Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EKG Praktis
Uploaded by
Fyana Putri100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
105 views133 pagesGambaran ElektroCardioGram. Materi Kuliah dr Masrul Syafri.
Sekilas tentang EKG dan maknanya.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentGambaran ElektroCardioGram. Materi Kuliah dr Masrul Syafri.
Sekilas tentang EKG dan maknanya.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
105 views133 pagesEKG Praktis
Uploaded by
Fyana PutriGambaran ElektroCardioGram. Materi Kuliah dr Masrul Syafri.
Sekilas tentang EKG dan maknanya.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 133
Masrul Syafri
Pusat Jantung Regional
RS Dr M Jamil Padang
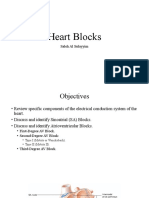
Anatomy of conduction system
Conduction system
SA Node
Internodal branch
AV Node
Hiss Bundle
Purkinje Fiber
Contraction
Electrical activity conversion to ECG
Basic Electrophysiology
The heart has two types of cells:
Electrical cells: Initiation and conduction of
impulses
Mechanical cells: Contraction in response to
stimulation
An EKG/ECG is a graphic representation
of electrical activity in the heart
Electrical activity precedes mechanical activity
Basic Electrophysiology
Polarization
The electrical charges in the cell are
balanced and ready for discharge
Depolarization
The discharge of energy and transfer of
electrical charges across the cell
membrane
Repolarization
The return of electrical charges to their
original state
Electrical Conduction System
Sinoatrial node (SA node)
Intra-atrial Pathways
Atrioventricular node (AV node)
Bundle of His
Left and Right Bundle Branches
Purkinjie Fibers
The Electrocardiogram ( ECG )
P wave : atrial
depolarisation
QRS complex :
ventricular
depolarisation
T wave : ventricular
repolarisation
Atrial repolarisation
hidden by QRS
P
Q
R
S
T
The P wave
The first wave form is called a P wave: it
represents Atrial depolarization.
It is gently rounded, and not larger than 2-
3 mm.
It is usually positive (above the isoelectric
line)
It should not be large, notched, or peaked
The QRS Complex
The QRS complex represents ventricular
depolarization.
The Q wave is the first negative deflection. It
should not be greater than 1mm wide or
larger than 1/3 height of R wave. There may
not be a Q wave in some cases.
The R wave is the first positive deflection
after the Q wave.
The S wave is the first negative deflection
after the R wave
The normal QRS complex should be < .12
sec.
The T wave
The T wave represents ventricular
repolarization.
It is usually positive, but can be negative
or biphasic.
It is usually the same polarity as the QRS
complex.
The PR Interval
The PR interval is measured from the
beginning of the P wave to the
beginning of the QRS complex.
The PR interal measures the beginning
of atrial depolarization through the
beginning of ventricular depolarization.
The normal PR interval is from .12-.20
seconds.
The QT Interval
The QT interval is measured from the
beginning of the Q wave to the end of the
T wave. This measures ventricular
depolarization and repolarization.
Any QT longer than .50 seconds can
predispose certain dangerous arrhythmias.
ST Segment
The ST segment is measured from the end of
the S wave to the beginning of the T wave.
The ST segment is normally isoelectric, or
curves slightly upwards into the T wave.
Horizontal or downsloping ST depression of 2
mm or more is abnormal, indicating ishemia.
