Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Air Conditioning
Uploaded by
mechgokulOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Air Conditioning
Uploaded by
mechgokulCopyright:
Available Formats
Home Cooling
EGEE 102
EGEE 102 - Pisupati 2
Function of an Air
conditioner
EGEE 102 - Pisupati 3
Humidity in air
Relative Humidity
A measure of of
much water is
in the air
relative to the
maximum
amount air can
hol at that
tmperature
EGEE 102 - Pisupati 4
http://www.ae.iastate.edu/Ast473/Lectures/%285%29Psychrometric_Chart/sld024.htm
EGEE 102 - Pisupati 5
Principle
A. Expansion Valve
B. Compressor
EGEE 102 - Pisupati 6
Arrangement
EGEE 102 - Pisupati 7
TYPES OF AIR
CONDITIONERS
Room air conditioners
Central air conditioning systems
Heat pumps
Evaporative coolers
EGEE 102 - Pisupati 8
Air Conditioning
EGEE 102 - Pisupati 9
Room air conditioner
Room air conditioners cool rooms rather than
the entire home.
Less expensive to operate than central units
Their efficiency is generally lower than that of
central air conditioners.
Can be plugged into any 15- or 20-amp, 115-
volt household circuit that is not shared with
any other major appliances
EGEE 102 - Pisupati 10
EGEE 102 - Pisupati 11
Central Air conditioning
Circulate cool air through a system of supply
and return ducts. Supply ducts and registers
(i.e., openings in the walls, floors, or ceilings
covered by grills) carry cooled air from the air
conditioner to the home.
This cooled air becomes warmer as it
circulates through the home; then it flows
back to the central air conditioner through
return ducts and registers
EGEE 102 - Pisupati 12
Types of Central AC
split-system
an outdoor metal cabinet contains
the condenser and compressor,
and an indoor cabinet contains the
evaporator
Packaged
the evaporator, condenser, and
compressor are all located in one
cabinet
EGEE 102 - Pisupati 13
Outside air is drawn in,
filtered and heated before it
passes through the main air
conditioning devices. The
colored lines in the lower
part of the diagram show the
changes of temperature and
of water vapor concentration
(not RH) as the air flows
through the system.
EGEE 102 - Pisupati 14
Total Air Conditioning
EGEE 102 - Pisupati 15
Variable fresh air mixer and dust and
pollutant filtration.
Supplementary heating with radiators in
the outer rooms and individual mini
heater and
Humidifier in the air stream to each
room.
EGEE 102 - Pisupati 16
how large your home is and how many
windows it has;
how much shade is on your home's windows,
walls, and roof;
how much insulation is in your home's ceiling
and walls;
how much air leaks into your home from the
outside; and
how much heat the occupants and appliances
in your home generate
EGEE 102 - Pisupati 17
Energy Consumption
Air conditioners are rated by the number of
British Thermal Units (Btu) of heat they can
remove per hour. Another common rating
term for air conditioning size is the "ton,"
which is 12,000 Btu per hour.
Room air conditioners range from 5,500 Btu
per hour to 14,000 Btu per hour.
EGEE 102 - Pisupati 18
Energy Efficiency
Today's best air conditioners use 30%
to 50% less energy than 1970s
Even if your air conditioner is only 10
years old, you may save 20% to 40% of
your cooling energy costs by replacing it
with a newer, more efficient model
EGEE 102 - Pisupati 19
Energy Efficiency
Rating is based on how many Btu per hour
are removed for each watt of power it draws
For room air conditioners, this efficiency
rating is the Energy Efficiency Ratio, or EER
For central air conditioners, it is the Seasonal
Energy Efficiency Ratio, or SEER
EGEE 102 - Pisupati 20
Room Air Conditioners
Built after January 1, 1990, need have
an EER of 8.0 or greater
EER of at least 9.0 if you live in a
mild climate
EER over 10 for warmer climates
EGEE 102 - Pisupati 21
Central AC
National minimum standards for central
air conditioners require a SEER of
9.7 for single-package and
10.0 for split-systems
Units are available with SEERs
reaching nearly 17
EGEE 102 - Pisupati 22
Energy Saving Methods
Locate the air conditioner in a window
or wall area near the center of the room
and on the shadiest side of the house.
