Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Principles of Marketing: New Product Development and Product Life-Cycle Strategies
Uploaded by
Kara Mae Pagcanlungan SuguiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Principles of Marketing: New Product Development and Product Life-Cycle Strategies
Uploaded by
Kara Mae Pagcanlungan SuguiCopyright:
Available Formats
9-1
Chapter 9
New Product Development
and
Product Life-Cycle Strategies
PRINCIPLES OF MARKETING
9-2
Causes of New Product Failures
Overestimation of Market Size
Product Design Problems
Product Incorrectly Positioned, Priced or
Advertised
Costs of Product Development
Competitive Actions
To create successful new products, the
company must:
understand its customers, markets and
competitors
develop products that deliver superior value to
customers.
9-3
New Product Development
Process
Idea Generation and Screening
Concept Development and Testing
Marketing Strategy
Business Analysis
Product Development
Test Marketing
Commercialization
9-4
New Product Development Process
Step 1. Idea Generation
Systematic Search for New Product
Ideas
Internal sources
Customers
Competitors
Distributors
Suppliers
9-5
Process to spot good ideas and drop
poor ones
Criteria
Market Size
Product Price
Development Time & Costs
Manufacturing Costs
Rate of Return
New Product Development Process
Step 2. Idea Screening
9-6
New Product Development Process
Step 3. Concept Development & Testing
1. Develop Product Ideas into
Alternative
Product Concepts
2. Concept Testing - Test the
Product Concepts with Groups
of Target Customers
3. Choose the Best One
9-7
New Product Development Process
Step 4. Marketing Strategy Development
Part Two - Short-Term:
Products Planned Price
Distribution
Marketing Budget
Part Three - Long-Term:
Sales & Profit Goals
Marketing Mix Strategy
Marketing Strategy Statement Formulation
Part One - Overall:
Target Market
Planned Product Positioning
Sales & Profit Goals
Market Share
9-8
New Product Development Process
Step 5. Business Analysis
Step 6. Product Development
Business Analysis
Review of Product Sales, Costs,
and Profits Projections to See if
They Meet Company Objectives
If Yes, Move to
Product Development
If No, Eliminate
Product Concept
9-9
New Product Development Process
Step 7. Test Marketing
Standard
Test Market
Full marketing campaign
in a small number of
representative cities.
Simulated
Test Market
Test in a simulated
shopping environment
to a sample of
consumers.
Controlled
Test Market
A few stores that have
agreed to carry new
products for a fee.
9-10
Product Life Cycle
Time
Product
Develop-
ment
Introduction
Profits
Sales
Growth Maturity Decline
Losses/
Investments ($)
Sales and
Profits ($)
9-11
Introduction Stage of the
PLC
Sales
Costs
Profits
Marketing Objectives
Product
Price
Low sales
High cost per customer
Negative
Create product awareness
and trial
Offer a basic product
Use cost-plus
Distribution Build selective distribution
Advertising
Build product awareness among
early adopters and dealers
9-12
Growth Stage of the PLC
Sales
Costs
Profits
Marketing Objectives
Product
Price
Rapidly rising sales
Average cost per customer
Rising profits
Maximize market share
Offer product extensions,
service, warranty
Price to penetrate market
Distribution Build intensive distribution
Advertising
Build awareness and interest in
the mass market
9-13
Maturity Stage of the PLC
Sales
Costs
Profits
Marketing Objectives
Product
Price
Peak sales
Low cost per customer
High profits
Maximize profit while defending
market share
Diversify brand and models
Price to match or best
competitors
Distribution Build more intensive distribution
Advertising
Stress brand differences and
benefits
9-14
