
performance relative to a buyers expectations.
Care must be taken when setting expectations:
If performance is lower than expectations, satisfaction is
low.
If performance is higher than expectations, satisfaction is
high.
Customer satisfaction often leads to consumer loyalty.
Some firms seek to DELIGHT customers by exceeding
expectations.
MARKETING MANAGEMENT
The art and science of choosing target markets
and building profitable relationships with them.
Requires that consumers and the marketplace
be fully understood.
Aim is to find, attract, keep, and grow customers
by creating, delivering, and communicating
superior value.
MARKETING MANAGEMENT
Marketing managers must consider the following,
to ensure a successful marketing strategy:
1. What customers will we serve?
What is our target market?
2. How can we best serve these
customers?
What is our value proposition?
CHOOSING A VALUE PROPOSITION
The set of benefits or values a company promises
to deliver to consumers to satisfy their needs.
Value propositions dictate how firms will
differentiate and position their brands in the
marketplace.
THE MARKETING CONCEPT
The marketing concept:
A marketing management philosophy that holds
that achieving organizational goals depends on
knowing the needs and wants of target markets
and delivering the desired satisfaction better than
competitors.
CUSTOMER PERCEIVED VALUE
Customer perceived value:
Customers evaluation of the difference between all of the
benefits and all of the costs of a marketing offer relative to
those of competing offers. (Armstrong & Kotler)
Perceptions may be subjective
Consumers often do not objectively judge values and costs.
Customer value = perceived benefits perceived sacrifice.
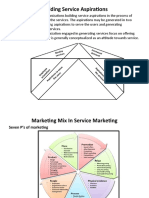
THE MARKETING MIX
The set of controllable, tactical marketing tools that
the firm blends to produce the response it wants in
the target market.
Product: Variety, features, brand name, quality,
design, packaging, and services.
Price: List price, discounts, allowances, payment
period, and credit terms.
Place: Distribution channels, coverage, logistics,
locations, transportation, assortments, and
inventory.
Promotion: Advertising, sales promotion, public
relations, and personal selling.
CUSTOMER-DRIVEN MARKETING STRATEGY
Requires careful customer analysis.
To be successful, firms must engage in:
Market segmentation
Market targeting
Differentiation
Positioning
MARKET SEGMENTATION AND TARGETING
Segmentation:
The process of dividing a market into
distinct groups of buyers with different
needs, characteristics, or behavior who
might require separate products of
marketing programs.
Targeting:
Involves evaluating each market segments
attractiveness and selecting one or more
segments to enter.
DIFFERENTIATION AND POSITIONING
Differentiation:
Creating superior customer value by
actually differentiating the market offering.
Positioning:
Arranging for a product to occupy a clear,
distinctive, and desirable place relative to
competing products in the minds of target
consumers.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
Key segmenting variables:
Geographic
Demographic
Psychographic
Behavioral
Different segments desire different benefits from
products.
Best to use multivariable segmentation bases in order
to identify smaller, better-defined target groups.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
Why Segment?:
Meet consumer needs more precisely
Increase profits
Segment leadership
Retain customers
Focus marketing
communications
EVALUATING MARKET SEGMENTS
Segment size and growth:
Analyze current segment sales, growth rates, and
expected profitability.
Segment structural attractiveness:
Consider competition, existence of substitute products,
and the power of buyers and suppliers.
Company objectives and resources:
Examine company skills and resources needed to
succeed in that segment.
Offer superior value and gain advantages over
competitors.
MARKET TARGETING
Market targeting involves:
Evaluating marketing segments.
Segment size, segment structural attractiveness,
and company objectives
and resources are considered.
Selecting target market segments.
Alternatives range from undifferentiated
marketing to micromarketing.
Being socially responsible.
DIFFERENTIATION AND POSITIONING
A products position is:
The way the product is defined by
consumers on important attributesthe
place the product occupies in consumers
minds relative to competing products.
Perceptual positioning maps can help define
a brands position relative to competitors.
