Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 11: The Eyes
Uploaded by
riley2021Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 11: The Eyes
Uploaded by
riley2021Copyright:
Available Formats
SPECIAL SENSES: EYES
Chapter 11
Classroom Activity to Accompany
Medical Terminology Simplified,
Fourth Edition
Barbara A. Gylys Regina M. Masters
Copyright 2010 by F.A. Davis Company.
All rights reserved. This product is
protected by copyright. No part of it may be
reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or
transmitted in any form or by any means
electronic, mechanical, photocopying,
recording, or otherwisewithout written
permission from the publisher.
3
Structure
Globe-shaped, 2.5 cm in
diameter
Three layers
Fibrous outer tunic
Vascular middle tunic
Sensory inner tunic
Spaces within the eye are
filled with fluids to
support internal
structures
11
SPECIAL SENSES: EYES
4
Function
Eyes and accessory structures
Receptor organs provide vision.
Refraction system focuses light rays on
receptors in the retina.
11
SPECIAL SENSES: EYES
5
Structure and Function Exercise
Q: What is the composition of the outer layer of the eyeball?
A: Sclera, white of eye, is the outer layer and is made of
fibrous connective tissue.
Q: What does the middle layer of the eyeball consist of?
A: The middle layer is the vascular layer. It includes choroid,
ciliary body, and iris.
Q: What does the inner layer consist of?
A: The inner tunic consists of the retina, which contains the
visual receptor cells (photoreceptors).
11
SPECIAL SENSES: EYES
6
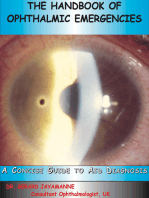
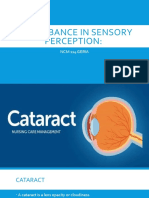
Cataract
Signs and Symptoms
Opacity or cloudiness of lens or its surrounding
membrane.
Develops slowly, most frequently due to aging
and can be familial.
May occur after eye injury or surgery, or with
diabetes.
Gradual loss or blurring of vision, but painless.
As cataract matures, pupil of the eye may appear
white.
SPECIAL SENSES: EYES
11
7
Cataract
Treatment
Depends on degree of visual impairment.
Depends on age, general health, and
occupation of the individual.
Glasses for mild cases. Surgery when
vision is impaired.
Surgical extraction of defective lens.
SPECIAL SENSES: EYES
11
8
Cataract
Treatment (continued)
Lens extraction followed by use of
eyeglasses, contact lenses, or surgically
implanted lenses called intraocular lenses
(IOLs).
Two most common surgical methods to
remove cataracts: phacoemulsification and
intracapsular and extracapsular extraction.
SPECIAL SENSES: EYES
11
9
Clinically Related Exercise
Q: An 80-year-old woman presents for an annual check up and asks the
ophthalmologist what causes cataracts.
A: The doctor explains it is a change in chemical composition of the lens
with loss of lens transparency. Also, it is attributed to aging (senile
cataracts), eye injuries (traumatic cataracts), certain diseases
(secondary cataracts), and heredity or birth defects (congenital
cataracts).
Q: Mary presents to OP surgery for cataract repair. The surgeon will use
ultrasonic vibrations to break the lens into tiny particles and then
suction it out of the eye. This surgical procedure is called
(keratectomy, laser iridectomy, phacoemulsification).
A: phacoemulsification
Q: Fred is having cataract surgery followed by a surgically implanted
lens. The abbreviation for intraocular lenses is _________________.
A: IOL
SPECIAL SENSES: EYES
11
10
Strabismus
Signs and Symptoms
Eyes cannot be
directed to focus on
the same object.
Esotropia, also called
cross-eye
Exotropia, also
called wall-eye
11
SPECIAL SENSES: EYES
11
Strabismus
Treatment
Depends on the cause.
Often consists of covering the normal eye,
forcing the child to use the deviating one.
Exercises and corrective lenses may be
ordered.
Surgical correction may be necessary.
11
SPECIAL SENSES: EYES
12
Clinically Related Exercise
Q: When eyes deviate from the normal position toward various directions, the
diagnosis is _____________________.
A: strabismus
Q: A 5-year-old girl is diagnosed with strabismus. She has a deviation of one
eye toward the other eye. This is often referred to as cross-eye. The
medical term for this type of strabismus is __________________.
A: esotropia
Q: A 7-year-old boy displays deviation of the visual axis of one eye toward
the other and complains of double vision. The MA charts the symptom of
double vision as _________________.
A: diplopia
Q: Toms right eye intermittently deviates away from the other eye. The
medical term for this type of strabismus is __________________.
