Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Antigen-Antibody Interactions: Principles of Immunology
Uploaded by
summiyaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Antigen-Antibody Interactions: Principles of Immunology
Uploaded by
summiyaCopyright:
Available Formats
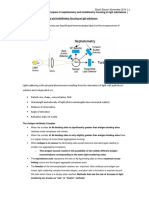
Principles of Immunology
Antigen-Antibody Interactions
4/25/06
Word/Terms List
Agglutinin
EIA
Equivalence zone
FIA
Immunodiffusion
Immunoelectrophoresis
RIA
Titer
Affinity = attractive and repulsive forces
Ab
Ag
High Affinity
Ab
Ag
Low Affinity
Affinity
Strength of the reaction between a single antigenic
determinant and a single Ab combining site
Specificity
The ability of an individual antibody
combining site to react with only one
antigenic determinant.
The ability of a population of antibody
molecules to react with only one antigen.
Cross Reactivity
The ability of an individual Ab combining site to react with
more than one antigenic determinant.
The ability of a population of Ab molecules to react with
more than one Ag
Anti-A
Ab
Ag A
Anti-A
Ab
Ag B
Shared epitope
Anti-A
Ab
Ag C
Similar epitope
Cross reactions
Factors Affecting Measurement of
Ag/Ab Reactions
Affinity
Avidity
Ag:Ab ratio
Physical form of Ag
Ab excess Ag excess
Equivalence Lattice formation
Tests Based on Ag/Ab Reactions
All tests based on Ag/Ab reactions will
have to depend on lattice formation
or they will have to utilize ways to
detect small immune complexes
All tests based on Ag/Ab reactions
can be used to detect either Ag or Ab
Agglutination Tests
Lattice Formation
Agglutination/Hemagglutination
Definition - tests that have as their endpoint
the agglutination of a particulate antigen
Agglutinin/hemagglutinin
+
Qualitative agglutination test
Ag or Ab
Agglutination/Hemagglutination
Quantitative agglutination test
Titer
Prozone
1
/
2
1
/
4
1
/
8
1
/
1
6
1
/
3
2
1
/
6
4
1
/
1
2
8
1
/
2
5
6
1
/
5
1
2
1
/
1
0
2
4
P
o
s
.
N
e
g
.
Titer
64
8
512
<2
32
128
32
4
Patient
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Agglutination/Hemagglutination
Definition
Qualitative test
Quantitative test
Applications
Blood typing
Bacterial infections
Fourfold rise in titer
Practical considerations
Easy
Semi-quantitative
1
/
2
1
/
4
1
/
8
1
/
1
6
1
/
3
2
1
/
6
4
1
/
1
2
8
1
/
2
5
6
1
/
5
1
2
Passive Agglutination/Hemagglutination
Definition - agglutination test done with a
soluble antigen coated onto a particle
+
Applications
Measurement of antibodies to soluble antigens
Agglutination/Hemagglutination Inhibition
Definition - test based on the inhibition of agglutination due
to competition with a soluble Ag
+
Prior to Test
+
+
Test
Patients sample
Agglutination/Hemagglutination Inhibition
Applications
Measurement of soluble Ag
Practical considerations
Same as agglutination test
Definition
Precipitation Tests
Lattice Formation
Radial Immunodiffusion
Interpretation
Diameter of ring
is proportional to
the
concentration
Quantitative
Ig levels
Method
Ab in gel
Ag in a well
Ag Concentration
D
i
a
m
e
t
e
r
2
Ag Ag Ag Ag
Ab in gel
Immunoelectrophoresis
Method
Ags are separated by electrophoresis
Interpretation
Precipitin arc represent individual antigens
Ag
-
+
Ag
Ab
Ag
Ab
Immunoelectrophoresis
Method
Interpretation
Qualitative
Relative concentration
Radioimmuoassays (RIA)
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent
Assays (EIA)
Lattice formation not required
Competitive RIA/ELISA for Ag
Method
Determine
amount of Ab
needed to bind to
a known amount
of labeled Ag
+
Prior to Test
Labeled
Ag
+
Test
+
Patients
sample
Labeled
Ag
+
Use predetermined
amounts of labeled Ag
and Ab and add a
sample containing
unlabeled Ag as a
competitor
Solid Phase Non-Competitive RIA/ELISA
Ab detection
Immobilize Ag
Incubate with
sample
Add labeled anti-Ig
Amount of labeled
Ab bound is
proportional to
amount of Ab in the
sample
Solid
Phase
Ag
Immobilized
Ab in
Patients
sample
Labeled
Anti-Ig
Solid Phase Non-Competitive RIA/ELISA
Ag detection
Immobilize Ab
Incubate with sample
Add labeled antibody
Amount of labeled Ab
bound is proportional to
the amount of Ag in the
sample
Solid
Phase
Ag
Immobilized
Ag in
Patients
sample
Labeled
Ab
Tests for Cell Associated
Antigens
Lattice formation not required
Immunofluorescence
Direct
Ab to tissue Ag is labeled with fluorochrome
Ag
Fluorochrome
Labeled Ab
Tissue Section
Immunofluorescence
Indirect
Ab to tissue Ag is
unlabeled
Fluorochrome-labeled
anti-Ig is used to
detect binding of the
first Ab.