DIFFERENTIATION AND POSITIONING
Identifying possible value differences and
competitive advantages:
Key to winning target customers is to
understand their needs better than
competitors do and to deliver more value.
Competitive advantage:
Extent to which a company can position
itself as providing superior value.
Achieved via differentiation.
You might also like
- Introduction To Marketing: Miss Mary Lynn MundellDocument26 pagesIntroduction To Marketing: Miss Mary Lynn MundellManoj Kumar GeldaNo ratings yet
- 1, 2, 3. Chapter 1 - IntroductionDocument28 pages1, 2, 3. Chapter 1 - IntroductionAhmed HassanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Marketing: Ignatio Madanhire 0712 453 451Document25 pagesIntroduction To Marketing: Ignatio Madanhire 0712 453 451Anesu ChimhowaNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Marketing Concepts and StrategiesDocument27 pagesIntroduction to Marketing Concepts and StrategiesIrfan QadirNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management ReviewerDocument6 pagesMarketing Management ReviewerRozette MacapazNo ratings yet
- Cap 1Document19 pagesCap 1Tina CRNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Digital Marketing in HospitalityDocument33 pagesIntroduction to Digital Marketing in HospitalityL.No ratings yet
- Tourism Segmentation Dr. May Su Myat Htway Aung Professor, Department of Commerce Yangon University of EconomicsDocument38 pagesTourism Segmentation Dr. May Su Myat Htway Aung Professor, Department of Commerce Yangon University of EconomicsKyi Cin ShweNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Understanding Marketing and The Marketing ProcessDocument42 pagesChapter 1 Understanding Marketing and The Marketing ProcessJolinaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Marketing: Miss Mary Lynn MundellDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Marketing: Miss Mary Lynn MundellIvan TayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Marketing - Creating Customer Value and EngagementDocument12 pagesChapter 1: Marketing - Creating Customer Value and EngagementT.Thomas100% (1)
- Chapter One: Marketing-Managing Profitable Customer RelationshipsDocument4 pagesChapter One: Marketing-Managing Profitable Customer RelationshipsbarmarwanNo ratings yet
- 02 Marketing OverviewDocument52 pages02 Marketing OverviewSage MainNo ratings yet
- PMarketing - Chap1Document8 pagesPMarketing - Chap1yuixNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. Marketing Creating and Capturing Customer ValueDocument6 pagesChapter 1. Marketing Creating and Capturing Customer ValueAnna PanteNo ratings yet
- Tourism Hospitality Marketing: Topic 1Document34 pagesTourism Hospitality Marketing: Topic 1Debe SadoNo ratings yet
- PMK SumDocument59 pagesPMK SumNgan DinhNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 - Creating - and - Capturing - Customer - Value - ELDocument45 pagesChapter - 1 - Creating - and - Capturing - Customer - Value - ELMaya Dana100% (1)
- Principles of MarketingDocument6 pagesPrinciples of Marketingsaralbaker0814No ratings yet
- What Is Marketing? ExplainedDocument15 pagesWhat Is Marketing? ExplainedIbrahim Tahayna100% (1)
- Marketing: Creating and Capturing Customer ValueDocument37 pagesMarketing: Creating and Capturing Customer ValueAtika AsadNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management NotesDocument41 pagesMarketing Management NotesKris TineNo ratings yet
- Explain in Details The Concept of Marketing Mix PDFDocument4 pagesExplain in Details The Concept of Marketing Mix PDFVincent ChilesheNo ratings yet
- MM Short MaterialDocument24 pagesMM Short MaterialThippana GomathiNo ratings yet
- Customer Driven StrategyDocument12 pagesCustomer Driven StrategyKhiezna PakamNo ratings yet
- Mar Chap 1Document6 pagesMar Chap 11st BackupNo ratings yet
- Marketing Full SummaryDocument33 pagesMarketing Full SummaryMariia RumiansevaNo ratings yet
- IM1019 L1 Overview of MarketingDocument52 pagesIM1019 L1 Overview of MarketingDƯƠNG NGUYỄN THÁI BÌNHNo ratings yet
