Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Poc Scoliosis
Uploaded by
Sugar Capule - Manuel0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
88 views20 pagesScolio
Original Title
POC SCOLIOSIS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentScolio
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
88 views20 pagesPoc Scoliosis
Uploaded by
Sugar Capule - ManuelScolio
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 20
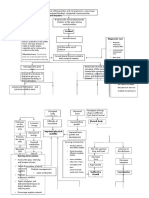
SCOLIOSIS
It is the lateral curvature of the spine may
occur in the thoracic, lumbar, or
thoracolumbar segment.
The curve may be convex to the right (more
common in thoracic curves) or to the left
(more common in lumbar curves)
Rotation of the vertebrae column around its
axis occurs and may cause rib cage deformity.
Functional
Structural
Congenital
Neuromuscular
Degenerative
Idiopathic
Structural
Nonstructural
A tilted head that does not line up over the
hips
Protruding shoulder blades
Asymmetrical waist line one hip or shoulder
that is higher than the other, causing an
uneven hem or shirt line
Uneven neckline
A sideways lean- leaning more to one side
than the other
In developing girls, breast appear to be
unequal in size
Rib hump one side of the upper back is
higher than the other when the child bends
over, knees together, with the arms dangling
down
Severe scoliosis can cause back pain and
difficulty breathing.
-Mild scoliosis - <25 degrees
-Moderate scoliosis between 25 and 40
degrees
-Dangerous 40 degrees or more
Severe scoliosis 70 degrees
Very severe over 100 degrees
Adams forward bending test patient place her palms
together and slowly bend forward, feet together and knees
straight while dangling the arms and keeping her head
down.
Scoliometer - can be used to measure and
estimate the rotation of the spinal curve.
X-ray of the spine may be taken to get a more
precise measurement of the spinal curve.
Cobb method calculates the degree of the
curve
MRI identify spinal cord and brain stem
abnormalities.
MRI identify spinal cord and brain stem abnormalities.
In the physical exam, the doctor will observe
posture, range of motion, and physical
condition, noting any movements that cause
pain. The doctor will feel the spine, note its
curvature and alignment, and feel for muscle
spasm.
During the neurological exam, the doctor will
test reflexes, muscle strength, other nerve
changes, and pain spread. This is all to get a
better picture of general health.
Congenital Scoliosis
Disturbance in vertebral development during six to eight weeks of embryonic
development
Failure of formation
Failure of segmentation
Absence of portion
of the vertebra.
-hemivertebra
(absence of the
whole side of
vertebrae).
-wedge
vertebrae(missing
only one portion of
the vertebrae).
Absence of normal separation between vertebrae.
Anomalies and neurologic complications if the spine is involved.
Absence of normal separation between vertebrae.
Anomalies and neurologic complications if the spine is involved.
Absence of normal separation between vertebrae.
Anomalies and neurologic complications if the spine is involved.
Absence of normal
separation between
vertebrae.
Anomalies and
neurologic
complications if the
spine is involved.
Neuromuscular Scoliosis Neuropathic/Myopathic
dse.( Cerebral palsy, Myodysplasia poliomyelitis) C-
shaped curved from the cervical to the sacral region.
Idiopathic Scoliosis- no known cause has
been established. Considering hereditary
(mother-daugther) but identical twins are not
uniformly affected.
Brace management goal is to prevent
progression of the curve. Yamamoto,
Milwaukee
Cast: Rizzers jacket, Minerva(not commonly
used)
Traction: Halo-pelvic, Halo-femoral, Cotrels
Surgery: Spinal fusion
Prepare the patient for casting or immobilization
procedure by showing materials to be used and describing
procedure in age-appropriate terms.
Promote comfort with proper fit of brace or cast.
Provide opportunity for the child to express fears and ask
questions about deformity and brace wear.
Assess skin integrity under and around the brace or cast
frequently.
Provide good skin care to prevent breakdown around any
pressure areas.
