Professional Documents
Culture Documents
OFDMA
Uploaded by
Mostafa Mohammed EladawyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
OFDMA
Uploaded by
Mostafa Mohammed EladawyCopyright:
Available Formats
OFDM
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing For LTE
Radio Frequency Team
Etisalat Egypt
Mostafa Adawy
Work Shop Agenda
oDigital Signal
oChannel Impact
oNoise
oError Rate
oChannel Paths
oNarrow band Transmission
oFDM (Frequency Division Multiplexing)
oOFDM(Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing)
Digital Signal
Time Domain
Digital Signal
Digital Signal in Transmission
Base Band Digital Signal
During Transmission No need for Carrier
Short Range
oWire line
oOptical Fibre
oTransmission Line
oShort Range Transmission
Pass Band Digital Signal
During Transmission a Carrier is needed
Long Range Transmission
Wireless Transmission
oModulation is needed
o Base band Signal (No need for Carrier ,Short Range Transmission )
Channel
Channel
Digital Signal (Contd)
RX TX
oPass Band Signal (Wireless Transmission need a carrier )
Why I need a Carrier ?
Wave Length = C/F Frequency is Small Will be large Antenna Will be large
Signal Range 2KHZ up to 20 KHZ C= 3*10^8 m/s
= 10 Km Antenna with Range in KM
TX M
DM
Rx
Channel Impact ?
Transmission of digital data over a channel typically suffers
oNoise
oMulti Path
Inter-symbol interference (ISI)
oNoise / Multi paths often occur simultaneously.
oDuring Solving the Case ?
oFor simplicity, During analysis treat each separately.
oNoise
oMulti paths
Channel
Channel Impact
TX
Rx
Channel
Noise
TX
Noise Problem
oNoise is Random signal (+ve /-ve)
oSolution of Noise
oGet Max SNR at the output for the signal So that I can decode
oHow I can get Max SNR ?
Add Filter at the Rx
o Matched Filter :Designed to get samples with Max SNR
Noise Problem
Channel
Noise
TX
Matched Filter
H(t)
t=T
At t=T
Max SNR
Matched Filter
oDoesnt make Amplification why? (Not Amplifier)
oIf it make amplification I will make noise enhancement
oHave chance to get signal (Sample at MAX SNR )
oDesigned with H(t) so that the Out signal has max SNR
Matched Filter
H(t)
0 T
Integrate
0 T
oIntegration as if I make Summation at all the points
oSummation is Good for noise
As the Noise is random +ve or ve
So that the noise can disappear
oIncrease the signal amplitude
oIncrease the duration
Get better SNR
Noise Problem (Contd)
Max SNR
Matched Filter
H(t)
Summation of all points
Threshold
y(T)
> Threshold +1
< Threshold -1
Channel
Noise
TX
Matched
Filter
H(t)
t=T
At t=T
Max SNR
Decision
Device
output
Y(t)
Y(T)
Noise Problem (Contd)
SNR and Error Rate
Any Receiver should have acceptable Error Rate to Decode
Performance of Digital system is measured by Error Rate
oBER
oFER
oSER
BER =10^-5
Every 100 000 Bit we have one bit wrong on average
To decode a signal (Voice ) I should have acceptable Error Rate
BER
SNR
Rx1 $ $
@ high noise I can
Rx2 Rx3
SNR Decreased BER increase cant decode
SNR and Decoding
RX
Acceptable
Error Rate
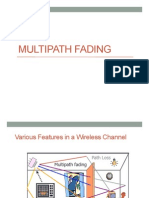
Channel Paths
Channel Paths
Ideal Channel
Channel response
(t)
Ideal Channel
(t)
ISI Channel
Inter symbol
interference
(t)
3
Main Path
Path 1
Path 2
Frequency Domain
Limited Time Unlimited in Freq
Freq Freq
Time Domain
You need Cure
Channel (Contd)
Equalization
oEqualizer to overcome multi path channel impact
oShadow
oFading
Solution
Equalizer
Channel H(f)
S(t)
Noise=0
Equalizer
S(t)
Channel
Equalizer
H(f)
1/H(f)
Overcome
Channel Impact
oSignal pass through equalizer whose response (Transfer function) is the inverse of the
channel
What is the problem now ? (Noise Matched Filter / Channel Paths Equalizer)
oChannel : Time variant channel
oThe Equalizer design is very difficult
Channel Estimation
Design the equalizer response (difficult ==> time variant channel)
Channel (Contd)
h(t)
t
Channel paths
Echo's
Delay spread of the channel
h(f)
f
There is No way I can see the channel flat
Time Domain
Frequency domain
As the delay increase the frequency variations are high
Channel (Contd)
No Problem
Narrow band Transmission
FM Radio
GSM
h(f)
f
Narrow band Transmission
o200 KHz
oChannel is almost flat
oIF the transmission BW is almost narrow enough
Channel is almost flat
No need to make equalization
Even if equalizer is present it will be very simple
Narrow band Transmission
oNarrow band Transmission
Radio Signal (AM ,FM Radio signal band 200 KHz up to 400 KHz )
2G Signal
Both signals combined
in the air interface
SC Code 1 Frequency
A
m
p
l
i
t
u
d
e
Signal 1
SC Code 2
Frequency
A
m
p
l
i
t
u
d
e
Signal 2
Spread Spectrum
Processing Gain
SC Code 1
Signal 1 is reconstructed
Signal 2 looks like noise
Both signals are
received together
AT THE RECEIVER...