- Study Guide. Marketing 3300 Ch. 1: ContemporaryDocument33 pagesStudy Guide. Marketing 3300 Ch. 1: ContemporaryAngelica TrevinoNo ratings yet
- Marketing Strategy for Customer Value and SatisfactionDocument10 pagesMarketing Strategy for Customer Value and SatisfactionTHƯ LÊNo ratings yet
- Principles of Marketing - NotesDocument17 pagesPrinciples of Marketing - NotesDipti Milani86% (7)
- Module - 2 (HM322)Document24 pagesModule - 2 (HM322)rfgvgfNo ratings yet
- book 1Document55 pagesbook 1Suzanne BeyomaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 MarketingDocument2 pagesChapter 1 MarketingYousef Abdullah GhundulNo ratings yet
- Strategic Marketing SummaryDocument21 pagesStrategic Marketing SummaryMariam KhailanyNo ratings yet
- Principles of Marketing: Unit-I What Is Marketing?Document11 pagesPrinciples of Marketing: Unit-I What Is Marketing?Ansh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document27 pagesUnit 2elon muskNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Marketing: Boot-CampDocument30 pagesIntroduction To Marketing: Boot-CampAyesha AyubNo ratings yet
- Ch1 1Document41 pagesCh1 1Ali AlousNo ratings yet
- Marketing: Creating Customer Value and EngagementDocument33 pagesMarketing: Creating Customer Value and EngagementLydia ApriliaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01Document42 pagesChapter 01Yuan ThongNo ratings yet
- Marketing AssignmentDocument16 pagesMarketing AssignmentGetahun Mulat100% (1)
- Creating and Capturing Customer Value: What is MarketingDocument20 pagesCreating and Capturing Customer Value: What is MarketingH mmNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: Creating & Capturing Customer ValueDocument22 pagesChapter One: Creating & Capturing Customer ValueAisha SharafdinNo ratings yet
- PM CH1Document49 pagesPM CH1rana hijjawiNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management Chapter 1 and 2 SummaryDocument33 pagesMarketing Management Chapter 1 and 2 Summaryanishabataju100% (1)
- Marketing Concepts and Customer Value CreationDocument4 pagesMarketing Concepts and Customer Value Creationesjay19No ratings yet
- MKT 100 PPT SegmentationDocument22 pagesMKT 100 PPT SegmentationbrandinoNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Marketing, Creating Customer ValueDocument3 pagesWeek 1 - Marketing, Creating Customer ValueMaureen Kristianne VillavertNo ratings yet
- Key Terms of MarketingDocument8 pagesKey Terms of MarketingĐức Nguyễn Trần TríNo ratings yet
- Client Marketing PlanDocument5 pagesClient Marketing PlanMOHIT GUPTANo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Introduction To Tourism MarketingDocument32 pagesTopic 1 Introduction To Tourism MarketingMalik MohamedNo ratings yet
- Market Analysis and Planning and SegmentationDocument59 pagesMarket Analysis and Planning and SegmentationShailendra ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management: Philip KotlerDocument33 pagesMarketing Management: Philip Kotlersucianny hartandiaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Marketing: Tutorial 1Document22 pagesIntroduction To Marketing: Tutorial 1Norizati ReesaNo ratings yet
- Marketing Summary Chapter 1Document8 pagesMarketing Summary Chapter 1hamanNo ratings yet
- ReadingsDocument20 pagesReadingsVandana NautiyalNo ratings yet
- What Do We Mean by Marketing? What Is A Market? Marketing ConceptsDocument38 pagesWhat Do We Mean by Marketing? What Is A Market? Marketing ConceptsBob LowNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1.Marketing:Creating and Capturing Customer ValueDocument41 pagesChapter 1.Marketing:Creating and Capturing Customer ValueIndravarmanRajeswaranNo ratings yet
- The Secret Journey of Marketing: Unveiling the Magical Secrets of Marketing World for Beginners. A Complete Guide to the Marketing Universe.From EverandThe Secret Journey of Marketing: Unveiling the Magical Secrets of Marketing World for Beginners. A Complete Guide to the Marketing Universe.No ratings yet
