Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Feedback Amplifiers
Uploaded by
kanagalasasankCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Feedback Amplifiers
Uploaded by
kanagalasasankCopyright:
Available Formats
1
K L UNIVERSITY ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING
BY
DEPT. OF ECE
ramguda1978@kluniversity.in
CONCEPT OF FEED-BACK:
The process where by a part of the output is fed back to input
is called feed back.
OR
The process where some part of the output is added to the
input signal is called feed back.
2
K L UNIVERSITY
Amplifier
A
f/b
sample
X
S
X
i
X
f
X
O
X
O
X
O
Source
Mixer
3
K L UNIVERSITY
X
S
= Source Signal
X
i
= Input signal of the amplifier
X
O
= Output signal of the amplifier
X
f
= feedback signal
A = Open loop Gain of the amplifier = X
O
/X
i
= Feedback factor = X
S
/X
O
Gain with feedback
=
1
+ sign for negative feedback.
- Sign for positive feedback.
4
Classification of feedback amplifiers:
K L UNIVERSITY
Positive feedback amplifiers:
Feedback amplifiers in which the phase difference
between the input (X
S
) and output signal (X
O
) is 0 or 360
degrees. It is also called as regenerative feed back
Negative feedback amplifiers:
Feedback amplifiers in which the phase difference
between the input (X
S
) and output signal (X
O
) is 180 degrees.
. It is also called as degenerative feed back
5
Negative feedback amplifiers:
VOLTAGE SERIES FEEDBACK AMPLIFIER
VOLTAGE SHUNT FEEDBACK AMPLIFIER
CURRENT SERIES FEEDBACK AMPLIFIER
CURRENT SHUNT FEEDBACK AMPLIFIER
K L UNIVERSITY 6
If the feedback network samples the output voltage, it is
voltage feedback. If it samples the output current, it is
current feedback.
The feedback signal can be connected in series or in parallel
with the signal source and the amplifier input terminals, so
called series feedback and parallel feedback.
In voltage feedback, the input terminals of the feedback
network are in parallel with the load, and the output voltage
appears at the input terminals of the feedback block.
Whereas in current feedback, the input terminals of the feedback
network are in series with the load, and the load current flows
through the input of the feedback block.
As a result, a simple test on the feedback type is to open-circuit
or short-circuit the load. If the feedback signal vanishes for an
open-circuit load, then it is current feedback. If the feedback
signal vanishes for a short-circuit load, it is voltage feedback.
K L UNIVERSITY 7
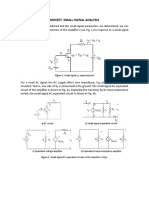
Voltage Series Feed Back(Voltage Amplifier )
K L UNIVERSITY 8
Current Series Feed Back (Transconductance Amplifier)
K L UNIVERSITY 9
Voltage Shunt Feed Back(Trans resistance Amplifier)
K L UNIVERSITY 10
Current Shunt Feed Back(Current Amplifier)
11
Amplifier negative feedback types
12
Effects of negative feedback:
Decrease in gain
Increase in bandwidth
Decrease in frequency & phase distortion
Decrease in non linear distortion
Decrease in noise
Increase in input impedance
Decrease in output impedance
13
Effect of negative feedback on gain
The Voltage gain of the amplifier with negative
feed back is given by
If we make A >>1, then one may be neglected
in comparison to A
The above equation shows that the gain Af of
the feedback amplifier is independent of the
internal gain A and depends only on feedback
fraction
K L UNIVERSITY 14
dA
f
=
1 +
2
=
+
(+)
+
X
K L UNIVERSITY 15
- represents the fractional change in
amplifier voltage gain with feedback
- denotes the fractional change in
thevoltage gain without feed back.
