Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cholecystitis
Uploaded by
api-26762768100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
1K views34 pagesCholecystitis is inflammation of the gallbladder, usually caused by a gallstone blocking the cystic duct. This prevents bile from leaving the gallbladder. There are two main types: acute and chronic. Acute cholecystitis causes severe abdominal pain and may lead to infection if not treated by removing the gallbladder, often using laparoscopic surgery. Chronic cholecystitis results from long-term inflammation and damage from repeated gallstone attacks.
Original Description:
Original Title
cholecystitis
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCholecystitis is inflammation of the gallbladder, usually caused by a gallstone blocking the cystic duct. This prevents bile from leaving the gallbladder. There are two main types: acute and chronic. Acute cholecystitis causes severe abdominal pain and may lead to infection if not treated by removing the gallbladder, often using laparoscopic surgery. Chronic cholecystitis results from long-term inflammation and damage from repeated gallstone attacks.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
1K views34 pagesCholecystitis
Uploaded by
api-26762768Cholecystitis is inflammation of the gallbladder, usually caused by a gallstone blocking the cystic duct. This prevents bile from leaving the gallbladder. There are two main types: acute and chronic. Acute cholecystitis causes severe abdominal pain and may lead to infection if not treated by removing the gallbladder, often using laparoscopic surgery. Chronic cholecystitis results from long-term inflammation and damage from repeated gallstone attacks.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 34
Cholecystitis
A Cause For Pain
Background
• Presence of gallstones in the gallbladder.
• Spectrum ranges from asymptomatic,
colic, cholangitis, choledocholithiasis,
cholecystitis.
• Colic is a temporary blockage,
cholecystitis is inflammation from
obstruction of cystic duct, cholangitis is
infection of the biliary tree.
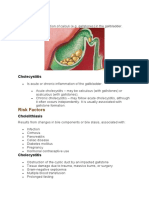
Cholecystitis is inflammation of the gallbladder, usually
resulting from a gallstone blocking the cystic duct.
Gallbladder inflammation usually results from a gallstone
blocking the flow of bile.
Typically, people have abdominal pain that lasts more than
6 hours, fever, and nausea.
Ultrasonography can usually detect signs of gallbladder
inflammation.
The gallbladder is removed, often using a laparoscope.
Cholecystitis is the most common problem resulting from
gallbladder stones.
It occurs when a stone blocks the cystic duct, which
carries bile from the gallbladder.
Cholecystitis is classified as acute or chronic.
Pathophysiology
• Three types of stones, cholesterol, pigment,
mixed.
• Formation of each types is caused by
crystallization of bile.
• Cholesterol stones most common.
• Bile consists of lethicin, bile acids,
phospholipids in a fine balance.
• Impaired motility can predispose to stones.
Pathophysiology
• Sludge is crystals without stones. It may
be a first step in stones, or be independent
of it.
• Pigment stones (15%) are from calcium
bilirubinate. Diseases that increase RBC
destruction will cause these. Also in
cirrhotic patients, parasitic infections.
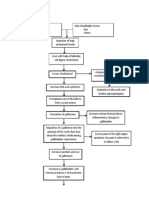
Acute Cholecystitis: Acute cholecystitis begins
suddenly, resulting in severe, steady pain in the upper
abdomen.
At least 95% of people with acute cholecystitis have
gallstones.
The inflammation almost always begins without
infection, although infection may follow later.
Inflammation may cause the gallbladder to fill with fluid
and its walls to thicken.
Rarely, a form of acute cholecystitis without gallstones
(acalculous cholecystitis) occurs.
Critical illnesses such as serious injuries, major burns,
and bodywide infections (sepsis) Intravenous feedings for
a long time Fasting for a prolonged time A deficiency in
the immune system It can occur in young children,
perhaps developing from a viral or another infection.
Chronic Cholecystitis: Chronic cholecystitis is
gallbladder inflammation that has lasted a long time.
It almost always results from gallstones.
It is characterized by repeated attacks of pain (biliary
colic).