Minimize air leakage by fitting the room
air conditioner snugly into its opening
and sealing gaps with a foam weather
stripping material.
EGEE 102 - Pisupati 23
Numerical Problem
A EER from 5.0 to 9 saving and pay
back period
You might also like
- Home Cooling Systems: Types, Components, EfficiencyDocument23 pagesHome Cooling Systems: Types, Components, EfficiencyKhushboo PriyaNo ratings yet
- Air ConditioningDocument23 pagesAir Conditioningsimran sharmaNo ratings yet
- Energy-Efficient Ducted Evaporative Coolers: How WorksDocument2 pagesEnergy-Efficient Ducted Evaporative Coolers: How Worksrajesh0145No ratings yet
- Energy-Efficient Air Conditioning: E E R EDocument8 pagesEnergy-Efficient Air Conditioning: E E R EezifirNo ratings yet
- (Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy ClearinghoDocument8 pages(Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy Clearinghockw30571No ratings yet
- AC CH 1Document36 pagesAC CH 1GETACHEWNo ratings yet
- Air ConditionersDocument13 pagesAir ConditionersMd Abdul RahemanNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning in Interior Design: Ar. Amit MehtaDocument31 pagesAir Conditioning in Interior Design: Ar. Amit MehtaAr Amit MehtaNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning PPT of EMEDocument24 pagesAir Conditioning PPT of EMEDineshKumar VermaNo ratings yet
- Evs Submission 29 AugDocument10 pagesEvs Submission 29 AugRHUTI NAIKNo ratings yet
- Lib Ks Selectin A Home Coooling SystemDocument8 pagesLib Ks Selectin A Home Coooling Systemm1984946203No ratings yet
- Packaged HVAC Systems for Small-Medium SpacesDocument31 pagesPackaged HVAC Systems for Small-Medium Spacesvishnu_2008100% (1)
- Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning: Types of HVAC SystemsDocument20 pagesHeating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning: Types of HVAC SystemsAsmara KanthiNo ratings yet
- Manualul Pentru Incalzire Danfoss - Chapter6Document26 pagesManualul Pentru Incalzire Danfoss - Chapter6valicanNo ratings yet
- 1 - Air Conditioning Systems PDFDocument29 pages1 - Air Conditioning Systems PDFMayaNo ratings yet
- Passive HouseDocument16 pagesPassive HouseZarkima RanteNo ratings yet
- Bon 698 Cooling Brochure Jan 12Document11 pagesBon 698 Cooling Brochure Jan 12Nina ParsonsNo ratings yet
- What Is HVAC?: Cooling Only Split-SystemDocument7 pagesWhat Is HVAC?: Cooling Only Split-Systemjabi_shaik_1No ratings yet
- Saumitra Thakur - 1st JuneDocument1 pageSaumitra Thakur - 1st JuneSAUMITRA THAKURNo ratings yet
- Compressor Types and Roles in Refrigeration CycleDocument9 pagesCompressor Types and Roles in Refrigeration CycleCharu GargNo ratings yet
- Window & Packaged Ac Chilled Water Plant: G.Siddharth Moorthe 12RBAR033Document14 pagesWindow & Packaged Ac Chilled Water Plant: G.Siddharth Moorthe 12RBAR033Logesh WaranNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About Air ConditionersDocument39 pagesEverything You Need to Know About Air ConditionersRaymond Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Psychrometry - VentilationDocument14 pagesPsychrometry - VentilationLARA JOANNE DORIANo ratings yet
- How To Install and Use A Whole House FanDocument4 pagesHow To Install and Use A Whole House FanIon VasileNo ratings yet
- Types of Air Conditioning Systems ExplainedDocument7 pagesTypes of Air Conditioning Systems ExplainedzzzmartcNo ratings yet
- HVAC Fundamentals: Fresh Air Calculation and ComponentsDocument24 pagesHVAC Fundamentals: Fresh Air Calculation and ComponentsAaron LisboaNo ratings yet
- ENERGY EFFICIENCY MEASURES PP 19-32Document14 pagesENERGY EFFICIENCY MEASURES PP 19-32Sophia Manila SillaNo ratings yet