1
1+
- is sensitivity
Thus it shows that the percentage change in Af
is much less than the percentage change in A
K L UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF ECE
DESIGN OF ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS
16
Gain with feed-back
Gain without feedback is A , Feedback Factor
Gain with feedback is 1+A
Parameter Voltage Series Voltage Shunt Current Series Current Shunt
Gain with out
feedback A
Feedback factor
Gain with feedback
A
f
K L UNIVERSITY 17
INCREASE IN BAND WIDTH
K L UNIVERSITY 18
DECREASE IN FREQUENCY DISTORTION
When A>>1, then Af = A / (1+A ) =1/
Here feedback is completely resistive and thus
frequency distortion arising because of varying gain
with frequency is considerably
K L UNIVERSITY 19
REDUCTION IN NONLINEAR DISTORTION
Let the amplifier with gain A produces a distortion D
without feed back
When feed back is applied ,the amplifier gain Af
produces a distortion Df
Fraction of output distortion fed back to input = Df
After amplification, the distorted output = ADf
Net distortion = original distortion + distorted output
Df = D ADf => D=Df + ADf
Df = D / 1+A
Thus the distortion is reduced by a factor (1 + A )
K L UNIVERSITY 20
REDUCTION IN NOISE
The output of the ampifier consists of output
signal and noise voltage(N).
After Amplification the noise voltage is given by
Nf = N/(1+A)
Thus the noise is reduced by a factor of 1+A
K L UNIVERSITY 21
INCREASE IN INPUT IMPEDANCE
Zi Input impedance of the amplifier without feedback
Zif Input impedance of the amplifier with negative feedback
Ii input current then
Zif = Vs / Ii and Zi = Vi / Ii
Vi = Vs Vo but Vo = Avi
Vi = Vs AVi => Vs = Vi(1+A )
Dividing both sides by Ii we get
Zi(1+A )= Zif
Thus the input impedance of the amplifier is increased by a
factor of 1+A
K L UNIVERSITY 22
DECREASE IN OUTPUT IMPEDANCE
In order to find the output impedance of thee feed back amplifier with feed back,
short-circuit the input source Vs and connect a Voltage source Vo at the output
terminals.
The Output side has been replaced by an equivalent voltage source AVo.
Let Io be the current from the applied source
For the output circuit
Vo + AVo = Zo Io
Vo(1 + A) = Zo Io
Thus the output impedance is reduced by a factor of 1 + A
K L UNIVERSITY 23
METHOD OF IDENTIFYING FEED BACK TOPOLOGY
STEP 1:
1. To find the type of sampling network
(i). By shorting the output, if feed back signal becomes zero voltage
sampling
(ii). By opening the output loop, if feed back signal becomes zero current
sampling
2. To find the type of mixing network
(i). If the feedback signal is subtracted from the externally applied signal as a
voltage in the input loop series mixing
(ii). If the feedback signal is subtracted from the externally applied signal as a
current in the input loop shunt mixing
Thus by finding the type of sampling network and mixing network, the type of
the feedback amplifier can be determined
K L UNIVERSITY 24
STEP-2:
1. TO FIND THE INPUT CIRCUIT
(I). For voltage sampling , the output voltage is made zero by shorting
the output
(ii). For current sampling , the output current is made zero by opening
the output loop
STEP-3:
(i) for series mixing the input current is made zero by opening the input
loop
(ii). For shunt mixing the input voltage is made zero by shorting the
input loop
Ensure the feedback is reduced to zero without altering the loading on the amplifier
K L UNIVERSITY 25
STEP-4
Replace each active device by its h-paramerter model at low frequency
if required
STEP 5:
Find A, the open loop gain of the amplifier
STEP-6:
Indicate Xf and Xo on the circuit and evaluate =Xf Xo
STEP - 7:
From A and find D,Af,Rif, Rof and R`of
K L UNIVERSITY 26
NYQUEST CRITERION
IT IS USED TO PLOT GAIN AND PHASE SHIFT AS A FUNCTION OF FREQUENCY
ON COMPLEX PLANE
A Is a complex number and function of frequency, points in the complex
plane are obtained for the value of A corresponding to values of f from
to +
The Locus of all points forms a closed curve
Nyquist criterion for stability states that an amplifier is unstable of the Nyquist
curve encloses the (-1+j0) point. and if the amplifier is stable if the curve does
not encloses this point.
1+A = 1 represents a circle of unit radius with the centre at (-1+j0) point.
