Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Transport in Humans - 2013 - Lesson4 - Blood Vessels
Uploaded by
kalpanaparikh200033310 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views14 pagesPresentation for IGCSE Biology
Original Title
Transport in Humans- 2013- Lesson4- Blood Vessels
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPresentation for IGCSE Biology
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views14 pagesTransport in Humans - 2013 - Lesson4 - Blood Vessels
Uploaded by
kalpanaparikh20003331Presentation for IGCSE Biology
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
-Lesson 4 - Types of Blood vessels
-_ Blood vessels of the body.
Starter
How is clean water
supplied to your
home?
How is it distributed
within your home?
How is the used water
removed from your
home?
Where does this water
go?
How can you relate
water supply in your
homesto blood supply
in your body?
Clean water = oxygenated
blood
Used water = deoxygenated
blood
Pipes = blood vessels
Water pipes = arteries
Sewage pipes = veins
Connecting pipes within the
house = capillaries
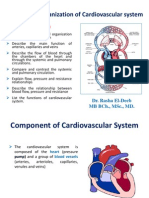
Lesson 4 Objectives:
Students shall be able to
describe the structures of arteries , veins and
capillaries.
associate their structures to their functions.
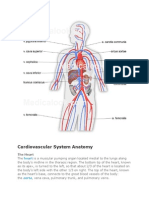
Identify the major blood vessels of the body.
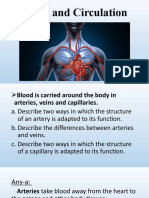
What are blood vessels?
passageways through which blood is
distributed from heart to all parts of body
and back to heart
Students shall be able to
describe the structures of arteries , veins and capillaries.
Blood vessels
Students shall be able to
describe the structures of arteries , veins and capillaries.
Arteries - carry blood away from heart
Arterioles - small arteries that deliver
blood to capillaries
Capillaries thin walled vessels allow for
exchange between blood and tissue cells
Venules - collect and drain blood into
veins
Veins - return blood to heart
6
Students shall be able to
describe the structures of arteries , veins and capillaries.
Observe the images of the blood vessels and list atleast 2 characteristics for each of
them.
Arteries
Carry blood away from the heart
Carries blood at high pressure
Carry oxygenated blood (except for the pulmonary
artery)
Thick muscular walls 3 layers
Thin tough outer layer
Thick elastic and muscular middle layer
Thin inner layer of cells
Small lumen
Do have a pulse
No valves
Students shall be able to
describe the structures of arteries , veins and capillaries.
How are these
structural features
related to the
function of
arteries?
Arteries
Carries blood at high pressure so that it reaches
every cell in the body
Thick muscular walls to withstand the high
pressure of flow of blood & control blood supply
to the organs
Elastic walls to allow stretch and recoil
Small lumen to help maintain pressure for flow
Do have a pulse corresponding to the contraction
and relaxation of the ventricles
No valves - pressure of flow does not permit
backflow
Students shall be able to
describe the structures of arteries , veins and capillaries.
associate their structures to their functions.
Veins
Carry blood toward the heart
Carry blood at Low pressure
Carry deoxygenated blood (except for the pulmonary
vein)
Thinner more flexible walls 3 layers
Thick tough outer layer
Muscular middle layer
Thin inner layer of cells
Large lumen
Does not have a pulse
Valves present
Students shall be able to
describe the structures of arteries , veins and capillaries.
Veins
Carry blood toward the heart
Carry blood at Low pressure no pump to return
blood to the heart
Carry deoxygenated blood (except for the pulmonary
vein) oxygen diffused to the tissues
Thinner more flexible walls due to low pressure
Large lumen - no resistance to return of blood to
the heart
Does not have a pulse no pump to push it
Valves present to prevent backflow since blood is
returning to the heart
Students shall be able to
describe the structures of arteries , veins and capillaries.
Capillaries
Penetrate all tissues
Very narrow only one cell wide
One cell thick walls allows transport of oxygen and
nutrient into body cells and wastes out of cells
Students shall be able to
describe the structures of arteries , veins and capillaries.
Students shall be able to
describe the structures of arteries , veins and capillaries.
Blood pressure in blood vessels
Arteries Veins
Transport blood away from the heart;
Transport blood towards the heart;
Carry Oxygenated Blood
(except in the case of the Pulmonary Artery);
Carry De-oxygenated Blood
(except in the case of the Pulmonary Vein);
Have relatively narrow lumens (see diagram above); Have relatively wide lumens (see diagram above);
Have relatively more muscle/elastic tissue; Have relatively less muscle/elastic tissue
Transports blood under higher pressure (than veins);
Transports blood under lower pressure (than arteries);
Do not have valves (except for the semi-lunar valves of
the pulmonary artery and the aorta).
