Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Uploaded by
Erick Figueroa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
49 views11 pagesfor rhematoid arthitis acute
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentfor rhematoid arthitis acute
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
49 views11 pagesRheumatoid Arthritis
Uploaded by
Erick Figueroafor rhematoid arthitis acute
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
A chronic multisystem disease of unknown
etiology characterized by persistent
inflammatory synovitis involving peripheral
joints in a symmetric fashion
Hallmarks :
Cartilaginous destruction, bony erosions,
and joint deformity
The course is variable
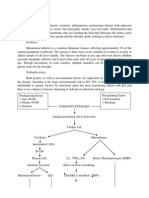
An immunologically mediated event in
which joint injury occurs from synovial
hyperplasia; lymphocytes infiltration of
synovium; and local production of
cytokines and chemokines by activated
lymphocytes, macrophages, and
fibroblasts
RA occurs in 0.8 % of the population
Women affected 3 times more often
than men
Prevalence increases with age
Onset most frequent in fourth and fifth
decades
Articular Manifestations
A symmetric polyarthritis of peripheral
joints with pain, tenderness and swelling
of affected joints
Morning stiffness
PIP and MCP joints involved
Joints deformities may develop after
persistent inflammation
Extraarticular Manifestations
Cutaneous rheumatoid nodules,
vasculitis
Pulmonary nodules, interstitial disease
Ocular episcleritis, scleritis
Hematologic anemia , feltys syndrome
Cardiac pericarditis, myocarditis
Neurologic myelopathies secondary to
cervical spine disease
Hx and physical exam
Rheumatoid factor is present in 85 % of pts;
its presence correlates with severe disease,
nodules, extraarticular features
Other laboratories : CBC, ESR
Synovial fluids analysis
Radiograph juxtaarticular osteopenia, joint
space narrowing, marginal erosions. CXR should
be obtained
Not difficult in pts with typical
established disease
May be confusing early
Classification criteria were developed
for investigational purposes
Differential diagnosis :
Gout, SLE, psoriatic arthritis, infectious
arthritis, osteoarthritis, sarcoid
CLASSIFICATION CRITERIA FOR RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
[*]
1. Morning stiffness (1 hr)
2. Swelling (soft tissue) of three or more joints
3. Swelling (soft tissue) of hand joints (PIP, MCP, or wrist)
4. Symmetrical swelling (soft tissue)
5. Subcutaneous nodules
6. Serum rheumatoid factor
7. Erosions and/or periarticular osteopenia in hand or wrist joints seen
on radiograph
*
Criteria 1 through 4 must have been continuously present for 6 wk or
longer, and criteria 2 through 5 must be observed by a physician
. A classification as rheumatoid arthritis requires that four of the seven
criteria be fulfilled. MCP = metacarpophalangeal; PIP = proximal
interphalangeal
TABLE 285-3 -- DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF
RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
Disorder Subcutaneous Nodules Rheumatoid Factor
-Viral arthritis (hepatitis B and C, parvovirus,
rubella, others)
- Bacterial endocarditis
+ Rheumatic fever +
- Sarcoidosis + + Reactive arthritis - - Psoriatic
arthritis - - Systemic lupus erythematosus
+ Primary Sjgren's syndrome
+ Chronic tophus gout + - Calcium pyrophosphate
disease - -
Polymyalgia rheumatica - - Osteoarthritis (erosive) -
- - = not present; + = frequently present; =
occasionally present
Pt education on disease, joint protection
Physical and occupational therapy
Aspirin or NSAIDs
Intra articular glucocorticoids
Systemic glucocorticoids
DMARDs (Disease Moving Anti Rheumatic
Drugs)
Anti-cytokine therapy
Immunosuppressive therapy
Surgery may be considered
You might also like
- ArthritisDocument56 pagesArthritisyulitamustikasariNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument19 pagesRheumatoid ArthritisLiya AnjelinaNo ratings yet
- AR - Clínica y LaboratorioDocument8 pagesAR - Clínica y LaboratoriomonseibanezbarraganNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Presented By: Layan S. Barqawi Supervisor: Dr. Dirar DibsDocument10 pagesRheumatoid Arthritis: Presented By: Layan S. Barqawi Supervisor: Dr. Dirar Dibsasop06No ratings yet
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: By: Claudio Wangta Oky CahyantoDocument18 pagesRheumatoid Arthritis: By: Claudio Wangta Oky CahyantoEditya AprilianiNo ratings yet
- Overview of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Naureen Mirza, MD May 10, 2010Document34 pagesOverview of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Naureen Mirza, MD May 10, 2010csingleton2364No ratings yet
- Juvenile Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument30 pagesJuvenile Rheumatoid Arthritispragna VanapalaNo ratings yet
- Juvenile Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument30 pagesJuvenile Rheumatoid ArthritisAnonymous dFSZ2k2IUNo ratings yet
- Poliartr - Reumatoida EnglezaDocument104 pagesPoliartr - Reumatoida EnglezaGermanyNo ratings yet
- باطنة تمريض rheumatologyDocument6 pagesباطنة تمريض rheumatologyAbdullmlik AlfurasNo ratings yet
- Pag 001 190 GeorgescuDocument19 pagesPag 001 190 GeorgescuBooker DewittNo ratings yet
