Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PR Ése Ntation 1
Uploaded by
Julien ContaminesOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PR Ése Ntation 1
Uploaded by
Julien ContaminesCopyright:
Available Formats
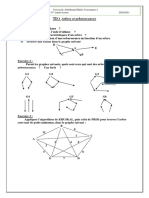
1
2
3
4
7
5
8
9
6
Affichage :
Explications :
On parcourt larbre de la racine vers les
feuilles.
Le parcours commence donc par le
noeud 1.
Parcours infixe de larbre
1
2
3
4
7
5
8
9
6
Affichage :
Explications :
Le noeud 1 possde un sous-graphe
gauche.
Avec un parcours infixe, on traite le
sous-graphe gauche avant le noeud
courant.
Le noeud courant devient le noeud 2.
Parcours infixe de larbre
1
2
3
4
7
5
8
9
6
Affichage :
Explications :
Le noeud courant est le noeud 2.
Pour la mme raison, le noeud courant
va devenir le noeud 4.
Parcours infixe de larbre
1
2
3
4
7
5
8
9
6
Affichage :
4
Explications :
Le noeud courant est le noeud 4.
Le noued 4 na pas de sous-graphe
gauche.
Avec un parcours infixe, le noeud
courant est trait avant son sous-graphe
droit.
Par consquent, on affiche le noeud 4.
Parcours infixe de larbre
1
2
3
4
7
5
8
9
6
Affichage :
4
Explications :
Le noeud 4 affich.
Avec le parcours infixe, on parcourt
prsent le sous-graphe droit du noeud
courant.
Le noeud 5 devient le noeud courant.
Le noued 5 possde un sous-graphe
gauche.
Parcours infixe de larbre
15
2
3
4
7
5
8
9
6
Affichage :
4, 7
Explications :
Le noeud 7 est le noeud courant.
Il na pas de sous-graphe gauche.
Par consquent, on affiche le noeud 7.
Le noeud 7 na pas de sous-graphe
droit.
Le noeud 5 devient le noeud coruant.
Parcours infixe de larbre
15
2
3
4
7
5
8
9
6
Affichage :
4, 7, 5
Explications :
Le noeud 5 est le noeud courant.
Le sous-graphe gauche a t explor.
Daprs le parcours infixe, on traite le
noeud courant avant son sous-graphe
droit.
Par consquent, on affiche le noeud 5.
On explore le sous-graphe droit.
Parcours infixe de larbre
15
2
3
4
7
5
8
9
6
Affichage :
4, 7, 5, 8
Explications :
Le noeud 8 est le noeud courant.
Ce noeud na pas de sous-graphe
gauche.
Par consquent, on affiche le noeud 8.
Le noeud 8 na pas de sous-graphe droit.
On retourne au noeud 2.
Parcours infixe de larbre
1
2
3
4
7
5
8
9
6
Affichage :
4, 7, 5, 8, 2
Explications :
Le noeud 2 est le noeud courant.
Son sous-graphe gauche a t explor.
Daprs infixe, on traite le noeud
courant avant son sous-graphe droit.
Par consquent, on affiche le noeud 2.
Le noeud 2 na pas de sous-graphe droit.
On retourne au noeud 1.
Parcours infixe de larbre
1
2
3
4
7
5
8
9
6
Affichage :
4, 7, 5, 8, 2, 1
Explications :
Le noeud 1 est le noeud courant.
Son sous-graphe gauche a t explor.
Daprs infixe, on traite le noeud
courant avant son sous-graphe droit.
Par consquent, on affiche le noeud 1.
On explore le sous-graphe droit du
noeud 1.
Parcours infixe de larbre
1
2
3
4
7
5
8
9
6
Affichage :
4, 7, 5, 8, 2, 1, 3
Explications :
Le noeud 3 est le noeud courant.
Il na pas de sous-graphe gauche.
Daprs infixe, on traite le noeud
courant avant son sous-graphe droit.
Par consquent, on affiche le noeud 3.
On explore le sous-graphe droit du
noeud 3.
Parcours infixe de larbre
1
2
3
4
7
5
8
9
6
Affichage :
4, 7, 5, 8, 2, 1, 3
Explications :
Le noeud 6 est le noeud courant.
Daprs infixe, on traite le noeud
courant aprs son sous-graphe gauche.
Par consquent, le noeud courant
devient le noeud 9.
Parcours infixe de larbre
1
2
3
4
7
5
8
9
6
Affichage :
4, 7, 5, 8, 2, 1, 3, 9
Explications :
Le noeud 9 est le noeud courant.