Ag
Fluorochrome
Labeled Anti-Ig
Tissue Section
Unlabeled
Ab
Qualitative to Semi-
Quantitative
Assays Based on
Complement
Lattice formation not required
Complement Fixation
Ag mixed with test serum to be assayed for Ab
Standard amount of complement is added
Erythrocytes coated with Abs is added
Amount of erythrocyte lysis is determined
Ag
Patients
serum
Ag No Ag
Ag
You might also like
- Methods For Preclinical Evaluation of Bioactive Natural ProductsFrom EverandMethods For Preclinical Evaluation of Bioactive Natural ProductsNo ratings yet
- A Laboratory Manual of Physical PharmaceuticsFrom EverandA Laboratory Manual of Physical PharmaceuticsRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (2)
- Ag-Ab Reactions Tests For Ag-Ab ReactionsDocument36 pagesAg-Ab Reactions Tests For Ag-Ab ReactionssummiyaNo ratings yet
- Serology NewDocument116 pagesSerology NewFarlogyNo ratings yet
- Principles of Immunoassay TechniquesDocument35 pagesPrinciples of Immunoassay TechniquesBRENDA NHERERANo ratings yet
- Immuno As SayDocument33 pagesImmuno As SayShankar RajNo ratings yet
- Antibody and Soluble Antigen Precipitation Reactions PrecipitinsDocument25 pagesAntibody and Soluble Antigen Precipitation Reactions PrecipitinsRakin Bin RaihanNo ratings yet
- Antigen-Antibody Interactions: Classification & TestsDocument10 pagesAntigen-Antibody Interactions: Classification & TestsPalagiri MadhuNo ratings yet
- Agglutination & NTII - PPT 28.04.Document31 pagesAgglutination & NTII - PPT 28.04.Meenakshisundaram CNo ratings yet
- Ag Ab ReactionsDocument43 pagesAg Ab ReactionsNiyaz ShahriarNo ratings yet
- ElisaDocument76 pagesElisaSobha MatthewNo ratings yet
- Antigen - Antibody Reactions: DR - Gomathi M.D.Document22 pagesAntigen - Antibody Reactions: DR - Gomathi M.D.Meenakshisundaram CNo ratings yet
- Antigen-Antibody Reactions: Key Concepts and Types ExplainedDocument37 pagesAntigen-Antibody Reactions: Key Concepts and Types ExplainedJennifer DixonNo ratings yet
- Agglutination TestDocument34 pagesAgglutination TestAJAYNo ratings yet
- Agglutination and PrecipitationDocument35 pagesAgglutination and PrecipitationIsak Isak IsakNo ratings yet
- SEO SerologyDocument43 pagesSEO SerologyAlvin OccianoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Antigen-Antibody Reaction & Diagnostic TestsDocument30 pagesLecture 5 - Antigen-Antibody Reaction & Diagnostic TestsJeanPaule JoumaaNo ratings yet
- Principles of nephelometry and turbidimetry focusing on IgG subclassesDocument11 pagesPrinciples of nephelometry and turbidimetry focusing on IgG subclassesalexis mae IsonNo ratings yet
- 15.antigen - Antibody Reactions Part 2Document34 pages15.antigen - Antibody Reactions Part 2Manas DixitNo ratings yet
- 10 Immunological TestsDocument71 pages10 Immunological Testsozerbilge24No ratings yet
- Serologic ProceduresDocument77 pagesSerologic ProceduresWynlor AbarcaNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (Elisa) : Definition and TypesDocument10 pagesEnzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (Elisa) : Definition and TypesPalagiri MadhuNo ratings yet
- Ag Ab Reaction - 30th August 2013Document34 pagesAg Ab Reaction - 30th August 2013Rajkishor YadavNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 - Ag Ab Reactions PDFDocument34 pagesLecture 10 - Ag Ab Reactions PDFUPENDRA KUMAR SinghNo ratings yet
- (MID) IMMUNOSERO - Chapter 10 - Labeled ImmunoassaysDocument4 pages(MID) IMMUNOSERO - Chapter 10 - Labeled ImmunoassaysAisle Malibiran PalerNo ratings yet