1+A > 1 represents negative feed back
1+A < 1 represents positive feed back
If the locus A does not enclose the point (-1+j0) i.e 1+A > 1 then the
amplifier is stable and the feedback is negative for all frequencies
K L UNIVERSITY 27
K L UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF ECE
DESIGN OF ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS
28
You might also like
- Fundamentals of Electronics 2: Continuous-time Signals and SystemsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 2: Continuous-time Signals and SystemsNo ratings yet
- EC - Unit 4 - Negative FeedbackDocument12 pagesEC - Unit 4 - Negative Feedbacknanobala15No ratings yet
- Power AmplifiersDocument29 pagesPower AmplifiersShailesh KuknaNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing Systems: Implementation Techniques: Advances in Theory and ApplicationsFrom EverandDigital Signal Processing Systems: Implementation Techniques: Advances in Theory and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Operational Amplifier Circuits: o o o oDocument21 pagesOperational Amplifier Circuits: o o o oVarun BishtNo ratings yet
- Partial-Update Adaptive Signal Processing: Design Analysis and ImplementationFrom EverandPartial-Update Adaptive Signal Processing: Design Analysis and ImplementationNo ratings yet
- Harish A R Sachidananda M Antennas and Wave PDFDocument411 pagesHarish A R Sachidananda M Antennas and Wave PDFNandiniManinarayanaNo ratings yet
- BE MWE MaterialDocument81 pagesBE MWE Materialsravan_4510% (1)
- Differential AmplifierDocument15 pagesDifferential AmplifierrppvchNo ratings yet
- Analog and Digital CommunicationDocument11 pagesAnalog and Digital CommunicationKarthi KeyanNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 Communication ConceptsDocument91 pagesChapter3 Communication ConceptsNikunj ShahNo ratings yet
- Feedback Amplifiers PDFDocument2 pagesFeedback Amplifiers PDFMariaNo ratings yet
- Topic 4-Multistage AmplifierDocument29 pagesTopic 4-Multistage AmplifierSha Edd'sNo ratings yet
- Me1100 Digital RF CommunicationsDocument141 pagesMe1100 Digital RF CommunicationsAmrAraagNo ratings yet
- Operational Amplifiers Questions and AnswersDocument4 pagesOperational Amplifiers Questions and AnswersSuresh L100% (1)
- DSPDocument94 pagesDSPRasha Hassan0% (1)
- Colpitts OscillatorDocument15 pagesColpitts OscillatorCaine de Leon0% (1)
- Analog Electronic Circuits Lab ManualDocument86 pagesAnalog Electronic Circuits Lab ManualsanjuNo ratings yet
- CH 4 B P LathiDocument99 pagesCH 4 B P LathiHarsh LuharNo ratings yet
- Thevenins & Nortons Theorem and Maximum Power Transfer Theorem PDFDocument13 pagesThevenins & Nortons Theorem and Maximum Power Transfer Theorem PDFVasu RamNo ratings yet
- CPE223-Signals and Systems Lab ManualDocument135 pagesCPE223-Signals and Systems Lab ManualMuhammad Hamza TariqNo ratings yet
- Angle Modulation NOTESDocument2 pagesAngle Modulation NOTESJay Amiel Ajoc50% (2)
- Chapter 02 Basic Concepts in RF DesignDocument110 pagesChapter 02 Basic Concepts in RF Designpriyanka patel100% (3)
- CH 2 - Op-Amp ApplicationDocument52 pagesCH 2 - Op-Amp Applicationknighthood4all100% (2)
- DSB SSB Am Transmitter Trainer Kit Scientech 2201Document2 pagesDSB SSB Am Transmitter Trainer Kit Scientech 2201mohitNo ratings yet
- Digital Circuits and Microprocessors K-NotesDocument47 pagesDigital Circuits and Microprocessors K-NotesAyan SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Waves and Transmission LinesDocument180 pagesElectromagnetic Waves and Transmission LinesGurusreenuNo ratings yet
- LIC+COM Lab Manual - 17ECL48Document58 pagesLIC+COM Lab Manual - 17ECL48Surendra K V100% (4)