Two Transmitters at the same frequency
Frequency
Frequency
Frequency
3G ?
As if Narrow band
Problem
Wide band Transmission
oWide band Transmission
LTE service
Internet service (WiMAX)
TV channel (5Mhz ) DVBH
oWide band Transmission : BW 1.4 MHZ to 20 MHZ
Wide band Transmission
h(f)
f
Wide Band Tran.
oTo Find equalizer can remove the channel impact is very complex
Time variant channel
oSolution 1
Time variant equalizer (adaptive equalizer )
Solution 2
OFDM
Orthogonal Frequency division
multiplexing
OFDM orthogonal Frequency division multiplexing
oUsed in Wide band Transmission
oTechnique at which data is sent on many carriers
f
h(f)
oDivide the wide band channel into narrow band channels
Channel is almost flat within Subcarrier
As if dealing with narrow band channels
LTE :
Each sub channel is 15 KHZ
BW =5 MHZ
512 sub channel
FACTS
Main Path
Path 1
ISI Impact is Very High
Pulse Stretch
ISI Impact is Little
o(Pulse Shaping-time stretch)
oIncreasing the duration leads to decrease the ISI impact
oIncrease the Duration leads to decrease the channel impact
Freq. variations will be in limited band
Ts
1/Ts 2/Ts 3/Ts 4/Ts 5/Ts
-1/Ts -3/Ts -2/Ts -4/Ts
Time
Frequency
S(t)
S(f)
Time Domain
Frequency domain
Go to Zero at 1/Ts pulse duration
I need the peak
Ts
1/Ts 2/Ts 3/Ts 4/Ts 5/Ts -1/Ts
-3/Ts
-2/Ts -4/Ts
Frequency
4 Symbols each of Duration Ts
[S(f)]
Frequency division multiplexing (FDM)
Put the Symbols on the BW
S(0)
S(1)
S(3)
S(2)
Peak of one is the Zero of the others
Example
Frequency
2/Ts 2/Ts 2/Ts 2/Ts
Band Width
Is the FDM is band width efficient ?
