Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2311-MDGs Are Human Development Goals - Presentation
Uploaded by
saurav_sushant8600Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2311-MDGs Are Human Development Goals - Presentation
Uploaded by
saurav_sushant8600Copyright:
Available Formats
The Millennium Development Goals and
Human Development
Sakiko Fukuda-Parr
Director Human Development Report Office
UNDP
International symposium, Tokyo 9 October, 2002
The millennium goals are human
development goals
Progress is too slow
What it will take
Nationally: Democratic governance
Internationally: Partnership of rich
countries
An overview
The millennium goals: an overview
1. Eradicate extreme poverty and hunger (1.2 billion have less than $1
a day, 800 million are hungry)
2. Achieve universal primary education (113 million children are not in
school)
3. Promote gender equality and empower women (60% of children
not in school are girls, women have on average only 14% of seats in parliaments)
4. Reduce child mortality (every day 30,000 children die of preventable
causes.)
5. Improve maternal health (In Africa, a woman has 1 chance in 13 of dying
in childbirth)
6. Combat HIV/AIDS, malaria and other diseases (40 million are
living with HIV/AIDS, 75% of them in Africa)
7. Ensure environmental sustainability (1.1 billion people do not have
access to clean water, over 2 billion to sanitation)
8. Develop a global partnership for development (ODA declined from
53 to 51 billion from 1990 to 2001)
What are MDGs
What are MDGs
The millennium goals: an overview. By 2015:
1. Eradicate extreme poverty and hunger
a. Halve the proportion living on less than $1
a day
b. Halve the proportion suffering from hunger
2. Achieve universal primary education
a. Ensure universal primary education
3. Promote gender equality and empower
women
a. Eliminate gender disparities in education.
What are MDGs
The millennium goals: an overview
4. Reduce child mortality
a. Reduce infant and under-five mortality by 2/3
5. Improve maternal health
a. Reduce maternal mortality by
6. Combat HIV/AIDS, malaria and other diseases
a. Halt and begin to reverse the spread of
HIV/AIDS
b. Halt and begin to reverse the spread of malaria
and other major diseases
What are MDGs
The millennium goals: an overview
7. Ensure environmental sustainability
a. Integrate the principles of sustainable
development and begin to reverse the loss of
environmental resources
b. Halve the proportion without access to safe
drinking water
c. Improve the lives of at least 100million slum
dwellers (by 2020)
What are MDGs
The millennium goals: an overview
8. Develop a global partnership for development
a. Develop further an open, rule based
predictable, non-discriminatory trading and
financial system
b. Include the commitment to good governance,
development and poverty reduction both
nationally and internationally
What are MDGs
The millennium goals: an overview
8. Develop a global partnership for development
c. Address the special needs of the least
developed countries, including tariff and quota
free access for LDC exports. Enhanced
programme of debt relief for HIPCs and
cancellation of official bi-lateral debt and
generous ODA for countries committed to
poverty reduction.
d. Address the special needs of landlocked
countries and small island developing states.
What are MDGs
The millennium goals: an overview
8. Develop a global partnership for development
e. Deal comprehensively with the debt problems
of developing countries, through national and
international measures in order to make debt
sustainable in the long-term
f. In co-operation with developing countries
develop and implement strategies for decent
and productive work for youth.
What are MDGs
The millennium goals: an overview
8. Develop a global partnership for development
g. In co-operation with pharmaceutical
companies provide access to affordable
essential drugs in developing countries.
h. In co-operation with the private sector make
available the benefits of new technologies,
especially information and communications.
MDGs are human development goals
Human development is about widening choices
people have in life, to lead a life to its full
potential and in dignity. At the core of this
process is expanding capabilities:
1. To be knowledgeable
2. To be healthy and survive
3. To enjoy a decent standard of living
4. To enjoy political and civil liberties, and
participate in the life of a community.
MDGs are HD goals - a tool of mobilisation and framework of
accountability
The MDGs represent an unprecedented political
consensus on time bound quantified indicators.
MDGs are:
Not a new model of development, but
A tool of political mobilization
A framework of accountability for national
governments, international donors, and many
other actors that have a role in development
local NGOs, international NGOs, womens
groups, trade unions, private businesses, the
media, the judiciary.global citizens
MDGs are HD goals a historical perspective
on setting goals
Setting goals is the easy part.
The bad,
DAC commits to 0.7% GDP in 1970; average
disbursements in 2000 was 0.22%
Health for all by 2000 set in 1978
the good,
UNICEFs immunization goals
and the possible?
