Professional Documents
Culture Documents
FOrm 5 SPM PhysicsElectronics
Uploaded by
Vjayan DharmaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
FOrm 5 SPM PhysicsElectronics
Uploaded by
Vjayan DharmaCopyright:
Available Formats
Electronics
SPM
Form 5
Physics
Chapter 4
CATHODE RAY OSCILLOSCOPE
Thermionic emission is the process of
emission of electrons from a heated
metals surface.
How does thermionic emission
occur?
Metal consists of a large number of electrons
which are free to move.
At room temperature, the electrons are free to
move but remain inside the metal.
The electrons cannot escape at the surface
because they are held back by the attractive
forces of the atomic nucleus.
If the metal is heated at a high temperature,
some of the free electrons may gain sufficient
energy to escape from the metal.
Cathode Ray
Thermionic emissions can be used to produce
a continuous flow of electrons in a cathode
ray tube.
When the cathode is connected to the anode
by an extra high tension (EHT) voltage supply,
a narrow beam of fast electrons will move to
the anode.
The beam of electrons moving from the
cathode to the anode is called cathode rays.
Properties of Cathode Rays
Cathode rays can be used in picture tube of a
television, a cathode ray oscilloscope and the
visual display on a radar screen.
The properties of cathode rays can be
summarized:
Negatively charged particles called electrons.
Travel in straight lines and cast sharp shadows.
Travel at very high speed and have kinetic energy.
Can cause fluorescence. (A process where the
kinetic energy of the electrons is converted into
light energy)
Deflected by electric and magnetic fields.
Cathode Ray Oscilloscope
Uses a cathode ray tube that converts
electronic and electrical signals to a visual
display.
The graph produced consist of a horizontal
axis which is normally a function of time, and
a vertical axis which is a function of the input
voltage.
The components in a cathode ray tube
consists of a vacuum glass tube with an
electron gun, a deflection system for
deflecting the electron beam and a
fluorescent coated screen.
Application of CRO
Measuring potential difference
Measuring short intervals
displaying wave forms
Semiconductor Diodes
Semiconductor
A material that has an electrical conductivity
that is between that of a conductor and an
insulator.
The resistance of semiconductors is between
that of conductors and insulators.
Semiconductors can be pure element such as
silicon or germanium.
At 0 Kelvin it behaves as an insulator. When the
temperature increases, the conductivity of the
electricity will increase because its resistance
will be lowered.
Charge carrier
Electron which is negatively charge
Hole which is positively charge
Transistor
A transistor has three leads
connected to the emitter, base and
collector.
The emitter emits or sends charge
carriers through the thin base layer to
be collected by the collector
There is two-type of transistor: npn
transistor and pnp transistor.
In an npn transistor the emitter sends
negative electrons to the collector.
In an pnp transistor, the p-type
emitter sends positive holes to the
collector.
The current in the collector lead is called
collector current, I
C
The base current, I
B
is used to control the
collector current through the transistor.
The base current can be used to switch
the collector current on or off.
Transistor as automatic switch
If the variable resistor = 0,
base voltage = 0 and the
transistor remains off.
If the variable resistor is
increased, the base
voltage increases.
When the base voltage
reaches certain minimum
value, the base current
switches the transistor on.
The large collector current
flows through the transistor
causing the bulb to light
up.
Logic Gates
The switching on and off operations are controlled by
electronic switches made up of logic gates.
Logic gates work using tiny transistors as switches.
They are manufactured as integrated circuit (IC), with
each chip holding several gates.
A logic gate is a circuit that has one or more input
signals but only one output signal.
For each gate, the input or inputs are on the left of
the symbol. The output is on the right
Each input and output can be either high (logic 1) or
low (logic 0).
A binary 0 represents 0 V, and a binary 1
represents a non zero voltage.