In chronic cholecystitis, the gallbladder is damaged by
repeated attacks of acute inflammation, usually due to
gallstones, and may become thick-walled, scarred, and
small.
The gallbladder usually contains sludge (microscopic
particles of materials similar to those in gallstones), or
gallstones that either block its opening into the cystic duct
or reside in the cystic duct itself.
You might also like
- Cholelithiasis: Group MembersDocument12 pagesCholelithiasis: Group MembersShiela GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Cholecystitis Litiasis EctomyDocument23 pagesCholecystitis Litiasis EctomyTimothy WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Gastric Outlet Obstruction, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandGastric Outlet Obstruction, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Liver AbscessDocument6 pagesLiver AbscessKenneth SunicoNo ratings yet
- HemorrhoidectomyDocument5 pagesHemorrhoidectomydrnareshkumar3281100% (1)
- PancreatitisDocument12 pagesPancreatitismardsz100% (5)
- CholelitiasisDocument42 pagesCholelitiasisEdwin YosuaNo ratings yet
- Liver AbscessDocument3 pagesLiver AbscessLyiuiu TranNo ratings yet
- Carcinoma StomachDocument43 pagesCarcinoma StomachRukman Mecca100% (1)
- HIV and Its TreatmentDocument24 pagesHIV and Its Treatmentaathira_kNo ratings yet
- Gastric Carcinoma: Professor Ravi KantDocument44 pagesGastric Carcinoma: Professor Ravi KantDaniel Alfredo Tenorio GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Liver CancerDocument2 pagesLiver CancerPrincess Barnuevo100% (2)
- Acute Cholecystitis: Pableo, Rachel MDocument47 pagesAcute Cholecystitis: Pableo, Rachel MLd Rachel PableoNo ratings yet
- CHOLELITHIASISSDocument29 pagesCHOLELITHIASISSAngelica Mercado SirotNo ratings yet
- Extrahepatic Biliary Tract Pathology - Cholidolithiasis, Cholidocholithiasis, Cholecystitis and CholangitisDocument60 pagesExtrahepatic Biliary Tract Pathology - Cholidolithiasis, Cholidocholithiasis, Cholecystitis and CholangitisDarien LiewNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Obstruction 4Document25 pagesIntestinal Obstruction 4Muvenn KannanNo ratings yet
- CHOLEDOCHOLITHIASISDocument38 pagesCHOLEDOCHOLITHIASISPrecious Cofreros100% (3)
- CHOLEDOCHOLITHIASISDocument8 pagesCHOLEDOCHOLITHIASISkuncupcupu1368No ratings yet
- Anal Canal: Fissure in Ano HaemorrhoidsDocument37 pagesAnal Canal: Fissure in Ano Haemorrhoidsyash shrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Gastric CancerDocument7 pagesGastric CancerMicah PingawanNo ratings yet
- Case UreterolithiasisDocument26 pagesCase UreterolithiasisPutri Dwi Kartini0% (1)
- Chronic PyelonephritisDocument5 pagesChronic PyelonephritisIsak ShatikaNo ratings yet
- Risk Factors: CholelithiasisDocument10 pagesRisk Factors: CholelithiasisRoyster CabralNo ratings yet
- LI - Physical Examination - AbdomenDocument6 pagesLI - Physical Examination - AbdomenTravis DonohoNo ratings yet
- Cholelithiasis Treatment & ManagementDocument8 pagesCholelithiasis Treatment & ManagementRayhanun MardhatillahNo ratings yet
- Cholecystitis: Bonoan, Camille Grace Chua, ManilynDocument29 pagesCholecystitis: Bonoan, Camille Grace Chua, ManilynCams BonoanNo ratings yet
- Lower GIT BleedingDocument30 pagesLower GIT BleedingRonald Joy DatuNo ratings yet
- Cholelithiasis Brief DiscussionDocument8 pagesCholelithiasis Brief Discussionriel100% (6)
- Chronic PyelonephritisDocument6 pagesChronic PyelonephritisKaustav JainNo ratings yet
