Professional Documents
Culture Documents
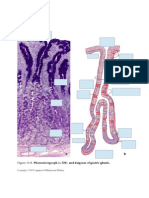
Cytology
Uploaded by
elvinang0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
53 views71 pagesThe CELL is a system by itself that can exist in a medium from other living organisms. It is made up of Plasma / cell membrane, a semi-permeable layer with protein, and a cell wall made up of cellulose in plants and algae; murein in bacteria and chitin in fungi. Cytoplasm - contains the organelles which are integral components of the cell.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe CELL is a system by itself that can exist in a medium from other living organisms. It is made up of Plasma / cell membrane, a semi-permeable layer with protein, and a cell wall made up of cellulose in plants and algae; murein in bacteria and chitin in fungi. Cytoplasm - contains the organelles which are integral components of the cell.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
53 views71 pagesCytology
Uploaded by
elvinangThe CELL is a system by itself that can exist in a medium from other living organisms. It is made up of Plasma / cell membrane, a semi-permeable layer with protein, and a cell wall made up of cellulose in plants and algae; murein in bacteria and chitin in fungi. Cytoplasm - contains the organelles which are integral components of the cell.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 71
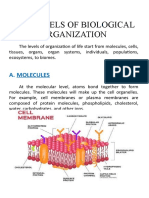
THE CELL
1. Definition of the Cell:
- the structural and functional unit of living
organisms
- is a system by itself that can exist in a
medium from other living organisms
- Discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665 from
the bark of a tree
II. Structures of the Cell:
1. Plasma / Cell Membrane
is a thin limiting membrane that encloses
the cell, defining the boundaries between
the ECF and ICF
it functions for: support, protection, and
passage of substances to and from the
cell
is semi-permeable and is made up of
bilipid layer with protein
- provides identity to the cell
Cell Wall:
is found outside the cell membrane
made up mainly of cellulose in plants and
algae; murein in bacteria and chitin in
fungi
2. Protoplasm
- the living substance within the cell
- located inner to the cell
membrane
- Physical properties:
1. Colloidal
2. Transparent
3. Colorless
4. Elastic
- Chemical Properties
1. Inorganic Compounds:
a. Water most abundant,
makes up 80-85%
- absorbs heat
b. Salts and Minerals
c. Gases
d. Organic Compounds:
d.1. Carbohydrates supply
energy for metabolic
processes
types:
1. Monosaccharides : glucose,
fructose & galactose
2. Disaccharides : lactose, maltose
& sucrose
3. Polysaccharides: cellulose,
starch, glycogen
d.2. Lipids
constituent of the cell membrane
types:
1. fats
2. oil
d.3. Proteins
- responsible for growth, repair and
differentiation of worn out tissues
3. Cytoplasm
- contains the organelles which are
the integral components of the
cell
a. Mitochondria
-ovoid/filamentous/sausage-shaped
-has 2 layers
- in-foldings of the inner layer are
termed cristae
- called as the powerhouse of the
cell
- produce energy (ATP)- adenosine
triphosphate
- chief center during cellular
respiration
b. GolgiBodies/Complex/Apparatus
/Dictyosomes
- stacks of 5-15 cisternae
associated with small vesicles
and large clear vacuoles
- size: 0.5-2um
- number per cell: 400
- function:
packaging stations of the cell
- was discovered by Camille Golgi
c. Ribosomes
- small, spherical or granular
bodies
- size: 15-25 um
- number per cell: 500,000
function:
- protein synthesis
d. Endoplasmic Reticulum
is a winding network of
membranes interconnected with
each other
it provides channels which
transport materials to the
cytoplasm
Types:
a. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
(ER)
contains ribosomes on its
surface
function:
- protein synthesis
b. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
(SER)
devoid of ribosomes
function: produces lipids,
examples: cholesterol,
carbohydrates (glycogen)
e. Lysosomes
vesicles present only among animal
cells which are surrounded by a
membrane
contain hydrolytic enzymes w/c break
down large organic molecules e.g.