- BLCKDocument1 pageBLCKPiyush ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- PassportApplicationForm Main English V3.0Document1 pagePassportApplicationForm Main English V3.0Piyush ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- HHH 8Document1 pageHHH 8Piyush ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument1 pageNew Microsoft Word DocumentPiyush ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word Document - For Merge1Document1 pageNew Microsoft Word Document - For Merge1Piyush ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Tai Pie 101 Building AnalysisDocument3 pagesTai Pie 101 Building AnalysisPiyush ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument1 pageNew Microsoft Word DocumentPiyush ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument1 pageNew Microsoft Word DocumentPiyush ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument1 pageNew Microsoft Word DocumentPiyush ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument1 pageNew Microsoft Word DocumentPiyush ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument1 pageNew Microsoft Word DocumentPiyush ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument1 pageNew Microsoft Word DocumentPiyush ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- BBA FreshersDocument5 pagesBBA FreshersPiyush ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word Document - For MergeDocument1 pageNew Microsoft Word Document - For MergePiyush ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- TopicDocument7 pagesTopicPiyush ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Home News Topics Resources Job Sites About UsDocument1 pageHome News Topics Resources Job Sites About UsPiyush ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word Document - For Merge1Document1 pageNew Microsoft Word Document - For Merge1Piyush ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Jniujjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjj 9000000000000000000000000Document1 pageJniujjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjjj 9000000000000000000000000Piyush ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Compatibility Changes Between VersionsDocument2 pagesCompatibility Changes Between VersionsPiyush ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Piyush CVDocument2 pagesPiyush CVPiyush ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- When Timing Is EverythingDocument8 pagesWhen Timing Is EverythingPiyush ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Piyush CVDocument2 pagesPiyush CVPiyush ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Siti Faridah Ab RahmanDocument24 pagesSiti Faridah Ab RahmanPiyush ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Ujnunhuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuhujhurfh4hgfutruhgv3hgv3htgh34fhu4tfvhjbvfb4t8vib43tg0899thhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhCustomize Keyboard ShortcutsDocument3 pagesUjnunhuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuuhujhurfh4hgfutruhgv3hgv3htgh34fhu4tfvhjbvfb4t8vib43tg0899thhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhCustomize Keyboard ShortcutsPiyush ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Obtain A Digital Certificate To Create A Digital SignatureDocument3 pagesObtain A Digital Certificate To Create A Digital SignaturePiyush ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- AstrologyDocument4 pagesAstrologyPiyush ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Top of FormDocument4 pagesTop of FormPiyush ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Item Code Description Rate Quantity On Hand Value of StockDocument1 pageItem Code Description Rate Quantity On Hand Value of StockPiyush ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Home News Topics Resources Job Sites About UsDocument1 pageHome News Topics Resources Job Sites About UsPiyush ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Sheemaduchisstaganeshaynamah!!: International Trade Cross Border Investment Reallocation of Capital Nation StatesDocument1 pageSheemaduchisstaganeshaynamah!!: International Trade Cross Border Investment Reallocation of Capital Nation StatesPiyush ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Spec Com Final1Document153 pagesSpec Com Final1Paula Bianca EguiaNo ratings yet