Instruct the patient to examine brace daily for
signs of loosening or breakage.
Instruct patient to wear cotton shirt under brace
to avoid rubbing.
Instruct about which previous activities can be
continued in the brace.
Provide a peer support person when possible so
the child can associate positive outcomes and
experiences from others.
Promoting positive body image
Encourage patient to express feelings and concerns about body
image.
Encourage patient to express concerns about wearing a brace.
Discuss options for brace wearing .
Encourage patient to discuss scoliosis with his/her peers,
including disease process and treatment.
Provide a peer support when possible so the child can associate
positive outcomes and expression from others.
You might also like
- Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Lenke's Classification Type 3 ADocument49 pagesAdolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Lenke's Classification Type 3 AAndi HumairahNo ratings yet
- Spinal Dysraphisms-Congenital Spinal Cord AbnormalitiesDocument43 pagesSpinal Dysraphisms-Congenital Spinal Cord Abnormalitiesrizki giofaniNo ratings yet
- Classification of Adolescent Idiopathic ScoliosisDocument4 pagesClassification of Adolescent Idiopathic ScoliosisBangkit PrimayudhaNo ratings yet
- AO Spine Textbook Comprehensive Overview On Surgical Management of The Spine by Michael P .Steinmetz 2020Document631 pagesAO Spine Textbook Comprehensive Overview On Surgical Management of The Spine by Michael P .Steinmetz 2020Alexandru CalinNo ratings yet
- Sma SyndromeDocument34 pagesSma SyndromeElandha PutriNo ratings yet
- Axial Plane Analysis of Lenke 1A Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis As An Aid To Identify Curve Characteristics - Atmaca Et Al. 2014Document9 pagesAxial Plane Analysis of Lenke 1A Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis As An Aid To Identify Curve Characteristics - Atmaca Et Al. 2014Mohammad KaramNo ratings yet
- Skeletal Dysplasias & Congenital MalformationsDocument366 pagesSkeletal Dysplasias & Congenital MalformationsCarlos Hernan Castañeda RuizNo ratings yet
- Sindromul Leser-TrelatDocument3 pagesSindromul Leser-Trelatvecerzan_lilianaNo ratings yet
- Meningococcal Meningitis - DR Ooi Phaik YeeDocument66 pagesMeningococcal Meningitis - DR Ooi Phaik YeeNg Chee KeongNo ratings yet
- Broncho PneumoniaDocument46 pagesBroncho PneumoniaAfrianzah Sevenfoldism100% (1)
- Cancerul Bronhopulmonar: Universitatea de Medicina Si Farmacie "Gr. T. Popa" IasiDocument60 pagesCancerul Bronhopulmonar: Universitatea de Medicina Si Farmacie "Gr. T. Popa" IasiPaduraru CalinNo ratings yet
- Infanticide. NeonaticideDocument29 pagesInfanticide. NeonaticidedewiulfaNo ratings yet
- Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Staging by CT and MRIDocument134 pagesNasopharyngeal Carcinoma Staging by CT and MRIإسلام الجزيريNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination of SpleenDocument5 pagesPhysical Examination of SpleenRatusweethella Intan Yudagrahania PuspitaNo ratings yet
- Approach To The Patient With Rheumatic DiseaseDocument11 pagesApproach To The Patient With Rheumatic DiseasetedplushNo ratings yet
- Forensic TraumatologyDocument31 pagesForensic TraumatologyZulhida YuniNo ratings yet
- Gallstone Ileus PDFDocument4 pagesGallstone Ileus PDFmonika100% (1)
- AO - Trans Obturator Technique Versus Suburethral Tape PDFDocument15 pagesAO - Trans Obturator Technique Versus Suburethral Tape PDFGustavo flores quispeNo ratings yet
