Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Brake System: By: Katiuska Vidal Talledo
Uploaded by
thzuska0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views13 pagesDisc brakes are fairly simple to work with, once you know the parts and their functions. Calipers clamp on to metal discs supported by the suspension to slow their rotation, and then slow or stop the car. Drum brake system fits over wheel hub or rotor.
Original Description:
Original Title
Brake System
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDisc brakes are fairly simple to work with, once you know the parts and their functions. Calipers clamp on to metal discs supported by the suspension to slow their rotation, and then slow or stop the car. Drum brake system fits over wheel hub or rotor.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
30 views13 pagesBrake System: By: Katiuska Vidal Talledo
Uploaded by
thzuskaDisc brakes are fairly simple to work with, once you know the parts and their functions. Calipers clamp on to metal discs supported by the suspension to slow their rotation, and then slow or stop the car. Drum brake system fits over wheel hub or rotor.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 13
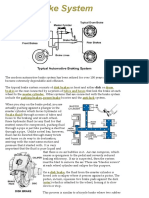
Brake System
By: Katiuska Vidal Talledo
ABS System
Normal operation when in conventional mode (if warning
light, disables ABS)
Heavy braking causes hydraulic pressure modulation (Pedal
Feel)
Integrated System (Combined parts)227C
Non-Integrated System (Separate Parts)
ABS operates independently of base system
Component ABS System
Inputs and Outputs (228C)
Some ABS ECUs have dual boards
Controls HCU
Full Diagnostics
Controls Warning Lights
Can control each wheel brake
independently. (four channel) Most
are three channel
Mechanical Noises
Hidraulic Control Unit
Anti-Lock
Brake Module
Speed
Sensor
Pressure
Valve
Dump/Vent Valve
Master Cylinder
Assembly
Anti Lock
12 V
During pressure
increase mode of
operation fluid is
allowed to flow
through both
solenoids to the brake
caliper
Solenoid 1
Pressure increase
Solenoid 2
Pressure
decrease/Vent solenoid
Brake line under
pressure
Brake fluid line not under
pressure
During Pressure Hold
mode of operation
both solenoids are
closed and no
additional fluid is
allowed to flow to
brake calipers.
Solenoid 1
Pressure increase
Solenoid 2
Pressure decrease/Vent
Solenoid 1
Pressure increase
Solenoid 2
Pressure decrease/Vent
During Pressure Vent
mode the pressure
increase solenoid is
closed. The Vent solenoid
opens allowing fluid to
vent into an accumulator
chamber
Disk Brake System
Disc brakes are fairly simple to work with,
once you know the parts and their functions.
Typically, there are 4 main parts of a system:
Mounting Bracket
Rotor
Caliper
Pads
Rotors are metal discs supported by the
suspension. The Calipers clamp on to them to
slow their rotation, and then slow or stop the
car
Vented Rotors have Fins in the spaces between
their machined surfaces. These spaces allow air
to pass through, which helps carry heat away.
Non Vented Rotors are used on smaller
vehicles, and have no cooling fins
Components of Disk Brake System
Operation disk brake System
Caliper
Rotor
Piston
Brake
Pads
Brake
Line
Piston applies pressure to Inboard
pad. As the pad contacts the rotor,
the caliper slides along the pins,
pulling the outboard pad into
contact.
Drum Brake System
Drum fits over
wheel hub or
drive flange.
The drum provides a friction
surface for the brake linings. It
also dissipates heat, and can
support wheel bearings
or road wheel.
Drums sometimes
have fins to aid
cooling.
