Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Normal Distribution
Uploaded by
aamirali31Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Normal Distribution
Uploaded by
aamirali31Copyright:
Available Formats
Normal Distribution
Saroj Kumar Roy
01496403610
Objectives
Introduce the Normal Distribution
Properties of the Standard Normal
Distribution
Introduce the Central Limit Theorem
Use Normal Distribution in an inferential
fashion
Normal Distribution
Why are normal distributions so important?
Many dependent variables are commonly
assumed to be normally distributed in the
population
If a variable is approximately normally
distributed we can make inferences about
values of that variable
Example: Sampling distribution of the mean
Normal Distribution
Symmetrical, bell-shaped curve
Also known as Gaussian distribution
Point of inflection = 1 standard deviation
from mean
Mathematical formula
f (X)
1
2
(e)
( X )
2
2
2
Normal Distribution Curve
A normal distribution curve is symmetrical,
bell-shaped curve defined by the mean and
standard deviation of a data set.
The normal curve is a probability distribution
with a total area under the curve of 1.
Normal Distribution Curve
Since we know the shape of the curve, we can
calculate the area under the curve
The percentage of that area can be used to determine
the probability that a given value could be pulled
from a given distribution
The area under the curve tells us about the probability- in
other words we can obtain a p-value for our result (data)
by treating it as a normally distributed data set.
Key Areas under the Curve
For normal
distributions
+ 1 SD ~ 68%
+ 2 SD ~ 95%
+ 3 SD ~ 99.9%
One standard deviation away from the mean (miu ) in either direction on the
horizontal axis accounts for around 68 percent of the data. Two standard
deviations away from the mean accounts for roughly 95 percent of the
data with three standard deviations representing about 99.7 percent of the
data.
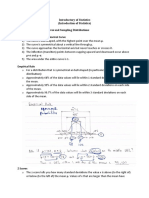
Example IQ mean = 100 s = 15
Problem:
Each normal distribution with its own values of
and would need its own calculation of the area
under various points on the curve
Normal Probability Distributions
Standard Normal Distribution N(0,1)
We agree to use the
standard normal
distribution
Bell shaped
=0
=1
Note: not all bell
shaped distributions are
normal distributions
Normal Probability Distribution
Can take on an infinite
number of possible
values.
The probability of any
one of those values
occurring is essentially
zero.
Curve has area or
probability = 1
Normal Distribution
The standard normal distribution will allow us
to make claims about the probabilities of
values related to our own data
How do we apply the standard normal
distribution to our data?
Z-score
If we know the population mean and
population standard deviation, for any value
of X we can compute a z-score by subtracting
the population mean and dividing the result by
the population standard deviation
z
X
Important z-score info
Z-score tells us how far above or below the mean a
value is in terms of standard deviations
It is a linear transformation of the original scores
Multiplication (or division) of and/or addition to (or
subtraction from) X by a constant
Relationship of the observations to each other remains the
same
Z = (X-)/
then
X = Z +
[equation of the general form Y = mX+c]
Probabilities and z scores: z tables
Total area = 1
Only have a probability from width
For an infinite number of z scores each point has
a probability of 0 (for the single point)
Typically negative values are not reported
Symmetrical, therefore area below negative value
= Area above its positive value
Always helps to draw a sketch!
Probabilities are depicted by areas under the curve
Total area under the curve
is 1
The area in red is equal to
p(z > 1)
The area in blue is equal to
p(-1< z <0)
Since the properties of the
normal distribution are
known, areas can be looked
up on tables or calculated
on computer.
Strategies for finding probabilities for the
standard normal random variable.
Draw a picture of standard normal
distribution depicting the area of interest.
Re-express the area in terms of shapes like
the one on top of the Standard Normal
Table
Look up the areas using the table.
Do the necessary addition and subtraction.