- CR MOD 17 Heating and Cooling09Document36 pagesCR MOD 17 Heating and Cooling09MMMOH200No ratings yet
- Airconditioning: Ventilation in Buildings Types of Fans Types of Air ConditionersDocument51 pagesAirconditioning: Ventilation in Buildings Types of Fans Types of Air ConditionersSassyNo ratings yet
- Classification of AC SystemsDocument38 pagesClassification of AC Systemsrohan.nextitNo ratings yet
- SNS COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY SEMINAR ON AIR CONDITIONING & ITS TYPESDocument17 pagesSNS COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY SEMINAR ON AIR CONDITIONING & ITS TYPEScoc dhineshNo ratings yet
- Modern Day Poultry FarmingDocument27 pagesModern Day Poultry FarmingAkhlaqAhmad100% (1)
- Electrical Heating Solutions BrochureDocument52 pagesElectrical Heating Solutions BrochureMolnár GyulaNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning & HVAC Systems: Building Utility & ServicesDocument85 pagesAir Conditioning & HVAC Systems: Building Utility & ServicesphuongnhsfcNo ratings yet
- ENERGY AUDIT AND CONSERVATION: 11 WAYS TO CREATE ENERGY EFFICIENT HOMESDocument39 pagesENERGY AUDIT AND CONSERVATION: 11 WAYS TO CREATE ENERGY EFFICIENT HOMESNmg KumarNo ratings yet
- HVAC Systems Analysis and DesignDocument67 pagesHVAC Systems Analysis and DesignSidd SalNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Air Conditioning SystemsDocument40 pagesIntroduction to Air Conditioning SystemsSACHIDANANDA SNo ratings yet
- Centralised20ac20system 190120171416Document23 pagesCentralised20ac20system 190120171416Saba ArifNo ratings yet
- Essential Guide to HVAC SystemsDocument31 pagesEssential Guide to HVAC SystemsLeobert De Villa100% (1)
- Chapter 7 Heating Ventilation Air ConditioningDocument28 pagesChapter 7 Heating Ventilation Air ConditioningLaurentiuNo ratings yet
- Window Air Conditioner GuideDocument51 pagesWindow Air Conditioner GuideSHREYA SHARMA IET Lucknow StudentNo ratings yet
- Classifications of Air Conditioning System: Based On Major FunctionDocument67 pagesClassifications of Air Conditioning System: Based On Major Functionjet latorreNo ratings yet
- Air-Source Heat Pumps: How They WorkDocument8 pagesAir-Source Heat Pumps: How They WorkmaverickrzysNo ratings yet
- VentilationDocument29 pagesVentilationGaurika GroverNo ratings yet
- Designing efficient heating systemsDocument26 pagesDesigning efficient heating systemsArekNo ratings yet
- Air ConditioningDocument22 pagesAir ConditioningEmmanuel BuhwaNo ratings yet
- Hvac and Air ConditioningDocument69 pagesHvac and Air ConditioningEtee AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning PPT of EMEDocument24 pagesAir Conditioning PPT of EMEAbhishek Agrahari100% (1)
- M1 Air ConditioningDocument5 pagesM1 Air Conditioningsopan saNo ratings yet
- Building Service PDFDocument35 pagesBuilding Service PDFamirahNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iv-Air Water SystemDocument6 pagesUnit-Iv-Air Water SystemManjeet CinghNo ratings yet
- Hvac DesignDocument84 pagesHvac DesignShine Kumar100% (4)
- Fundamentals of Refrigeration and Air ConditioningDocument56 pagesFundamentals of Refrigeration and Air ConditioningMANSI SALUNKENo ratings yet
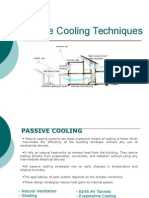
- Passive Cooling TechniquesDocument16 pagesPassive Cooling TechniquesPrakhar JainNo ratings yet
- HVAC System AnalysisDocument9 pagesHVAC System AnalysisAvery DuckworthNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning and RefrigerationDocument21 pagesAir Conditioning and Refrigerationrajnikanth pNo ratings yet
- Types of Air ConditionersDocument3 pagesTypes of Air ConditionersHanurag GokulNo ratings yet