Brake cylinder
assembly:
Backing plate
Brake shoe
Brake shoe
Handbrake cable
Tension
springs
Retracting
springs
Handbrake lever
Drum Brake Assembly
You might also like
- Chevy Differentials: How to Rebuild the 10- and 12-BoltFrom EverandChevy Differentials: How to Rebuild the 10- and 12-BoltRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (8)
- Donny’S Unauthorized Technical Guide to Harley-Davidson, 1936 to Present: Volume I: the Twin CamFrom EverandDonny’S Unauthorized Technical Guide to Harley-Davidson, 1936 to Present: Volume I: the Twin CamNo ratings yet
- Under Chassis Preventive Maintenance: Brake System GuideDocument31 pagesUnder Chassis Preventive Maintenance: Brake System GuideFrancis Martinez100% (1)
- Audi Adaptive Air Suspension PDFDocument45 pagesAudi Adaptive Air Suspension PDFJOHNNY537786% (7)
- Donny’S Unauthorized Technical Guide to Harley-Davidson, 1936 to Present: Volume Iv: Performancing the EvolutionFrom EverandDonny’S Unauthorized Technical Guide to Harley-Davidson, 1936 to Present: Volume Iv: Performancing the EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Signal Circuit LessonDocument1 pageSignal Circuit Lessonapi-208557858No ratings yet
- Hydraulic Brake: This Article Is Missing - Please Help AddDocument5 pagesHydraulic Brake: This Article Is Missing - Please Help AddthatsopurvaNo ratings yet
- Abs TheoryDocument40 pagesAbs TheoryBiswadip BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic brake system basicsDocument6 pagesHydraulic brake system basicsVijayakumar NatarajanNo ratings yet
- VIJAYDocument7 pagesVIJAYKatreddy Hemanth reddyNo ratings yet
- Palli Goutham Reddy 17BME0720: Hydraulic BrakesDocument2 pagesPalli Goutham Reddy 17BME0720: Hydraulic BrakesGoutham ReddyNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic BrakeDocument6 pagesHydraulic BrakeHemantha DalugamaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Brakes and Their TypesDocument5 pagesUnderstanding Brakes and Their TypesMoiz AamirNo ratings yet
- Braking System-By GirlsDocument23 pagesBraking System-By Girlskrish0690No ratings yet
- Braking SystemDocument19 pagesBraking SystemArvind YadavNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Braking Systems ExplainedDocument31 pagesMechanical Braking Systems ExplainedSan Surya80% (5)
- Hydraulic BrakeDocument5 pagesHydraulic BrakenvjkhfghfNo ratings yet
- ATT Brakes - Example TextbookDocument15 pagesATT Brakes - Example TextbookSooraj KrishnaNo ratings yet
- To Whom It May ConcernDocument96 pagesTo Whom It May ConcernKamal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Anti Lock Braking SystemDocument29 pagesAnti Lock Braking SystemPravin DeshmaneNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Braking Systems ExplainedDocument31 pagesMechanical Braking Systems ExplainedSan Surya100% (4)
- Week 4 Disc Brake System - Lecture PDFDocument76 pagesWeek 4 Disc Brake System - Lecture PDFamr yosryNo ratings yet
- Seminar Presentation: Braking System, TyreDocument28 pagesSeminar Presentation: Braking System, TyreGuru MaheshNo ratings yet
- 058 - Engine Mechanical - 2.4L (LEA LUK) - Description and OperationDocument9 pages058 - Engine Mechanical - 2.4L (LEA LUK) - Description and OperationGedas Gvildys100% (1)
- Anti Lock Braking SystemDocument29 pagesAnti Lock Braking SystemRaghavendra RaghavNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic BrakeDocument7 pagesHydraulic BrakeA. A. SherpedoNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Brake SystemDocument5 pagesHydraulic Brake SystemSatyanshu Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Differential SystemDocument75 pagesDifferential SystemNARAVENI RAM MOHANNo ratings yet