Suppose Z has standard normal distribution
Find p(0<Z<1.23)
Find p(-1.57<Z<0)
Find p(Z>.78)
Z is standard normal
Calculate p(-1.2<Z<.78)
You might also like
- Normal DistributionDocument29 pagesNormal Distributionatul_rockstarNo ratings yet
- Normal DistributionDocument29 pagesNormal DistributionMohamed Abd El-MoniemNo ratings yet
- Week11-Normal Distribution (Ekstra-Week)Document59 pagesWeek11-Normal Distribution (Ekstra-Week)düşünennurNo ratings yet
- Chapter_03-Normal_DistributionsDocument28 pagesChapter_03-Normal_DistributionsamandaluvsanimalsNo ratings yet
- Normal Distribution and Probability: Mate14 - Design and Analysis of Experiments in Materials EngineeringDocument23 pagesNormal Distribution and Probability: Mate14 - Design and Analysis of Experiments in Materials EngineeringsajeerNo ratings yet
- Topic 6-7 ProbabilityDocument46 pagesTopic 6-7 ProbabilityRamesh paiNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Standard Normal DistributionsDocument7 pages3.2 Standard Normal DistributionsTheory SummersNo ratings yet
- 5 BMGT 220 Normal DistributionDocument10 pages5 BMGT 220 Normal DistributionPamela Chimwani100% (1)
- Normal Random VariableDocument8 pagesNormal Random VariableLoraine Buen FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Statistics - 160: The Normal Probability DistributionDocument17 pagesStatistics - 160: The Normal Probability DistributionALLAPARTHI SHANMUKHA PRIYA RAMA ABHILASH 15MIS0077No ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document4 pagesChapter 7Riezel PepitoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Modeling Distributions of Data: Section 2.2Document17 pagesChapter 2: Modeling Distributions of Data: Section 2.2张书No ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document4 pagesChapter 7Riezel PepitoNo ratings yet
- The Normal DistributionDocument9 pagesThe Normal DistributionDog VenturesNo ratings yet
- NormalDistribution ExamplesDocument45 pagesNormalDistribution ExamplesDeniz ArasNo ratings yet
- Week#7 SIM (Normal Distribution)Document27 pagesWeek#7 SIM (Normal Distribution)Mr.JoJINo ratings yet
- Group 1 Report (1) (Autosaved)Document51 pagesGroup 1 Report (1) (Autosaved)Rheanna Nogales BanguilanNo ratings yet
- StatisticsDocument27 pagesStatisticsBernice Mikaela IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Eco 2Document31 pagesEco 2Nebiyu WoldesenbetNo ratings yet
- MA EDLM CH 4Document17 pagesMA EDLM CH 4fikru terfaNo ratings yet
- Normal Distribution & Z-ScoresDocument82 pagesNormal Distribution & Z-Scoresgela tinNo ratings yet
- The Normal Distributions Density CurveDocument2 pagesThe Normal Distributions Density CurveNabilla JasmineNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 The Normal DistributionDocument12 pagesChapter 4 The Normal Distributionleonessa jorban cortesNo ratings yet
- MS104 March 2 DiscussionDocument36 pagesMS104 March 2 DiscussionEminNo ratings yet
- Biostatistics For Academic3Document28 pagesBiostatistics For Academic3Semo gh28No ratings yet
- How to normalize an image to zero mean and unit varianceDocument16 pagesHow to normalize an image to zero mean and unit varianceGuru Ballur0% (1)
- Topic20 8p7 GalvinDocument53 pagesTopic20 8p7 GalvinJude SantosNo ratings yet
- 02.4 Probability - CPDDocument23 pages02.4 Probability - CPDRomel DecenillaNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - Probability and Normal DistributionDocument30 pagesWeek 2 - Probability and Normal DistributionAbrashiNo ratings yet
- L4 Continuous ProbabilityDocument28 pagesL4 Continuous ProbabilityKelyn KokNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Normal Distribution PDFDocument24 pages2.3 Normal Distribution PDFChelsea RoqueNo ratings yet
- 04 NormalDistributionDocument43 pages04 NormalDistributionShane Olen GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Univariate StatisticsDocument7 pagesUnivariate StatisticsDebmalya DuttaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2: Normal DistributionDocument47 pagesLesson 2: Normal DistributionMARITESS COLLADONo ratings yet
- CHAP 4 Normal DistributionDocument7 pagesCHAP 4 Normal DistributionFatin Farzanah ZakariaNo ratings yet
- statsDocument3 pagesstatsdream is my husbandNo ratings yet
- Ap Stats Chapter 2 Glossary of Important Terms Tps4eDocument2 pagesAp Stats Chapter 2 Glossary of Important Terms Tps4eapi-295686071No ratings yet
- Introduction to Continuous Probability DistributionsDocument46 pagesIntroduction to Continuous Probability Distributionsrenna_magdalenaNo ratings yet
- Continuous Random Variables: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDocument38 pagesContinuous Random Variables: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinadamNo ratings yet
- MASTAT - Ch5 Continuous Distributions - 022518Document7 pagesMASTAT - Ch5 Continuous Distributions - 022518ventus5thNo ratings yet
- A. The Standard Normal DistributionDocument9 pagesA. The Standard Normal DistributionAlexa LeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 06Document70 pagesChapter 06Angelo Mikko RosarioNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - CH6 Normal Distribution and Other Continuous DistributionsDocument6 pagesWeek 3 - CH6 Normal Distribution and Other Continuous DistributionsAya AdelNo ratings yet
- Stat 3rd Week 3Document12 pagesStat 3rd Week 3Reyboy TagsipNo ratings yet