- The Home Owner's Guide to HVAC: The Envelope and Green TechnologiesFrom EverandThe Home Owner's Guide to HVAC: The Envelope and Green TechnologiesNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesFrom EverandMechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesNo ratings yet
- 100 Things Every Homeowner Must KnowFrom Everand100 Things Every Homeowner Must KnowFamily HandymanNo ratings yet
- Solar Energy Notes 3Document5 pagesSolar Energy Notes 3mechgokulNo ratings yet
- Professional Ethics ObjectiveDocument5 pagesProfessional Ethics ObjectivemechgokulNo ratings yet
- U-3 Rankine CycleDocument12 pagesU-3 Rankine CyclemechgokulNo ratings yet
- Pollution From Si Engines & Their ControlDocument49 pagesPollution From Si Engines & Their Controlewee76No ratings yet
- 151 ADocument19 pages151 AViru JaiNo ratings yet
- Subhashri - M P No. 11 of 2013Document29 pagesSubhashri - M P No. 11 of 2013mechgokulNo ratings yet
- National Certification Examination 2004: FOR Energy ManagersDocument6 pagesNational Certification Examination 2004: FOR Energy ManagersAnonymous syHQ7YANo ratings yet
- Cryogenics Liquid Hydrogen StorageDocument17 pagesCryogenics Liquid Hydrogen Storagemechgokul0% (1)
- Radiation Heat TransferDocument36 pagesRadiation Heat TransfermechgokulNo ratings yet
- Biogas genset prototypes for low power applicationsDocument1 pageBiogas genset prototypes for low power applicationsmechgokulNo ratings yet
- QpmeDocument16 pagesQpmeSandeep PandeyNo ratings yet
- 2.5 Insulation & RefractoriesDocument9 pages2.5 Insulation & Refractoriesriyazcomm_257961932No ratings yet
- GATE Mechanical Question Paper 2013Document13 pagesGATE Mechanical Question Paper 2013robinthomas9900No ratings yet
- Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (Bio-Energy Technology Development Group-BGFP)Document3 pagesMinistry of New and Renewable Energy (Bio-Energy Technology Development Group-BGFP)mechgokul100% (1)
- Planning and Design For Commercialization of Biogas Bottling Plant For Production of Green and Low Cost Fuel With Utilization of Biomass ResourcesDocument4 pagesPlanning and Design For Commercialization of Biogas Bottling Plant For Production of Green and Low Cost Fuel With Utilization of Biomass ResourcesBiswa Jyoti GuptaNo ratings yet
- MM4GDP - Final Report - Biogas PDFDocument52 pagesMM4GDP - Final Report - Biogas PDFmechgokulNo ratings yet
- Cogeneration Question BankDocument9 pagesCogeneration Question BankSagar Sanjay SonawaneNo ratings yet
- You Should Spend About 20 Minutes On This Task.: DearDocument2 pagesYou Should Spend About 20 Minutes On This Task.: DearmechgokulNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Fuels - CombustionDocument8 pages2.1 Fuels - Combustionank_mehraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.3: Steam System: Part-I: Objective Type Questions and AnswersDocument7 pagesChapter 2.3: Steam System: Part-I: Objective Type Questions and Answersmaran2786No ratings yet
- Question bank on furnaces for energy managersDocument7 pagesQuestion bank on furnaces for energy managersSagar Sanjay SonawaneNo ratings yet
- 2.8 Waste Heat BasicsDocument9 pages2.8 Waste Heat BasicsRajwardhan PawarNo ratings yet
- FBC BoilersDocument8 pagesFBC Boilerssk3146No ratings yet
- 2.2 BoilersDocument9 pages2.2 BoilersSalihibnuali KpNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document28 pagesUnit 2mechgokulNo ratings yet
- Em3a PDFDocument7 pagesEm3a PDFMayukh DebdasNo ratings yet
- Cryogenics Liquid Hydrogen StorageDocument17 pagesCryogenics Liquid Hydrogen Storagemechgokul0% (1)
- Evolution of Entrepreneurship in IndiaDocument10 pagesEvolution of Entrepreneurship in IndiamechgokulNo ratings yet
