Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Maslows' Need Hierarchy of Motivation: Submitted By: Aditya Patel
Uploaded by
Aditya PatelOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Maslows' Need Hierarchy of Motivation: Submitted By: Aditya Patel
Uploaded by
Aditya PatelCopyright:
Available Formats
SUBMITTED BY:
ADITYA PATEL
MASLOWS NEED HIERARCHY OF
MOTIVATION
Key Elements
1. Intensity: how hard a person tries
2. Direction: toward beneficial goal
3. Persistence: how long a person tries
Motivation
The processes that account for an individuals
intensity, direction, and persistence of effort toward
attaining a goal.
What is Motivation?
Abraham Maslow (1908-1970)
Humanistic-Existential Paradigm
Self-actualization Theory
ABRAHAM MASLOW
Theory of Human Motivation
INTRODUCTION:
The basis of Maslow's theory is that human beings are
motivated by unsatisfied needs, and that certain lower
needs need to be satisfied before higher needs can be
satisfied. According to Maslow, there are general types
of needs (physiological, safety, love, and esteem) that
must be satisfied before a person can act unselfishly. He
called these needs "deficiency needs." As long as we
are motivated to satisfy these cravings, we are moving
towards growth, toward self-actualization. Satisfying
needs is healthy, while preventing gratification makes
us sick or act evilly.
Maslows Need Hierarchy
Maslows theory assumes that a person
attempts to satisfy the more basic needs before
directing behavior toward satisfying upper-level
needs.
Lower-order needs must be satisfied before a
higher-order need begins to control a persons
behavior.
A satisfied need ceases to motivate.
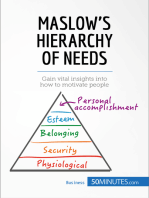
Maslows Hierarchy of Needs
PHYSIOLOGICAL OR SURVIVAL NEEDS
MOST NEEDS HAVE TO DO WITH
SURVIVAL PHYSICALLY AND
PSYCHOLOGICALLY
Maslows Hierarchy of Needs
PHYSIOLOGICAL OR SURVIVAL NEEDS
SAFETY NEEDS
ON THE WHOLE AN INDIVIDUAL
CANNOT SATISFY ANY LEVEL
UNLESS NEEDS BELOW ARE
SATISFIED
Maslows Hierarchy of Needs
PHYSIOLOGICAL OR SURVIVAL NEEDS
SAFETY NEEDS
LOVE, AFFECTION, AND
BELONGINGNESS NEEDS
Maslows Hierarchy of Needs
PHYSIOLOGICAL OR SURVIVAL NEEDS
SAFETY NEEDS
LOVE, AFFECTION, AND
BELONGINGNESS NEEDS
ESTEEM NEEDS
Maslows Hierarchy of Needs
SELF-
ACTUALIZATION
NEED
FOR
MASLOW EMPHASIZES NEED FOR SELF
ACTUALIZATION IS
A HEALTHY INDIVIDUALS PRIME
MOTIVATION
Physiological Needs
Physiological needs are those required to sustain life,
such as:
Air
Water
Food
Sleep
Safety Needs
Once physiological needs are met, one's attention turns to
safety and security in order to be free from the threat of
physical and emotional harm. Such needs might be
fulfilled by:
Living in a safe area
Medical insurance
Job security
Financial reserves
Social Needs
Once a person has met the lower level physiological
and safety needs, higher level needs awaken. The
first level of higher level needs are social needs.
Social needs are those related to interaction with
others and may include:
Friendship
Belonging to a group
Giving and receiving love
Esteem Needs
Once a person feels a sense of "belonging", the need to feel
important arises. Esteem needs may be classified as
internal or external.
Internal esteem needs are those related to self-esteem such
as self respect and achievement
External esteem needs are those such as social status and
recognition. Some esteem needs are:
Self-respect
Achievement
Attention
Recognition
Reputation
Self-Actualization
Self-actualization is the summit of Maslow's hierarchy of
needs. It is the quest of reaching one's full potential as a
person.
Self-actualized people tend to have needs such as:
Truth
Justice
Wisdom
Meaning
The Criticisms of the theory include the
following
The needs may not follow a definite hierarchical
order. For example, even if safety need is not
satisfied, the social need may emerge.
The need priority model may not apply at all times
in all places.
The level of motivation may be permanently lower
for some people. For example, a person suffering
from chronic unemployment may remain satisfied
for the rest of his life if only he get enough food.