- Definition:: ParametersDocument3 pagesDefinition:: ParametersEmman TariqNo ratings yet
- The Normal Distribution and Other Continuous Distribution: Dr. K. M. Salah UddinDocument50 pagesThe Normal Distribution and Other Continuous Distribution: Dr. K. M. Salah UddinfaisalNo ratings yet
- PO 1-09 Normal Distribution PDFDocument4 pagesPO 1-09 Normal Distribution PDFshynaNo ratings yet
- Normal DistributionDocument3 pagesNormal DistributionSangeetha SumamNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 Normal Distribution Z-ScoresDocument33 pagesCHAPTER 4 Normal Distribution Z-Scoresapi-3729261100% (7)
- Continuous Probability DistributionDocument60 pagesContinuous Probability DistributionJethro MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Normal Distribution-7Document5 pagesNormal Distribution-7Shobha Kumari ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- M3.Normal Distribution - Final PDFDocument23 pagesM3.Normal Distribution - Final PDFÖzZíé Ming RenNo ratings yet
- M3.Normal Distribution - Final PDFDocument23 pagesM3.Normal Distribution - Final PDFÖzZíé Ming RenNo ratings yet
- 08 08 28 Statistics For Business Research-DKPDocument8 pages08 08 28 Statistics For Business Research-DKPvinniieeNo ratings yet
- Normal Distirbution: 5.1 Meaning of Normal DistributionDocument13 pagesNormal Distirbution: 5.1 Meaning of Normal DistributionAllina PonganNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document54 pagesModule 3Alrac Anacta MalaitNo ratings yet
- 3 4 DistributionsDocument24 pages3 4 DistributionsStephania ImbachiNo ratings yet
- The Normal Distribution: ConceptsDocument17 pagesThe Normal Distribution: ConceptsJay Ian GeronaNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- 4th Semester SyllabusDocument13 pages4th Semester SyllabusMugu MadhavNo ratings yet
- APMA 3100 Probability Fall 2013 SyllabusDocument3 pagesAPMA 3100 Probability Fall 2013 SyllabusbrentbaumNo ratings yet
- Fat Tails Statistical ConsequencesDocument364 pagesFat Tails Statistical ConsequencesJuan Carlos Florez100% (2)
- Ebook PDF Business Statistics 2nd Edition by Robert A Donnelly PDFDocument41 pagesEbook PDF Business Statistics 2nd Edition by Robert A Donnelly PDFmichael.alexander940100% (27)
- Probability Lecture Notes (MSD) 2Document9 pagesProbability Lecture Notes (MSD) 2MrigankaNo ratings yet
- HW1Document2 pagesHW1Ahmet GülverenNo ratings yet
- Spearman's Rank Correlation Coefficient - WikipediaDocument10 pagesSpearman's Rank Correlation Coefficient - WikipediaHin HuchNo ratings yet
- (EP2091) Tugas ProbstatDocument8 pages(EP2091) Tugas ProbstatReza DarmawanNo ratings yet
- Questions Short Concept QuestionsDocument61 pagesQuestions Short Concept QuestionsNg Win WwaNo ratings yet
- Table Z Test and T TestDocument3 pagesTable Z Test and T Testmariell quitorianoNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems - AnsDocument3 pagesPractice Problems - AnsAshok ThiruvengadamNo ratings yet
- Statistics Notes - Normal Distribution, Confidence Interval & Hypothesis TestingDocument2 pagesStatistics Notes - Normal Distribution, Confidence Interval & Hypothesis Testingwxc1252No ratings yet
- P&S Unit-4 and 5Document3 pagesP&S Unit-4 and 5zzzzzNo ratings yet
- Bruce Hajek - Probability With Engineering Applications - Jan 2017Document291 pagesBruce Hajek - Probability With Engineering Applications - Jan 2017Siddharth JhaNo ratings yet
- Poisson Distribution and Traffic ApplicationsDocument2 pagesPoisson Distribution and Traffic ApplicationsMomanyi IvyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Lesson 3 Statisticall Independent and Statistically Dependent EventsDocument16 pagesChapter 2 - Lesson 3 Statisticall Independent and Statistically Dependent EventsChi VirayNo ratings yet
- CFA Level I SmartSheet 2020Document9 pagesCFA Level I SmartSheet 2020yousefNo ratings yet
- Evaluating The Predictive Accuracy of Volatility Models: Jose A. LopezDocument47 pagesEvaluating The Predictive Accuracy of Volatility Models: Jose A. LopezrifkiboyzNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Software Reliability Models and TechniquesDocument79 pagesUnit 2: Software Reliability Models and TechniquesKartik Gupta 71No ratings yet
- Statistics Paper 2015Document3 pagesStatistics Paper 2015Sumra KhanNo ratings yet
- 1332 7369 1 PBDocument33 pages1332 7369 1 PBsamyNo ratings yet
- Sampling Distributions & Point EstimationDocument17 pagesSampling Distributions & Point EstimationBui Tien DatNo ratings yet
- A Beginner's Guide To Fragility, Vulnerability, and RiskDocument104 pagesA Beginner's Guide To Fragility, Vulnerability, and RiskSaharAkthamNo ratings yet
- A2 Math C3 DoneDocument53 pagesA2 Math C3 DoneWuileapNo ratings yet
- Measures of Variability and DispersionDocument4 pagesMeasures of Variability and DispersionAustin Capal Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- 7 International Probabilistic WorkshopDocument588 pages7 International Probabilistic WorkshopDproske100% (1)
- Stat and Prob Q3 W3&4 WHLPDocument6 pagesStat and Prob Q3 W3&4 WHLPDianne TelmoNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet STAT1301Document3 pagesFormula Sheet STAT1301janeNo ratings yet
- Chi Square Test (Research Methodology) PDFDocument11 pagesChi Square Test (Research Methodology) PDFUtpal BoraNo ratings yet
- Biol3090 Probability ProblemDocument8 pagesBiol3090 Probability ProblemFranz Anthony TinioNo ratings yet