- Tetanus PDFDocument10 pagesTetanus PDFVina MuspitaNo ratings yet
- Urethral Injuries: Ahmed S. ZugailDocument56 pagesUrethral Injuries: Ahmed S. Zugailmanoj bhartiNo ratings yet
- Exemplu Audit ClinicDocument16 pagesExemplu Audit ClinicVioleta GeileanuNo ratings yet
- Meningitis and Acute MeningococcemiaDocument16 pagesMeningitis and Acute Meningococcemiaalfaz lakhaniNo ratings yet
- Damage Control OrthopaedicsDocument16 pagesDamage Control OrthopaedicsPatrick LukitoNo ratings yet
- Krok 2 2002-2003 HygieneDocument8 pagesKrok 2 2002-2003 HygieneAli ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- Krok 1anatomy2Document1 pageKrok 1anatomy2Sandeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Gallstone Disease and Acute Cholecystitis MADDocument21 pagesGallstone Disease and Acute Cholecystitis MADMuhammad AbdurrahmanNo ratings yet
- C Difficile DiarrheaDocument12 pagesC Difficile DiarrheaSi vis pacem...No ratings yet
- Alterations in The Surgical Patient Updated 2010Document122 pagesAlterations in The Surgical Patient Updated 2010zorrotranNo ratings yet
- Spina BifidaDocument35 pagesSpina BifidaConstanzza Arellano LeivaNo ratings yet
- Hallux Valgus SXDocument569 pagesHallux Valgus SXandi100% (2)
- Summary of Clinical Tests and Signs in Orthopedics - EpomedicineDocument2 pagesSummary of Clinical Tests and Signs in Orthopedics - EpomedicineSubhajitPaulNo ratings yet
- Scoliosis: Laguna College San Pablo CityDocument5 pagesScoliosis: Laguna College San Pablo CitychristianjomariNo ratings yet
- ScoliosisDocument18 pagesScoliosisMj EnofnaNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation ScoliosisDocument7 pagesCase Presentation ScoliosisKhrizjan RebloraNo ratings yet
- Scoliosis, Kyphosis, LordosisDocument54 pagesScoliosis, Kyphosis, LordosisMj Briones100% (1)
- Scolio SIS: Submitted ToDocument10 pagesScolio SIS: Submitted Tojean thereseNo ratings yet
- Pathway - Skoliosis GROUPDocument12 pagesPathway - Skoliosis GROUPAnonymous NZTQVgjaNo ratings yet
- ScoliosisDocument3 pagesScoliosisannkramNo ratings yet
- Scoliosis Disease OverviewDocument7 pagesScoliosis Disease OverviewReema Akberali nooraniNo ratings yet
- Types of Spine Curvature DisordersDocument7 pagesTypes of Spine Curvature DisordersNicu MacariNo ratings yet
- Scoliosis Clinical & ExerciseDocument14 pagesScoliosis Clinical & ExercisePurohit_RNo ratings yet
- Scoliosis: By: Manilyn B. Lin Bsn-IiiDocument13 pagesScoliosis: By: Manilyn B. Lin Bsn-IiiWillie100% (1)
- ScoliosisDocument25 pagesScoliosisshanel18100% (1)
- Scoliosis ReportingDocument13 pagesScoliosis ReportingJULIENNE CHYLA IBENo ratings yet
- Share 'DEFORMITIES - PPTX'Document105 pagesShare 'DEFORMITIES - PPTX'Hunaid 1000No ratings yet
- Anomalies of Skeletal System-1Document44 pagesAnomalies of Skeletal System-1Meena KoushalNo ratings yet
- ScoliosisDocument4 pagesScoliosisDharline Abbygale Garvida AgullanaNo ratings yet
- Scoliosis Surgery IannnDocument8 pagesScoliosis Surgery IannnAnie ZacariasNo ratings yet
- Scoliosis: Spinal Curvature, KyphoscoliosisDocument3 pagesScoliosis: Spinal Curvature, Kyphoscoliosisiamweena17No ratings yet
- What Is KyphosisDocument6 pagesWhat Is Kyphosisسانو روديلNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of ScoliosisDocument6 pagesAnatomy of ScoliosisDaniel MañalacNo ratings yet
