Professional Documents
Culture Documents
RAD57&CO
Uploaded by
Djbat Bat0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views29 pagesCarbon monoxide is the leading cause of poisoning in the u.s. For the last 100 years. This program is not meant as a substitute for a program or course of study. Seek direction and approval from your physician prior to using this program.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCarbon monoxide is the leading cause of poisoning in the u.s. For the last 100 years. This program is not meant as a substitute for a program or course of study. Seek direction and approval from your physician prior to using this program.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views29 pagesRAD57&CO
Uploaded by
Djbat BatCarbon monoxide is the leading cause of poisoning in the u.s. For the last 100 years. This program is not meant as a substitute for a program or course of study. Seek direction and approval from your physician prior to using this program.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 29
2008 Masimo Corporation
Includes a review on Carbon Monoxide
Poisoning For Emergency Responders
Version 2.0F, 07.02.08
Monitoring CO Poisoning
with the Rad-57
TM
2008 Masimo Corporation
IMPORTANT NOTICE
This program is not meant as a substitute for a program or
course of study in carbon monoxide recognition and treatment,
or emergency medicine. This is for review only. Please refer to
your physician or local Medical Director for approved content
and medical protocols.
This program is not meant as a substitute for the
manufacturers operator manual for the Masimo Rad-57. Please
refer to the manufacturer for complete operating instructions.
There are two versions of operating software that also include
faceplate changes. Please review slide 28 for key version
differences.
2008 Masimo Corporation
Section 1
Review: Carbon Monoxide Poisoning For Emergency Responders
2008 Masimo Corporation
Introduction
Carbon monoxide is the leading cause of poisoning in the United
States for the last 100 years and is a common hazard to First
Responders.
Until recently, the only way to reliably diagnose carbon monoxide
poisoning was to draw blood and check the carbon monoxide levels
in a lab. With the introduction of the Masimo Rad-57, testing for
carbon monoxide can now be done quickly and easily, allowing for
prompt screening and treatment.
This training program covers carbon monoxide poisoning
recognition and treatment and the use of the Masimo Rad-57 Pulse
CO-Oximeter
TM
. As always, seek direction and approval from your
physician or Medical Director prior to using this training program or
a Masimo Rad-57.
2008 Masimo Corporation
Definition
Carbon monoxide is a colorless, odorless,
tasteless, toxic gas that, when inhaled, can
cause serious physical problems and even
death.
Carbon monoxide is often referred to as
CO, which is its chemical symbol. Even at
low levels, carbon monoxide may cause long-
term cardiovascular and neurological
disorders.
Carbon monoxide can be a serious and
sometimes deadly threat to Firefighters and
EMS personnel. Firefighters have regular
contact with carbon monoxide at fire and
rescue scenes, increasing their health risks.
2008 Masimo Corporation
Incomplete combustion of any carbon-based material will produce carbon
monoxide. Closed or confined spaces are particularly hazardous. Common
sources are:
Automobiles, trucks, buses
Boats, campers
Gas heaters, furnaces, and hot water heaters
Gas-powered generators
Small gasoline engines
Portable / space heaters
Barbecues / fireplaces
Cigarette smoke
Lanterns
Methylene chloride (paint stripper)
Liver converts to CO
Structure / wildland fires
Common Sources
2008 Masimo Corporation
Physiology
Carbon monoxide is inhaled and
passes from the lungs to the blood
where it binds with hemoglobin
Produces carboxyhemoglobin
Affinity to hemoglobin is greater than 200 X
that of oxygen
Reduces oxygen carrying capacity of blood
Alters release of remaining oxygen to cells
Acts as an intracellular toxin
Poisons tissues and cells
Binds with myoglobin in muscle
Interferes with heart and skeletal
muscle
Immediate threat to life
Oxygen starvation
Cardiac arrhythmias
Alters judgment, reasoning
Long-term health effects
Central nervous system damage
Cardiovascular damage
2008 Masimo Corporation
Signs and Symptoms
SpCO % Clinical Manifestations
0-4% None - Normal
5-9% Minor Headache
10-19%
Headache, Shortness of
Breath
20-29%
Headache, Nausea,
Dizziness, Fatigue
30-39%
Severe Headache, Vomiting,
Vertigo, ALOC
40-49%
Confusion, Syncope,
Tachycardia
50-59%
Seizures, Shock, Apnea,
Coma
60% -up Coma, Death
Koster LA, Rupp T.The Silent Killer, Recognizing and Treating Carbon
Monoxide Poisoning. J EMS. October 2005
2008 Masimo Corporation
Treatment Considerations
Scene safety, protect yourself:
Consider SCBA
Remove patient away from the poison!