Truth Table
You might also like
- Chapter 4 ElectronicDocument45 pagesChapter 4 ElectronicThomas CheahNo ratings yet
- 4 ElectronicDocument47 pages4 ElectronicAudrey ChangNo ratings yet
- CRT AssignmentDocument21 pagesCRT AssignmentRittika RatawaNo ratings yet
- Full Summary (Floyd)Document8 pagesFull Summary (Floyd)Adrian BagayanNo ratings yet
- ElectronicsDocument12 pagesElectronicsKirvy ParNo ratings yet
- Electronics Engineering (Survival Kit)Document45 pagesElectronics Engineering (Survival Kit)spidyanNo ratings yet
- The Oscilloscope: Cathode Ray Tube and Other Internal ComponentsDocument19 pagesThe Oscilloscope: Cathode Ray Tube and Other Internal ComponentsParag NikhraNo ratings yet
- F5C4-Electronics PpsDocument22 pagesF5C4-Electronics PpsRebecca TaiiNo ratings yet
- Electronics in Nursing: Diode: A Diode Is A Two Terminal Electronic Device, Made of Semiconductor Materials, WhichDocument10 pagesElectronics in Nursing: Diode: A Diode Is A Two Terminal Electronic Device, Made of Semiconductor Materials, Whichmanibalan100% (1)
- Unit-III (Topic - 3)Document61 pagesUnit-III (Topic - 3)vsresika20No ratings yet
- SPM PHYSICS SHORT NOTES CHAPTER 9 ElectronicsDocument9 pagesSPM PHYSICS SHORT NOTES CHAPTER 9 ElectronicsJay Bee100% (1)
- What is a CRO and how does it workDocument4 pagesWhat is a CRO and how does it workRai Mudassar IqbalNo ratings yet
- What Is A CRO (Cathode Ray Oscilloscope) & Its WorkingDocument4 pagesWhat Is A CRO (Cathode Ray Oscilloscope) & Its WorkingRai Mudassar IqbalNo ratings yet
- Workshop Lab Manual - 25.5.2022Document30 pagesWorkshop Lab Manual - 25.5.2022shreyarajput92542No ratings yet
- Reviewer in EST LEC AND LABDocument8 pagesReviewer in EST LEC AND LABKhrisha TindoyNo ratings yet
- RDR SourcesDocument82 pagesRDR Sourcescolantonio.paolo69No ratings yet
- CHMA Unit - IIIDocument6 pagesCHMA Unit - IIISayyan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- B.SC Electronics D2 P3 (2022) SolutionsDocument18 pagesB.SC Electronics D2 P3 (2022) SolutionsShubham KeshriNo ratings yet
- Phy Chapter yDocument14 pagesPhy Chapter yS. KhanNo ratings yet
- ESC IV: Introduction to Electronics and Electrical EngineeringDocument43 pagesESC IV: Introduction to Electronics and Electrical EngineeringShamil GadaNo ratings yet
- Electronics Viva Based QuestionsDocument5 pagesElectronics Viva Based QuestionsArpitNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics: PresentationDocument46 pagesBasic Electronics: PresentationdennyNo ratings yet
- Chapter Six: PhysicsDocument8 pagesChapter Six: Physicssaed cabdiNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Important Questions-Semiconductor DevicesDocument7 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Important Questions-Semiconductor DevicesGanesh Dhyani0% (1)
- 1 CRTDocument11 pages1 CRTSuvesh nlnNo ratings yet
- CRO Title for Cathode Ray Oscilloscope IntroductionDocument12 pagesCRO Title for Cathode Ray Oscilloscope IntroductionAddisu Safo BoseraNo ratings yet
- Electronics 230617 194751Document22 pagesElectronics 230617 194751JessNo ratings yet
- Linear Accelerator (Linac: Prepared by Seemab Zakir Biomedical EngineerDocument22 pagesLinear Accelerator (Linac: Prepared by Seemab Zakir Biomedical Engineerihsan ul haqNo ratings yet
- ESC IV: Introduction To Electronics and Electrical EngineeringDocument43 pagesESC IV: Introduction To Electronics and Electrical EngineeringChirag GuptaNo ratings yet
- CRO and its applicationsDocument16 pagesCRO and its applicationsAtif MehfoozNo ratings yet
- Electronic Components - Functions& SymbolsDocument3 pagesElectronic Components - Functions& SymbolsGil Nacario91% (58)
- ELEX1 Lecture 01 PDFDocument10 pagesELEX1 Lecture 01 PDFBarn Go100% (1)
- EE 316 - Electronic Design Project, Metal Detector Project Final ReportDocument15 pagesEE 316 - Electronic Design Project, Metal Detector Project Final Reportherrberk100% (1)
- Electrical JINIsshDocument6 pagesElectrical JINIsshGROOT GamingYTNo ratings yet
- Theory of TransistorsDocument11 pagesTheory of TransistorssamactrangNo ratings yet