- Antigenandantibodyreaction 120515041533 Phpapp01Document44 pagesAntigenandantibodyreaction 120515041533 Phpapp01Azhar Clinical Laboratory TubeNo ratings yet
- Immunology and Serology Part 3Document117 pagesImmunology and Serology Part 3UnixoftNo ratings yet
- Radioimmunoassay & Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay: M K Unnikrishnan (Aug 2006)Document16 pagesRadioimmunoassay & Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay: M K Unnikrishnan (Aug 2006)May AbusalahNo ratings yet
- Ag-Ab ReactionsDocument27 pagesAg-Ab ReactionsSumihar PasaribuNo ratings yet
- Immunodiffusion Principles and ApplicationDocument29 pagesImmunodiffusion Principles and ApplicationBassem AhmedNo ratings yet
- 4.prinsip Pemeriksaan ElisaDocument37 pages4.prinsip Pemeriksaan ElisaDorotea NinaNo ratings yet
- Ag-Ab Reactions in Serological DiagnosisDocument46 pagesAg-Ab Reactions in Serological Diagnosissazia gaurNo ratings yet
- LAB PROCEDURES BLOOD BANKINGDocument76 pagesLAB PROCEDURES BLOOD BANKINGWenz MacuteNo ratings yet
- Antigen - Antibody Reactions Part 3Document25 pagesAntigen - Antibody Reactions Part 3Manas DixitNo ratings yet
- Labeled ImmunoassaysDocument6 pagesLabeled ImmunoassaysAngelica Mae LasamNo ratings yet
- Antibody Screening - Kupang - 2016Document59 pagesAntibody Screening - Kupang - 2016yuni.kartika.ndoen92No ratings yet
- Ag - Ag InteractionDocument22 pagesAg - Ag Interactionaaryasuxena16No ratings yet
- Elisa PresentationDocument26 pagesElisa Presentationanitasingh714100% (1)
- RadioimmunoassayDocument16 pagesRadioimmunoassaysr_bakegNo ratings yet
- SerologyDocument34 pagesSerologyJennifer HerediaNo ratings yet
- RiaDocument57 pagesRiagannysun100% (4)
- Antiglobulin TestDocument28 pagesAntiglobulin TestAvi Verma100% (1)
- RadioimmunoassaysDocument16 pagesRadioimmunoassaysSonali DasNo ratings yet
- Antigen and Antibody ReactionDocument43 pagesAntigen and Antibody ReactionSubash SubaNo ratings yet
- Methods of Hormone AnalysisDocument23 pagesMethods of Hormone AnalysisKumar SaketNo ratings yet
- ELISA (Aslam Sir), Pharmaceutical BiotechnologyDocument8 pagesELISA (Aslam Sir), Pharmaceutical Biotechnologypolashsd091No ratings yet
- Ag-Ab ReactionsDocument44 pagesAg-Ab ReactionsMuratNo ratings yet
- Antigen Antibody Reaction 2014Document48 pagesAntigen Antibody Reaction 2014Arko Roy0% (1)
- Ag - Ab ReactionsDocument50 pagesAg - Ab ReactionsRangineni PradaNo ratings yet
- Immunological ReationsDocument76 pagesImmunological ReationsSaba AmanNo ratings yet
- Radioimmunoassay & Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent AssayDocument16 pagesRadioimmunoassay & Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent AssayPavan KumarNo ratings yet
- Antigen - Antibody Reactions: Dr.D.BinduDocument46 pagesAntigen - Antibody Reactions: Dr.D.Bindubindu dhanapalNo ratings yet
- Ag Ab ReactionDocument31 pagesAg Ab ReactionmaniiiiiiiiNo ratings yet
- Antigen-Antibody Reaction 1Document133 pagesAntigen-Antibody Reaction 1ShineeNo ratings yet
- Label ImmunoassayDocument92 pagesLabel ImmunoassayCherry Reyes-Principe100% (3)
- Serology Part1Document18 pagesSerology Part1Alina Mihaela MarianNo ratings yet
- Antigen Antibody Interactions: Serology Test: Serological Diagnostic TestsDocument44 pagesAntigen Antibody Interactions: Serology Test: Serological Diagnostic Testssultan khabeebNo ratings yet
- Radio Immuno As SayDocument3 pagesRadio Immuno As SaySai SridharNo ratings yet
- Radioimmunoassay PrinciplesDocument6 pagesRadioimmunoassay Principlesandi novrianiNo ratings yet