- Rural EntrepreneurshipDocument32 pagesRural EntrepreneurshipmechgokulNo ratings yet
- Rural EntrepreneurshipDocument32 pagesRural EntrepreneurshipmechgokulNo ratings yet
- The Curse 5aDocument5 pagesThe Curse 5aDhanaletchimi SankaralingamNo ratings yet
- Evs Project Global Warming PDFDocument2 pagesEvs Project Global Warming PDFBrian25% (4)
- Laxmipur District - Ramgati UpazilaDocument15 pagesLaxmipur District - Ramgati UpazilaCDMP BangladeshNo ratings yet
- ORALcOM Week7-FINALDocument19 pagesORALcOM Week7-FINALZakina OctavianoNo ratings yet
- Eco-Fertilization Using ML TechniqueDocument4 pagesEco-Fertilization Using ML TechniqueInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- SFI 100 Ex No. 4Document5 pagesSFI 100 Ex No. 4Kyle Raymond Arcilla UmipigNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Aspha-Min Zeolite For Use in Warm Mix Asphalt: NCAT Report 05-04Document35 pagesEvaluation of Aspha-Min Zeolite For Use in Warm Mix Asphalt: NCAT Report 05-04arjunohioNo ratings yet
- Large-Eddy Simulations of Turbulence - Lesieur Et AlDocument233 pagesLarge-Eddy Simulations of Turbulence - Lesieur Et AlEdis KuznierNo ratings yet
- Location of the PhilippinesDocument49 pagesLocation of the PhilippinesNunag Mary Ann100% (2)
- Serif Business LetterDocument18 pagesSerif Business LetterNeerajha RabindranathNo ratings yet
- Red Dot R-9727 Off-Road Rooftop Air ConditionerDocument3 pagesRed Dot R-9727 Off-Road Rooftop Air ConditionerMarcelo MendozaNo ratings yet
- Newar HouseDocument3 pagesNewar HousePoojaNo ratings yet
- Extraction of Caffeine From TeaDocument2 pagesExtraction of Caffeine From TeaIshan ModiNo ratings yet
- Se40 4bDocument5 pagesSe40 4bnknfiveNo ratings yet
- Review of Estimation Methods For Crop Evapotranspiration and Irrigation Water Requirement of Different CropsDocument9 pagesReview of Estimation Methods For Crop Evapotranspiration and Irrigation Water Requirement of Different CropsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- The Future Is Now: It's Heading Right at Us, But We Never See It ComingDocument6 pagesThe Future Is Now: It's Heading Right at Us, But We Never See It ComingNickGuy100% (1)
- Study Island-4Document5 pagesStudy Island-4api-196718607No ratings yet
- Weather Patara 209308 - Google SearchDocument3 pagesWeather Patara 209308 - Google SearchAbhay ThakurNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Operations: Flight Crew Training ManualDocument55 pagesAbnormal Operations: Flight Crew Training ManualJoao MeloNo ratings yet
- Northern Mountains Lesson NotesDocument4 pagesNorthern Mountains Lesson NotesChandrika UdeshiNo ratings yet
- Not Afraid LyricsDocument3 pagesNot Afraid Lyricsbdjn bdjn100% (1)
- Chennai PDFDocument1,233 pagesChennai PDFApple AdsNo ratings yet
- Antonyms: Test MasterDocument4 pagesAntonyms: Test MasterSophie GalileoNo ratings yet
- Erthq Case Study PDFDocument235 pagesErthq Case Study PDF3319826No ratings yet
- Environmental Systems and Societies Paper 2 SL MarkschemeDocument8 pagesEnvironmental Systems and Societies Paper 2 SL MarkschemeAfra LamisaNo ratings yet
- Calcining CopperasDocument3 pagesCalcining Copperasanaaziz100% (1)
- Major Deserts Around the WorldDocument7 pagesMajor Deserts Around the WorldAndreea V.A.F.No ratings yet
- RB 53100 EngDocument2 pagesRB 53100 EngOmar SaeedNo ratings yet
- JSW GGBS by Shailesh GosaviDocument54 pagesJSW GGBS by Shailesh GosaviRohan Bagadiya100% (1)
- Dwnload Full Econ Macro Principles of Macroeconomics Canadian 1st Edition Oshaughnessy Test Bank PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Econ Macro Principles of Macroeconomics Canadian 1st Edition Oshaughnessy Test Bank PDFnoahsmqjst100% (8)