A: exotropia
SPECIAL SENSES: EYES
11
13
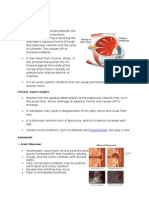
Glaucoma
Signs and Symptoms
Accumulated fluid
pressure within the
eye damages the
retina and optic nerve,
often causing
blindness.
11
SPECIAL SENSES: EYES
14
Glaucoma
Signs and Symptoms (continued)
Common forms develop asymptomatically.
Often not detected until irreparable
damage occurs to the retinas or optic
nerves.
When symptoms appear late, they may
include aching eyes and visual
disturbances such as seeing halos around
lights or a noticeable loss of peripheral
vision.
11
SPECIAL SENSES: EYES
15
Glaucoma
Treatment
Standard course of treatment is drug
therapy.
Certain types of drugs may be applied to
the surface of the eye to decrease
intraocular pressure.
Other drugs may be prescribed that
decrease production of aqueous humor.
Severe cases employ laser surgery to
promote drainage of aqueous humor.
11
SPECIAL SENSES: EYES
16
Clinically Related Exercise
Q: The ophthalmologist diagnoses Mrs. J with increased intraocular pressure.
The abbreviation for this diagnosis is _____________.
A: IOP
Q: A 67-year-old is diagnosed with glaucoma. The physician prescribes eye
drops to decrease aqueous humor production in the eyes. This type of
medication is known as an _____________________ agent.
A: antiglaucoma
Q: Mary presents with complaints of aching eyes and seeing halos around
lights. The ophthalmologist finds an increase in intraocular pressure and
chart the diagnosis as ________________________.
A: glaucoma
Q: The patient asks the ophthalmologist about complications of not treating
her glaucoma.
A: He tells her that accumulated fluid produces pressure within the eye which
damages the retina and optic nerve, and leads to total loss of vision.
SPECIAL SENSES: EYES
11
17
Medical Vocabulary
achromatopsia
apnea
astigmatism
blepharospasm
conjunctivitis
dacryorrhea
diabetic retinopathy
diplopia
11
SPECIAL SENSES: EYES
18
Medical Vocabulary
hordoleum
Purulent
inflammatory
infection of a
sebaceous gland of
the eyelid; also
called sty.
11
SPECIAL SENSES: EYES
19
Medical Vocabulary
iridotomy
macular
degeneration
11
SPECIAL SENSES: EYES
20
Diagnostic Procedures
Tonometry
Detects glaucoma
by measuring
increased
intraocular
pressure
Visual acuity test
11
SPECIAL SENSES: EYES
21
Word Building Exercise
Q: Instrument to measure hearing:
A: audiometer
Q: Examination of the pupil:
A: pupilloscopy
Q: Act of measuring tension:
A: tonometry
Q: Inflammation of the retina:
A: retinitis
Q: Fear of light:
A: photophobia
Q: Paralysis of the eye:
A: ophthalmoplegia
11
SPECIAL SENSES: EYES
22
Medical and Surgical Procedures
Cataract surgery
Phacoemulsification
Iridectomy
SPECIAL SENSES: EYES
11
23
Medical and Surgical Procedures
Laser photocoagulation
Seals leaking or hemorrhaging retinal
blood vessels associated with diabetic
retinopathy.
Light from laser creates heat that
coagulates the tissues.
SPECIAL SENSES: EYES
11
24
Clinically Related Exercise
Q: During eye surgery the ophthalmologist asks for the surgical instrument to
incise the cornea. This instrument is called a ____________.
A: keratotome
Q: After undergoing cataract surgery, a patient is unable to see. The
ophthalmologist suggests a surgical procedure that requires an incision into
the colored muscular layer that surrounds the pupil. This portion of the eye is
known as the ____________________.
A: iris
Q: A 62-year-old patient with drooping eyelids that impair her sight requires
surgery. The procedure for a surgical repair of the eyelids is referred to as
___________________________.
A: blepharoplasty
Q: Zia is diagnosed with glaucoma and is scheduled for an excision of a portion of
the iris to relieve intraocular pressure. This excision of the iris is documented
in the medical record as an __________________.
A: iridectomy
11
SPECIAL SENSES: EYES
25
Pharmacology
Antiglaucoma drugs
Miotics
Mydriatics
11
SPECIAL SENSES: EYES
26
Clinically Related Exercise
Q: Prior to an eye examination, the technician administers an agent
to dilate the pupils, which is known as a(n) (antiglaucoma drug,
miotic, mydriatic).
A: mydriatic
Q: The nurse administers drops to constrict the pupils. This
medication is known as a(n) (antiglaucoma drug, miotic,
mydriatic).