- About:: Birth Defects Muscular Dystrophy, Cerebral Palsy Marfan's DiseaseDocument4 pagesAbout:: Birth Defects Muscular Dystrophy, Cerebral Palsy Marfan's DiseaseAbie BeyNo ratings yet
- Anomalies of Skeletal System-1Document44 pagesAnomalies of Skeletal System-1Meena Koushal100% (1)
- A Comprehensive Study On Marma PointsDocument9 pagesA Comprehensive Study On Marma Pointsaaronjdriver2248100% (1)
- ScoliosisDocument9 pagesScoliosisLorebell80% (5)
- CARE of ADOLESCENTSDocument15 pagesCARE of ADOLESCENTSaprilkate banagodosNo ratings yet
- ScoliosisDocument3 pagesScoliosisYoshizawa MiharuNo ratings yet
- ScoliosisDocument5 pagesScoliosisIbe JulienneNo ratings yet
- Adolescent Idiopathic ScoliosisDocument8 pagesAdolescent Idiopathic ScoliosismoechielmoechieNo ratings yet
- Scoliosis and KyphosisDocument5 pagesScoliosis and KyphosisEufrasia VictaNo ratings yet
- NCP Copd AirwayDocument2 pagesNCP Copd AirwaySugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Goal Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Goal Intervention Rationale EvaluationSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- NCP TetanusDocument2 pagesNCP TetanusSugar Capule - Manuel0% (1)
- Thromboangiitis Obliterans: Also Known AsDocument7 pagesThromboangiitis Obliterans: Also Known AsSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- Femoral Neck FractureDocument21 pagesFemoral Neck FractureSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Goal Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Goal Intervention Rationale EvaluationSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord Injury: Philippine Orthopedic Center Group1 Section B "Reydi Badi"Document11 pagesSpinal Cord Injury: Philippine Orthopedic Center Group1 Section B "Reydi Badi"Sugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- NCP PTBDocument2 pagesNCP PTBMack Jhed AnarconNo ratings yet
- Nursing TheoristDocument1 pageNursing TheoristSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- Lapchole InstDocument4 pagesLapchole InstSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- CholelithiasisDocument11 pagesCholelithiasisSugar Capule - Manuel100% (1)
- Dermatitis HerpetiformisDocument11 pagesDermatitis HerpetiformisSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology CKDDocument2 pagesPathophysiology CKDSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- 3A Non Therapeutic CommDocument11 pages3A Non Therapeutic CommSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- HYEPERICUMDocument2 pagesHYEPERICUMSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- CA PsoriasisDocument3 pagesCA PsoriasisSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The GallbladderDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The GallbladderSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- FNCPDocument26 pagesFNCPSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- CHPT 70 Respiratory Part 2Document56 pagesCHPT 70 Respiratory Part 2helen brockNo ratings yet
- Journal ReadingDocument3 pagesJournal ReadingRachelle Anne LetranNo ratings yet
- Thesis OsteopathyDocument6 pagesThesis Osteopathygbv8rcfq100% (1)
- SDMS ID: P2010/0496-001 2.9/09WACS Title: Management of Postpartum HaemorrhageDocument11 pagesSDMS ID: P2010/0496-001 2.9/09WACS Title: Management of Postpartum HaemorrhageYwagar YwagarNo ratings yet
- (Serbian Journal of Dermatology and Venereology) National Guidelines For The Treatment of Atopic DermatitisDocument25 pages(Serbian Journal of Dermatology and Venereology) National Guidelines For The Treatment of Atopic DermatitisFebtri IRnawitaNo ratings yet
