Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Motivation and Behaviour
Uploaded by
biju0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
51 views53 pagesmotivation theories
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentmotivation theories
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
51 views53 pagesMotivation and Behaviour
Uploaded by
bijumotivation theories
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 53
Motivation is the force that initiates, guides
and maintains goal-oriented behaviors.
The forces that lie beneath motivation can be
biological, social, emotional or cognitive in
nature.
In 1927, a group of researchers led by Elton
Mayo and Fritz Roethlisberger were invited to
join in the studies at the Hawthorne Works of
Western Electric Company, Chicago.
The Hawthorne experiment consists of four
parts:-
Illumination Experiment.
Relay Assembly Test Room Experiment.
Interviewing Programme.
Bank Wiring Test Room Experiment
1. Illumination Experiment:
This experiment was conducted to establish
relationship between output and illumination.
When the intensity of light was increased, the
output also increased.
The output showed an upward trend even when
the illumination was gradually brought down to
the normal level.
Therefore, it was concluded that there is no
consistent relationship between output of
workers and illumination in the factory.
There must be some other factor which affected
productivity
2. Relay Assembly Test Room Experiment:
This phase aimed at knowing the impact of
illumination. length of the working day, rest hours,
and other physical conditions.
Small homogeneous work-group of six girls.
Friendly to each other and were asked to work in a
very informal atmosphere under the supervision of a
researcher.
Productivity and morale increased.
Pre-test conditions were reintroduced and still
productivity increased.
Socio-psychological factors such as feeling of being
important, recognition, attention, participation,
cohesive work-group, and non-directive
supervision held the key for higher productivity.
3. Mass Interview Programme:
Systematic study of the employees attitudes
which would reveal the meaning which their
working situation has for them.
Opinions on work, working conditions and
supervision.
Initially, a direct approach was used
Later the approach was replaced by an
indirect technique.
The findings confirmed the importance of
social factors at work in the total work
environment.
4. Bank Wiring Test Room Experiment:
Causes of lower output
Group of workers(14) under conditions
which were as close as possible to normal.
After the experiment, the production records
of this group were compared with their
earlier production records.
Group evolved its own production norms for
each individual worker, which was made
lower than those set by the management
defeating the incentive system.
The important features of the Hawthorne Experiment
are:-
A business organization is basically a social system.
It is not just a techno-economic system.
The employer can be motivated by psychological
and social wants because his behaviour is also
influenced by feelings, emotions and attitudes. Thus
economic incentives are not the only method to
motivate people.
Management must learn to develop co-operative
attitudes and not rely merely on command.
Participation becomes an important instrument in
human relations movement. In order to achieve
participation, effective two-way communication
network is essential
Productivity is linked with employee
satisfaction in any business organization.
Therefore management must take greater
interest in employee satisfaction.
Group psychology plays an important role in
any business organization. We must therefore
rely more on informal group effort.
The neo-classical theory emphasizes that
man is a living machine and he is far more
important than the inanimate machine. Hence,
the key to higher productivity lies in employee
morale. High morale results in higher output.
The Hawthorne Experiments are mainly criticised
on the following grounds :-
Lacks Validity : The Hawthorne experiments
were conducted under controlled situations.
More Importance to Human Aspects : The
Hawthorne experiments gives too much
importance to human aspects. Human aspects
alone cannot improve production. Production also
depends on technological and other factors.
More Emphasis on Group Decision-
making: In real situation, individual decision-
making cannot be totally neglected especially
when quick decisions are required and there
is no time to consult others.
Over Importance to Freedom of Workers :
It does not give importance to the constructive
role of the supervisors. In reality too much of
freedom to the workers can lower down their
performance or productivity.
The basis of Maslow's theory is
that human beings are motivated
by unsatisfied needs, and that
certain lower needs need to be
satisfied before higher needs can
be satisfied.
According to Maslow, there are general types
of needs (physiological, safety, love, and
esteem) that must be satisfied before a
person can act unselfishly. He called these
needs "deficiency needs." As long as we are
motivated to satisfy these cravings, we are
moving towards growth, toward self-
actualization.