- 9 Line Coding and ISIDocument17 pages9 Line Coding and ISIHarshil AmbagadeNo ratings yet
- Class B Amplifier: EfficiencyDocument5 pagesClass B Amplifier: EfficiencyKarthika LoganathanNo ratings yet
- Amplifiers and OscillatorsDocument10 pagesAmplifiers and OscillatorsKapil ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Passive Low Pass FilterDocument5 pagesPassive Low Pass FilterAnonymous SOQFPWBNo ratings yet
- Expt No. 03 - To Design and Test Op Amp Integrator For Given FrequenciesDocument7 pagesExpt No. 03 - To Design and Test Op Amp Integrator For Given FrequenciesPrakash Narkhede100% (1)
- MH 02N 2Document36 pagesMH 02N 2ganeshNo ratings yet
- Frequency Multipliers PDFDocument22 pagesFrequency Multipliers PDFduymanhhusNo ratings yet
- 00 Course Introduction Signal & SystemDocument14 pages00 Course Introduction Signal & SystemMuhammad AzwirNo ratings yet
- Antoniou Inductance-Simulation CircuitDocument10 pagesAntoniou Inductance-Simulation CircuitMidhunPNair100% (1)
- Principle of Communications Angle Modulation: Intro To Frequency ModulationDocument7 pagesPrinciple of Communications Angle Modulation: Intro To Frequency ModulationEunice Jane Bolgado-DoctorNo ratings yet
- General Characteristics of Negative Feedback AmplifiersDocument33 pagesGeneral Characteristics of Negative Feedback AmplifiersKishore Reddy100% (2)
- Tuned AmplifiersDocument9 pagesTuned AmplifiersMadhu Krishna KarthanNo ratings yet
- 3.analysis of Class B AmplifiersDocument24 pages3.analysis of Class B AmplifiersMbugua DuncanNo ratings yet
- Pam, PPM, PWMDocument9 pagesPam, PPM, PWMShathis Kumar100% (2)
- Analog To Digital ConverterDocument17 pagesAnalog To Digital ConverterIshita Sarkar100% (1)
- IntegratorDocument38 pagesIntegratorSyed AshmadNo ratings yet
- Operational AmplifiersDocument35 pagesOperational AmplifierskunwarNo ratings yet
- BE OPAMP Operational Amplifiers by TJ ShivaprasadDocument56 pagesBE OPAMP Operational Amplifiers by TJ ShivaprasadVedang PavanjeNo ratings yet
- Lecture21 Multistage AmplifiersDocument10 pagesLecture21 Multistage AmplifierscitraumariNo ratings yet
- Ece V Analog Communication (10ec53) NotesDocument74 pagesEce V Analog Communication (10ec53) NotesSanthosh Kumar H ONo ratings yet
- 2b RectifierDocument21 pages2b RectifierLove StrikeNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory (Eceg-1081) : Addis Ababa University Addis Ababa Institute of Technology (Aait)Document27 pagesCircuit Theory (Eceg-1081) : Addis Ababa University Addis Ababa Institute of Technology (Aait)AbcdNo ratings yet
- Signal Conditioning For Resistive, Rectance Varian and Self Generating SensorsDocument74 pagesSignal Conditioning For Resistive, Rectance Varian and Self Generating SensorsYash BhattNo ratings yet
- MOSFET Small Signal Analysy and BiasingDocument6 pagesMOSFET Small Signal Analysy and BiasingECHAVEZ TRILLOS FRANCISCO JAVIERNo ratings yet
- ME2142 T1 SolnDocument5 pagesME2142 T1 SolnDonguk Kim100% (1)
- Signals-and-Systems - Basics & Formula HandbookDocument19 pagesSignals-and-Systems - Basics & Formula HandbookKALAIMATHI100% (15)
- Source Transformation and Super Position Theorem PDFDocument13 pagesSource Transformation and Super Position Theorem PDFVasu RamNo ratings yet
- Measurements and InstrumentationDocument54 pagesMeasurements and InstrumentationVikas PsNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Differential Amplifiers 2nd LectureDocument35 pagesChapter Two Differential Amplifiers 2nd LectureTemesgen MekonenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document49 pagesChapter 1api-3733590No ratings yet