- Cholecystitis: A Case Presentation of Group 1&2Document73 pagesCholecystitis: A Case Presentation of Group 1&2MARIA STEPHANY DELA CRUZ100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Acute CholecystitisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Acute CholecystitisKush KhannaNo ratings yet
- CholecystectomyDocument6 pagesCholecystectomyTom Bayubs-tucsNo ratings yet
- Hiatal Hernia AchalasiaDocument22 pagesHiatal Hernia AchalasiaDhen MarcNo ratings yet
- Intestinal ObstructionDocument35 pagesIntestinal Obstructionwht89100% (1)
- Penetrating Abdominal Trauma Emergency ManagementDocument29 pagesPenetrating Abdominal Trauma Emergency Managementanjali singhNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis (History & Examination)Document6 pagesAppendicitis (History & Examination)Doctor Saleem Rehman75% (4)
- Peptic Ulcer DiseaseDocument20 pagesPeptic Ulcer Diseasedr_IstiqlalMiftahulJannahNo ratings yet
- Complete Intestinal ObstructionDocument8 pagesComplete Intestinal ObstructionThuganamix100% (2)
- Prostate CancerDocument6 pagesProstate CancerfheisanzNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation UrolithiasisDocument13 pagesCase Presentation UrolithiasisTeguh Soni ReksaNo ratings yet
- Cholangitis and Cholecystitis (DR - Dr. Hery Djagat Purnomo, SpPD-KGEH)Document47 pagesCholangitis and Cholecystitis (DR - Dr. Hery Djagat Purnomo, SpPD-KGEH)Aditya SahidNo ratings yet
- Lung CancerDocument2 pagesLung CancerAurea Jasmine DacuycuyNo ratings yet
- Casestudy Gastric CarcinomaDocument53 pagesCasestudy Gastric CarcinomaAngelaTrinidadNo ratings yet
- Liver Abscess Clinical Presentation - History, Physical Examination, ComplicationsDocument2 pagesLiver Abscess Clinical Presentation - History, Physical Examination, ComplicationsAdi Kurnia100% (1)
- Clinical Case StudyDocument5 pagesClinical Case Studyv2wish_iNo ratings yet
- Intestinal ObstructionDocument27 pagesIntestinal ObstructionAna AvilaNo ratings yet
- Colon CancerDocument17 pagesColon CancerYaska MusaNo ratings yet
- Acute Cholecystitis SeminarDocument42 pagesAcute Cholecystitis SeminarNatnaelNo ratings yet
- Abdominal TraumaDocument24 pagesAbdominal TraumaSurgeryClassesNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology FinalDocument2 pagesPathophysiology FinallarissedeleonNo ratings yet
- Cholecystitis and CholelithiasisDocument19 pagesCholecystitis and CholelithiasisChristine Salimbagat100% (1)
- Nu'man AS DaudDocument23 pagesNu'man AS DaudHidayat BazeherNo ratings yet
- Anemia of Chronic Disease - Inflammation - UpToDateDocument36 pagesAnemia of Chronic Disease - Inflammation - UpToDateDomenica MurilloNo ratings yet
- Wilms TumorDocument12 pagesWilms TumorKath CamachoNo ratings yet
- Community Acquired Pneumonia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandCommunity Acquired Pneumonia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Management of Tuberculosis: A guide for clinicians (eBook edition)From EverandManagement of Tuberculosis: A guide for clinicians (eBook edition)No ratings yet
- Hirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Parathyroid Adenoma, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Parathyroid Adenoma, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Approach To Right Hypochondrium PainDocument34 pagesApproach To Right Hypochondrium PainkhansamrNo ratings yet
- CHolelitiasis, CholesistitisDocument44 pagesCHolelitiasis, CholesistitistrianaamaliaNo ratings yet