Satisfying needs is healthy, while
preventing gratification makes us sick or act
evilly.
The human motivation listed by Maslow
in the following order:
1. Self-Actualization
2. Esteem Needs
3. Social Needs
4. Safety Needs
5. Physiological Needs
Physiological needs are those required to
sustain life, such as:
Air
Water
Food
Sleep
Once physiological needs are met, one's
attention turns to safety and security in
order to be free from the threat of
physical and emotional harm. Such
needs might be fulfilled by:
Living in a safe area
Medical insurance
Job security
Financial reserves
Once a person has met the lower level
physiological and safety needs, higher level
needs awaken. The first level of higher level
needs are social needs.
Social needs are those related to interaction
with others and may include:
Friendship
Belonging to a group
Once a person feels a sense of "belonging", the
need to feel important arises. Esteem needs
may be classified as internal or external.
Internal esteem needs are those related to self-
esteem such as self respect and achievement.
External esteem needs are those such as social
status and recognition. Some esteem needs are:
Self-respect
Achievement
Attention
Recognition
Reputation
Self-actualization is the summit of
Maslow's hierarchy of needs. It is the
quest of reaching one's full potential as a
person.
Self-actualized people tend to have
needs such as:
Truth
Justice
Wisdom
Meaning
In 1960, Douglas McGregor formulated
Theory X and Theory Y suggesting two
different views of individuals (employees):
one of which is negative, called as Theory X
and the other is positive, so called as Theory
Y. According to McGregor, the perception of
managers on the nature of individuals is
based on various assumptions.
An average employee intrinsically does not
like work and tries to escape it.
He must be persuaded, compelled, or
warned with punishment so as to achieve
organizational goals.
A close supervision is required on part of
managers. The managers adopt a more
dictatorial style.
Many employees rank job security on top,
and they have little or no aspiration/
ambition.
Employees generally dislike
responsibilities.
Employees resist change.
An average employee needs formal
direction.
Employees can perceive their job as relaxing
and normal. They exercise their physical and
mental efforts in an inherent manner in their
jobs.
Employees may not require only threat,
external control and coercion to work, but they
can use self-direction and self-control if
they are dedicated and sincere to achieve the
organizational objectives.
If the job is rewarding and satisfying, then it
will result in employees loyalty and
commitment to organization.
An average employee can learn to admit and
recognize the responsibility.
The employees have skills and capabilities
and can be utilized to solve organizational
problems.
Thus, we can say that Theory X presents a
pessimistic view of employees, while
Theory Y presents an optimistic view of the
employees.
McGregor views Theory Y to be more valid
and reasonable than Theory X. Thus, he
encouraged cordial team relations,
responsible and stimulating jobs, and
participation of all in decision-making process.
Quite a few organizations use Theory X today.
Theory X encourages use of tight control
and supervision. Thus, it does not
encourage innovation.
Theory Y implies that the managers should
create and encourage a work environment
which provides opportunities to employees
to take initiative and self-direction.
Encourages decentralization of authority,
teamwork and participative decision
making in an organization.
In 1959, Frederick Herzberg, a behavioural
scientist proposed a two-factor theory or the
motivator-hygiene theory.
According to Herzberg, there are some job
factors that result in satisfaction while there
are other job factors that prevent
dissatisfaction.
According to Herzberg, the opposite of
Satisfaction is No satisfaction and the
opposite of Dissatisfaction is No
Dissatisfaction.
Hygiene factors- Hygiene factors are those
job factors which are essential for existence
of motivation at workplace.
These do not lead to positive satisfaction
for long-term. But if these factors are absent,
then they lead to dissatisfaction.
Hygiene factors are also called as
maintenance factors as they are required to
avoid dissatisfaction.
Pay - The pay or salary structure should be
appropriate and reasonable. It must be equal and
competitive to those in the same industry in the
same domain.
Company Policies and administrative policies
- The company policies should not be too rigid.
They should be fair and clear. It should include
flexible working hours, dress code, breaks,
vacation, etc.