oFrom the above graph it is not BW efficient
oI Can get Smaller BW so that peak of one is the Zero of the others
Frequency division multiplexing (FDM)
1/Ts 2/Ts 3/Ts 4/Ts 5/Ts -1/Ts
-3/Ts
-2/Ts -4/Ts
Freq
2/Ts 2/Ts 2/Ts
F1 F3 F4
Freq
F2
Case 1 :FDM
Case 2 :
oPulse Shaping (Time stretch)
Decrease the BW
oChoose the correct Frequency
So that Peak of one is Zeros of others
Case 2
oBW is less than case 1
oCase 2 is more BW efficient
oI can chose frequency so that the peak of one is at the Zeros of the others
Time is stretched
Ts
S(0)
Ts Ts Ts
4Ts
S(0)
4Ts
S(1)
S(2)
S(4)
4Ts
4Ts
4Ts
Step 1 Parallel Transmission
/Stretching
F0 F2 F3
Frequency
F1
Step 2 :FDM
Chose freq at which the peak of one is the zeros of the others
FDM OFDM
S(1) S(2) S(3)
nTs
S/P
Orthogonality Rule
Fo=1/4Ts
F1=2/4TS
Fn= integers of 1/nTs
S(0)
S(n-1)
High BW
Serial
to
Parallel
Ts
nTs
Low BW
S(1)
S(0)
S(2)
S(n-1)
E^j2f0
E^j2f1
E^j2f2
E^j2f(n-1)
X(n)
f
h(f)
Peak of one is Zeros of others
Data on Sub Carriers
Narrow Band Transmission
IFFT (inverse frour Transform )
S(0)
S(n-1)
Serial to
Parallel
S(1)
S(0)
S(2)
S(n-1)
IFFT
X(n)
E^j2f0
E^j2f1
E^j2f(n-1)
X(n)
In LTE I have 512 subcarrier
So I will need 512 Crystal oscillator
Serial
to
Parallel
D/A
Converter
FFT
Parall
el To
Series
IFFT
Parallel
to series
Serial
to
Parallel
A/D
Converter
Thank You
You might also like
- GFSK IntroDocument5 pagesGFSK IntroJ Jesús Villanueva García100% (1)
- 9-MC Modulation and OFDMDocument36 pages9-MC Modulation and OFDMAbdul AzeezNo ratings yet
- Radio Frequency Team Etisalat Egypt: Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing For LTEDocument36 pagesRadio Frequency Team Etisalat Egypt: Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing For LTEMostafa Mohammed EladawyNo ratings yet
- Wireless TransmissionDocument147 pagesWireless TransmissionAshraf EltholthNo ratings yet
- OFDM LectureDocument128 pagesOFDM Lectureashugolu02No ratings yet
- Data and Computer CommunicationsDocument47 pagesData and Computer CommunicationsNaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- PCM (Pulse code modulation) : -Teacher: Masters Nguyễn Thanh Đức -Group memberDocument77 pagesPCM (Pulse code modulation) : -Teacher: Masters Nguyễn Thanh Đức -Group memberTao Thích Màu ĐenNo ratings yet
- Reviseio CSystemeeDocument25 pagesReviseio CSystemeeRaman TrivediNo ratings yet
- Channel Impairments: Muhammad Uzair Rasheed 2009-CPE-03 Uce&T Bzu MultanDocument25 pagesChannel Impairments: Muhammad Uzair Rasheed 2009-CPE-03 Uce&T Bzu MultanRaman TrivediNo ratings yet
- ECS455 - 5 - 1 - OFDM U1Document27 pagesECS455 - 5 - 1 - OFDM U1prapunNo ratings yet
- Advance Communication System Lectures Part 1Document36 pagesAdvance Communication System Lectures Part 1Shahzad Khalid ChNo ratings yet
- Introduction To WaveletDocument26 pagesIntroduction To WaveletSunil KumarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To WaveletDocument26 pagesIntroduction To WaveletNarasimhan KumaraveluNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Multipath FadingDocument37 pagesLecture 6 Multipath FadingWajeeha_Khan1No ratings yet
- 02 channels-VP PDFDocument27 pages02 channels-VP PDFSilicon DaltonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 FMDocument33 pagesChapter 2 FMSazali HusinNo ratings yet
- DSSDocument48 pagesDSSOmprakash YadavNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14Document20 pagesLecture 14Charles SchmidtNo ratings yet
- NT Old QuestionsDocument64 pagesNT Old QuestionsSomya SinghNo ratings yet
- Transmission Fundamentals: Slides Made by Yu-Chee TsengDocument36 pagesTransmission Fundamentals: Slides Made by Yu-Chee TsengAzwan MahmudNo ratings yet
- Speech Coders For Wireless CommunicationDocument53 pagesSpeech Coders For Wireless CommunicationVikas PsNo ratings yet
- Linear EqualizerDocument39 pagesLinear EqualizerVicky PatelNo ratings yet
- Wireless TransmissionDocument147 pagesWireless Transmissionepc_kiranNo ratings yet