- Arthritides 5th Year-UNZA LectureDocument76 pagesArthritides 5th Year-UNZA LectureMohammed AadeelNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid Arthritis PresentationDocument36 pagesRheumatoid Arthritis PresentationAsyaari ArifNo ratings yet
- DR - Farhad Salehzadeh Connective Tissue DiseaseDocument70 pagesDR - Farhad Salehzadeh Connective Tissue DiseaseLinux LinuxNo ratings yet
- Annie Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument65 pagesAnnie Rheumatoid Arthritissaroj yadavNo ratings yet
- Final Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument27 pagesFinal Rheumatoid ArthritisAmmarNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument7 pagesRheumatoid ArthritisPrince OcsanNo ratings yet
- Disorder of Musculo - System. LeatestDocument178 pagesDisorder of Musculo - System. LeatestCheru TecheNo ratings yet
- Clinical Therapeutics: Eva Fe R. Columna M D - 3 BDocument16 pagesClinical Therapeutics: Eva Fe R. Columna M D - 3 BMichelle Vera GabunNo ratings yet
- Approach To Arthritis PDFDocument54 pagesApproach To Arthritis PDFanahitshoNo ratings yet
- RematikDocument66 pagesRematikYolla LitaNo ratings yet
- Nitesh Kumar Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument8 pagesNitesh Kumar Rheumatoid Arthritisnitesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Classification of Disorders of Musculoskeletal System (MSK) : Presented By: Siti Sarah Maha Dewi Bong Jen NeeDocument69 pagesClassification of Disorders of Musculoskeletal System (MSK) : Presented By: Siti Sarah Maha Dewi Bong Jen NeeBONG AIKCHINGNo ratings yet
- Rheumatic FeverDocument27 pagesRheumatic FeverMalueth AnguiNo ratings yet
- Faculty of MedicineDocument28 pagesFaculty of MedicineRana AtefNo ratings yet
- 11th May MRCP RecallsDocument2,080 pages11th May MRCP Recallsgirlygirl10No ratings yet
- Rheumatoid Arthritis 1Document63 pagesRheumatoid Arthritis 1ycg9n6wq4rNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: By: Gaganpreet KaurDocument11 pagesRheumatoid Arthritis: By: Gaganpreet KaurGaganpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- (MS1R) Common Representative Rheumatic DiseasesDocument6 pages(MS1R) Common Representative Rheumatic DiseasesYana DizonNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument6 pagesRheumatoid ArthritisJayson Cruz100% (2)
- Reumatoid ArthritisFDH2013Document63 pagesReumatoid ArthritisFDH201395kodok85No ratings yet
- Diagnosing Acute Monoarthritis in Adults PDFDocument8 pagesDiagnosing Acute Monoarthritis in Adults PDF蔡季霖No ratings yet
- Pemicu 1 - MuskuloDocument27 pagesPemicu 1 - MuskuloRyanNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument11 pagesRheumatoid ArthritisAkshayNo ratings yet
- ArthritisDocument22 pagesArthritisAbhirami XII S1No ratings yet
- Avascular Necrosis of Femoral HeadDocument50 pagesAvascular Necrosis of Femoral HeadStar CruiseNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument66 pagesRheumatoid ArthritisSaeda AhmedNo ratings yet
- Reiter's SyndromeDocument17 pagesReiter's SyndromeSyed Khidir Al-AminNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis of Transverse MielitisDocument14 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of Transverse MielitisLuminița VelceanNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (Ra)Document41 pagesRheumatoid Arthritis (Ra)manisha paikarayNo ratings yet
- Final Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument58 pagesFinal Rheumatoid ArthritisShivalingaiah GirishNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid Athritis (Ra)Document24 pagesRheumatoid Athritis (Ra)Malueth Angui100% (1)
- Joint PainDocument8 pagesJoint Painحنين حسن عبد علي حسينNo ratings yet
- PyomyositisDocument23 pagesPyomyositisIbrahim Ahmed IbrahimNo ratings yet
- InjuryDocument50 pagesInjuryRenaldas AugulisNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Airlangga UniversityDocument37 pagesRheumatoid Arthritis: Airlangga UniversityDwiyNo ratings yet
- SBRC RheumatologyDocument26 pagesSBRC RheumatologyErin HillNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument6 pagesRheumatoid ArthritislianausinNo ratings yet
- PolymyositisDocument5 pagesPolymyositisdeea03No ratings yet
- Approach To Arthritis: Clinical GuideDocument4 pagesApproach To Arthritis: Clinical GuideaveekumbharNo ratings yet
- Chap 321: GideonjcaballesDocument73 pagesChap 321: GideonjcaballesMichelle ThereseNo ratings yet
- Ar PDFDocument26 pagesAr PDFBárbara Romero OlateNo ratings yet
- Rheumatology Saif 2013 Wesmosis PDFDocument30 pagesRheumatology Saif 2013 Wesmosis PDFMohamed A SalehNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument23 pagesRheumatoid Arthritisfabunmiopeyemiv23No ratings yet
- Rheumatoid Arthritis by DR Bashir Ahmed Dar Associate Professor Medicine Sopore KashmirDocument220 pagesRheumatoid Arthritis by DR Bashir Ahmed Dar Associate Professor Medicine Sopore KashmirProf Dr Bashir Ahmed Dar Chinki Pora Sopore KashmirNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Foot, Diabetic Foot Ulcer & Diabetic Foot Care: Prepared by Munirah Supervised by DR NaqibDocument49 pagesDiabetic Foot, Diabetic Foot Ulcer & Diabetic Foot Care: Prepared by Munirah Supervised by DR NaqibAfifah SelamatNo ratings yet
- Neuroendocrine Tumors: Surgical Evaluation and ManagementFrom EverandNeuroendocrine Tumors: Surgical Evaluation and ManagementJordan M. CloydNo ratings yet