- Candida Urinary Tract Infections-TreatmentDocument10 pagesCandida Urinary Tract Infections-TreatmentsummiyaNo ratings yet
- Candida UTI DiagnosisDocument5 pagesCandida UTI DiagnosissummiyaNo ratings yet
- Update 2014, 7 Discontinuation of Salmonella Serology Test AKUHDocument1 pageUpdate 2014, 7 Discontinuation of Salmonella Serology Test AKUHsummiyaNo ratings yet
- Critically Ill Elderly Man with Disseminated Candidiasis Following Colonic SurgeryDocument20 pagesCritically Ill Elderly Man with Disseminated Candidiasis Following Colonic SurgerysummiyaNo ratings yet
- Candidiasis MedscapeDocument36 pagesCandidiasis MedscapesummiyaNo ratings yet
- C-Reactive Protein (CRP) : Mohammad Zeeshan Resident MicrobiologyDocument30 pagesC-Reactive Protein (CRP) : Mohammad Zeeshan Resident MicrobiologysummiyaNo ratings yet
- Candidemia in Neonatal ICU - Experience From A Tertiary Care HospitalDocument5 pagesCandidemia in Neonatal ICU - Experience From A Tertiary Care HospitalsummiyaNo ratings yet
- Candida UTI TreatmentDocument10 pagesCandida UTI TreatmentsummiyaNo ratings yet
- Candidemia in Neonatal ICU - Experience From A Tertiary Care HospitalDocument5 pagesCandidemia in Neonatal ICU - Experience From A Tertiary Care HospitalsummiyaNo ratings yet
- Trypanosoma MCQDocument2 pagesTrypanosoma MCQsummiya100% (2)
- Dengue Infection in Cancer Patients: Department of MedicineDocument18 pagesDengue Infection in Cancer Patients: Department of MedicinesummiyaNo ratings yet
- Vaccine Updates UkDocument4 pagesVaccine Updates UksummiyaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Patient Develops Mucormycosis After ChemotherapyDocument32 pagesDiabetes Patient Develops Mucormycosis After ChemotherapysummiyaNo ratings yet
- Cases in TransplantationDocument59 pagesCases in TransplantationsummiyaNo ratings yet
- Id SuggestionDocument2 pagesId SuggestionsummiyaNo ratings yet
- Case 8 TBDocument41 pagesCase 8 TBsummiyaNo ratings yet
- Bio SafetyDocument68 pagesBio SafetysummiyaNo ratings yet
- CASE FILES Hiv MeaslesDocument15 pagesCASE FILES Hiv MeaslessummiyaNo ratings yet
- Congenital Hydrocephalus Child With VP Shunt Obstruction And Ceftriaxone Resistant E. coli CSF InfectionDocument15 pagesCongenital Hydrocephalus Child With VP Shunt Obstruction And Ceftriaxone Resistant E. coli CSF InfectionsummiyaNo ratings yet
- Bio SafetyDocument68 pagesBio SafetysummiyaNo ratings yet
- An Unusual Cause of Osteomyelitis: DR Summiya NizamuddinDocument43 pagesAn Unusual Cause of Osteomyelitis: DR Summiya NizamuddinsummiyaNo ratings yet
- Blood Culture Collection 2Document14 pagesBlood Culture Collection 2summiyaNo ratings yet
- An Unusual Cause of Osteomyelitis: DR Summiya NizamuddinDocument43 pagesAn Unusual Cause of Osteomyelitis: DR Summiya NizamuddinsummiyaNo ratings yet
- Bacterial ShapesDocument28 pagesBacterial ShapessummiyaNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (AST)Document41 pagesAntimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (AST)summiya100% (1)
- 4-ZN StainDocument66 pages4-ZN StainsummiyaNo ratings yet
- Aspergillus and AspergillosisDocument35 pagesAspergillus and AspergillosissummiyaNo ratings yet
- Antigen-Antibody Interactions: Principles of ImmunologyDocument27 pagesAntigen-Antibody Interactions: Principles of ImmunologysummiyaNo ratings yet
- Molecular Cloning Technical GuideDocument40 pagesMolecular Cloning Technical GuideRNo ratings yet
- 2010 FulltextDocument410 pages2010 FulltextNajam Din SahitoNo ratings yet