ST segment elevation > 1mm indicates
myocardial infarction
Anatomy of ECG
Rhythm : Sinus rhythm
Rate : 60 100
P wave : Normal in configuration; precede each QRS
PR : Normal ( 0. 12 0.20 seconds )
QRS : Normal ( less than 0.12 seconds )
Normal ECG
P Wave
P Pulmonale
P Mitrale
PR Interval
QRS Complex
ST Segment
Important in:
Myocardial ischemia
Drugs & electrolyte
abnormality
Myocarditis & other
cardiac disease
T Wave
L V H
L V H
L V H
R V H
R V H
R V H
Rhythm : Regular
Rate : Usually normal
P wave : Sinus P wave present; one P wave to each QRS
PR : Prolonged ( greater than 0.20 seconds )
QRS : Normal
First-degree AV block
Rhythm : Irregular
Rate : Usually slow but can be normal
P wave : Sinus P wave present;
some not followed by QRS complexes
PR : Progressively lengthens
QRS : Normal
Second-degree AV block, Mobitz I
Rhythm : Regular usually;
can be irreguler if conduction ratios vary
Rate : Usually slow
P wave : Two, three, or four P waves before each QRS
PR : PR interval of beat with QRS is constant;
PR interval may be normal or prolonged
QRS : Normal if block in His bundle;
wide if block involves bundle branches
Second-degree AV block, Mobitz II
Rhythm : Regular
Rate : 40 60 if block in His bundle;
30 40 if block involves bundle branches
P wave : Sinus P wave present; bear no relationship to QRS;
can be found hidden in QRS complexes and T waves
PR : Varies greatly
QRS : Normal if block in His bundle;
wide if block involves bundle branches
Third-degree AV block
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome
Thank You
Coronary Arteries
Left Main Coronary Artery
- Left Anterior Descending Artery (LAD)
- Circumflex Artery (CX)
Right Coronary Artery (RCA)
Left Coronary Artery
Supplies blood to:
septum, the bundle branches and the left ventricle through the LAD and
CX..
Right Coronary Artery
Supplies blood to: Right Ventricle
Through Posterior descending branch supplies
blood to inferior and posterior of L. ventricle
Coronary Arteries
Can be variations in areas of heart supplied by Left and
Right CoronaryArteries
Conduction system blood supply
SA and AV nodes, Bundle of HIS and Bundle Branches
Precordial Septal Leads
V1 V2
Look at the Septum of the heart
The septal branch of the LAD supplies
blood to the septum
Septum contains the bundle of HIS and the
bundle branches
Occlusions in this branch produce:
2Type II heart block, 3 heart blocks.
Precordial Septal
Leads V1 - V2
Precordial
Anterior Leads
V3 V4
Look at the anterior wall of the left ventricle
The LAD (diagonal branch) supplies this
area
Occlusions can lead to LV dysfunction
CHF
Cardiogenic Shock
Precordial Anterior
Leads V3 - V4
Anterior-Septal Terminology
Lateral Precordial Leads
I,AVL,V5 V6
Faces lateral of the left ventricle
The circumflex supplies this area
AV nodal blocks can occur
Usually occur with other areas of infarct
Precordial Lateral
Leads V5 - V6
P Wave
P Pulmonale
P Mitrale
PR Interval
QRS Complex
ST Segment
T Wave
Normal Sinus Rhythm
Rhythm : Regular
Rate : 60 100
P wave : Normal in configuration; precede each QRS
PR : Normal ( 0. 12 0.20 seconds )
QRS : Normal ( less than 0.12 seconds )
First-degree AV block
Rhythm : Regular
Rate : Usually normal
P wave : Sinus P wave present; one P wave to each QRS
PR : Prolonged ( greater than 0.20 seconds )
QRS : Normal
Second -degree AV block, Mobitz I
Rhythm : Irregular
Rate : Usually slow but can be normal
P wave : Sinus P wave present;
some not followed by QRS complexes
PR : Progressively lengthens
QRS : Normal
Second-degree AV block, Mobitz II
Rhythm : Regular usually;
can be irreguler if conduction ratios vary
Rate : Usually slow
P wave : Two, three, or four P waves before each QRS
PR : PR interval of beat with QRS is constant;
PR interval may be normal or prolonged
QRS : Normal if block in His bundle;
wide if block involves bundle branches
Third-degree AV block
Rhythm : Regular
Rate : 40 60 if block in His bundle;
30 40 if block involves bundle branches
P wave : Sinus P wave present; bear no relationship to QRS;
can be found hidden in QRS complexes and T waves
PR : Varies greatly
QRS : Normal if block in His bundle;
wide if block involves bundle branches
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome
ST depresi dan perubahan gelombang T
ST depresi dianggap bermakna bila > 1 mm di bawah garis dasar PT di titik J
Titik J didefinisikan sebagai akhir kompleks QRS dan permulaan segmen ST
Bentuk segmen ST :
up-sloping ( tidak spesifik )
horizontal ( lebih spesifik untuk iskemia )
down-sloping ( paling terpercaya untuk iskemia )
Perubahan gelombang T pada
iskemia kurang begitu spesifik
Gelombang T hiperakut
kadang2 merupakan satu-satunya
perubahan EKG yang terlihat
Anatomi Koroner dan EKG 12 sandapan
Sandapan V1 dan V2 menghadap septal area ventrikel kiri
Sandapan V3 dan V4 menghadap dinding anterior ventrikel kiri
Sandapan V5 dan V6 ( ditambah I dan avL ) menghadap
dinding lateral ventrikel kiri
Sandapan II, III dan avF menghadap dinding inferior ventrikel kiri
Unstable angina
Acute anteroseptal myocardial infarction.