- Microwave Communication PrincipleDocument47 pagesMicrowave Communication Principleanimshakya100% (1)
- NOTES 99-5 Modulation and Demodulation Modems For Data Transmission Over Analog LinksDocument13 pagesNOTES 99-5 Modulation and Demodulation Modems For Data Transmission Over Analog LinksKwadwo Ntiamoah-sarpongNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals Satellite Communication Part 4Document61 pagesFundamentals Satellite Communication Part 4tunisianouNo ratings yet
- Basics of Data Transmission: Our Objective Is To UnderstandDocument29 pagesBasics of Data Transmission: Our Objective Is To UnderstandswatagodaNo ratings yet
- Lecture3 - Small Scale FadingDocument24 pagesLecture3 - Small Scale FadingKarthik Mohan KNo ratings yet
- 1 What Is OFDM?: X (T) C eDocument15 pages1 What Is OFDM?: X (T) C eRajib MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- VP Cwsystems, SyctemsDocument36 pagesVP Cwsystems, SyctemsShinichi KudoNo ratings yet
- Phase NoiseDocument4 pagesPhase NoisetranthinhamNo ratings yet
- GMDSS - R5 - 2020 - 01 04 Radio EquipmentDocument67 pagesGMDSS - R5 - 2020 - 01 04 Radio EquipmentChristopher HawleyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document32 pagesLecture 5Muhammad Amin BangashNo ratings yet
- Fred Harris Multirate DSP Part 1 - Virginia Tech Tutorial 2011Document52 pagesFred Harris Multirate DSP Part 1 - Virginia Tech Tutorial 2011Citalac011No ratings yet
- Channels and Channel Models: EIT 140, Tom AT Eit - Lth.seDocument33 pagesChannels and Channel Models: EIT 140, Tom AT Eit - Lth.seindameantimeNo ratings yet
- Signal Encoding and Modulation TechniquesDocument21 pagesSignal Encoding and Modulation Techniqueschetanajitesh76No ratings yet
- Slides - Ofdm Tutorial 2008 - MMDocument25 pagesSlides - Ofdm Tutorial 2008 - MMNPHNPHNo ratings yet
- Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing OfdmDocument137 pagesOrthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing Ofdmskhushi_10No ratings yet
- Spread Spectrum Signal For Digital CommunicationDocument27 pagesSpread Spectrum Signal For Digital CommunicationMurugesan EswaranNo ratings yet
- S-72.245 Transmission Methods in Telecommunication Systems (4 CR)Document24 pagesS-72.245 Transmission Methods in Telecommunication Systems (4 CR)vamseeNo ratings yet
- DSP-1 (Intro) (S)Document77 pagesDSP-1 (Intro) (S)karthik0433No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Communication SystemDocument61 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Communication SystemIzlaikha AzizNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Diversity Motivation: BranchesDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Diversity Motivation: BranchesDaniel MarosNo ratings yet
- Modul 5 - FadingMitigation - REVISI - WCSDocument57 pagesModul 5 - FadingMitigation - REVISI - WCSDian Adventien NokeNo ratings yet
- Speech Coding TechniquesDocument38 pagesSpeech Coding TechniquesJacob JayaseelanNo ratings yet
- ChannelDocument16 pagesChannelaungsoe02No ratings yet
- Data and Computer CommunicationsDocument45 pagesData and Computer CommunicationsSam ZahzouhiNo ratings yet
- Cprogramming TutorialDocument157 pagesCprogramming TutorialBenard JosephNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 PDFDocument5 pagesLecture 10 PDFMehdi RabbaniNo ratings yet
- T - CS513 - 02 Wireless TransmissionDocument40 pagesT - CS513 - 02 Wireless TransmissionHeba MaNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing - 1Document77 pagesDigital Signal Processing - 1Sakib_SL100% (1)
- LTE CourseDocument164 pagesLTE Coursefgfdfdsd9104100% (2)
- TDM & FDMDocument9 pagesTDM & FDMSiddharth KumraNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing: Instant AccessFrom EverandDigital Signal Processing: Instant AccessRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Single Channel Phase-Aware Signal Processing in Speech Communication: Theory and PracticeFrom EverandSingle Channel Phase-Aware Signal Processing in Speech Communication: Theory and PracticeNo ratings yet