Fringe benefits - The employees should be
offered health care plans (mediclaim), benefits for
the family members, employee help programmes,
etc.
Physical Working conditions - The working
conditions should be safe, clean and hygienic.
The work equipments should be updated and
well-maintained.
Status - The employees status within the
organization should be familiar and retained.
Interpersonal relations - The relationship of the
employees with his peers, superiors and
subordinates should be appropriate and
acceptable. There should be no conflict or
humiliation element present.
Job Security - The organization must provide job
security to the employees
Motivational factors: The motivational
factors yield positive satisfaction. These
factors motivate the employees for a superior
performance. These factors are called
satisfiers.
Employees find these factors intrinsically
rewarding. The motivators symbolized the
psychological needs that were perceived as
an additional benefit.
Recognition - The employees should be
praised and recognized for their
accomplishments by the managers.
Sense of achievement - The employees
must have a sense of achievement. This
depends on the job. There must be a fruit of
some sort in the job.
Growth and promotional opportunities -
There must be growth and advancement
opportunities in an organization to motivate
the employees to perform well.
Responsibility - The employees must hold
themselves responsible for the work. The
managers should give them ownership of the
work. They should minimize control but retain
accountability.
Meaningfulness of the work - The work itself
should be meaningful, interesting and
challenging for the employee to perform and
to get motivated.
Overlooks situational variables.
Herzberg assumed a correlation between
satisfaction and productivity. But the research
conducted by Herzberg stressed upon satisfaction and
ignored productivity.
No comprehensive measure of satisfaction was
used. An employee may find his job acceptable
despite the fact that he may hate/object part of his job.
The two factor theory is not free from bias as it is
based on the natural reaction of employees . They
will blame dissatisfaction on the external factors such
as salary structure, company policies and peer
relationship. Also, the employees will give credit to
themselves for the satisfaction factor at work.
The theory ignores blue-collar workers.
The Two-Factor theory implies that the
managers must stress upon guaranteeing the
adequacy of the hygiene factors to avoid
employee dissatisfaction.
Also, the managers must make sure that the
work is stimulating and rewarding.
This theory emphasize upon job-enrichment
so as to motivate the employees. The job
must utilize the employees skills and
competencies to the maximum.
Given by Chris Argyris
Proposed that the degree of
development of an individuals
personality can be explained in seven
dimensions
Argyris felt that, as people matured, they
desired independence,
more variety in their activities,
and more control over their own actions.
To give them these things would motivate them.
To treat them as immature and ignore these
factors would demotivate them.
Immaturity characteristics Maturity characteristics
Passivity
Dependence
Few ways of behaving
Shallow interests
Short-time perspective
Subordinate position
Lack of self
awareness
Activity
Independence
Diverse ways of
behaving
Deep interests
Long time perspective
Superordinate position
Self awareness and
control
The personalities of employees in an
organization are generally at the mature end
of the continuum. However, organizations
fail to recognize this maturity and treat
employees as if they are immature. This
leads to conflict.
The extent that individuals and groups
perceive their own goals as being satisfied by
the accomplishment of organizational goals is
the degree of integration of goals. When
organizational goals are shared by all, the
term goal congruence can be used.
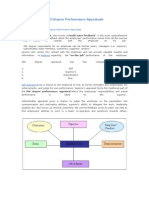
To illustrate this concept, we can divide an
organization into two groups, management
and subordinates
The respective goals of these two groups
and the resultant attainment of the goals of
the organization to which they belong can be
illustrated with the help of a daigram
In 1960s, Edwin Locke put forward the Goal-
setting theory of motivation
It states that specific and challenging goals
along with appropriate feedback contribute
to higher and better task performance.
In simple words, goals indicate and give
direction to an employee about what needs
to be done and how much efforts are required
to be put in.
They provide a useful framework for
managing motivation since employees can
set their own goals.
Goals are an effective control device; control
is the monitoring by management of how well
the organization is performing.
Clear, particular and difficult goals are
greater motivating factors than easy, general
and vague goals.