proteins, lipids, carbohydrates
f. Centrioles
granular bodies located outside
the nucleus ; are involved in the
movement of chromosomes
during cell division
h. Microfilaments
are thread-like structures for
support and movement
present among muscle cells
3. Nucleus
- the control center of the cell
- regulates growth and
reproduction of the cell
Ergastic Substances:
- are the non-living substances
within the cell
- lifeless accumulations inside the
cell
a. Vacuoles
are membrane-bound bodies
containing various substances in
dilute solution for food storage
(food vacuole); removal of waste
(excretory vacuole) and water
storage (central vacuole
Plant Cells
1.Cell Wall
- rigid; non-living that is secreted by the
protoplast
- skeletal framework
- secreted by the protoplast
- made up of cellulose
- its older portion is on the outside; its
newer one on the inside
2. Protoplast portion within the cell wall
A. Plasma/Cell Membrane found outside
the cytoplasm next to the cell wall
- is semi-permeable
- controls the exchange of materials into
and out of the cell
2. Cytoplasm protoplasm outside the
nucleus
A. Cytoplasmic Organelles:
a. Plastids spherical/ovoid/collar-
shaped/ribbon-like
- can replicate
types:
a.1. Chloroplasts seat of photosynthesis
among green plants
- have green pigments: chlorophyll a & b
a.2. Chromoplasts yellow/orange/red
pigments
- are found in fruits and petals of
flowers
a.3. Leucoplasts colorless plastids; found
in epidermal cells of leaves
and bulbs
- types:
1. amyloplasts storage of starch
2. lipids/oil - elaioplasts
3. proteins - aleurone -plasts
b. Mitochondria -ovoid/filamentous/sausage-
shaped
c. Dictyosomes/Golgi bodies
d. Ribosomes small, spherical or granular
bodies
e. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
f. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
- types:
g.1. peroxisomes isolated from leaves
- contain oxidative enzymes
g.2. glyoxysomes isolated from castor
bean seeds
- contain oxidative enzymes
h. Spherosomes
spherical organelles
-size: 2 um
- function: storage of lipid materials
- called as lipid bodies/fat bodies/wax
bodies
- found in: cotyledons of many seeds
3. Nucleus
- Control center of the cell
- parts:
1. Nuclear Membrane/ Nucleolemma
2. Nuclear Sap/Karyolymph
3. Nucleolus
4. Nuclear Net/Chromatin Network
Ergastic Substances:
1. Water vacuoles
- small or large cavities having more
content than the rest of the cytoplasm
- cell sap- is the fluid within;
g. Microbodies
- spherical organelles about the size of
the mitochondria or smaller
- size: 0.5-1.5 um
- contain oxidative enzymes or hydrolytic
enzymes
2. Crystals
first objects seen in plant cell
- waste products or excretory materials of
the protoplast
- they are located inside the water vacuoles
and they contain calcium oxalate
3. Stored Foods
= these materials are formed when excess
foods are produced by the plant
= are broken down and utilized by the plant
during periods when food is not produced
in sufficient qualities or when seed
germinates or when tuber sprouts to form
a new plant
1. Starch Grains
e.g. cells of potato tubers and in green
leaves
2. Oil Globules e.g. cells of avocado fruits
3. Aleurone Grains
stored proteins in cells of many seeds
You might also like
- Activity IntoleranceDocument3 pagesActivity IntoleranceCorinne Fatima de AsisNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic System and Non-Immune ResponseDocument11 pagesThe Lymphatic System and Non-Immune ResponseSheena PasionNo ratings yet
- Approach To The Patient With Endocrine DisordersDocument17 pagesApproach To The Patient With Endocrine Disordersseun williamsNo ratings yet
- Microbial Metabolism of Food ComponentDocument23 pagesMicrobial Metabolism of Food ComponentNur AnisaNo ratings yet
- Embryology of The Female Genital TractDocument11 pagesEmbryology of The Female Genital TractzoviNo ratings yet
- CH 54 Chemical SensesDocument2 pagesCH 54 Chemical SensesJulienne Sanchez-SalazarNo ratings yet
- Clinical Case Study Wk1Document1 pageClinical Case Study Wk1seigelysticNo ratings yet
- Exam 2Document6 pagesExam 24157No ratings yet
- MLT Student NotesDocument5 pagesMLT Student NotesClaire GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Inflammation Chronic Diseases and Cancer - Cell and Molecular Biology Immunology and Clinical Bases PDFDocument442 pagesInflammation Chronic Diseases and Cancer - Cell and Molecular Biology Immunology and Clinical Bases PDFsatriomega100% (1)