Have valves throughout the main veins of the body.
These are to prevent blood flowing in the wrong
direction, as this could (in theory) return waste
materials to the tissues
Students shall be able to
describe the structures of arteries , veins and capillaries.
associate their structures to their functions.
Students shall be able to
outline the blood vessels of the body
You might also like
- Circulatory System: A Tutorial Study GuideFrom EverandCirculatory System: A Tutorial Study GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Transport System-Structure of Blood Vessels f4Document4 pagesTransport System-Structure of Blood Vessels f4sadziwan01No ratings yet
- The Human Circulatory System: Grade 9 - Sussex - Wennappuwa - ScienceDocument23 pagesThe Human Circulatory System: Grade 9 - Sussex - Wennappuwa - ScienceSwarnapaliliyanageNo ratings yet
- Module 3 The Circulatory SystemDocument11 pagesModule 3 The Circulatory SystemAndriya JoshyNo ratings yet
- Bio AS Topic 1.B (By Natalie)Document28 pagesBio AS Topic 1.B (By Natalie)nataliealkhatibNo ratings yet
- Transport in Animals-Topic 9Document14 pagesTransport in Animals-Topic 9sukiiNo ratings yet
- W.G. Igcse Transport in HumansDocument20 pagesW.G. Igcse Transport in Humansbloodshooter1996No ratings yet
- Review and Comprehension (Blood Vessel)Document4 pagesReview and Comprehension (Blood Vessel)9pjh6pzxmsNo ratings yet
- Pressure and Flow in Blood VesselsDocument51 pagesPressure and Flow in Blood VesselsDagmawe ZewengelNo ratings yet
- Blood VesselsDocument16 pagesBlood Vesselsapi-247243068No ratings yet
- Grade 7 CH 4.06 What Makes Blood FlowDocument18 pagesGrade 7 CH 4.06 What Makes Blood FlowMunmun AfnanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of BVDocument16 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of BVMarivic DianoNo ratings yet
- A Review of The Cardiovascular System and ECG Performance, Troubleshooting, and InterpretationDocument47 pagesA Review of The Cardiovascular System and ECG Performance, Troubleshooting, and InterpretationRetroPilotNo ratings yet
- Arteries Elastic Arteries Distributing Arteries Arterioles Capillaries Venules Veins Subclavian Vein Jugular Vein Renal Vein Iliac Vein Venae CavaeDocument8 pagesArteries Elastic Arteries Distributing Arteries Arterioles Capillaries Venules Veins Subclavian Vein Jugular Vein Renal Vein Iliac Vein Venae Cavaesabrina yeasmineNo ratings yet
- Blood VesselsDocument8 pagesBlood VesselsEmmanuel A. GalvanNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System ExplainedDocument16 pagesCardiovascular System ExplainedJosh DeeNo ratings yet
- Bio Transport in HumansDocument24 pagesBio Transport in HumansNicoleNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 NotesDocument18 pagesTopic 1 NotesKesithan AnandarashNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Transport in HumansDocument11 pages5.2 Transport in Humans박찬우No ratings yet
- Dr. Aaijaz Ahmed Khan Sr. Lecturer in Anatomy PPSP, UsmDocument38 pagesDr. Aaijaz Ahmed Khan Sr. Lecturer in Anatomy PPSP, UsmeliseudesafateNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Anatomy: The HeartDocument5 pagesCardiovascular System Anatomy: The HeartSyafiq RozaliNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument7 pagesCirculatory SystemWisdom DzombeNo ratings yet
- PALMA, LYCA D. - CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM (Heart and Blood Vessels)Document6 pagesPALMA, LYCA D. - CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM (Heart and Blood Vessels)G-Palma, Lyca D.No ratings yet
- 3 Circulation in ManDocument7 pages3 Circulation in ManAnasatcia Mcpherson 9c FNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 CH 4.06 What Makes Blood FlowDocument18 pagesGrade 7 CH 4.06 What Makes Blood FlowWakif Khan PrantoNo ratings yet
- (03des) Slide Artery and VenaDocument30 pages(03des) Slide Artery and VenaAbigaleNo ratings yet
- Arteries, Veins & CapillariesDocument12 pagesArteries, Veins & CapillariesMarcus GohNo ratings yet
- Transport in Man NotesDocument9 pagesTransport in Man NotesYeo JhNo ratings yet
- Bio Psychology Notes 2Document8 pagesBio Psychology Notes 2Zubin Jammaa FulaniNo ratings yet