Thank you
You might also like
- Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs: Gain vital insights into how to motivate peopleFrom EverandMaslow's Hierarchy of Needs: Gain vital insights into how to motivate peopleRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- 3.3 Motivation TheoriesDocument14 pages3.3 Motivation Theoriespriynka1990100% (3)
- Maslow'S Theory of Motivation: Submitted by Yadhu Krishna R.SDocument10 pagesMaslow'S Theory of Motivation: Submitted by Yadhu Krishna R.SNandagopan NanduNo ratings yet
- Exam Need TheoryMASLOWDocument9 pagesExam Need TheoryMASLOWYasmeen JafferNo ratings yet
- Abraham Maslow: Theory of Human MotivationDocument9 pagesAbraham Maslow: Theory of Human MotivationDevika RaniNo ratings yet
- Maslow Hierarchy of NeedsDocument4 pagesMaslow Hierarchy of NeedsMalak Kinaan88% (8)
- Maslow's Hierarchy Theory: Needs), and The Top Level Is Known As Growth or Being Needs (B-Needs)Document12 pagesMaslow's Hierarchy Theory: Needs), and The Top Level Is Known As Growth or Being Needs (B-Needs)Suresh Kutty MNo ratings yet
- Basic Human NeedsDocument12 pagesBasic Human NeedsMd Imamul Hasan ArifNo ratings yet
- Motivation Theories: Figure 1. Motivation Theories (Source: Author's Own Figure)Document15 pagesMotivation Theories: Figure 1. Motivation Theories (Source: Author's Own Figure)Keshav Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Motivation TheoriesDocument15 pagesMotivation TheoriesFahd Ȝziz EldienNo ratings yet
- Motivation TheoriesDocument18 pagesMotivation TheoriesMM Ayehsa Allian Schück100% (1)
- Motivation Theories: Figure 1. Motivation Theories (Source: Author's Own Figure)Document22 pagesMotivation Theories: Figure 1. Motivation Theories (Source: Author's Own Figure)jovilyn briosoNo ratings yet
- Brown and Beige Aesthetic Vintage Group Project Presentation - 20231120 - 234416 - 0000Document24 pagesBrown and Beige Aesthetic Vintage Group Project Presentation - 20231120 - 234416 - 0000Margot Yasmin YumulNo ratings yet
- MotivationDocument14 pagesMotivationTanjilNo ratings yet
- Study MaterialDocument78 pagesStudy MaterialpikubkNo ratings yet
- Motivation Theories: Figure 1. Motivation Theories (Source: Author's Own Figure)Document15 pagesMotivation Theories: Figure 1. Motivation Theories (Source: Author's Own Figure)SunnyNo ratings yet
- Motivation Theories: Figure 1. Motivation Theories (Source: Author's Own Figure)Document15 pagesMotivation Theories: Figure 1. Motivation Theories (Source: Author's Own Figure)Sweta SinghNo ratings yet
- HM AssigmentDocument19 pagesHM AssigmentZainab ImranNo ratings yet
- Muskan PreDocument18 pagesMuskan Premushkkhan.345No ratings yet
- Maslow's Hierarchy of NeedsDocument33 pagesMaslow's Hierarchy of NeedsAndrew PamhareNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Motivation TheoriesDocument16 pages3.3 Motivation TheoriesPrince Nanaba EphsonNo ratings yet
- Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs: By: Rhica Mae P. SibagDocument13 pagesMaslow's Hierarchy of Needs: By: Rhica Mae P. SibagJade Harris ColorjeNo ratings yet
- Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs: By: Rhica Mae P. SibagDocument13 pagesMaslow's Hierarchy of Needs: By: Rhica Mae P. SibagJade Harris ColorjeNo ratings yet
- Basic Human NeedsDocument22 pagesBasic Human NeedsSimran ChauhanNo ratings yet
- MaslowDocument2 pagesMaslowFatima Ezzahra BencheqrounNo ratings yet
- HRM Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs ExplainedDocument4 pagesHRM Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs ExplainedVillaruz Shereen MaeNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Motivation NotesDocument20 pagesModule 2 Motivation Notesrahul rameshNo ratings yet
- Funda LectureDocument12 pagesFunda LectureWeng RamojalNo ratings yet
- MaslowDocument8 pagesMaslowJawehNo ratings yet
- Humanistic Approach and ST Thomas AquinasDocument90 pagesHumanistic Approach and ST Thomas Aquinasmaylene marquezNo ratings yet
- Basic Human NeedsDocument3 pagesBasic Human NeedsMd Imamul Hasan ArifNo ratings yet
- Representations: Maslow's Hierarchy of NeedsDocument2 pagesRepresentations: Maslow's Hierarchy of NeedsVishnu RajNo ratings yet
- Basic Human Needs NewDocument13 pagesBasic Human Needs Newpriya9balan-863873No ratings yet