Hyperacute T-wave changes are noted
Acute anterolateral myocardial infarction
High lateral infarction
Inferior myocardial infarction
Acute inferoposterior myocardial infarction
L V H
L V H
L V H
R V H
R V H
R V H
1. RATE AND REGULARITY
2. P-WAVE MORPHOLOGY
3. PR INTERVAL
4. QRS-COMPLEX MORPHOLOGY
5. ST-SEGMENT MORPHOLOGY
6. T-WAVE MORPHOLOGY
7. U-WAVE MORPHOLOGY
8. QTC INTERVAL
9. RHYTHM
1 & 9 ARE OF PRIMARY IMPORTANCE IN THE
EVALUATION OF CARDIAC RHYTHM
NINE FEATURES OF
ELECTROCARDIOGRAM THAT SHOULD
BE EXAMINED SYSTEMATICALLY :
Heart Rhythm P Wave PR Interval QRS
Rate (in seconds) (in seconds)
60 100 bpm Regular Before each QRS, .12 - .20 < .12
NORMAL SINUS RHYTHM
DALAM MENDIAGNOSIS ARITMIA:
1. BACA EKG SECARA CEPAT DAN
AKURAT
2. KENALI AKIBAT KLINIS
3. KETAHUI UNDERLYING DISEASE
PHYSIOLOGIC BASIS OF
PACEMAKER CELLS
CARDIAC ARRHYTMIA :
IMPULSE
CONDUCTION
BOTH
MECHANISM OF ABNORMAL
IMPULSE FORMATION :
TRIGGER ACTIVITY
REENTRY
FIBRILATION
FOUR BASIC TYPES OF
ARRHYTHMIAS:
1. SINUS ORIGIN
2. ECTOPIC RHYTHMS
3. CONDUCTION BLOCKS
4. PREEXCITATION SYNDROMES
1. SINUS ORIGIN
SINUS BRADYCARDIA (< 60 BTS/MIN)
SINUS TACHYCARDIA (>100 BTS/MIN AT REST)
SINUS ARRHYTHMIA:
o COULD BE NORMAL RATE BUT RATE CHANGES
(DOES NOT REMAIN REGULAR)
SINUS ARREST
o ESCAPE BEATS
SA block
SA pause
2. ECTOPIC RHYTHMS ORIGINATE
OUTSIDE OF THE SA NODE.
PAROXYSMAL SUPRAVENTRICULAR
TACHYCARDIA
ATRIAL FLUTTER
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
MULTIFOCAL ATRIAL TACHYCARDIA
NOTE: IF A NORMAL RATE, THEN CALLED A
WANDERING PACEMAKER.
Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardial (PSVT)
ATRIAL FLUTTER
UNIFORM,CEPAT, SAW TOOTH APPEARANCE,
TIDAK ADA INTERVAL ISOELEKTRIK ANTARA
GELOMBANG F
GELOMBANG F PALING JELAS DI II,III,AVF DAN V1
FLUTTER RATE BIASANYA 300 KALI/
VENTRICULAR RATE BIASANYA 150 X/ DENGAN
KONDUKSI 2:1
BIASANYA KOMPLEKS QRS NORMAL
ATRIAL FIBRILASI
ATRIAL RATE 400-700 X/
IREGULER VENTRICULAR RESPONSE
MULTIFOKAL ATRIAL TAKIKARDI
ATRIAL RATE 100-250 KALI/
ISOELEKTRIK INTERVAL ANTARA GEL P
BENTUK GELOMBANG P BERMACAM-MACAM
JUNCTIONAL TACHYCARDIA
RATE 100-170 X/
GEL P SEBELUM QRS, SEGERA SETELAH QRS
ATAU TIDAK TAMPAK GELOMBANG P
NON-SUSTAINED ABNORMAL BEATS
PREMATURE ATRIAL CONTRACTION (PAC)
o CAN OCCUR ON T WAVE
o MAY BE NONCONDUCTED
o P WAVE MAY BE MISSING
PREMATURE JUNCTIONAL CONTRACTION (PJC)
o RETROGRADE P WAVES
o P WAVES AFTER QRS
o P WAVE MAY BE MISSING
PREMATURE VENTRICULAR
CONTRACTION (PVC)
MULTIFOCAL
COUPLETS
BIGEMINI AND TRIGEMINI
VENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA
VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION
VENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA (VT)
KRITERIA
RATE: TIGA ATAU LEBIH IRAMA VENTRIKEL
DENGAN NADI LEBIH DARI 100
KALI/MENIT
KOMPLEKS QRS MEMENUHI KRITERIA SATU
ATAU LEBIH:
a. DURASI QRS 0,16 DETIK
b.GELOMBANG R TINGGI ATAU RR DI V1 (RABBIT
EAR PATTERN)
c. QS ATAU RS DENGAN S YANG LEBAR DAN
DALAM
d.CONCORDANCE POSITIF ATAU NEGATIF V1-6
e. AKSIS KE KIRI
AKTIFITAS ATRIUM : DISOSIASI AV
VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION (VF)
DEFLEKSI YANG SANGAT CEPAT DAN IREGULAR.
DEFLEKSI DAPAT LEBAR DAN KASAR, ATAU
SEMPIT DAN HALUS ATAU KOMBINASI KEDUANYA.
PREEXCITATION SYNDROMES
WPW SYNDROME
SHORT PR INTERVAL
DELTA WAVE
WIDE QRS COMPLEX
PERUBAHAN ARAH ST SEGMEN KEBALIKAN DARI
DELTA WAVE
Supraventricular tachycardia
Long QT Syndrome (pria QTC n <0,44det,wanita<0,46det)
a.Acquired long QT syndrome
Akibat obat antiaritmia,obat
psikotropik,hipokalemia,perdarahan subarachnoid
b. Congenital Long QT syndrome
Jervel-longe-nielsen dan Romano-Ward Syndrome
Bahaya untuk torsade de pointes
Brugada Syndrome
Penyebab kematian mendadak di eropa dan asia
tenggara
ST elevasi di V1 sampai V3 dengan atau tanpa RBBB
Tidak ada kelainan struktural
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Sajjan M MBBS Learn ECG in A Day A Systemic ApproachDocument99 pagesSajjan M MBBS Learn ECG in A Day A Systemic Approachv@r0_5100% (9)
- Supraventricular Tachycardia: Arun Umesh Mahtani,, Devi Gopinath NairDocument17 pagesSupraventricular Tachycardia: Arun Umesh Mahtani,, Devi Gopinath Nairwindar baquero100% (1)
- Gangguan Dan Keseimbangan Cairan Dan ElektrolitDocument37 pagesGangguan Dan Keseimbangan Cairan Dan ElektrolitFyana PutriNo ratings yet
- Citicoline DossierDocument14 pagesCiticoline DossierFyana PutriNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Drugs For Tropical Parasitic Infections (2nd)Document192 pagesHandbook of Drugs For Tropical Parasitic Infections (2nd)Fyana PutriNo ratings yet
- ChemoStabilityChartApril2013 Formatted 2Document90 pagesChemoStabilityChartApril2013 Formatted 2Fyana PutriNo ratings yet