- Colon 2014597 D FHTDocument4 pagesColon 2014597 D FHTyoohooNo ratings yet
- LWT - Food Science and TechnologyDocument8 pagesLWT - Food Science and TechnologyAzb 711No ratings yet
- NSABB Final Report Recommendations Evaluation Oversight Proposed Gain of Function Research May 2016Document109 pagesNSABB Final Report Recommendations Evaluation Oversight Proposed Gain of Function Research May 2016Jim Hoft100% (1)
- Essay On Physical SelfDocument2 pagesEssay On Physical Selfcmestrada03No ratings yet
- Antinfek 10HDocument20 pagesAntinfek 10Hmistytewest100% (1)
- Komiyama Et Al., (2008) Allometry, Biomass, and Productivity of Mangrove Forests A ReviewDocument11 pagesKomiyama Et Al., (2008) Allometry, Biomass, and Productivity of Mangrove Forests A ReviewVandhi Amali100% (1)
- Thailand Orchids Producer & Exporter Kultana Orchids Product ListDocument45 pagesThailand Orchids Producer & Exporter Kultana Orchids Product ListMalakh Raziel0% (2)
- General Biology 2 Budget of WorkDocument3 pagesGeneral Biology 2 Budget of WorkMaricris BalboaNo ratings yet
- Summary of Qualitative Tests (Pharmacognosy)Document8 pagesSummary of Qualitative Tests (Pharmacognosy)kidsaintfineNo ratings yet
- C Specialized GeneralBiology1 Sem1 Clas3 CellsinPlantand-AnimalTissue v2Document14 pagesC Specialized GeneralBiology1 Sem1 Clas3 CellsinPlantand-AnimalTissue v2ダギア メイ アニアNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument40 pagesCardiovascular SystemMudasir Hussain TuriNo ratings yet
- Neolithic RevolutionDocument40 pagesNeolithic RevolutionJoselito DemeterioNo ratings yet
- 02 Anatomy and Histology PLE 2019 RatioDocument69 pages02 Anatomy and Histology PLE 2019 RatioPatricia VillegasNo ratings yet
- Cosmeceutic ALS: Cosmetics and PharmaceuticalsDocument19 pagesCosmeceutic ALS: Cosmetics and PharmaceuticalssowjanyaNo ratings yet
- Ancient Healing Rods Reveal Secrets of PharaohsDocument28 pagesAncient Healing Rods Reveal Secrets of PharaohsMiguel Angelum100% (4)
- 4546-LacOperon InstsDocument14 pages4546-LacOperon InstsScribd_is_GreatNo ratings yet
- IN SEARCH OF SEXUAL ENHANCEMENT THROUGH PILLS AND DRUGSDocument16 pagesIN SEARCH OF SEXUAL ENHANCEMENT THROUGH PILLS AND DRUGSJakob AndradeNo ratings yet
- Mengenali Konflik Dalam Negosiasi Oleh: Zumaeroh: PendahuluanDocument47 pagesMengenali Konflik Dalam Negosiasi Oleh: Zumaeroh: PendahuluanrahmatNo ratings yet
- 1.4 - Diffusion and Osmosis - CrosswordPuzzleDocument1 page1.4 - Diffusion and Osmosis - CrosswordPuzzlemmssthNo ratings yet
- Lipid Movement BiochemDocument9 pagesLipid Movement BiochemCrowNo ratings yet
- Environmental Science: GE 15 - Subject Code: 1603Document18 pagesEnvironmental Science: GE 15 - Subject Code: 1603japheth louie m. gofredoNo ratings yet
- Non-symbiotic Nitrogen FixersDocument21 pagesNon-symbiotic Nitrogen Fixersrajiv pathakNo ratings yet
- UAS Writing For Discourse - 4 Pagi OkDocument1 pageUAS Writing For Discourse - 4 Pagi Oksalwa syabinaNo ratings yet
- Gene TherapyDocument1 pageGene TherapyJenevieve B. CañeteNo ratings yet
- The Anatomy, Physiology, and Pathophysiology of Muscular SystemDocument55 pagesThe Anatomy, Physiology, and Pathophysiology of Muscular SystemAnisaNo ratings yet
- Microbial Healing of Cracks in ConcreteDocument15 pagesMicrobial Healing of Cracks in ConcreteasdasdasdasNo ratings yet
- The Science of NeglectDocument20 pagesThe Science of NeglectdrdrtsaiNo ratings yet
- WCH03 01 Que 20180124Document16 pagesWCH03 01 Que 20180124Rameez Mazhar SiddiqiNo ratings yet