Specific and clear goals lead to greater
output and better performance.
Goals should be realistic and challenging.
Better and appropriate feedback of results
directs the employee behaviour
Participation of setting goal, however,
makes goal more acceptable and leads to
more involvement.
Goal setting theory is a technique used to
raise incentives for employees to complete
work quickly and effectively.
Goal setting leads to better performance by
increasing motivation and efforts, but also
through increasing and improving the
feedback quality.
At times, the organizational goals are in
conflict with the managerial goals.
Difficult and complex goals stimulate riskier
behaviour.
If the employee lacks skills and
competencies to perform actions essential
for goal, then the goal-setting can fail and
lead to undermining of performance.
There is no evidence to prove that goal-
setting improves job satisfaction.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- 1.1: Accounting Conventions and Standards ObjectivesDocument6 pages1.1: Accounting Conventions and Standards ObjectivesbijuNo ratings yet
- Module 1: Indian Contract ActDocument1 pageModule 1: Indian Contract ActbijuNo ratings yet
- 1.1: Accounting Conventions and Standards ObjectivesDocument6 pages1.1: Accounting Conventions and Standards ObjectivesbijuNo ratings yet
- 1.1: Accounting Conventions and Standards ObjectivesDocument6 pages1.1: Accounting Conventions and Standards ObjectivesbijuNo ratings yet
- 1.1: Accounting Conventions and Standards ObjectivesDocument6 pages1.1: Accounting Conventions and Standards ObjectivesbijuNo ratings yet
- An Understanding of The Indian Legal System International Law EssayDocument9 pagesAn Understanding of The Indian Legal System International Law EssaybijuNo ratings yet
- An Understanding of The Indian Legal System International Law EssayDocument9 pagesAn Understanding of The Indian Legal System International Law EssaybijuNo ratings yet
- Jaiib mcq2 Nov08Document51 pagesJaiib mcq2 Nov08Dipti Jain100% (2)
- BANKING MCQDocument23 pagesBANKING MCQbijuNo ratings yet
- BANKING MCQDocument23 pagesBANKING MCQbijuNo ratings yet
- BANKING MCQDocument23 pagesBANKING MCQbijuNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Jaiib mcq2 Nov08Document51 pagesJaiib mcq2 Nov08Dipti Jain100% (2)
- An Understanding of The Indian Legal System International Law EssayDocument9 pagesAn Understanding of The Indian Legal System International Law EssaybijuNo ratings yet
- Definition of Mercantile Law or Business LawDocument2 pagesDefinition of Mercantile Law or Business LawbijuNo ratings yet
- CGDocument4 pagesCGbijuNo ratings yet
- Agm and CSDocument5 pagesAgm and CSbijuNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 CGDocument11 pagesUnit 2 CGbijuNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 CGDocument11 pagesUnit 2 CGbijuNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 CGDocument22 pagesUnit 1 CGbijuNo ratings yet
- Bgs SchemeDocument4 pagesBgs SchemebijuNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Joint Stock CompanyDocument2 pagesJoint Stock CompanybijuNo ratings yet
- Bank LendingsDocument19 pagesBank LendingsbijuNo ratings yet
- Class VIDocument2 pagesClass VIbijuNo ratings yet
- SN P&P 2013 PDFDocument188 pagesSN P&P 2013 PDFMixxmixouNo ratings yet
- Insurance Business Environment An IntroductionDocument30 pagesInsurance Business Environment An Introductionbiju83% (6)
- CaseDocument5 pagesCasebijuNo ratings yet
- New AccountDocument2 pagesNew AccountbijuNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Chapter Three: Consumer Markets and Consumer Buyer BehaviorDocument33 pagesChapter Three: Consumer Markets and Consumer Buyer BehaviorJiya AshNo ratings yet