- Maslow's Theory of Motivation - Hierarchy of NeedsDocument5 pagesMaslow's Theory of Motivation - Hierarchy of NeedsVinay NayakNo ratings yet
- Esteem Needs: Truth Justice Wisdom MeaningDocument3 pagesEsteem Needs: Truth Justice Wisdom MeaningAnuraj AroraNo ratings yet
- Miss. Diksha P. JindeDocument13 pagesMiss. Diksha P. JindeDiksh JindeNo ratings yet
- Abraham Maslow's Hierarchy of NeedsDocument9 pagesAbraham Maslow's Hierarchy of NeedsRuchita SinghalNo ratings yet
- Hierarchy of Need by Abraham MaslowDocument8 pagesHierarchy of Need by Abraham MaslowCarlito FantilaganNo ratings yet
- InclusiveDocument5 pagesInclusiveAlexander KirosNo ratings yet
- Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs - Forensic PsychologyDocument14 pagesMaslow's Hierarchy of Needs - Forensic Psychologyvedika.uniNo ratings yet
- Assignment On MotiavtionDocument14 pagesAssignment On MotiavtionMd Salahuddin SakibNo ratings yet
- Dr. Sakshi Yadav - OBDocument10 pagesDr. Sakshi Yadav - OBSakshi YadavNo ratings yet
- 20bco082 Vitraagchaudhary Maslow'spyramidDocument5 pages20bco082 Vitraagchaudhary Maslow'spyramidVitraagNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Maslow's Hierarchy of NeedsDocument5 pagesAssignment On Maslow's Hierarchy of NeedsTwasin WaresNo ratings yet
- 7.analyze The Importance of Abhraham Maslows Heirarchical TheoryDocument50 pages7.analyze The Importance of Abhraham Maslows Heirarchical TheoryAswathiNo ratings yet
- Maslow's: Hierarchy of NeedsDocument38 pagesMaslow's: Hierarchy of NeedsJazzene ManzelNo ratings yet
- Motivation 2Document30 pagesMotivation 2aysha farihaNo ratings yet
- Motivation Theories: Figure 1. Motivation Theories (Source: Author's Own Figure)Document16 pagesMotivation Theories: Figure 1. Motivation Theories (Source: Author's Own Figure)Praveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Maslow TheoryDocument3 pagesMaslow TheorySam100% (1)
- General - Maslow's Hiearchy of NeedsDocument1 pageGeneral - Maslow's Hiearchy of NeedsAndrea CabutihanNo ratings yet
- Maslow TheoryDocument10 pagesMaslow Theoryraza20100% (1)
- Maslow's TheoryDocument4 pagesMaslow's TheoryJen SchnarrNo ratings yet
- MaslowDocument4 pagesMaslowsrashta gargNo ratings yet
- Intro To PerDevDocument10 pagesIntro To PerDevEl JohnNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Motivation TheoriesDocument14 pages3.3 Motivation TheoriesAsep Abdul RahmanNo ratings yet
- 4 ModuleDocument12 pages4 ModuleAkshita SinghNo ratings yet
- Activity 3Document2 pagesActivity 3Mar TundagNo ratings yet
- How To Improve Self-Esteem: The Peaceful Path to Building Lasting Self-EsteemFrom EverandHow To Improve Self-Esteem: The Peaceful Path to Building Lasting Self-EsteemNo ratings yet
- The Gaps Model of Service QualityDocument25 pagesThe Gaps Model of Service QualityAditya Patel100% (1)
- Customer Satisfaction With Reference To Icecream inDocument26 pagesCustomer Satisfaction With Reference To Icecream inGio Joy100% (14)
- Summer Internship Report VadilalDocument106 pagesSummer Internship Report VadilalAditya PatelNo ratings yet
- Resume GaurDocument4 pagesResume GaurAditya PatelNo ratings yet
- Maslows' Need Hierarchy of Motivation: Submitted By: Aditya PatelDocument17 pagesMaslows' Need Hierarchy of Motivation: Submitted By: Aditya PatelAditya PatelNo ratings yet
- Retail Management 1Document11 pagesRetail Management 1Aditya PatelNo ratings yet
- Vadilal Industries LimitedDocument8 pagesVadilal Industries Limitedchetu009No ratings yet
- Vadilal QuestioneryDocument3 pagesVadilal QuestioneryAditya PatelNo ratings yet
- (Click Here To Print Your Application) : EKVGJ18-13050Document1 page(Click Here To Print Your Application) : EKVGJ18-13050Aditya PatelNo ratings yet
- FMCGDocument32 pagesFMCGAditya PatelNo ratings yet
- All Dealer Survey On Ice Cream IndustryDocument13 pagesAll Dealer Survey On Ice Cream IndustryAditya PatelNo ratings yet
- Every Dealer SurveyDocument2 pagesEvery Dealer SurveyJayantibhaipatel1668No ratings yet
- Vadi LalDocument58 pagesVadi LalAditya PatelNo ratings yet
- A Project Report On The Marketing Department of Madhur Dairy PVT - Ltd. in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirement ForDocument48 pagesA Project Report On The Marketing Department of Madhur Dairy PVT - Ltd. in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirement ForAditypatel451_548818No ratings yet