Decline Stage of the PLC
Sales
Costs
Profits
Marketing Objectives
Product
Price
Declining sales
Low cost per customer
Declining profits
Reduce expenditure and milk the
brand
Phase out weak items
Cut price
Distribution
Go selective: phase out
unprofitable outlets
Advertising
Reduce to level needed to retain
hard-core loyal customers
You might also like
- New Product Development Strategies and Life Cycle StagesDocument14 pagesNew Product Development Strategies and Life Cycle StagesPiyush ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- Principles of Marketing: New Product Development and Product Life-Cycle StrategiesDocument14 pagesPrinciples of Marketing: New Product Development and Product Life-Cycle StrategiesIsmatullah ZazaiNo ratings yet
- New Product Failure Rate May Be 80%: New Products Drive Sales and Profit GrowthDocument18 pagesNew Product Failure Rate May Be 80%: New Products Drive Sales and Profit GrowthAgha HusainNo ratings yet
- Adbms New ProductDocument23 pagesAdbms New ProductPinkNo ratings yet
- Development: New ProductDocument12 pagesDevelopment: New ProductSavan BhattNo ratings yet
- Product Life CycleDocument14 pagesProduct Life CycleSrushti GadgeNo ratings yet
- New Product DevelopmentDocument17 pagesNew Product DevelopmentAyshwar Venkatesh0% (1)
- Product Design and Produc Development With Product Life CycleDocument25 pagesProduct Design and Produc Development With Product Life CycleVikrant LadNo ratings yet
- New Product Development and Product Life-Cycle Strategies: Prof. Ahimpreet Jurrymarketing Managementpgp/Ss/2010-12//Sem1Document20 pagesNew Product Development and Product Life-Cycle Strategies: Prof. Ahimpreet Jurrymarketing Managementpgp/Ss/2010-12//Sem1vishakha_rm2000No ratings yet
- New Product DevelopmentDocument24 pagesNew Product DevelopmentSaurabh JindalNo ratings yet
- New-Product Development and Product Life-Cycle StrategiesDocument21 pagesNew-Product Development and Product Life-Cycle StrategiesDr Rushen SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document14 pagesChapter 6liniegurlthanarajNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 Product development &product life cycleDocument18 pagesUNIT 2 Product development &product life cycletherashijain16No ratings yet
- New Product DevelopmentDocument27 pagesNew Product DevelopmentRishabh Jain100% (3)
- New-Product Development and Product Life-Cycle StrategiesDocument24 pagesNew-Product Development and Product Life-Cycle StrategiesKamran AzizNo ratings yet
- Strategy Product-PLCDocument19 pagesStrategy Product-PLCKikiNo ratings yet
- New-Product Development and Product Life-Cycle StrategiesDocument12 pagesNew-Product Development and Product Life-Cycle StrategieslulughoshNo ratings yet
- CH.9. New Product Development and PLCDocument21 pagesCH.9. New Product Development and PLCDina Abdelaziz EltaweelNo ratings yet
- New Product DevelopmentDocument48 pagesNew Product DevelopmentMuraliNo ratings yet
- Mod Kotler 09Document30 pagesMod Kotler 09Muhieddine TabshNo ratings yet
- Product Life CycleDocument16 pagesProduct Life CycleSantosh SinghNo ratings yet
- NPD PLC LecDocument30 pagesNPD PLC Lecviraj_wadkarvivaNo ratings yet
- New Product Development and Product Life Cycle StrategiesDocument25 pagesNew Product Development and Product Life Cycle StrategiesMahima RojithNo ratings yet
- 4 New Product Development, Product Testing & MarketDocument29 pages4 New Product Development, Product Testing & MarketFahad KhotNo ratings yet
- PositioningDocument18 pagesPositioningPriyanka SharmaNo ratings yet
- New Product Development & Product Life CycleDocument24 pagesNew Product Development & Product Life Cycleuzmatabassum1996No ratings yet