A: miotic
Q: To reduce intraocular pressure by lowering the amount of
aqueous humor in the eyeball and increase aqueous humor
outflow, a(n) (antiglaucoma drug, miotic, mydriatic) is
prescribed.
A: antiglaucoma drug
11
SPECIAL SENSES: EYES
You might also like
- Ectropion, (Everted Eyelid) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandEctropion, (Everted Eyelid) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Eye & Vision DisordersDocument72 pagesChapter 11 Eye & Vision DisordersMYLENE GRACE ELARCOSANo ratings yet
- VI (Visual ImpairmentDocument24 pagesVI (Visual ImpairmentSanishka NiroshanNo ratings yet
- GlaucomaDocument3 pagesGlaucomaPuviyarasiNo ratings yet
- Glaucoma and CataractDocument30 pagesGlaucoma and CataractJayselle ArvieNo ratings yet
- Glaucoma Case StudyDocument5 pagesGlaucoma Case StudyEdgel QuidolesNo ratings yet
- Glaucoma Case StudyDocument5 pagesGlaucoma Case StudyEdgel QuidolesNo ratings yet
- Northern Medical Colleges Cataract CaseDocument4 pagesNorthern Medical Colleges Cataract CaseSIJINo ratings yet
- Cataract Surgery - : After The ProcedureDocument16 pagesCataract Surgery - : After The ProcedureAmandeep Singh GandhiNo ratings yet
- Two Major Forms of Glaucoma: Acute and ChronicDocument5 pagesTwo Major Forms of Glaucoma: Acute and ChronicKath CuevasNo ratings yet
- Glaucoma 191024141130Document25 pagesGlaucoma 191024141130Broz100% (1)
- NCM 116: Care of Clients With Problems in Nutrition and Gastrointestinal, Metabolism and Endocrine,, Acute and ChronicDocument18 pagesNCM 116: Care of Clients With Problems in Nutrition and Gastrointestinal, Metabolism and Endocrine,, Acute and ChronicDiego DumauaNo ratings yet
- 20 Questions Eye EmergenciesDocument4 pages20 Questions Eye EmergenciesZoe ZooNo ratings yet
- GLAUCOMADocument5 pagesGLAUCOMArocioisabelacamposNo ratings yet
- Glaucoma Detection and Disc AssessmentDocument49 pagesGlaucoma Detection and Disc AssessmentMiazan SheikhNo ratings yet
- Age-Related Cataract & GlaucomaDocument26 pagesAge-Related Cataract & Glaucomasweetyeyal2002No ratings yet
- 1 - MyopiaDocument9 pages1 - MyopiaSpislgal PhilipNo ratings yet
- Basic Eye ExamDocument8 pagesBasic Eye ExamLisa AguilarNo ratings yet
- Glaucoma NCLEX Questions QuizDocument22 pagesGlaucoma NCLEX Questions QuizGabrielle G. MaldoNo ratings yet
- Blindness: Introduction:-Low Vision Is A General Term Describing Visual Impairment That Requires Patients To UseDocument12 pagesBlindness: Introduction:-Low Vision Is A General Term Describing Visual Impairment That Requires Patients To UseaparnaNo ratings yet
- Ocular EmergenciesDocument26 pagesOcular EmergenciesYukianesa100% (1)
- K.15 Ophtalmologic EmergenciesDocument35 pagesK.15 Ophtalmologic EmergenciesZikri Putra Lan Lubis100% (1)
- Case Report PresentationDocument34 pagesCase Report PresentationDwi Permana PutraNo ratings yet
- GlaucomaDocument3 pagesGlaucomaAgustinus BethaNo ratings yet
- Eye Problems in ChildrenDocument6 pagesEye Problems in ChildrenSachin CharodiNo ratings yet
- 35 Golden Eye RulesDocument7 pages35 Golden Eye RulesJethro WuNo ratings yet
- Cataract SurgeryDocument14 pagesCataract SurgeryRenato AbellaNo ratings yet
- EyeDocument322 pagesEyeEdd Monzon DelamideNo ratings yet
- Glaucoma & Retinal Detachment-1Document29 pagesGlaucoma & Retinal Detachment-1Priya bhattiNo ratings yet
- Glacoma What You Should KnowDocument26 pagesGlacoma What You Should KnowTaranisaNo ratings yet
- Lay Forum NotesDocument7 pagesLay Forum NotesCleoGomezNo ratings yet
- Opthalmology CasesDocument10 pagesOpthalmology CasesAhmad SobihNo ratings yet
- Downloadophthalmology Cases All Team PDF PDF Free - HTMLDocument23 pagesDownloadophthalmology Cases All Team PDF PDF Free - HTMLDương Yến TrânNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology Clerks: Alea, Denz Marc Custodio, Audreyfil Perez, Francis MiguelDocument14 pagesOphthalmology Clerks: Alea, Denz Marc Custodio, Audreyfil Perez, Francis MiguelDenz Marc AleaNo ratings yet