- Dashen Brewery internship report on beer production process and quality controlDocument92 pagesDashen Brewery internship report on beer production process and quality controltesfayregs gebretsadikNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Notes Chapers 1-2Document3 pagesMicrobiology Notes Chapers 1-2dinkinpdNo ratings yet
- HISTOLOGY STAIN GUIDEDocument3 pagesHISTOLOGY STAIN GUIDEGodwin HalfonNo ratings yet
- Histology+Notes For Exam 3Document38 pagesHistology+Notes For Exam 3Jennifer Firestone0% (1)
- General Biology 1Document12 pagesGeneral Biology 1Samariah Nicole AbajeroNo ratings yet
- Recap Biological FactsDocument28 pagesRecap Biological FactsJesenth ColicoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 BioDocument28 pagesLesson 7 BioEunice Patricia M. VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- BIO ReviewerDocument14 pagesBIO ReviewerRenjyl Gay DeguinionNo ratings yet
- Biology 1st DiscussionDocument52 pagesBiology 1st DiscussionBea BulasaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Cell Structure and FunctionsDocument31 pagesModule 2 Cell Structure and FunctionsConcepcion, Jemaelah P.No ratings yet
- Plant Organology Notes PDFDocument18 pagesPlant Organology Notes PDFCaitlin SnymanNo ratings yet
- Cells: Unicellular vs Multicellular OrganismsDocument6 pagesCells: Unicellular vs Multicellular Organismspraneeth satishNo ratings yet
- GenBio Notes Lesson 1 and 2Document7 pagesGenBio Notes Lesson 1 and 2The GreatNo ratings yet
- Nature and Composition of Plants NotesDocument15 pagesNature and Composition of Plants NotesMc Wilson DecenaNo ratings yet
- Week 4 - Plant Structure and FunctionsDocument50 pagesWeek 4 - Plant Structure and FunctionsPrincess De LeonNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and OrganisationDocument106 pagesCell Structure and Organisationwienna1987No ratings yet
- Biology Form 4: Chapter 2: Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationDocument4 pagesBiology Form 4: Chapter 2: Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationSera ChanNo ratings yet
- The Structure and Organelles of Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic CellsDocument3 pagesThe Structure and Organelles of Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic CellsPERJES, Sigrid Maial A.No ratings yet
- Cell TopicDocument6 pagesCell TopicUbaid Ur rahmanNo ratings yet
- Activity 2. Plant Cell Vs Animal CellDocument5 pagesActivity 2. Plant Cell Vs Animal CellMary Joyce BonayonNo ratings yet
- Makalah Kelompok 1bDocument20 pagesMakalah Kelompok 1bRizky BluesNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell: Cellular Structure and FunstionsDocument4 pagesEukaryotic Cell: Cellular Structure and FunstionsCiara PanenNo ratings yet
- C1Document256 pagesC1azfdin100% (4)
- The Nature and Composition of PlantsDocument70 pagesThe Nature and Composition of PlantsJhunell Juan100% (3)
- Earth and Life Science ReviewerDocument11 pagesEarth and Life Science ReviewerVicente MarkNo ratings yet
- Cell organelles and structuresDocument8 pagesCell organelles and structuresANGEL RIZARENo ratings yet
- 2.6 Plant and Animal CellDocument28 pages2.6 Plant and Animal Cellthethtarhoney12No ratings yet
- Earth and ScieDocument3 pagesEarth and SciesideyysNo ratings yet
- The Cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument10 pagesThe Cell Structure and TaxonomyKingJayson Pacman06No ratings yet
- Bayern MunchenDocument23 pagesBayern MunchenKepa KepaNo ratings yet
- K00229 - 20190917121248 - Chap1 & 2SBC 3023Document64 pagesK00229 - 20190917121248 - Chap1 & 2SBC 3023Anonymous oJQblq0ONo ratings yet
- The Parts of The Cell and Their FunctionsDocument1 pageThe Parts of The Cell and Their Functionscherry.tempongNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles: Structures and FunctionsDocument6 pagesCell Organelles: Structures and FunctionsSai Deekshita VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- Cell SamralaGDocument26 pagesCell SamralaGapi-3731257No ratings yet
- Notes For CH. CellDocument5 pagesNotes For CH. Celladityamanik.121No ratings yet
- Trixie OrganellesDocument2 pagesTrixie OrganellesMir SantillanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document7 pagesChapter 2Kaness MathzNo ratings yet
- CellDocument7 pagesCellnik29569No ratings yet
- Botany 2Document4 pagesBotany 2Hindreen ObaidNo ratings yet
- MLG 2 (Part 1) The Cell Theory and Cell Structure and FunctionsDocument5 pagesMLG 2 (Part 1) The Cell Theory and Cell Structure and FunctionsJohn Tolentino LaronaNo ratings yet
- Levels of Biological OrganizationsDocument23 pagesLevels of Biological OrganizationsYuu KieNo ratings yet
- General Biology ReviewerDocument4 pagesGeneral Biology ReviewerJm Gutierrez50% (6)