- Principles of Marketing: New-Product Development and Product Life-Cycle StrategiesDocument46 pagesPrinciples of Marketing: New-Product Development and Product Life-Cycle Strategiesanum arifNo ratings yet
- Prinsip - Prinsip Marketing: Pengembangan Produk Baru Dan Siklus Hidup ProdukDocument23 pagesPrinsip - Prinsip Marketing: Pengembangan Produk Baru Dan Siklus Hidup ProdukRatna SaridewiNo ratings yet
- New Product Development and Product Life Cycle StrategiesDocument44 pagesNew Product Development and Product Life Cycle Strategieshiutkwok3No ratings yet
- New Product StrategyDocument11 pagesNew Product StrategylulughoshNo ratings yet
- Developing New Products: Isaa Ruth F. Lesma Marketing Management G14-0139Document16 pagesDeveloping New Products: Isaa Ruth F. Lesma Marketing Management G14-0139Isaa Ruth FernandezNo ratings yet
- Product Life-Cycle: Asst. Prof. Sovan MangarajDocument8 pagesProduct Life-Cycle: Asst. Prof. Sovan MangarajSovan MangarajNo ratings yet
- Dr. Ibha Rani - New Product DevelopmentDocument25 pagesDr. Ibha Rani - New Product DevelopmentIbha RaniNo ratings yet
- Product Lifecycle and BCG-GE MatrixDocument26 pagesProduct Lifecycle and BCG-GE MatrixChessWriterNo ratings yet
- Product Life Cycle (PLC) StrategiesDocument31 pagesProduct Life Cycle (PLC) StrategiesPeggy ChengNo ratings yet
- NPD N PLCDocument40 pagesNPD N PLCShivam TrivediNo ratings yet
- New-Product Development and Product Life-Cycle StrategiesDocument25 pagesNew-Product Development and Product Life-Cycle StrategiesRony G RabbyNo ratings yet
- New Product Development and Life-Cycle StrategiesDocument24 pagesNew Product Development and Life-Cycle StrategiesTarun UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - New Product Development and Product Life-Cycle StrategiesDocument2 pagesChapter 10 - New Product Development and Product Life-Cycle StrategiesBaraaNo ratings yet
- Learning Objectives: After Studying This, You Should Be Able ToDocument31 pagesLearning Objectives: After Studying This, You Should Be Able Tonick john caminadeNo ratings yet
- New-Product Development and Product Life-Cycle StrategiesDocument36 pagesNew-Product Development and Product Life-Cycle StrategiesAjeeb RafeekahammedNo ratings yet
- Product StrategiesDocument28 pagesProduct StrategiesBasab PalNo ratings yet
- Product Life Cycle FinalDocument9 pagesProduct Life Cycle FinalFritz JennelieNo ratings yet
- Module 8 Creating New Products and ServicesDocument39 pagesModule 8 Creating New Products and ServicesBruno SaturnNo ratings yet
- New Product Development: Product Life Cycle StrategiesDocument25 pagesNew Product Development: Product Life Cycle StrategiesKarthika RadhakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Product Life-Cycle StrategiesDocument13 pagesProduct Life-Cycle StrategiesramstexNo ratings yet
- Types of Innovation and Product Development ProcessDocument19 pagesTypes of Innovation and Product Development ProcessMehtab KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 SummaryDocument4 pagesChapter 9 SummaryEugene OeiNo ratings yet
- Product Management: Session 8 & 9Document37 pagesProduct Management: Session 8 & 9Deepshikha AlhaNo ratings yet
- 5.2. New Product DevDocument15 pages5.2. New Product DevJillianne JillNo ratings yet
- Amol 34Document24 pagesAmol 34Amol AmraleNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Marketing Product Management and New-Product DevelopmentDocument37 pagesEssentials of Marketing Product Management and New-Product DevelopmentGunjan AroraNo ratings yet
- Pre-Test:: Is The Process of Designing, Creating and Marketing New Products or Services To Benefit CustomersDocument78 pagesPre-Test:: Is The Process of Designing, Creating and Marketing New Products or Services To Benefit CustomersMarylyn Tenorio LaxamanaNo ratings yet