- Part 3Document51 pagesPart 3Mostafa Mohammed EladawyNo ratings yet
- Part 2Document28 pagesPart 2Mostafa Mohammed EladawyNo ratings yet
- Part 1Document71 pagesPart 1Mostafa Mohammed EladawyNo ratings yet
- Intra Cell HODocument10 pagesIntra Cell HOMostafa Mohammed EladawyNo ratings yet
- SilverCrest Aspirator de Mana 279206 - RO - 21Document73 pagesSilverCrest Aspirator de Mana 279206 - RO - 21Nicoleta PopescuNo ratings yet
- Position Control of A DC Servo Using A PID PDFDocument28 pagesPosition Control of A DC Servo Using A PID PDFBrasoveanu Gheorghita0% (1)
- Use of SCADA Systems in Power System AutomationDocument10 pagesUse of SCADA Systems in Power System AutomationKamlesh KumarNo ratings yet
- SETRA Company ProfileDocument21 pagesSETRA Company ProfileRafi RafNo ratings yet
- EE1110 - High Voltage Engineering Unit-4Document85 pagesEE1110 - High Voltage Engineering Unit-4Sameer AbulNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 FPGA PDFDocument44 pagesLecture 2 FPGA PDFAshraful Islam MridhaNo ratings yet
- 2PAA111637 A en Freelance Rack HardwareDocument2 pages2PAA111637 A en Freelance Rack HardwarerabloNo ratings yet
- Premier 300: CT/VT-Operated Energy MeterDocument6 pagesPremier 300: CT/VT-Operated Energy Meterveera chaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Safety Single Phase Equipment A3 PosterDocument1 pageElectrical Safety Single Phase Equipment A3 PosterDavid GoNo ratings yet
- Durag Dust MonitorDocument13 pagesDurag Dust MonitorVivek KumarNo ratings yet
- Irf3710 PDFDocument8 pagesIrf3710 PDFJose M PeresNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 13Document15 pagesLecture Notes 13Abdul Hakeem Semar KamaluddinNo ratings yet
- CM2 User Manual, Magnetometer Supplement 1 - 1Document10 pagesCM2 User Manual, Magnetometer Supplement 1 - 1quangNo ratings yet
- Microwave Journal-March 2021Document168 pagesMicrowave Journal-March 2021Petros TsenesNo ratings yet
- CS KOM Fin Jan2021-V2Document1 pageCS KOM Fin Jan2021-V2Osman Agâh YILDIRIMNo ratings yet
- Motor HP Voltage To Amp ChartDocument1 pageMotor HP Voltage To Amp ChartjituplanojrNo ratings yet
- Jasco Fp920 Manual 1995 EngDocument106 pagesJasco Fp920 Manual 1995 Eng82ghost82No ratings yet
- Project MicroprocessoresDocument22 pagesProject Microprocessoresshahd dawoodNo ratings yet
- CMOS Interview QuestionsDocument9 pagesCMOS Interview QuestionsarunNo ratings yet
- KNL394Document2 pagesKNL394projects spdclNo ratings yet
- Saudi Aramco Test ReportDocument8 pagesSaudi Aramco Test Reportkarthi51289No ratings yet
- 590G-V2 in A4 CatalogueDocument6 pages590G-V2 in A4 CatalogueMATIAS_CNo ratings yet
- SIG de 22 Diagrama de Cableado TD3 B102 E 10Document10 pagesSIG de 22 Diagrama de Cableado TD3 B102 E 10Jorge PalacioNo ratings yet
- Arduino Based Home Automation System Using Bluetooth Through An Android Mobile PDFDocument72 pagesArduino Based Home Automation System Using Bluetooth Through An Android Mobile PDFsaigdv197859% (17)
- Sentry EEx User's Guide Jun 2015Document76 pagesSentry EEx User's Guide Jun 2015Paul BrooksNo ratings yet
- CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor)Document5 pagesCMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor)Hirakjyoti GoswamiNo ratings yet
- 2019 Led LCD TV Tcom e Painel-1-375 (201-375)Document175 pages2019 Led LCD TV Tcom e Painel-1-375 (201-375)Sergio CamilattoNo ratings yet
- Electrical Design Criteria - Electrical KnowhowDocument6 pagesElectrical Design Criteria - Electrical KnowhowdedeerlandNo ratings yet
- P I C D A A U S I 8 2 4 A D: Erformance Mprovements IN Lass Udio Mplifiers Sing X Udio RiversDocument12 pagesP I C D A A U S I 8 2 4 A D: Erformance Mprovements IN Lass Udio Mplifiers Sing X Udio RiversluizcpimentaNo ratings yet
- 4.1overview of Preventive MaintenanceDocument32 pages4.1overview of Preventive MaintenanceVANESSA ESAYASNo ratings yet