The MDGs have mobilized more political
momentum than any goals before
Progress is too slow: globally
7
Safe water
Maternal mortality
Child malnutrition
Gender equality
Basic education
Child mortality
HIV/AIDS
Poverty
Achieved To be achieved
No reliable and comparable data
1990 2000 2015
MDG progress in 1990s
40%
HDR2002: MDG analysis overall (119
countries)
0
20
40
60
On track in
less than half
Half to three-
quarters
Over three-
quarters
0
20
40
60
23
33
8
31
55
2
SSA
26% 33% 23%
Progress is too slow: for many
countries
HDR2002: MDG analysis goal by goal
Failing to grow out of income poverty
20
52
20
75
4
24
Falling
income
0 to 3.7%
growth
over 3.7%
growth
SSA
Total
Progress is too slow goal by goal
Progress is too slow: which
countries are failing
Overall regional performance: % of countries in region on track
0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% 100%
Eastern Europe &CIS
South Asia
East Asia
Arab States
Latin America
Sub-Saharan Africa
On track in:
Less than 1/2
1/2 to
3/4 Over 3/4
MDGs: An advantage to the more developed?
0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9
HDI value
On track
in:
3/4 or more
Less than 1/2
1/2 to 3/4
Medium HD Low HD High HD
The less developed fairing worse
Progress is too slow: which countries
are failing?
Number of countries in conflict by MDG
performance
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
<1/2 1/2 to 3/4 3/4 + No data
Afghanistan
Burundi
India
Iraq
Myanmar
Pakistan
Philppines
Turkey
Algeria
Indonesia
Iran
Mauritius
Peru
Russia
Sri Lanka
Sudan
Angola
Congo, dem.
Israel
Rwanda
Somalia
Source: Stokholm Int. Peace Institute. >1000 conflict related deaths per year
Conflict and performance in the MDGS
Progress is too slow: which countries are failing?
Is Growth a pre-requisite to MDG success?
13
7
17
15
13
17
24
17
4
6
14
5
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
Less than 1/2 1/2 to 3/4 More than 3/4 No data
Negative
growth
0 to 3%
growth
over 3%
growth
Progress is too slow: which countries
are failing?
Getting poorer but progressing
9
3
2 2
1
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
EE & CIS Arab
states
East Asia Latin
America
SSA
Belarus
Kazakhstan
Kyrgyzatan
Latvia
Lithuania
Macedonia
Moldova
Romania
Russia
Algeria
Kuwait
Saudi
Arabia
Brunei Dar.
Mongolia
Paraguay
Ecuador
Comoros
Progress is too slow: which countries
are failing?
What it will take - nationally
Public policy that responds to the needs of ordinary
people, especially the poor. That happens when:
Decision makers are accountable to people
Ordinary people have a say in decision making -
with one person one voice
Governance is not just efficient but fair and
protects human rights, when governance is
democratic.
What it will take nationally
deepening democracy
Deepening democracy requires:
Spread of democratic institutions
Spread of democratic politics
What it will take: Deepening democracy
Deepening democracy
Direct role to be able to participate
and effect the decisions that effect your
life is an integral part of human
development
Indirect role participating in the
political process can lead to
improvements in other aspects of human
development
What it will take: partnership with rich
countries
Goal 8: Develop a global partnership for
development
Aid
Debt
Trade
Technology
What it will take: partnership with rich
countries
What it will take: partnership
with rich countries
0.00
0.10
0.20
0.30
0.40
0.50
0.60
0.70
1990 2000
A
i
d
a
s
%
o
f
G
N
P
EU
Japan
USA
DAC target
0.7%
Aid from donor countries
What it will take: partnership
with rich countries
Aid to recipient countries
0.0
5.0
10.0
15.0
20.0
25.0
30.0
35.0
1990 2000
A
i
d
p
e
r
c
a
p
i
t
a
(
$
U
S
)
Arab states
Africa
LDCs
Latin America
East Asia
South Asia
What it will take: partnership
with rich countries
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
16
Industrial
products
Labour intensive
manufacturing
Agricultural
goods
%
Tariff protection imposed by high-income
countries
What it will take: partnership
with rich countries
20803
16028
410
0
5000
10000
15000
20000
25000
US EU Low income
countries
Subsidy per farmer
Average per
capita income in
low income
countries
Subsidizing agriculture
What it will take: partnership with rich
countries
What it will take: partnership
with rich countries
The Economist
A level playing field?...