- ChemoStabilityChartApril2013 Formatted 2Document90 pagesChemoStabilityChartApril2013 Formatted 2Fyana PutriNo ratings yet
- ECG InterpretationDocument81 pagesECG Interpretationd.ramadhan100% (3)
- TV 2021Document17 pagesTV 2021c4fcz9dj4fNo ratings yet
- Advanced ECG AnalysisDocument90 pagesAdvanced ECG AnalysisnursewinstonNo ratings yet
- ECG in Emergency Room, HowDocument43 pagesECG in Emergency Room, HowFabian Fabiansyah100% (1)
- Atypical Bypass Tracts 2019Document21 pagesAtypical Bypass Tracts 2019Võ Từ NhấtNo ratings yet
- ArrthymiasDocument11 pagesArrthymiasSyafiq AbeNo ratings yet
- A Review of The Cardiovascular System and ECG Performance, Troubleshooting, and InterpretationDocument47 pagesA Review of The Cardiovascular System and ECG Performance, Troubleshooting, and InterpretationRetroPilotNo ratings yet
- Aer 06 29Document4 pagesAer 06 29Vimal NishadNo ratings yet
- Canine Dilated Cardiomyopathy enDocument2 pagesCanine Dilated Cardiomyopathy endafne_ramírez_12No ratings yet
- Introd 0907Document104 pagesIntrod 0907Jason LinNo ratings yet
- 22 Disritmia 2018Document60 pages22 Disritmia 2018Nur akilaNo ratings yet
- Heart BlocksDocument3 pagesHeart BlockslhenNo ratings yet
- Pre-Excitation Syndromes in Children: Dr.K.MaheshDocument105 pagesPre-Excitation Syndromes in Children: Dr.K.MaheshNischal ShahNo ratings yet
- A Combined Algorithm For Identification and Differentiation of Atrial Flutter and Atrial Fibrillation Based On ECG AnalysisDocument4 pagesA Combined Algorithm For Identification and Differentiation of Atrial Flutter and Atrial Fibrillation Based On ECG AnalysisOana DrăganNo ratings yet
- Coarctation of Aorta (Paed)Document18 pagesCoarctation of Aorta (Paed)NadiaMichu100% (1)
- Basic EKG Dysrhythmia IdentificationDocument40 pagesBasic EKG Dysrhythmia IdentificationIlda Dhe Devis Spaho100% (1)
- Heart BlocksDocument20 pagesHeart BlocksGhaida AlshehriNo ratings yet
- Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and ManagementDocument8 pagesParoxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and ManagementLaurensia Sherly SusiloNo ratings yet
- Atrial Fibrillation HandoutDocument5 pagesAtrial Fibrillation HandoutAlfa AlfinNo ratings yet
- Heart AnatomyDocument178 pagesHeart AnatomysubbuNo ratings yet
- ArrhythmiasDocument48 pagesArrhythmiasHarshan JeyakumarNo ratings yet
- DosulepinDocument4 pagesDosulepinbrickettNo ratings yet
- Paramedic Inter Facility Transfer TrainingDocument168 pagesParamedic Inter Facility Transfer TrainingnikunjhirparaNo ratings yet
- Ecg 1Document50 pagesEcg 1Rohit DagarNo ratings yet
- Cardiology MneumonicsDocument14 pagesCardiology Mneumonicsadwait marhattaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular History and ExaminationDocument6 pagesCardiovascular History and ExaminationHarry CenNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Arrhythmias: Belay E. MD December 2015Document53 pagesPathophysiology of Arrhythmias: Belay E. MD December 2015Amanuel MaruNo ratings yet
- Pharma Super TableDocument87 pagesPharma Super TableMarton Emile DesalesNo ratings yet