- Strategic Innovation Platforms Drive DSM's NPD SuccessDocument42 pagesStrategic Innovation Platforms Drive DSM's NPD SuccessAtul KashyapNo ratings yet
- New Product Development and Product Life-Cycle Strategies: A Global PerspectiveDocument33 pagesNew Product Development and Product Life-Cycle Strategies: A Global PerspectiveLakshmikanthBalasubramanianNo ratings yet
- Abbie Griffen, University of Illinois, Urbana-ChampaignDocument40 pagesAbbie Griffen, University of Illinois, Urbana-ChampaignPinkAlert100% (9)
- Chapter 09Document33 pagesChapter 09Anonymous ed8Y8fCxkSNo ratings yet
- Unlock the Secrets of Profitable Dropshipping: A Comprehensive Guide to Building a Successful Online BusinessFrom EverandUnlock the Secrets of Profitable Dropshipping: A Comprehensive Guide to Building a Successful Online BusinessNo ratings yet
- 160204111221Document2 pages160204111221praveenpersonelNo ratings yet
- "Being Me" Savings Account: W.E.F. 1st April 2014Document2 pages"Being Me" Savings Account: W.E.F. 1st April 2014praveenpersonelNo ratings yet
- Password ManagerDocument1 pagePassword ManagerpraveenpersonelNo ratings yet
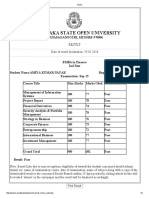
- Karnataka State Open University: Print ResultDocument1 pageKarnataka State Open University: Print ResultpraveenpersonelNo ratings yet
- Password ManagerDocument1 pagePassword ManagerpraveenpersonelNo ratings yet
- Foods You Should Not Feed Your DogDocument2 pagesFoods You Should Not Feed Your DogpraveenpersonelNo ratings yet
- E Book E CommerceDocument1 pageE Book E CommercepraveenpersonelNo ratings yet
- MB0038 Management Process and Organizational Behavior Assignment Feb 11Document2 pagesMB0038 Management Process and Organizational Behavior Assignment Feb 11sandy_002No ratings yet
- Biodata For Marriage - Ganeshji Format 1Document2 pagesBiodata For Marriage - Ganeshji Format 1Sai Gowtham50% (10)
- CET+MS+Excel+2007+Training+Manual+v1 1Document32 pagesCET+MS+Excel+2007+Training+Manual+v1 1Faheem MukhtarNo ratings yet
- ERail Hsra To BNCDocument1 pageERail Hsra To BNCpraveenpersonelNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - Essentials of ManagementDocument1 pageSyllabus - Essentials of ManagementpraveenpersonelNo ratings yet
- EggsDocument1 pageEggspraveenpersonelNo ratings yet
- Company and Marketing Strategy: Partnering To Build Customer RelationshipsDocument49 pagesCompany and Marketing Strategy: Partnering To Build Customer RelationshipspraveenpersonelNo ratings yet
- Marketing Information SystemsDocument10 pagesMarketing Information SystemspraveenpersonelNo ratings yet
- Mbe 1Document55 pagesMbe 1praveenpersonelNo ratings yet
- Videocon RechargeDocument1 pageVideocon RechargepraveenpersonelNo ratings yet
- The Staffing Process: Labor Union - Represents Workers and Protects TheirDocument28 pagesThe Staffing Process: Labor Union - Represents Workers and Protects TheirkamalkantmbbsNo ratings yet
- OBDocument1 pageOBpraveenpersonelNo ratings yet
- SomethingDocument1 pageSomethingAriac PancNo ratings yet
- MGL Economics Notes Module 1, 2 and 4Document59 pagesMGL Economics Notes Module 1, 2 and 4mohanraokp2279No ratings yet
- OBDocument144 pagesOBpraveenpersonelNo ratings yet
- Pricelist of Computer AccessoriesDocument32 pagesPricelist of Computer AccessoriesRajesh VenkateshNo ratings yet
- Thai Visa Application FormDocument1 pageThai Visa Application FormTouring Myanmar100% (5)
- BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT 1st, Semester Notes Mba UNIT - 1 BUSINESS AS A SOCIAL SYSTEMDocument2 pagesBUSINESS ENVIRONMENT 1st, Semester Notes Mba UNIT - 1 BUSINESS AS A SOCIAL SYSTEMpraveenpersonelNo ratings yet