- Hydrolic Breaking SystemDocument56 pagesHydrolic Breaking SystemAnkush JainNo ratings yet
- Explaination For Brake System in Aircraft PDFDocument153 pagesExplaination For Brake System in Aircraft PDFal sarNo ratings yet
- AbsDocument30 pagesAbsEhtishaam AbbasNo ratings yet
- Federal University of Technology Minna in Affiliation With Federal College of Education (Tech) AkokaDocument13 pagesFederal University of Technology Minna in Affiliation With Federal College of Education (Tech) AkokaChandra SekarNo ratings yet
- Palli Goutham Reddy 17BME0720: Hydraulic BrakesDocument3 pagesPalli Goutham Reddy 17BME0720: Hydraulic BrakesGoutham ReddyNo ratings yet
- To Study About Various Types of Braking SystemDocument24 pagesTo Study About Various Types of Braking SystemRavi Donga100% (1)
- Hydraulic brake system explainedDocument38 pagesHydraulic brake system explainedAryan AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Brake Operating SystemDocument18 pagesBrake Operating SystemWoong-Sub LeeNo ratings yet
- How Disc Brakes WorkDocument50 pagesHow Disc Brakes WorkSleepy SpettoNo ratings yet
- BRAKESDocument46 pagesBRAKESDianna MadejaNo ratings yet
- Dismantle & Assemble Hermetic CompressorDocument6 pagesDismantle & Assemble Hermetic CompressorHritik Mali PatilNo ratings yet
- Other Systems That Are Connected With The Brake SystemDocument13 pagesOther Systems That Are Connected With The Brake SystemEnoch MwesigwaNo ratings yet
- CBLM Brake SystemDocument15 pagesCBLM Brake Systemace ebradoNo ratings yet
- Subaru Mod. 501 Brake Systems PDFDocument56 pagesSubaru Mod. 501 Brake Systems PDFDavid VelazquezNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Braking Systems GuideDocument14 pagesAircraft Braking Systems GuideLivil Lyle100% (1)
- Please install relays 1 & 2. Depress brake pedal fully 20 times, holding for 3 sec on each depression. Check fluid level and top off if needed.”5. To bleed the actuatorDocument82 pagesPlease install relays 1 & 2. Depress brake pedal fully 20 times, holding for 3 sec on each depression. Check fluid level and top off if needed.”5. To bleed the actuatorAbishake KoulNo ratings yet
- 2.0L FsiDocument46 pages2.0L Fsismellybum67% (3)
- Lab Manual Rac MaintenanceDocument42 pagesLab Manual Rac Maintenanceonkar kalaskarNo ratings yet
- Small Engines and Outdoor Power Equipment: A Care & Repair Guide for: Lawn Mowers, Snowblowers & Small Gas-Powered ImplementsFrom EverandSmall Engines and Outdoor Power Equipment: A Care & Repair Guide for: Lawn Mowers, Snowblowers & Small Gas-Powered ImplementsNo ratings yet
- The Book of the Singer Junior - Written by an Owner-Driver for Owners and Prospective Owners of the Car - Including the 1931 SupplementFrom EverandThe Book of the Singer Junior - Written by an Owner-Driver for Owners and Prospective Owners of the Car - Including the 1931 SupplementNo ratings yet
- Operator's Guide to General Purpose Steam Turbines: An Overview of Operating Principles, Construction, Best Practices, and TroubleshootingFrom EverandOperator's Guide to General Purpose Steam Turbines: An Overview of Operating Principles, Construction, Best Practices, and TroubleshootingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 10 Tips on How To Take Care of Your Car: Automotive Maintenance Anyone Can Do, #1From Everand10 Tips on How To Take Care of Your Car: Automotive Maintenance Anyone Can Do, #1No ratings yet
- Master the T-CLOCS Pre-Ride Safety Inspection in 15 MinutesFrom EverandMaster the T-CLOCS Pre-Ride Safety Inspection in 15 MinutesNo ratings yet
- Southern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IiFrom EverandSouthern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IiNo ratings yet