- Poison and Antidote ChartDocument5 pagesPoison and Antidote ChartSusanne Mae Gonzales50% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan CholecystectomyDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Cholecystectomyderic87% (23)
- Addendum Temocillin Breakpoints and AST 2020Document3 pagesAddendum Temocillin Breakpoints and AST 2020Marcelo UGNo ratings yet
- Manual Terapia DigitalDocument38 pagesManual Terapia DigitalPaolaQuitian0% (1)
- Cytomegalovirus Infection: Dr. Hendra Purnasidha Bagaswoto, M.SC, Sp.A SMF Anak RSUP Dr. Soeradji Tirtonegoro KlatenDocument40 pagesCytomegalovirus Infection: Dr. Hendra Purnasidha Bagaswoto, M.SC, Sp.A SMF Anak RSUP Dr. Soeradji Tirtonegoro KlatenDonniehh Assassintilldeath NothinglastforeverNo ratings yet
- Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone Secretion SIADHDocument14 pagesSyndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone Secretion SIADHbhatubim100% (1)
- Drug Study Er MedsDocument12 pagesDrug Study Er MedsJerald S. OlaloNo ratings yet
- NSG 117 PerfusionDocument55 pagesNSG 117 PerfusionAnonymous UJEyEsNo ratings yet
- Nursing Pharmacology Immunity Study GuideDocument18 pagesNursing Pharmacology Immunity Study GuideChelsea SmithNo ratings yet
- Ospe & Osce-1Document9 pagesOspe & Osce-1AMY LALRINGHLUANI M.Sc. Child Health (Paediatric ) NursingNo ratings yet
- SixthEditionSyllabus2008 01 23Document44 pagesSixthEditionSyllabus2008 01 23kresennnNo ratings yet
- VRP One Page Handout 3-11-10Document1 pageVRP One Page Handout 3-11-10Jennifer TankersleyNo ratings yet
- Abdominal TuberculosisDocument9 pagesAbdominal TuberculosisImmanuelNo ratings yet
- High-Risk Prenatal Client - Hiv - AidsDocument20 pagesHigh-Risk Prenatal Client - Hiv - AidsMichael Angelo SeñaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Carbocisteine, Paracetamol, Ampicillin. GentamicinDocument4 pagesDrug Study: Carbocisteine, Paracetamol, Ampicillin. Gentamicinpammy28No ratings yet
- Motion To DismissDocument16 pagesMotion To DismissBasseemNo ratings yet
- Hyperthyroidism in Children and Adolescents: What Is The Thyroid Gland?Document3 pagesHyperthyroidism in Children and Adolescents: What Is The Thyroid Gland?Neha ReddyNo ratings yet
- MCQ Anaethesia Posting Group 4 2014Document4 pagesMCQ Anaethesia Posting Group 4 2014Law YouNo ratings yet
- Trichomonas Rapid Test: CLIA Complexity: WaivedDocument8 pagesTrichomonas Rapid Test: CLIA Complexity: WaivedRabecca TobingNo ratings yet
- Xv. Discharge Plan METHODS - Medication, Exercise, Treatment, Health Teaching, Out-Patient, Diet, Sexuality/SpiritualDocument4 pagesXv. Discharge Plan METHODS - Medication, Exercise, Treatment, Health Teaching, Out-Patient, Diet, Sexuality/SpiritualMichael Bon MargajaNo ratings yet
- GBS Review2Document64 pagesGBS Review2Vladimir BasurtoNo ratings yet
- Degenerative Disc DiseaseDocument13 pagesDegenerative Disc DiseaseSisuka CeritaNo ratings yet
- Duties and Responsibilities of Allied Health PersonalDocument41 pagesDuties and Responsibilities of Allied Health PersonalPushpinder Singh Sandhu100% (1)
- Introduction To Pharmacology AntibioticDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Pharmacology AntibioticZaira Reine SantosNo ratings yet
- English Course Guide Ws 2017Document165 pagesEnglish Course Guide Ws 2017César TapiaNo ratings yet