ABCs (airway, breathing and circulation)
Check CO level with Pulse CO-Oximeter
High levels treated with 100% oxygen:
Decrease half-life of CO in blood
Increase delivered oxygen in blood
Support ventilations as needed
Transport to closest, most appropriate facility
Consider hyperbaric treatment center:
Adults >25%, Pedi & Pregnant female >15%
Neurologic compromise
Monitor vital signs and SpCO
Always follow local EMS protocols
2008 Masimo Corporation
Suggested Triage Algorithm
Hampson NB, Weaver LK JEMS 2006
Measure SpCO
SpCO 0-3% SpCO >3%
No further medical
evaluation of SpCO
needed
Loss of consciousness
or neurological
impairment or SpCO
>25% ?
Yes No
Transport on 100%
oxygen for ED
evaluation. Consider
transport to hospital
with hyperbaric chamber
SpCO >12 SpCO <12
Transport on 100%
oxygen for ED
evaluation
Symptoms of CO
exposure?
Transport on 100%
oxygen for ED
evaluation
No further evaluation of
SpCO needed.
Determine source of CO
if nonsmoker
Yes No
2008 Masimo Corporation
Half-Life
Half-life: The amount of time required
to reduce the blood level of CO by
50%. These are estimates for patients
that otherwise are healthy. Age and
health will impact the half-life of CO.
Breathing Room Air: Carbon Monoxide
half-life in blood is ~ 240 minutes
High-flow oxygen (100%) via non-
rebreather mask: Decreases CO Half-
life in blood to 40-60 minutes
Hyperbaric Oxygen Treatment (HBOT)
at 2.5 to 3 Atmospheres: Decreases CO
half-life in blood to 20 -24 minutes
2008 Masimo Corporation
Understanding PPM & SpCO
PPM or Parts Per Million is the
atmospheric concentration of the gas
PPM is common fireground safety
measurement, often misleading as CO
forms in pockets
SpCO - noninvasive measurement of CO in
the blood
SpCO as measured by RAD-57 is a function
of PPM CO and total time of exposure of the
poison
Age, health and respiratory rate may be a
factor
Even low PPM levels can lead to high SpCO
if exposure is long enough, common in
overhaul
Even an exposure of 50 PPM for 60 minutes
requires assessment and possible medical
treatment with oxygen
2008 Masimo Corporation
Firefighter Risk
CO levels may be highest during the post-fire or
overhaul phase, search & rescue operations
and wildland firefighting
Periods that self-contained breathing apparatus
(SCBA) are not worn or not functioning properly
CO poisoning is often unrecognized due to the
presence of exhaustion, heat stress, illness or
injuries
Studies have shown low levels of untreated CO
lead to central nervous system and
cardiovascular disease
Moderate to high levels are immediate threats to
health and safety, and cause cardiovascular
injury
2008 Masimo Corporation
Section 2
Overview: Using the Rad-57 Pulse CO-Oximeter
Note: This is NOT intended to replace or act as a substitute for the
Operators Manual. Please refer to the manufacturers Operator
Manual for complete information on the operation and safety of the
Rad-57 Pulse CO-Oximeter.
2008 Masimo Corporation
RAD-57 Pulse CO-Oximeter
The Masimo RAD-57 is the worlds first and only Pulse CO-Oximeter
Signal Extraction Technology (SET
)
SpO
2
(oxygen saturation)
Pulse rate
Measure through motion and low perfusion
Rainbow
SET Technology
Analyzes 7+ wavelengths of light
Accurately measures carboxyhemoglobin (SpCO) levels
noninvasively, in SECONDS!