- Blood Vessels: By: Saiyed Falakaara Assistant Professor Department of Pharmacy Sumandeep VidyapeethDocument10 pagesBlood Vessels: By: Saiyed Falakaara Assistant Professor Department of Pharmacy Sumandeep VidyapeethFalak AaraNo ratings yet
- Functional organization of the cardiovascular systemDocument19 pagesFunctional organization of the cardiovascular systemIbtesam Mohammed100% (2)
- Notes Grade: 9 Subject: Biology Chapter No: 9 Chapter Name: Transport in Animals ObjectivesDocument36 pagesNotes Grade: 9 Subject: Biology Chapter No: 9 Chapter Name: Transport in Animals Objectivespraneeth satishNo ratings yet
- Life Processes - Transportation in Human Beings 1.PptxDocument24 pagesLife Processes - Transportation in Human Beings 1.PptxraghavrungtambwaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-11: Transportation in Animals and PlantsDocument10 pagesChapter-11: Transportation in Animals and PlantsNorika PariharNo ratings yet
- Human Cardiovascular System: Introduction ToDocument76 pagesHuman Cardiovascular System: Introduction ToJunje SemeonNo ratings yet
- Session #33 SAS - AnaPhy (Lab)Document5 pagesSession #33 SAS - AnaPhy (Lab)G INo ratings yet
- MATERIALS TRANSPORTED IN UNICELLULAR AND MULTICELLULAR ORGANISMSDocument207 pagesMATERIALS TRANSPORTED IN UNICELLULAR AND MULTICELLULAR ORGANISMSNorizan Darawi0% (1)
- ANAPHY Lec Session #16 - SAS (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Document10 pagesANAPHY Lec Session #16 - SAS (Agdana, Nicole Ken)Nicole Ken AgdanaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory system l: The mammalian HeartDocument4 pagesCirculatory system l: The mammalian HeartAaron WongNo ratings yet
- Blood and CirculationDocument7 pagesBlood and CirculationMd Atikur AminNo ratings yet
- Research Questions-: How The Blood FlowsDocument5 pagesResearch Questions-: How The Blood FlowsAasritha SenagapallyNo ratings yet
- Bio Form5 Chapter1 Transport 1-2aDocument11 pagesBio Form5 Chapter1 Transport 1-2aWati WatakNo ratings yet
- CirculationDocument9 pagesCirculationbriannahunter518No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System AnatomyDocument16 pagesCardiovascular System AnatomyJona Addatu0% (1)
- Pp17. Bloodvessels and Valves Structure and FunctionsDocument10 pagesPp17. Bloodvessels and Valves Structure and Functionsdakalothathani029No ratings yet
- Science Form 3: Chapter 2 Blood Circulation and TransportDocument39 pagesScience Form 3: Chapter 2 Blood Circulation and TransportNadzirah RedzuanNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System AnatomyDocument13 pagesCardiovascular System AnatomyDwi Junita SariNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument40 pagesCardiovascular SystemLouise TanNo ratings yet
- Chp 05 (Blood and Circulation) DrRiyadAhmed PC 3Document69 pagesChp 05 (Blood and Circulation) DrRiyadAhmed PC 3Kamrun NaherNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Structures and FunctionsDocument11 pagesCardiovascular System Structures and FunctionsGodfrey Loth Sales Alcansare Jr.No ratings yet
- The Heart Presentation Compairing Veins EtcDocument2 pagesThe Heart Presentation Compairing Veins Etcasuccesfulstudent24No ratings yet
- Chapter 21 - Blood VesselsDocument6 pagesChapter 21 - Blood Vesselstomorrow.today.yesterday .yesterdayNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Circulatory System: Dr. Sura AlhussainyDocument21 pagesAnatomy Circulatory System: Dr. Sura Alhussainyصرخات راحلNo ratings yet
- Class 9-Biology-Lesson 8-Circulatory System3Document7 pagesClass 9-Biology-Lesson 8-Circulatory System3Shlok JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Mang, Normal PhysiologyDocument5 pagesMang, Normal PhysiologyThartea RokhumNo ratings yet
- Biology AS Revision: Single Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesBiology AS Revision: Single Circulatory SystemKieran ArronNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System PPT FeDocument26 pagesCardiovascular System PPT FeAngel Grace GaliasNo ratings yet
- Circulatory Systems Transport Nutrients and GasesDocument10 pagesCirculatory Systems Transport Nutrients and GasesRudy MunandarNo ratings yet