- Feminist Therapy: Miller Enns Espin BrownDocument21 pagesFeminist Therapy: Miller Enns Espin BrownHaru RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Motivational Factors in LearningDocument4 pagesMotivational Factors in LearningRiz GetapalNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Job Satisfaction of EmployeesDocument11 pagesProject Report On Job Satisfaction of EmployeesRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Gender Issues in Career CounselingDocument2 pagesGender Issues in Career CounselingNur Qatrunnada100% (2)
- Humanistic Approach To CounsellingDocument2 pagesHumanistic Approach To CounsellingJoseph Hong100% (2)
- Journal of Hospitality, Leisure, Sport & Tourism Education: Practice PapersDocument10 pagesJournal of Hospitality, Leisure, Sport & Tourism Education: Practice PapersselfiNo ratings yet
- Human Behaviour of Organisation........Document9 pagesHuman Behaviour of Organisation........pdudhaneNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire REPAIREDDocument3 pagesQuestionnaire REPAIREDCK Kyah MindalanoNo ratings yet
- Patterson Operation Case Study PresentationDocument8 pagesPatterson Operation Case Study Presentationceilhyn0% (2)
- (Yap, Jun Zen Ralph V.) - NSTP 1Document5 pages(Yap, Jun Zen Ralph V.) - NSTP 1Junzen Ralph YapNo ratings yet
- Alternatives To Out of School SuspensionDocument58 pagesAlternatives To Out of School Suspensionapi-202351147No ratings yet
- Multiple Intelligence Theory and Its ImplicationsDocument10 pagesMultiple Intelligence Theory and Its Implicationsapi-329914302No ratings yet
- Reflection On Learning EnvironmentDocument2 pagesReflection On Learning EnvironmentevamieNo ratings yet
- 15 Common Defense MechanismDocument5 pages15 Common Defense MechanismAndrea Marie T. Artajo-BoheromNo ratings yet
- 360 Degree Performance AppraisalsDocument5 pages360 Degree Performance AppraisalsJonathan BarretoNo ratings yet
- Nurse Patient/ Client (5 Years Old) Interpretation: Good Morning, Yao! "Good Ning" While Showing ADocument6 pagesNurse Patient/ Client (5 Years Old) Interpretation: Good Morning, Yao! "Good Ning" While Showing ALarr Sumalpong0% (1)
- Grinder Nueva PNLDocument18 pagesGrinder Nueva PNLalfa centauro100% (1)
- Influencer StudyDocument13 pagesInfluencer StudyJose PerezNo ratings yet
- Bullying in The WorkplaceDocument6 pagesBullying in The WorkplaceGaurav PareekNo ratings yet
- John W. Fleenor: Personnel Psychology Vol. 59, No. 2-Summer, 2006 457-500Document45 pagesJohn W. Fleenor: Personnel Psychology Vol. 59, No. 2-Summer, 2006 457-500francefrancemarocNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Personality Psychology McAdamsDocument92 pagesIntroduction To Personality Psychology McAdamsletsraceturtles100% (2)
- "What's Your Basic Leadership Style" in This Study, Count The Number of Situations ToDocument66 pages"What's Your Basic Leadership Style" in This Study, Count The Number of Situations ToShashank Vikram SinghNo ratings yet
- Trauma 101 Activity PacketDocument39 pagesTrauma 101 Activity PacketMs. Rachel SamsonNo ratings yet
- Introduction of SocializationDocument5 pagesIntroduction of SocializationOsama Aadil Saadi100% (2)
- Self-Love Lesson Plan: ObjectiveDocument8 pagesSelf-Love Lesson Plan: Objectiveapi-327713634No ratings yet
- Kathy Kawalec S 5 Step FormulaDocument20 pagesKathy Kawalec S 5 Step Formulashado23463No ratings yet
- Chapter 2.4 PDFDocument20 pagesChapter 2.4 PDFmahesh_khebadeNo ratings yet
- DLP in PERDEv 1Document4 pagesDLP in PERDEv 1nox pallon100% (1)
- Review For Mid-Term Exam - Course Organizational Behavior Mid-Term Exam-Ob CourseDocument4 pagesReview For Mid-Term Exam - Course Organizational Behavior Mid-Term Exam-Ob CoursePhúc DuyênNo ratings yet