- Activity5 (Retinal Detachment)Document3 pagesActivity5 (Retinal Detachment)Gabbii CincoNo ratings yet
- Eye Disorders Guide: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment of Cataracts and GlaucomaDocument90 pagesEye Disorders Guide: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment of Cataracts and GlaucomaMonica JubaneNo ratings yet
- Ophthobook PDFDocument135 pagesOphthobook PDFl33t54r62No ratings yet
- EYE DISORDERS: GLAUCOMA AND CATARACTSDocument127 pagesEYE DISORDERS: GLAUCOMA AND CATARACTSjoan olanteNo ratings yet
- Glaukoma Sudut Tertutup Primer Oculo Dextra SinistraDocument28 pagesGlaukoma Sudut Tertutup Primer Oculo Dextra SinistraMariskaND100% (1)
- Common Ocular EmergenciesDocument33 pagesCommon Ocular EmergenciesMaimoona AimanNo ratings yet
- Homeo Eye DiseaseDocument15 pagesHomeo Eye DiseaseAlbena Trifonova100% (3)
- Girl's Eye Injury After FallDocument4 pagesGirl's Eye Injury After FallNoemi Rebollos SuladayNo ratings yet
- CD 6 OphthalmologyDocument7 pagesCD 6 OphthalmologyؤيؤييسيNo ratings yet
- GUIDELINES FOR MANAGING GLAUCOMADocument30 pagesGUIDELINES FOR MANAGING GLAUCOMAYunita Eka Putri DunggaNo ratings yet
- Extracapsular Cataract Extraction (OR)Document4 pagesExtracapsular Cataract Extraction (OR)Jet-Jet GuillerganNo ratings yet
- Case ReportDocument29 pagesCase ReportRaisa AriesthaNo ratings yet
- Glaucoma: Information and TreatmentDocument22 pagesGlaucoma: Information and TreatmentsanjivdasNo ratings yet
- Eye Assessment: OptometristsDocument8 pagesEye Assessment: OptometristsLiam MaghanoyNo ratings yet
- Human Eye Diseases ExplainedDocument26 pagesHuman Eye Diseases ExplainedShruti LaskarNo ratings yet
- 05 DamageEye2017Document6 pages05 DamageEye2017sudhirksingh27No ratings yet
- Disturbance in Sensory PerceptionDocument48 pagesDisturbance in Sensory PerceptionKristine Louise JavierNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology Important QuestionsDocument9 pagesOphthalmology Important QuestionsGhaidaa SadeqNo ratings yet
- Ocular Emergencies 2017Document18 pagesOcular Emergencies 2017Sebastian BarreraNo ratings yet
- CLINICAL OPTOMETRY: INDICATIONS FOR DILATIONDocument9 pagesCLINICAL OPTOMETRY: INDICATIONS FOR DILATIONHenok BirukNo ratings yet
- Search Uptodate: Grade 1CDocument1 pageSearch Uptodate: Grade 1CGabriella TjondroNo ratings yet
- A Rare Case of Terson Syndrome With Subarachnoid HemorrhageDocument12 pagesA Rare Case of Terson Syndrome With Subarachnoid HemorrhageNinaNo ratings yet
- Iritis 8Document14 pagesIritis 8Alvis KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Questions and Answer Group 3 "Glaucoma" Nama: Gustin Ibrahim Umamah Kelas: A S1 FARMASI 2017 NIM: 821417021Document13 pagesQuestions and Answer Group 3 "Glaucoma" Nama: Gustin Ibrahim Umamah Kelas: A S1 FARMASI 2017 NIM: 821417021Afni YunitaNo ratings yet
- Retina Detachment, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionFrom EverandRetina Detachment, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionNo ratings yet
- Med Plan 2013Document24 pagesMed Plan 2013riley2021No ratings yet
- Med Plan 2013Document24 pagesMed Plan 2013riley2021No ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Special Senses: EarsDocument20 pagesChapter 11 Special Senses: Earsriley2021No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Slides - Cardiovascular and Lymphatic SystemsDocument61 pagesChapter 5 Slides - Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systemsriley2021No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Slides - Cardiovascular and Lymphatic SystemsDocument61 pagesChapter 5 Slides - Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systemsriley2021No ratings yet