- Electronic Devices & Applications: Unit 1: Tunned Amplifier SubjectDocument47 pagesElectronic Devices & Applications: Unit 1: Tunned Amplifier SubjectmulushewaNo ratings yet
- PLC & HMI Interfacing For AC Servo Drive: Naveen Kumar E T.V.Snehaprabha Senthil KumarDocument5 pagesPLC & HMI Interfacing For AC Servo Drive: Naveen Kumar E T.V.Snehaprabha Senthil KumarNay Ba LaNo ratings yet
- Medical AssistantDocument2 pagesMedical Assistantapi-78670766No ratings yet
- Davos ProgramDocument80 pagesDavos ProgramhamiltajNo ratings yet
- Argument Structure VII) Conclusion: Quick ReviewDocument3 pagesArgument Structure VII) Conclusion: Quick Reviewthao khanhNo ratings yet
- Release Notes: 2288H V5&1288H V5&2288C V5&5288 V5 CPLD V212Document6 pagesRelease Notes: 2288H V5&1288H V5&2288C V5&5288 V5 CPLD V212LTI MaintenanceNo ratings yet
- Crüe, Chatting Done CorrectlyDocument7 pagesCrüe, Chatting Done Correctlyctjw.financeNo ratings yet
- Amazon Web ServicesDocument85 pagesAmazon Web ServicesSrinivasa Reddy KarriNo ratings yet
- EXPATRIATESDocument38 pagesEXPATRIATESdsouzaa100% (2)
- Loss Prevention PresentationDocument46 pagesLoss Prevention PresentationThanapaet RittirutNo ratings yet
- Wambura Naomi Wasira - Managing Business ProjectsDocument31 pagesWambura Naomi Wasira - Managing Business ProjectsNaomi WasiraNo ratings yet
- Damodar Dharmananda Kosambi: Chalega-Better Than A Padma-This-That-Or-The-Other!Document3 pagesDamodar Dharmananda Kosambi: Chalega-Better Than A Padma-This-That-Or-The-Other!Sanjiv BokilNo ratings yet
- Design of Machine Members - Syllabus PDFDocument3 pagesDesign of Machine Members - Syllabus PDFVAIBHAV TIWARINo ratings yet
- PUP Manual EnglishDocument455 pagesPUP Manual EnglishCharo Pajuelo ChaskaNo ratings yet
- ENGLISH For You and MeDocument31 pagesENGLISH For You and Mejkhjhk100% (3)
- z80 LH0080 Tech ManualDocument25 pagesz80 LH0080 Tech ManualAnonymous 8rb48tZSNo ratings yet
- Fieldcrest Division of Fieldcrest MillsDocument3 pagesFieldcrest Division of Fieldcrest Millsmayur2510.20088662No ratings yet
- American Association For Medical Transcription 100 Sycamore Avenue, Modesto, CA 95354-0550 - 800-982-2182Document5 pagesAmerican Association For Medical Transcription 100 Sycamore Avenue, Modesto, CA 95354-0550 - 800-982-2182JijoNo ratings yet
- Summer Training Emp. SatisfactionDocument34 pagesSummer Training Emp. SatisfactionAkash DixitNo ratings yet
- ELTJ (1990) Pyramid Discussions - JordanDocument9 pagesELTJ (1990) Pyramid Discussions - Jordanmariangoud100% (2)
- Budi PekertiDocument13 pagesBudi PekertiAPRI100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesDetailed Lesson PlanMarjen MabasagNo ratings yet
- Types of EconomyDocument2 pagesTypes of EconomyAyush GargNo ratings yet
- Julia CheatsheetDocument1 pageJulia CheatsheetmixarimNo ratings yet
- Haidari Beverages Private LimitedDocument2 pagesHaidari Beverages Private LimitedZarish HinaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Premiere Pro Help - Keyboard Shortcuts in Premiere Pro CC PDFDocument11 pagesAdobe Premiere Pro Help - Keyboard Shortcuts in Premiere Pro CC PDFMunna TeronNo ratings yet
- Bcpp6e TB Ch01Document32 pagesBcpp6e TB Ch01tnguyen194No ratings yet
- DIGSI4 Process Data AnalysisDocument27 pagesDIGSI4 Process Data Analysismohammed youisfNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 6 ReflectionDocument4 pagesLesson Plan 6 Reflectionapi-295690946No ratings yet
- Anam CVDocument2 pagesAnam CVAnam AslamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Consumer Behavior - Market SegmentationDocument26 pagesChapter 2 - Consumer Behavior - Market SegmentationAhmed RaufNo ratings yet