- Forex Day Trading SystemDocument17 pagesForex Day Trading SystemSocial Malik100% (1)
- Please Refer Tender Document and Annexures For More DetailsDocument1 pagePlease Refer Tender Document and Annexures For More DetailsNAYANMANI NAMASUDRANo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Science Biology 1 DLPDocument13 pagesGrade 9 Science Biology 1 DLPManongdo AllanNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study Between Online and Offilne Learning With Reference of Tutedude E-LearningDocument61 pagesComparative Study Between Online and Offilne Learning With Reference of Tutedude E-LearningDeeksha Saxena0% (2)
- Lab Report SBK Sem 3 (Priscilla Tuyang)Document6 pagesLab Report SBK Sem 3 (Priscilla Tuyang)Priscilla Tuyang100% (1)
- Marketing Channels: A Strategic Tool of Growing Importance For The Next MillenniumDocument59 pagesMarketing Channels: A Strategic Tool of Growing Importance For The Next MillenniumAnonymous ibmeej9No ratings yet
- Speed, Velocity & Acceleration (Physics Report)Document66 pagesSpeed, Velocity & Acceleration (Physics Report)Kristian Dave DivaNo ratings yet
- Math Review CompilationDocument9 pagesMath Review CompilationJessa Laika CastardoNo ratings yet
- Jan 25th 6 TicketsDocument2 pagesJan 25th 6 TicketsMohan Raj VeerasamiNo ratings yet
- Eurocode 3: Design of Steel Structures "ReadyDocument26 pagesEurocode 3: Design of Steel Structures "Readywazydotnet80% (10)
- DFo 2 1Document15 pagesDFo 2 1Donna HernandezNo ratings yet
- Dakua Makadre PresentationDocument12 pagesDakua Makadre PresentationEli Briggs100% (1)
- Hydro Electric Fire HistoryDocument3 pagesHydro Electric Fire HistorygdmurfNo ratings yet
- ThorpeDocument267 pagesThorpezaeem73No ratings yet
- UM-140-D00221-07 SeaTrac Developer Guide (Firmware v2.4)Document154 pagesUM-140-D00221-07 SeaTrac Developer Guide (Firmware v2.4)Antony Jacob AshishNo ratings yet
- Toh MFS8B 98B 003-11114-3AG1 PDFDocument92 pagesToh MFS8B 98B 003-11114-3AG1 PDFDmitry NemtsoffNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Investigatory Project (R)Document23 pagesChemistry Investigatory Project (R)BhagyashreeNo ratings yet
- Arduino Uno CNC ShieldDocument11 pagesArduino Uno CNC ShieldMărian IoanNo ratings yet
- 5 Minute Pediatric ConsultDocument5 pages5 Minute Pediatric Consultajescool0% (4)
- Recruitment SelectionDocument11 pagesRecruitment SelectionMOHAMMED KHAYYUMNo ratings yet
- Acc116 Dec 2022 - Q - Test 1Document6 pagesAcc116 Dec 2022 - Q - Test 12022825274100% (1)
- Building and Structural Construction N6 T1 2024 T2Document9 pagesBuilding and Structural Construction N6 T1 2024 T2FranceNo ratings yet
- Santu BabaDocument2 pagesSantu Babaamveryhot0950% (2)
- Final WMS2023 HairdressingDocument15 pagesFinal WMS2023 HairdressingMIRAWATI SAHIBNo ratings yet
- Water Pump 250 Hrs Service No Unit: Date: HM: ShiftDocument8 pagesWater Pump 250 Hrs Service No Unit: Date: HM: ShiftTLK ChannelNo ratings yet
- The Mane Reason - UNDERSTANDING CONSUMER BEHAVIOUR TOWARDS NATURAL HAIR PRODUCTS IN GHANADocument68 pagesThe Mane Reason - UNDERSTANDING CONSUMER BEHAVIOUR TOWARDS NATURAL HAIR PRODUCTS IN GHANAYehowadah OddoyeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document6 pagesChapter 1Grandmaster MeowNo ratings yet
- Introduction - Livspace - RenoDocument12 pagesIntroduction - Livspace - RenoMêghnâ BîswâsNo ratings yet
- Top 100 Chemical CompaniesDocument11 pagesTop 100 Chemical Companiestawhide_islamicNo ratings yet
- Wwii TictactoeDocument2 pagesWwii Tictactoeapi-557780348No ratings yet