- The Dual Wheel Journey Motorcycle Terms Dictionary and Phrasebook: DWJ Dictionary, #2From EverandThe Dual Wheel Journey Motorcycle Terms Dictionary and Phrasebook: DWJ Dictionary, #2No ratings yet
- Decision Model Using ExcelDocument236 pagesDecision Model Using Excelসামিউল ইসলাম রাজু100% (3)
- Accelerate your career with online coursesDocument22 pagesAccelerate your career with online coursesAYEDITAN AYOMIDENo ratings yet
- OptQuest User ManualDocument190 pagesOptQuest User ManualYamal E Askoul TNo ratings yet
- Wi Cswip 3.1 Part 13Document7 pagesWi Cswip 3.1 Part 13Ramakrishnan AmbiSubbiahNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Gases in LaboratoryDocument7 pagesPreparation of Gases in LaboratoryChu Wai Seng50% (2)
- Service Manual (V1.22)Document529 pagesService Manual (V1.22)JensNo ratings yet
- What Is XRF ?: Prepared by Lusi Mustika SariDocument34 pagesWhat Is XRF ?: Prepared by Lusi Mustika SariBayuNo ratings yet
- Thermocouple Wire Reference Guide: WWW - Omega.co - Uk +44 (0) 161 777 6611 WWW - Omega.co - Uk +44 (0) 161 777 6611Document1 pageThermocouple Wire Reference Guide: WWW - Omega.co - Uk +44 (0) 161 777 6611 WWW - Omega.co - Uk +44 (0) 161 777 6611Mohamed MaltiNo ratings yet
- Cylindrical Plug Gage DesignsDocument3 pagesCylindrical Plug Gage DesignskkphadnisNo ratings yet
- Clone Steps RmanDocument10 pagesClone Steps RmanKishore AdikarNo ratings yet
- Coordinated Interference Management (Low-Frequency TDD) (5G RAN6.1 - Draft A)Document28 pagesCoordinated Interference Management (Low-Frequency TDD) (5G RAN6.1 - Draft A)VVLNo ratings yet
- Iygb Gce: Mathematics MP2 Advanced LevelDocument7 pagesIygb Gce: Mathematics MP2 Advanced Levelsingh cos tanNo ratings yet
- 4MA0 4HR Que 20140115Document24 pages4MA0 4HR Que 20140115Lalith77No ratings yet
- Splunk Skills Assessment-UpdatedDocument14 pagesSplunk Skills Assessment-Updatedtsegay.csNo ratings yet
- Rac NotesDocument16 pagesRac NotesJohnRay LominoqueNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Recommendations: Operation and Maintenance ManualDocument10 pagesMaintenance Recommendations: Operation and Maintenance ManualAmy Nur SNo ratings yet
- IMS2 Manual EngDocument61 pagesIMS2 Manual EngJhonatan BuenoNo ratings yet
- Ch01Document33 pagesCh01sakali aliNo ratings yet
- Inductive TransducersDocument12 pagesInductive TransducersMUKESH SUNDARARAJANNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01Document18 pagesLecture 01priyasonu049No ratings yet
- PSD60-2R: Operation ManualDocument22 pagesPSD60-2R: Operation ManualOscar SantanaNo ratings yet
- Matrix Inversion Note in Mathematics MagazineDocument2 pagesMatrix Inversion Note in Mathematics Magazinejuan carlos molano toroNo ratings yet
- Trenes de Engranajes - PresentaciónDocument17 pagesTrenes de Engranajes - PresentaciónPedro Jorge De los SantosNo ratings yet
- Bio Inorganic ChemistryDocument2 pagesBio Inorganic ChemistryMeghna KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit I The Scientific Approach in EducationDocument4 pagesUnit I The Scientific Approach in EducationadesaNo ratings yet
- Knight Boiler ManualDocument80 pagesKnight Boiler ManualAnonymous 7xHNgoKE6eNo ratings yet
- Lubricants For Cement ProductionDocument21 pagesLubricants For Cement Productiongrameshkreddy2013100% (1)
- Financial Accounting IIDocument16 pagesFinancial Accounting IIMiguel BuenoNo ratings yet
- TDT4171 Artificial Intelligence Methods Task 5 Creating A Decision Support SystemDocument12 pagesTDT4171 Artificial Intelligence Methods Task 5 Creating A Decision Support SystemKermess McNo ratings yet