- The Cell FinalDocument48 pagesThe Cell FinalJuliane Caniele IndiongcoNo ratings yet
- CYTOLOGYDocument3 pagesCYTOLOGYJessa Mae DarulloNo ratings yet
- g11 Els OrganellesDocument3 pagesg11 Els OrganellesJarod PeñaflorNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of Major and Subcellular OrganellesDocument4 pagesStructure and Function of Major and Subcellular OrganellesMEDRANO, Hana Jhiemyka O.No ratings yet
- CRPSCI 1100-Module4Document22 pagesCRPSCI 1100-Module4pantalunanhannamaeNo ratings yet
- The Nature and Composition of PlantsDocument23 pagesThe Nature and Composition of PlantsAndrea Nicole BalaresNo ratings yet
- Nota Biologi Tingkatan 4 BAB 2Document12 pagesNota Biologi Tingkatan 4 BAB 2Firas Muhammad100% (2)
- Plant Cell EmeDocument1 pagePlant Cell EmeErica LeysonNo ratings yet
- Right To HealthDocument9 pagesRight To HealthPriya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Perforamance Based AssessmentDocument2 pagesPerforamance Based AssessmentJocelyn Acog Bisas MestizoNo ratings yet
- Dr. Namrata Misra Head of Bioinnovations at KIIT UniversityDocument1 pageDr. Namrata Misra Head of Bioinnovations at KIIT Universitymanisha maniNo ratings yet
- MEDICO-LEGAL ASPECTS OF ASPHYXIADocument76 pagesMEDICO-LEGAL ASPECTS OF ASPHYXIAAl Giorgio SyNo ratings yet
- Steam System Design RequirementsDocument29 pagesSteam System Design RequirementsAthirahNo ratings yet
- DR - Hawary Revision TableDocument3 pagesDR - Hawary Revision TableAseel ALshareefNo ratings yet
- Practice of Epidemiology Performance of Floating Absolute RisksDocument4 pagesPractice of Epidemiology Performance of Floating Absolute RisksShreyaswi M KarthikNo ratings yet
- 559 Fault CodeDocument4 pages559 Fault Codeabdelbagi ibrahim100% (1)
- Gebauer 2012Document26 pagesGebauer 2012Seán GallagherNo ratings yet
- Retail Management PPT1Document14 pagesRetail Management PPT1Srilekha GubbalaNo ratings yet
- A. Kumar Aswamy Job Offer LetterDocument1 pageA. Kumar Aswamy Job Offer LetterHimanshu PatelNo ratings yet
- 2.1. Pharmacological Therapeutics. 2.2. Basic Cardiac Life Support (BCLS) and Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) in Neonates and ChildDocument3 pages2.1. Pharmacological Therapeutics. 2.2. Basic Cardiac Life Support (BCLS) and Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) in Neonates and Childclint xavier odangoNo ratings yet
- Malaysia's Trade Potential in Colourful AfricaDocument18 pagesMalaysia's Trade Potential in Colourful AfricaThe MaverickNo ratings yet
- RA8485 Animal Welfare Act (Carabao Slaughter)Document2 pagesRA8485 Animal Welfare Act (Carabao Slaughter)Jazreth Gaile100% (1)
- Study On Marketing Strategies of Fast Food Joints in IndiaDocument35 pagesStudy On Marketing Strategies of Fast Food Joints in IndiaNiveditaParaashar100% (1)
- Introduction To Animal Science For Plant ScienceDocument63 pagesIntroduction To Animal Science For Plant ScienceJack OlanoNo ratings yet
- Workplace Hazard Analysis ProcedureDocument12 pagesWorkplace Hazard Analysis ProcedureKent Nabz60% (5)
- Rockwool 159: 2.2 Insulation ProductsDocument1 pageRockwool 159: 2.2 Insulation ProductsZouhair AIT-OMARNo ratings yet
- 01 - 01 - SK10 - JXNipponDocument1 page01 - 01 - SK10 - JXNipponredevils86No ratings yet
- Practical Examination Marking Guideline Grade 12 Physical Science 2019 PDFDocument5 pagesPractical Examination Marking Guideline Grade 12 Physical Science 2019 PDFWonder Bee Nzama100% (1)
- The Danger of Microwave TechnologyDocument16 pagesThe Danger of Microwave Technologyrey_hadesNo ratings yet
- To The OneDocument8 pagesTo The OnePizzaCowNo ratings yet
- Esaote MyLabX7Document12 pagesEsaote MyLabX7Neo BiosNo ratings yet
- Material Handling EquipmentsDocument12 pagesMaterial Handling EquipmentsRahul SheelavantarNo ratings yet
- Classification of Nanomaterials, The Four Main Types of Intentionally Produced NanomaterialsDocument5 pagesClassification of Nanomaterials, The Four Main Types of Intentionally Produced NanomaterialssivaenotesNo ratings yet
- Poverty and Crime PDFDocument17 pagesPoverty and Crime PDFLudwigNo ratings yet
- Đề cương ôn tập tiếng anh 9Document28 pagesĐề cương ôn tập tiếng anh 9Nguyễn HoaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Plan of Care Concept Map - Immobility - Hip FractureDocument2 pagesNursing Plan of Care Concept Map - Immobility - Hip Fracturedarhuynh67% (6)
- Formularium ApotekDocument12 pagesFormularium ApotekNurul Evi kurniatiNo ratings yet
- Farid Jafarov ENG Project FinanceDocument27 pagesFarid Jafarov ENG Project FinanceSky walkingNo ratings yet