PI (perfusion index, strength of arterial pulse)
Low Signal IQ
indicator (poor SpO
2
signal quality)
Continuous color-coded CO bar graph
Adjustable parameter alarms
2008 Masimo Corporation
RAD-57 EMS Carry Case
Lightweight: 13 oz.
Small: 6.2 x 3.0 x 1.4
Portable: operates on 4 AA
batteries
Supplied with high-visibility,
water-resistant protective case
Protective cover
Reference card holder
Department ID holder
Pen holder
Spare battery pocket
Extra sensor pocket
2008 Masimo Corporation
RAD-57 Operation / Powering Up
POWER
Press to turn ON
Press and HOLD to turn OFF
Battery Indicator
4 Green LEDs
Each represents approximately 25%
battery life
Use only Alkaline batteries
Do Not use rechargeable batteries
Battery Compartment
Located in back panel
Holds 4 AA alkaline batteries
Operates 8-10 hours
2008 Masimo Corporation
RAD-57 Operation / Startup Sequence
Place sensor on finger (relatively clean & dry)
Press Power button
Verify All LEDs light up and a 1 second tone
is heard*
Startup mode begins
All preset configurations are displayed
Scrolling zeroes 0 0 0 and flashes
dashed lines
May take up to 25 seconds
Do not move sensor during startup
When complete reading is displayed
Begin patient monitoring
Defaults to pulse rate and oxygen
saturation reading
PI bar graph displays strength of
arterial perfusion
* Refer to operators manual for additional verifications prior to patient monitoring.
2008 Masimo Corporation
RAD-57 Operation / Sensor Placement
Sensor placement is very
IMPORTANT
When possible, use ring finger,
non-dominant hand
Insert finger until the tip of finger
hits the STOP Block
Sensor should not rotate or move
freely on finger
LEDs (red light) should pass
through mid-nail, not cuticle
There is a top and bottom, cable
should be on top (nail side)
Optimal LED path
2008 Masimo Corporation
RAD-57 Operation / Pulse Rate and Saturation
Display after Startup
Oxygen Saturation on top in
Red
Pulse Rate on bottom in Green
Green PI scale, indicates
strength of arterial pulse
Low SIQ LED indicates poor
SpO
2
signal quality
Press Display to display %
carboxyhemoglobin
Press Bell to silence alarms
Display button
toggles from
SpO
2
to SpCO
PI Scale
Low SIQ LED
Alarm Silence LED
Battery level
2008 Masimo Corporation
RAD-57 Operation / Alarms
When parameter is violated, audible alarm
will sound, parameter will flash
Preset at factory:
Sp0
2
(oxygen saturation)
Low: 90%
High: none
Pulse Rate
Low: 50
High: 140
SpCO (carboxyhemoglobin)
Low: none
High: 10%
Alarms adjust:
Press Mode/Enter twice
Press Next key to scroll through
parameters
Use up and down keys to adjust
Changes remain until user restores to
factory defaults
Alarm Indicator
(flashes)
2008 Masimo Corporation
RAD-57 Operation / Measuring CO
Press Display button for SpCO
reading
To scroll back to SpO
2
mode press
Display again
Carboxyhemoglobin displayed in % on
top
CO displayed on bottom confirming
mode
Real-time SpCO indicator continuously
reads SpCO
Green: 1-3%
Yellow: 4-11%
Red: 12% and above
Confirm abnormal readings by taking
several measurements on different
fingers and average the readings
Slow: Low SpCO Confidence
Fast: SpCO Alarm
CO label when SpCO
is displayed
2008 Masimo Corporation
RAD-57 Operation / Troubleshooting
Error Messages:
NO Cbl
Cable not seated properly into top of Rad-57
Defective cable
SEN OFF
Sensor off finger
Sensor misaligned
bAd CbL
Defective cable
Replace cable
CbL
Incompatible cable
Connect appropriate cable
bAd SEN
Defective sensor
Replace sensor
SEN
Unrecognized sensor
Connect appropriate sensor
2008 Masimo Corporation
RAD-57 Operation / Troubleshooting
Will not power on
Check battery compartment
Replace batteries
Continuous Startup mode (Scrolling zeroes 0
0 0 and flashes dashed lines)
Shield sensor from flashing lights,
strobes or high ambient light with Masimo
Light Shield*
Try other fingers
Single battery level indicator flashes (with
audible alarm)
Battery level too low
Replace batteries immediately
Err message
Return for service, Call 800-326-4890
Continuous Speaker Tone
Power down and remove batteries
Return for service, Call 800-326-4890
* Contact your Masimo sales rep to order a Masimo Light Shield.