- Effect of Anti-Inflammatory Regimen On Early Postoperative Inflammation After Cataract SurgeryDocument8 pagesEffect of Anti-Inflammatory Regimen On Early Postoperative Inflammation After Cataract SurgeryariestianiNo ratings yet
- Achieving Excellence in Cataract Surgery PDFDocument150 pagesAchieving Excellence in Cataract Surgery PDFLiyanti RinceNo ratings yet
- IOL Features and Manufacturer Appasamy Ocular DevicesDocument9 pagesIOL Features and Manufacturer Appasamy Ocular Devicesgan04eshNo ratings yet
- Trust, Compassion and Loyalty Seeing ClearlyDocument5 pagesTrust, Compassion and Loyalty Seeing Clearlysvetlana_sdNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - Post-OpDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan - Post-OpKismet Summons88% (8)
- Case Review - EndophthalmitisDocument4 pagesCase Review - EndophthalmitisDr Shawgat Ul Karim KhanNo ratings yet
- OSPE Eye (Sabiha Madam)Document83 pagesOSPE Eye (Sabiha Madam)Ggah VgggagagsgNo ratings yet
- English - XI - Sample PaperDocument9 pagesEnglish - XI - Sample PaperPranav katariaNo ratings yet
- Catarata Relacionado Con LaedadDocument11 pagesCatarata Relacionado Con LaedadMarcos Fernando Piñas CanchanyaNo ratings yet
- STAAR Surgical Executive Summary Final - RedactedDocument84 pagesSTAAR Surgical Executive Summary Final - RedactedLja CsaNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology PDFDocument5 pagesOphthalmology PDFstarsk777100% (1)
- Cataract: Case Presentation - M.E.T.H.O.DDocument7 pagesCataract: Case Presentation - M.E.T.H.O.DKismet SummonsNo ratings yet
- Dutta 1Document667 pagesDutta 1Jeel GaralaNo ratings yet
- Loteprednol etabonate: The designer steroid for eyesDocument40 pagesLoteprednol etabonate: The designer steroid for eyestanvirdhklimon100% (2)
- Correcting Presbyopia First Phakic Diffractive IOLDocument9 pagesCorrecting Presbyopia First Phakic Diffractive IOLFrancescFranquesaNo ratings yet
- Aspheric IOLs Fact vs MythDocument8 pagesAspheric IOLs Fact vs MythAnonymous h0DxuJTNo ratings yet
- Scleral-Fixated Intraocular Lens Implants-Evolution of Surgical Techniques and Future DevelopmentsDocument32 pagesScleral-Fixated Intraocular Lens Implants-Evolution of Surgical Techniques and Future DevelopmentsHariom ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Extracapsular Cataract Extraction (Ecce)Document9 pagesExtracapsular Cataract Extraction (Ecce)Nica Lopez FernandezNo ratings yet
- Cataract JournalDocument9 pagesCataract Journalmonica_gallardo_24No ratings yet
- New Management Strategies For Ectopia LentisDocument14 pagesNew Management Strategies For Ectopia LentisximoNo ratings yet
- Teknik Operasi KatarakDocument33 pagesTeknik Operasi KatarakD'Mhan MbozoNo ratings yet
- National Programme For Control of Blindness: Assistant Prof., Deptt. of Community Medicine GMCH ChandigarhDocument23 pagesNational Programme For Control of Blindness: Assistant Prof., Deptt. of Community Medicine GMCH ChandigarhSumon SarkarNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis Clear EyesDocument9 pagesCase Analysis Clear EyesAnkur Rao Bisen50% (4)
- Aios Glaucoma SXDocument79 pagesAios Glaucoma SXsubahNo ratings yet
- IOL Power Calculation, Correction of Defocus - CH 4Document18 pagesIOL Power Calculation, Correction of Defocus - CH 4riveliNo ratings yet
- Tugas ArtikelDocument4 pagesTugas Artikelaura009No ratings yet
- Specialisation Market Study of Cataract Surgery and Infigo StrategyDocument41 pagesSpecialisation Market Study of Cataract Surgery and Infigo StrategyVinay singhNo ratings yet
- Impact of Intraocular Lens Haptic Design and OrientationDocument19 pagesImpact of Intraocular Lens Haptic Design and Orientationvictor_napitupuluNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Guide To Managing Astigmatism in The Cataract PatientDocument6 pagesA Comprehensive Guide To Managing Astigmatism in The Cataract PatientRaúl Plasencia SaliniNo ratings yet
- Schedule CIOMDocument16 pagesSchedule CIOMBonita AsyigahNo ratings yet