- RT103 Anode, Cathode, X-Ray Circuitry, TransformerDocument7 pagesRT103 Anode, Cathode, X-Ray Circuitry, TransformerDGLNo ratings yet
- NPP 2021 02 06Document16 pagesNPP 2021 02 06Namitha RajeevNo ratings yet
- What are Electronic Circuit SymbolsDocument5 pagesWhat are Electronic Circuit SymbolsRolando Carlos FloresNo ratings yet
- ECE 422 REVIEWERDocument5 pagesECE 422 REVIEWERVince MarananNo ratings yet
- IP 4 TransistorDocument3 pagesIP 4 TransistorRifky OfficialNo ratings yet
- Physic 4.1 Cathode Ray OscilloscopeDocument25 pagesPhysic 4.1 Cathode Ray OscilloscopeSascha WuNo ratings yet
- Silicon ReportDocument8 pagesSilicon ReportSukhdeepNo ratings yet
- Full Summary (Floyd) Final EditDocument9 pagesFull Summary (Floyd) Final EditJoseph JeremyNo ratings yet
- Travelling Wave Tube: =V (Pitch/2πr)Document7 pagesTravelling Wave Tube: =V (Pitch/2πr)Sanket PatilNo ratings yet
- What Is LEDDocument5 pagesWhat Is LEDSanjana RathoreNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Transistors: Administrator 2 CommentsDocument103 pagesIntroduction To Transistors: Administrator 2 CommentsArinaitwe IvanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Summary (Introduction To Semiconductors) : Crystal Conduction ElectronsDocument14 pagesChapter 1 Summary (Introduction To Semiconductors) : Crystal Conduction ElectronsGregorio Miguel Borja AguilaNo ratings yet
- NAME: Moch Rissandi No: 14 Class: Ek-3A Individual Presentation 4 The TransistorDocument3 pagesNAME: Moch Rissandi No: 14 Class: Ek-3A Individual Presentation 4 The TransistorChoiril AthoNo ratings yet
- Class1 EEE4931Document24 pagesClass1 EEE4931qp245xk5wpNo ratings yet
- Radiation SensorDocument3 pagesRadiation SensormirfanbilalNo ratings yet
- Shockley Diode CharacteristicsDocument10 pagesShockley Diode CharacteristicsSamuel Caesar TalidroNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 ElectronicsDocument47 pagesCHAPTER 4 ElectronicsrenuNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor IntroDocument69 pagesSemiconductor IntroPePe ParkerNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Transistors and Their WorkingDocument22 pagesDifferent Types of Transistors and Their WorkingVenki EdeNo ratings yet
- Solid-State Circuits: Electrical Engineering DivisonFrom EverandSolid-State Circuits: Electrical Engineering DivisonRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Chapter 10 Group 2Document8 pagesChapter 10 Group 2Vjayan DharmaNo ratings yet
- STPM CHEMISTRY TERM 3: HYDROCARBONSDocument16 pagesSTPM CHEMISTRY TERM 3: HYDROCARBONSVjayan DharmaNo ratings yet
- Transport Substances in PlantsDocument5 pagesTransport Substances in PlantsVjayan DharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document1 pageChapter 5cikguanuar60% (5)
- CHAPTER 8 Dynamic EcosystemDocument16 pagesCHAPTER 8 Dynamic EcosystemVjayan DharmaNo ratings yet
- Latent HeatDocument6 pagesLatent HeatVjayan DharmaNo ratings yet
- What Is Symmetry?: Chapter 7: Symmetry 7.1 - Lines of SymmetryDocument4 pagesWhat Is Symmetry?: Chapter 7: Symmetry 7.1 - Lines of SymmetryVjayan DharmaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Formulae ExerciseDocument2 pagesChemical Formulae ExerciseVjayan DharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Cell DivisionDocument7 pagesChapter 5 Cell DivisionVjayan DharmaNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Science Chapter 7Document32 pagesForm 2 Science Chapter 7qq23582% (11)
- Verb Tenses DiagramDocument1 pageVerb Tenses DiagramKasturi KSNo ratings yet
- ElectromagnetismDocument42 pagesElectromagnetismVjayan Dharma100% (1)
- What Is Symmetry?: Chapter 7: Symmetry 7.1 - Lines of SymmetryDocument4 pagesWhat Is Symmetry?: Chapter 7: Symmetry 7.1 - Lines of SymmetryVjayan DharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Fractions and Decimals Form 2Document16 pagesChapter 4 Fractions and Decimals Form 2Vjayan DharmaNo ratings yet
- Cardiac CycleDocument1 pageCardiac CycleVjayan DharmaNo ratings yet
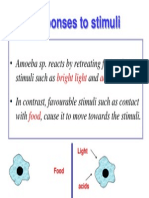
