Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Blow Out Fractur
Uploaded by
deaaannnnnnOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Blow Out Fractur
Uploaded by
deaaannnnnnCopyright:
Available Formats
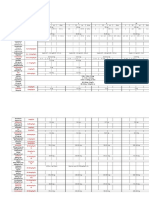
BLOW OUT FRACTUR
DEDY IRAWAN
DEFINISI
Blowout fractures are caused by direct
trauma to the globe which causes an
increase in intraorbital pressure and
decompression via fracture of the
orbital floor.
PATOFISIOLOGI
Blow-out fracture may result in cases of abrupt
trauma to the eye by any object >5cm in diameter.
Because the orbital rim is very strong, the forces of
blunt trauma are reflected back, compressing the
eye and creating a tremendous increase in pressure
within the orbit.
Since the larger bones which comprise the orbit
contain sinuses, the orbital walls are at great risk
for fracture; should the trauma be of sufficient
force, these walls can literally "blow out." The
medial wall (ethmoid bone) is occasionally affected.
But most commonly, the orbital floor (the superior
aspect of the maxillary bone) sustains the damage.
In cases of floor fractures, the eye may partially
drop down into the maxillary sinus, causing
enophthalmos and entrapment of the inferior rectus
or inferior oblique muscle.
This entrapment leads to a tethering effect, resulting in
a limited downgaze ability and, more notably, an
inability toward upgaze in the affected eye. While this
situation can be surgically corrected in the early stages,
prolonged entrapment leads to fibrosis of the muscle(s)
and permanent motility impairment. Associated medial
wall fractures may induce damage to the medial rectus
muscle and/or the lacrimal apparatus, but this is
uncommon.
In most cases, these fractures result in orbital
emphysema, creating a direct communication between
the ethmoid sinus and the orbit. This produces the
feeling of pressure within the orbit when the patient
attempts to blow his/her nose. The greatest risk to
consider with medial wall fractures is orbital cellulitis,
secondary to sinus infection, should pathogenic
organisms within the sinus invade the post-tarsal eyelid
SYMPTOM
Pain ( terutama saat gerak mata
vertikal )
Local tendernes
Double vision
Edema palpebra
Crepitus after nose blowing
Riwayat trauma
SIGN
CRITICAL SIGN
Pergerakan bola mata terbatas
Subcutan or conjungtiva emphysema
Hipestesia N. infraorbitalis
Point tendernes
enoftalmus
OTHERS
Nose bleeding
Edema & echymosis palpebra
Hipestesia N. supraorbitalis
Trismus
Malar flatening
Palpable stepoff deformity tripod
fracture
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSA
Edema orbita dan perdarahan tanpa
blow out fracture
Cranial nerve palasy
PLANNING DIAGNOSA
Pemeriksaan mata
Forced duction test
Foto waters
CT scan orbita
TREATMENT
Nasal decongestan
Antibiotik broad spectrum
Instruction the patient not to blow her
nose
Kompres es pada orbita
Surgical repair
Surgical repair
Immediate repair
If there is evidence on CT scan of
entrapped muscle or periorbital tissue in
combination with diplopia & non resolving
bradycardia, heart block, nausea, vomitus,
syncope
In patient < 16 th, with a quiet external
periocullar appearance and marked
motility retriction
Repair in 1-2 week
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Diverticulitis DiagnosisDocument5 pagesDiverticulitis DiagnosisFuture RN100% (1)
- Dosis PCT 10mg/kg/× Ibuprofen 5-10mg/kg/xDocument3 pagesDosis PCT 10mg/kg/× Ibuprofen 5-10mg/kg/xdeaaannnnnnNo ratings yet
- Dosis PCT 10mg/kg/× Ibuprofen 5-10mg/kg/xDocument3 pagesDosis PCT 10mg/kg/× Ibuprofen 5-10mg/kg/xdeaaannnnnnNo ratings yet
- TRIAGE PRINCIPLES FOR MASS CASUALTY INCIDENTSDocument8 pagesTRIAGE PRINCIPLES FOR MASS CASUALTY INCIDENTSdeaaannnnnnNo ratings yet
- Cover KLWDocument1 pageCover KLWdeaaannnnnnNo ratings yet
- Faktor-Faktor Yang Berhubungan Dengan Kelelahan Mata Pada Operator Komputer Di Kantor Samsat PalembangDocument5 pagesFaktor-Faktor Yang Berhubungan Dengan Kelelahan Mata Pada Operator Komputer Di Kantor Samsat PalembangWiwid HidayahNo ratings yet
- Lampiran 1 - Catatan Rekam MedisDocument4 pagesLampiran 1 - Catatan Rekam MedisdeaaannnnnnNo ratings yet