Il na pas de sous-graphe gauche.
Daprs le parcours infixe, on traite le
noeud courant avant le sous-graphe
droit.
Par consquent, on affiche le noeud 9.
Le noeud 9 na pas de sous-graphe droit.
Le noued 6 redevient le noeud courant.
Parcours infixe de larbre
1
2
3
4
7
5
8
9
6
Affichage :
4, 7, 5, 8, 2, 1, 3, 9, 6
Explications :
Le noeud 6 est le noeud courant.
Son sous-graphe gauche a t explor.
Daprs le parcours infixe, on traite le
noeud courant avant le sous-graphe
droit.
Par consquent, on affiche le noeud 6.
Le noeud 6 na pas de sous-graphe droit.
Fin de lexploration du graphe.
Parcours infixe de larbre
You might also like
- Arbres AVL Et RBDocument37 pagesArbres AVL Et RBLayl ZanNo ratings yet
- Algo Part 2Document92 pagesAlgo Part 2Bouchra BouihiNo ratings yet
- Cours TG Chapitre 3Document37 pagesCours TG Chapitre 3Mohamed AllagNo ratings yet
- Chap3 - Arbres Et CoarbresDocument8 pagesChap3 - Arbres Et CoarbresSaleh BgfNo ratings yet
- Decembre.09 CorDocument8 pagesDecembre.09 CorBest OffensiveNo ratings yet
- Chapitre 4Document21 pagesChapitre 4Mohamed walid SammariNo ratings yet
- Chapitre 2. Arbre CouvrantDocument39 pagesChapitre 2. Arbre CouvrantEya ChaouachiNo ratings yet
- Interrogation TD Algorithmique Et Structures de DonnéesDocument3 pagesInterrogation TD Algorithmique Et Structures de DonnéesBoualemDjillaliNo ratings yet
- Cours Chap 14 Arbre Couvrant MinimalDocument12 pagesCours Chap 14 Arbre Couvrant MinimalHanan TalibNo ratings yet
- ElementsDocument484 pagesElementsYoucef BenjillaliNo ratings yet
- Decembre 07Document10 pagesDecembre 07Best OffensiveNo ratings yet
- STP - Spanning Tree Protocol: Généralités VersionsDocument5 pagesSTP - Spanning Tree Protocol: Généralités VersionswalidNo ratings yet
- Cours 6Document13 pagesCours 6Mohamed SoumeurNo ratings yet
- 06 Arbres PDFDocument81 pages06 Arbres PDFUlrich EkeuNo ratings yet
- PrésentationDocument110 pagesPrésentationeden edenNo ratings yet
- Réseaux AsynchronesDocument60 pagesRéseaux Asynchronestenah hamidNo ratings yet
- 18 AcmDocument25 pages18 Acmvolt 3000No ratings yet
- CH 3-1 Arbres Binaires de RechercheDocument7 pagesCH 3-1 Arbres Binaires de Recherchekenza fertasNo ratings yet
- Falade Ben BaixoDocument3 pagesFalade Ben BaixoDiego CampoNo ratings yet
- Janvier.12 CorDocument8 pagesJanvier.12 CorBest OffensiveNo ratings yet
- TD3+Solution ThéorieDocument5 pagesTD3+Solution ThéorieabdiaceNo ratings yet
- 2015 2016 Graphe TD6 OptimationDocument5 pages2015 2016 Graphe TD6 OptimationSa LimNo ratings yet
- Structure de Données en Langage CDocument29 pagesStructure de Données en Langage Cbertagnolliverros.dr.qy.q585No ratings yet
- Suitesurlesarbres 1Document34 pagesSuitesurlesarbres 1Mohamed SoumeurNo ratings yet
- Cours - Chapitre 7 - Les ArbresDocument12 pagesCours - Chapitre 7 - Les ArbresYasser El hattabiNo ratings yet
- Arbres Binaires CorDocument6 pagesArbres Binaires CorMohamed AboulkhirNo ratings yet
- Controle 2015 (Arbres)Document2 pagesControle 2015 (Arbres)Achraf FikriNo ratings yet
- 1 Arbre BinaireDocument2 pages1 Arbre BinairenerminekilaniNo ratings yet
- Cours GrapheDocument29 pagesCours Graphevolt 3000No ratings yet
- Cours Arbres 1 2Document5 pagesCours Arbres 1 2Freddy RolandNo ratings yet