2008 Masimo Corporation
RAD-57 Operation / Light Shield Use
Face protrusion of light shield down, and
insert the end of the sensor into the hole
Ensure that sensor hits the back of the light
shield
Orient the sensor so the cable is coming out
of the top of the hole while in the light
shield
Open the sensor by applying pressure from
the top and bottom of the light shield
Insert finger until the tip of finger hits the
STOP Block
LEDs (red light) should pass through mid-
nail, not cuticle
Orient the sensor so the cable is running
over the top of the patients hand
Optimal LED path
Apply pressure
to open sensor
Protrusion
2008 Masimo Corporation
RAD-57 Operation / Improving Accuracy
The Rad-57 is designed with an accuracy of +/- 3 digits
with a range of 1% - 40% for one standard deviation (67%
of patients)
Example: A reading of 10% could have a range from
7% - 13%
Measurements may vary from reading to reading, even on
the same patient, within the accuracy specification
Proper probe placement may improve accuracy
If an abnormal level of CO is detected, always confirm by
measuring other fingers and average
Flashing lights, strobes or high ambient light may
interfere, use a Masimo Light Shield or other means
of shielding
2008 Masimo Corporation
RAD-57 Operation / Contraindications
Small physiological changes and acceptable levels of
arterial perfusion along with correct sensor placement
will provide a stable CO reading. Inaccurate
measurements may be caused by:
Incorrect sensor placement
Elevated levels of methemoglobin
Intravascular dyes such as indocyanine green or
methylene blue
Abnormal hemoglobin levels
Low arterial perfusion
Low arterial oxygen saturation levels
Elevated Total Bilirubin levels
Motion artifact
2008 Masimo Corporation
RAD-57 Version Differences
Version 1
Faceplate design
changes (see image)
SpCO button displays
value for 10 seconds
Upon Startup all LEDs
flash, dashed lines,
scrolling zeroes, followed
by flash dashed lines
Alarm settings revert
back to factory settings
upon power off
SpCO bar graph changes
color at 10% and 20%
Version 2
Faceplate design changes
(see image)
Display button allows user
to scroll through modes
(SpO
2
, SpCO and PI)
PI can be displayed as a
numeric value
Upon Startup all LEDs
flash, device presents all
configurations, then
scrolling zeroes and flash
dashed lines
Alarm settings are
retained after power off
SpCO bar graph changes
color at 3% and 12%
2008 Masimo Corporation
Resources
For more information on carbon monoxide poisoning and the Masimo Rad-57
www.masimo.com or call 800-326-4890
www.Firerehab.com
www.firegrantshelp.com
www.emsgrantshelp.com
www.naemse.org
www.naemt.org
www.iaff.org
www.carbonmonoxidekills.com/
www.epa.gov/iaq/pubs/coftsht.html
www.carbon-monoxide-poisoning.com
www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/carbonmonoxidepoisoning.html
www.emedicinehealth.com/carbon_monoxide_poisoning/article_em.htm
www.osha.gov/OshDoc/data_General_Facts/carbonmonoxide-factsheet.pdf
www.cdc.gov/co/
www.bt.cdc.gov/disasters/carbonmonoxide.asp
www.postgradmed.com/issues/1999/01_99/tomaszewski.htm
Masimo Corporation
40 Parker
Irvine, CA 92618
949-297-7000
All Rights Reserved
Masimo
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Gem Premier 3000 Operator's ManualDocument487 pagesGem Premier 3000 Operator's ManualQuang Pham Nhat86% (7)
- Manual Nova PhoxDocument169 pagesManual Nova PhoxAndi MunawirahNo ratings yet
- Om Gem3500Document310 pagesOm Gem3500Thanh Pham DuyNo ratings yet