- Lampiran 4 - Hasil Uji Korelasi SpearmanDocument1 pageLampiran 4 - Hasil Uji Korelasi SpearmandeaaannnnnnNo ratings yet
- Lampiran 3 - Hasil Uji Normalitas Kolmogorov-SmirnovDocument1 pageLampiran 3 - Hasil Uji Normalitas Kolmogorov-SmirnovdeaaannnnnnNo ratings yet
- Bluetooth Stack Installation GuideDocument1 pageBluetooth Stack Installation GuideDereje ZewduNo ratings yet
- DataDocument15 pagesDatadeaaannnnnnNo ratings yet
- New Text DocumentDocument1 pageNew Text DocumentdeaaannnnnnNo ratings yet
- Clinical Teaching Two-Week Rotation PlanDocument9 pagesClinical Teaching Two-Week Rotation PlanMarj Herrera0% (1)
- The Pre-Tox Protocol How To Prepare Your Body For DetoxificationDocument13 pagesThe Pre-Tox Protocol How To Prepare Your Body For DetoxificationSabrinaHaldemannNo ratings yet
- 15 Jaw Dropping Health Benefits of Papaya LeafDocument12 pages15 Jaw Dropping Health Benefits of Papaya LeafAireLibreNo ratings yet
- Pathology of Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Romeo Rivera Jr.Document1 pagePathology of Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Romeo Rivera Jr.romeo riveraNo ratings yet
- Hallmark Signs and Symptoms PDFDocument6 pagesHallmark Signs and Symptoms PDFjjNo ratings yet
- What Says Doctors About Kangen WaterDocument13 pagesWhat Says Doctors About Kangen Waterapi-342751921100% (2)
- Leukemia: Sucaldito, Jean Lizette Pulmones, Krystal Fe NicoleDocument27 pagesLeukemia: Sucaldito, Jean Lizette Pulmones, Krystal Fe NicoleKrystal PulmonesNo ratings yet
- Pinyin Dictionary M To e A5c1Document237 pagesPinyin Dictionary M To e A5c1Zianaly JeffryNo ratings yet
- Case 21-2012: A 27-Year-Old Man With Fatigue, Weakness, Weight Loss, and Decreased LibidoDocument13 pagesCase 21-2012: A 27-Year-Old Man With Fatigue, Weakness, Weight Loss, and Decreased Libidodamian velmonteNo ratings yet
- DDs of Fever With RashDocument18 pagesDDs of Fever With RashEBNo ratings yet
- Urinary System15Document47 pagesUrinary System15Michael John PaderesNo ratings yet
- About Flower RemediesDocument8 pagesAbout Flower RemediesPunit K MannNo ratings yet
- Enterobacteriaceae (Upload)Document48 pagesEnterobacteriaceae (Upload)Ibn Ubaidullah100% (1)
- Systemic Inflammatory Response SyndromeDocument43 pagesSystemic Inflammatory Response SyndromeherdikoshalatinNo ratings yet
- Nclex RN GI & Burns & FracturesDocument87 pagesNclex RN GI & Burns & Fracturesgraceface55100% (4)
- Alexithymia ArticleDocument14 pagesAlexithymia ArticleDomingo MosqueraNo ratings yet
- Bakteri Anaerob: Morfologi, Fisiologi, Epidemiologi, Diagnosis, Pemeriksaan Sy. Miftahul El J.TDocument46 pagesBakteri Anaerob: Morfologi, Fisiologi, Epidemiologi, Diagnosis, Pemeriksaan Sy. Miftahul El J.TAlif NakyukoNo ratings yet
- Facial and Mandibular FracturesDocument24 pagesFacial and Mandibular FracturesahujasurajNo ratings yet
- Case Report Juliet Closed Fracture Middle of The Left FemurDocument28 pagesCase Report Juliet Closed Fracture Middle of The Left FemurraniNo ratings yet
- Interviewing Skills for Filipino Medical LanguageDocument4 pagesInterviewing Skills for Filipino Medical LanguageMikmik DGNo ratings yet
- HOMEOPATIADocument2 pagesHOMEOPATIADominic NedelcuNo ratings yet
- STDs-Sexually Transmitted Diseases & Infections GuideDocument11 pagesSTDs-Sexually Transmitted Diseases & Infections GuideYoon Pwint PhyuNo ratings yet
- Case Study Final DraftDocument15 pagesCase Study Final Draftapi-608049224No ratings yet
- Frozen Shoulder ExercisesDocument7 pagesFrozen Shoulder ExercisesSumon PhysioNo ratings yet
- Reading Unit 9 CardiologyDocument4 pagesReading Unit 9 CardiologyChristian SilvaNo ratings yet
- Health Fitness in Motion: A Community Engagement Proposal For Locality of Gasak Foster Health AwarenessDocument3 pagesHealth Fitness in Motion: A Community Engagement Proposal For Locality of Gasak Foster Health AwarenessJanna MangaliliNo ratings yet
- Early Identification and Referral of Students in DistressDocument20 pagesEarly Identification and Referral of Students in DistressAndrea WheelerNo ratings yet
- Reduce Fast Food Intake QuestionnaireDocument3 pagesReduce Fast Food Intake QuestionnaireAsrulSupuNo ratings yet
- Internship ReportDocument80 pagesInternship ReportSafa AliNo ratings yet