- Responses To Stimuli of AmoebaDocument1 pageResponses To Stimuli of AmoebaVjayan DharmaNo ratings yet
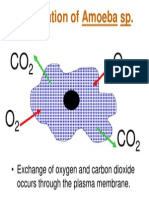
- Respiration of Amoeba SPDocument1 pageRespiration of Amoeba SPVjayan DharmaNo ratings yet
- Bio Form 4 CHP 3Document29 pagesBio Form 4 CHP 3Vjayan DharmaNo ratings yet
- SPM Transport Form 5Document107 pagesSPM Transport Form 5Vjayan DharmaNo ratings yet
- Government's Role On GM Food RegulationDocument7 pagesGovernment's Role On GM Food RegulationVjayan DharmaNo ratings yet
- Temperature Sensor AdvantagesDocument4 pagesTemperature Sensor AdvantagesSaiful Edwend Bin DaswirNo ratings yet
- Reading TipsDocument1 pageReading TipsVjayan DharmaNo ratings yet
- Galvanic Corrosion of Aluminium-Copper Model AlloysDocument9 pagesGalvanic Corrosion of Aluminium-Copper Model AlloysTrần NamNo ratings yet
- Theory of Arc Welding pt1Document115 pagesTheory of Arc Welding pt1Koushik SarkarNo ratings yet
- SCH4U VoltaicCellLabAssignmentDocument5 pagesSCH4U VoltaicCellLabAssignmentNamdeo JadhavNo ratings yet
- KFCL Summer ProjectDocument59 pagesKFCL Summer ProjectSumitMohanGuptaNo ratings yet
- Diode Characteristics and Rectifier CircuitsDocument30 pagesDiode Characteristics and Rectifier Circuitsnur ain natasyaNo ratings yet
- Electron Beam MachiningDocument9 pagesElectron Beam MachiningductuanvvNo ratings yet
- Gu301 ADocument3 pagesGu301 AJosé Da Silva MataNo ratings yet
- Ab Electronic Tubes and Quasi-Superconductivity at Room TemperatureDocument18 pagesAb Electronic Tubes and Quasi-Superconductivity at Room TemperatureAlexander BolonkinNo ratings yet
- MC Electrochemistry Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument32 pagesMC Electrochemistry Multiple Choice QuestionsglaubersgNo ratings yet
- C1 3 - Development of An Arduino Based Identification Diagnostic and Monitoring System - ADocument51 pagesC1 3 - Development of An Arduino Based Identification Diagnostic and Monitoring System - ALeigh NavalesNo ratings yet
- Electro FishingDocument2 pagesElectro FishingSujit ShandilyaNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Production by PEM Water Electrolysis - A ReviewDocument13 pagesHydrogen Production by PEM Water Electrolysis - A ReviewJOSE ESTEBAN LORA KLEBER100% (2)
- 9.a Modular Fuel Cell, Modular DC DC ConverterDocument62 pages9.a Modular Fuel Cell, Modular DC DC ConverterShareef KhanNo ratings yet
- 8051 Interfacing With Display SevicesDocument5 pages8051 Interfacing With Display Sevicesramjee26100% (1)
- ElectrogravimetryDocument10 pagesElectrogravimetrypatriciaNo ratings yet
- Sony Kdl-22ex425 32ex425 32ex525 40ex525 46ex525 Chassis Az2-F Rev.2 SMDocument96 pagesSony Kdl-22ex425 32ex425 32ex525 40ex525 46ex525 Chassis Az2-F Rev.2 SMLuiz Roberto Honório Alves FilhoNo ratings yet
- Maltese Cross TubeDocument18 pagesMaltese Cross TubeNiekey JohnNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper 3 PDFDocument81 pagesChemistry Paper 3 PDFVentusNo ratings yet
- Solid Electrolyte: The Key For High-Voltage Lithium BatterieSDocument21 pagesSolid Electrolyte: The Key For High-Voltage Lithium BatterieSrajafanNo ratings yet
- Rev0 (System Integration Guide)Document74 pagesRev0 (System Integration Guide)pridurok2013No ratings yet
- Question and AnswerDocument27 pagesQuestion and AnswerAarav KumarNo ratings yet
- Amptek Silicon Drift DetectorsDocument7 pagesAmptek Silicon Drift DetectorsIsmael ArceNo ratings yet
- Yan2017 PDFDocument90 pagesYan2017 PDFliber mutusNo ratings yet
- Vannevar Bush - Modern Arms and Free MenDocument296 pagesVannevar Bush - Modern Arms and Free Menh0ryNo ratings yet
- Met MicroprojectDocument13 pagesMet Microprojectkambleprasad1995No ratings yet
- ECE132 Exp5Document12 pagesECE132 Exp5Ashwin RasheedNo ratings yet
- Mobile Phone Charger with Emergency Light CircuitDocument7 pagesMobile Phone Charger with Emergency Light CircuitBerhe Dargo100% (1)
- Tube TopicsDocument31 pagesTube TopicsRicardo Jose PirelaNo ratings yet
- C2019 12787GalvanicCPwithVCIforASTsDocument13 pagesC2019 12787GalvanicCPwithVCIforASTsDAVID LARZON MARTINEZNo ratings yet