- KS3 Science Year 9 The Circulatory System-2Document15 pagesKS3 Science Year 9 The Circulatory System-2f72ktyd78nNo ratings yet
- As PE Lesson 20 Cir Syst 2013-14Document27 pagesAs PE Lesson 20 Cir Syst 2013-14mancollNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules, Diet and Human Nutrition - P 3 N 6 - Select QuestDocument12 pagesBiomolecules, Diet and Human Nutrition - P 3 N 6 - Select Questkalpanaparikh20003331100% (1)
- 9700 BIOLOGY: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2007 Question PaperDocument2 pages9700 BIOLOGY: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2007 Question Paperkalpanaparikh20003331No ratings yet
- Transport in Humans - Structured QuestionsDocument8 pagesTransport in Humans - Structured Questionskalpanaparikh20003331No ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument12 pagesEnzymeskalpanaparikh20003331No ratings yet
- VarsoiachampDocument7 pagesVarsoiachampapi-269171022No ratings yet
- Topic 6 Test 2022Document15 pagesTopic 6 Test 2022Ahmad OmarNo ratings yet
- Shurik and Kolya's Summer AdventuresDocument12 pagesShurik and Kolya's Summer Adventureskasi viswanathNo ratings yet
- Eagle Aluminium Brochure (Optimised) PDFDocument9 pagesEagle Aluminium Brochure (Optimised) PDFTonderai RusereNo ratings yet
- Registry Mechanic License KeyDocument1 pageRegistry Mechanic License KeyNoraini Abd KadirNo ratings yet
- 2021.08.29 News Chapter 5 ChainDocument53 pages2021.08.29 News Chapter 5 ChainMinh Hoa NguyenNo ratings yet
- D&D 3.5 - Dungeon Tiles Set 7 - Fane of The Forgotten GodsDocument16 pagesD&D 3.5 - Dungeon Tiles Set 7 - Fane of The Forgotten GodsKumo Wilendorf100% (2)
- Hand Lasting ProcessDocument8 pagesHand Lasting ProcessmanojNo ratings yet
- Minutes of The Meeting Boy Scouts of The PhilippinesDocument1 pageMinutes of The Meeting Boy Scouts of The PhilippinesRd DavidNo ratings yet
- Welcome To The Bishop Kelley Football Records Book! Season RecordsDocument18 pagesWelcome To The Bishop Kelley Football Records Book! Season RecordsbishopkelleyNo ratings yet
- The Flower Guarding Bells: Gu LongDocument1,435 pagesThe Flower Guarding Bells: Gu LongChadalavada Venkata Sai PradeepNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Musculoskeletal SystemDocument113 pagesChapter 1-Musculoskeletal SystemWang Ming YaNo ratings yet
- Mystery of The Invisible ThiefDocument53 pagesMystery of The Invisible ThiefNikhil Pramod67% (6)
- Mouse Guard 2nd Edition 2Document2 pagesMouse Guard 2nd Edition 2tawo0% (1)
- HomeostasisDocument8 pagesHomeostasisLely SharmaNo ratings yet
- A Beginners Guide To D&D Magic UsersDocument10 pagesA Beginners Guide To D&D Magic UsersminifezNo ratings yet
- Breakthrough at Orsha: Operation Bagration StartsDocument2 pagesBreakthrough at Orsha: Operation Bagration Startst1029No ratings yet
- Iyengar Yoga Home Practice Sequences 1 PDFDocument4 pagesIyengar Yoga Home Practice Sequences 1 PDFYogesh Sharma100% (1)
- 3rd IFK U-18 World Tournament WelcomeDocument50 pages3rd IFK U-18 World Tournament WelcomeBudo MediaNo ratings yet
- Jf016e Jf017e 1 PDFDocument4 pagesJf016e Jf017e 1 PDFValdir GomieroNo ratings yet
- Chiller Room Chiller Room: Entry Mep Room Entry Mep RoomDocument1 pageChiller Room Chiller Room: Entry Mep Room Entry Mep RoomBertha Vinola ChrisanNo ratings yet
- Earthdawn Extended Character Sheet 3eDocument7 pagesEarthdawn Extended Character Sheet 3eBilly MottNo ratings yet
- 1106D-E66TA 121.2 KW IOPUDocument2 pages1106D-E66TA 121.2 KW IOPUmhmd_saadNo ratings yet
- Potrosnja KalorijaDocument5 pagesPotrosnja KalorijaGee IvaNo ratings yet
- Feats of LashingDocument3 pagesFeats of Lashing枫的颜色No ratings yet
- Strainer Simple Mod. 72 - 10-18 - 125#Document1 pageStrainer Simple Mod. 72 - 10-18 - 125#Francisco Xavier Geronimo GarciaNo ratings yet
- Edward Winter - Capablanca Goes AlgebraicDocument7 pagesEdward Winter - Capablanca Goes AlgebraicNicolás MartínezNo ratings yet
- InternationalMaterialGradeComparisonTable PDFDocument9 pagesInternationalMaterialGradeComparisonTable PDFDragan MiladinovicNo ratings yet
- Pressure Vacuum Valves PDFDocument5 pagesPressure Vacuum Valves PDFFelipe Correa MahechaNo ratings yet