- Full Download Test Bank For Organic Chemistry 6th Edition Janice Smith PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Test Bank For Organic Chemistry 6th Edition Janice Smith PDF Full Chapterprivitywoolhall.8hvcd100% (18)
- Risk, Return and The Historical Record: Bodie, Kane, and Marcus Eleventh EditionDocument35 pagesRisk, Return and The Historical Record: Bodie, Kane, and Marcus Eleventh EditionFederico PortaleNo ratings yet
- Sgr.d.sheq.0068.v1.0 e - Annual Sheq Report - 2018Document40 pagesSgr.d.sheq.0068.v1.0 e - Annual Sheq Report - 2018Muthana JalladNo ratings yet
- Plead. Complaint (TC) (01461243xa9307)Document12 pagesPlead. Complaint (TC) (01461243xa9307)CBS News DetroitNo ratings yet
- Ensuring Global Insurance Compliance with Local LawsDocument9 pagesEnsuring Global Insurance Compliance with Local LawsDjordje NedeljkovicNo ratings yet
- Demolition Planning PDFDocument12 pagesDemolition Planning PDFimanbilly67% (3)
- MWSS vs. DawayDocument3 pagesMWSS vs. DawayLindsay Mills100% (1)
- Building Service AspirationsDocument14 pagesBuilding Service AspirationsVenkadesh JNo ratings yet
- Draft Invoice - Zuba CafeDocument1 pageDraft Invoice - Zuba Cafechandanprakash30No ratings yet
- Langkawi Discovery Park development timelineDocument1 pageLangkawi Discovery Park development timelineZharel AhmadNo ratings yet
- Coca Cola ScriptDocument4 pagesCoca Cola ScriptMohammadIbrahimNo ratings yet
- ch05 - Household BehaviorDocument38 pagesch05 - Household BehaviorSari MolisaNo ratings yet
- Sammy's Motor Repair Shop faces new competitionDocument3 pagesSammy's Motor Repair Shop faces new competitionSVPSNo ratings yet
- Assignment: DR Shazia RehmanDocument10 pagesAssignment: DR Shazia Rehmanumbreen100% (1)
- Quiz in AuditingDocument2 pagesQuiz in AuditingRose Medina Baronda100% (1)
- Introduction To Business EthicsDocument46 pagesIntroduction To Business EthicsGlai zaNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Gartner Places Generative AI On The Peak of Inflated Expectations On The 2023 Hype Cycle For Emerging TechnologiesDocument4 pages2.2 Gartner Places Generative AI On The Peak of Inflated Expectations On The 2023 Hype Cycle For Emerging TechnologiesDavi Campos DrummondNo ratings yet
- Sebi (Icdr), 2018Document63 pagesSebi (Icdr), 2018Vedant KshatriyaNo ratings yet
- What Is Lloyd's of London?: Key TakeawaysDocument2 pagesWhat Is Lloyd's of London?: Key Takeawaysenkhbayar munkhbatNo ratings yet
- Toon BrandingDocument80 pagesToon BrandingRonak GoelNo ratings yet
- Quality Management - Ch.9 2Document15 pagesQuality Management - Ch.9 2manarNo ratings yet
- Marketing Analytics PPT-2 (Customer Perspective MetricsDocument26 pagesMarketing Analytics PPT-2 (Customer Perspective MetricsMadeeha KhanNo ratings yet
- Channel Development at Max New York LifeDocument40 pagesChannel Development at Max New York LifePankaj ShahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Project Management Section 2.1 Critical Path Method (CPM) Using Activity On Arrow Example 2.1 Black Eyed Peas (I)Document5 pagesChapter 2 Project Management Section 2.1 Critical Path Method (CPM) Using Activity On Arrow Example 2.1 Black Eyed Peas (I)Michael BunyiNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Case Studies in Business Studies - Financial ManagementDocument46 pagesCBSE Class 12 Case Studies in Business Studies - Financial Managementgv4t47gx7dNo ratings yet
- How To Start Your Own Business in 2021Document8 pagesHow To Start Your Own Business in 2021Mustahsan ZohaibNo ratings yet
- CSG Intermediate BrochureDocument11 pagesCSG Intermediate BrochureLeonardo CapoNo ratings yet
- Financial ModelingDocument40 pagesFinancial ModelingmetrotorNo ratings yet
- August 2022Document1 pageAugust 2022amitdesai92No ratings yet