- Pilbeams Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 6th Edition Cairo Test BankDocument21 pagesPilbeams Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 6th Edition Cairo Test Bankhelgasophie7478k0100% (32)
- Johannes Gerbes, Frauke Van Der Werff - Fit Fürs Goethe-Zertifikat, A2 - Start Deutsch 2, Volume 2 (2007, Hueber Verlag)Document33 pagesJohannes Gerbes, Frauke Van Der Werff - Fit Fürs Goethe-Zertifikat, A2 - Start Deutsch 2, Volume 2 (2007, Hueber Verlag)kareemNo ratings yet
- Manuañ Oxicom3000Document76 pagesManuañ Oxicom3000Gestion BiomedicinaNo ratings yet
- Pulse Oximeter Principle 1Document8 pagesPulse Oximeter Principle 1Ell ElyanaNo ratings yet
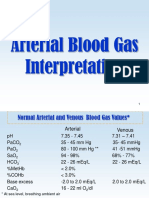
- Arterial Blood Gas InterpretationDocument65 pagesArterial Blood Gas InterpretationDaniel AryanNo ratings yet
- StatProfile PHOx UltraDocument6 pagesStatProfile PHOx UltraJose AzañaNo ratings yet
- Pulse Oximetry - UpToDateDocument23 pagesPulse Oximetry - UpToDateHardian RakhmawardanaNo ratings yet
- Blood Gas Questions With Answers - 1998Document11 pagesBlood Gas Questions With Answers - 1998somarajakNo ratings yet
- Carbon Monoxide Poisoning - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument19 pagesCarbon Monoxide Poisoning - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaSundar SugumarNo ratings yet
- Blood Gas Recommendations & ProblemsDocument47 pagesBlood Gas Recommendations & Problemsapi-3716250100% (1)
- Reference@ HB Spectrum - FullDocument6 pagesReference@ HB Spectrum - FullcdevikarNo ratings yet
- Arterial Blood Gas InterpretationDocument69 pagesArterial Blood Gas InterpretationostuffeNo ratings yet
- ABG and Oximetry StudentDocument86 pagesABG and Oximetry StudentAlexander Santiago ParelNo ratings yet
- Ashton Yeo - Siemens Healthineers Blood Gas - Providing End-To-End Blood Gas Testing SolutionsDocument33 pagesAshton Yeo - Siemens Healthineers Blood Gas - Providing End-To-End Blood Gas Testing SolutionsullifannuriNo ratings yet
- Interpretation of Arterial Blood Gases and Acid-Base DisordersDocument44 pagesInterpretation of Arterial Blood Gases and Acid-Base DisordersSuren VishvanathNo ratings yet
- CRT Exam Review Guide Chapter 8Document10 pagesCRT Exam Review Guide Chapter 8Dharlyn MungcalNo ratings yet
- Positron Emission Tomography - pg1018Document37 pagesPositron Emission Tomography - pg1018HammadNo ratings yet
- Electrolytes ACID BASE BALANCEDocument11 pagesElectrolytes ACID BASE BALANCEimbendo.cvtNo ratings yet
- OEM III Module SpecificationsDocument18 pagesOEM III Module SpecificationsCarlosperezm100% (1)
- Pulse Oximetry: Principles and Limitations: ReviewsDocument8 pagesPulse Oximetry: Principles and Limitations: ReviewsDavid González GamboaNo ratings yet
- K140582 手指血氧仪summaryDocument9 pagesK140582 手指血氧仪summarySujan KhanNo ratings yet
- Saturador de Oxigeno Tuffsat Datex OhmedaDocument43 pagesSaturador de Oxigeno Tuffsat Datex OhmedaEDGAR WILSON CRUZNo ratings yet
- Sat 801Document84 pagesSat 801Kittiwat WongsuwanNo ratings yet
- Case Report: Presenter: Irfan Tri Budi WardhanaDocument64 pagesCase Report: Presenter: Irfan Tri Budi Wardhanaabdul100% (1)
- 111 - StatProfile pHOx Ultra PDFDocument6 pages111 - StatProfile pHOx Ultra PDFkang opikNo ratings yet
- Pulse Oximeter Instruction ManualDocument15 pagesPulse Oximeter Instruction ManualpepeNo ratings yet
- Masimo Product CatalogDocument66 pagesMasimo Product CatalogFedeXMarNo ratings yet