For more: see
Human Development Report 2002: Deepening
Democracy in a Fragmented World
www.undp.org/hdro/
And wait for:
Human Development Report 2003: The Political
Economy of Achieving the MDGs
Publication forthcoming in September 2003
Thank you
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Organisational Environment Factors and Structures for Adapting to ChangeDocument10 pagesOrganisational Environment Factors and Structures for Adapting to Changesaurav_sushant8600No ratings yet
- 05-ITF-Tutorial To Help Me OutDocument8 pages05-ITF-Tutorial To Help Me OutSehon Richards100% (1)
- Chapter 9 Learning, Memory, and Product Positioning: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument28 pagesChapter 9 Learning, Memory, and Product Positioning: Multiple Choice Questionssaurav_sushant8600No ratings yet
- ItcDocument4 pagesItcsaurav_sushant8600No ratings yet
- Lecture 6 VirginDocument17 pagesLecture 6 Virginsaurav_sushant8600No ratings yet
- 4,5,6Document14 pages4,5,6saurav_sushant8600No ratings yet
- CRM BasicDocument34 pagesCRM Basicprasanna_lad11No ratings yet
- ITM Project Synopsis: Company Analysis and Financial Trend ForecastingDocument1 pageITM Project Synopsis: Company Analysis and Financial Trend Forecastingsaurav_sushant8600No ratings yet
- ItcDocument4 pagesItcsaurav_sushant8600No ratings yet
- Behavioral Finance Apr13Document48 pagesBehavioral Finance Apr13saurav_sushant8600No ratings yet
- Financial Accounting 1213527362725423 9Document259 pagesFinancial Accounting 1213527362725423 9Surendra Sharma100% (1)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Jan 24Document2 pagesJan 24charnold miolNo ratings yet
- 403Document12 pages403al hikmahNo ratings yet
- 7EC503 International Economics For Business and Finance: 01 - IntroductionDocument20 pages7EC503 International Economics For Business and Finance: 01 - IntroductionWahab Nurudeen OpeyemiNo ratings yet
- Major types of Retail Lending and Consumer Credit AnalysisDocument12 pagesMajor types of Retail Lending and Consumer Credit AnalysisGooby PlsNo ratings yet
- Porsche Changes TackDocument8 pagesPorsche Changes TackMahendra Singh DhoniNo ratings yet
- Piyush TahkitDocument44 pagesPiyush TahkitPankaj VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- M1 C2 Case Study WorkbookDocument25 pagesM1 C2 Case Study WorkbookfenixaNo ratings yet
- TUTORIAL 6 & 7 QuestionsDocument1 pageTUTORIAL 6 & 7 QuestionsgasdadsNo ratings yet
- R-APDRP Part-B Tender Specification Pre-Bid MeetingDocument69 pagesR-APDRP Part-B Tender Specification Pre-Bid MeetingChandu GowdaNo ratings yet
- 20 Accounting Changes and Error CorrectionsDocument17 pages20 Accounting Changes and Error CorrectionsKyll MarcosNo ratings yet
- London Circular Economy Jobs Report 2015Document20 pagesLondon Circular Economy Jobs Report 2015Matt MaceNo ratings yet
- 9.2 IAS36 - Impairment of Assets 1Document41 pages9.2 IAS36 - Impairment of Assets 1Given RefilweNo ratings yet
- Harmonisation of Accounting StandardsDocument157 pagesHarmonisation of Accounting StandardsMusab AhmedNo ratings yet
- Lean As A Universal Model of Excellence: It Is Not Just A Manufacturing Tool!Document8 pagesLean As A Universal Model of Excellence: It Is Not Just A Manufacturing Tool!Mona SayedNo ratings yet
- What Is Economic Development?Document5 pagesWhat Is Economic Development?Rio AlbaricoNo ratings yet
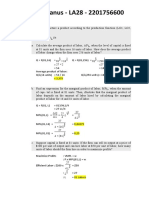
- Eric Stevanus - LA28 - Cost AnalysisDocument8 pagesEric Stevanus - LA28 - Cost Analysiseric stevanusNo ratings yet
- Change in Demand and Supply Due To Factors Other Than PriceDocument4 pagesChange in Demand and Supply Due To Factors Other Than PriceRakesh YadavNo ratings yet
- NoitesDocument4 pagesNoitesEdwinJugadoNo ratings yet
- How Businesses Have Adapted Their Corporate Social Responsibility Amidst the PandemicDocument7 pagesHow Businesses Have Adapted Their Corporate Social Responsibility Amidst the PandemicJapsay Francisco GranadaNo ratings yet
- SchmidtCo ERP Case AnalysisDocument8 pagesSchmidtCo ERP Case Analysisnitesh sharmaNo ratings yet
- Companies (Auditor's Report) Order, 2020: Companies Specifically Excluded From Its PurviewDocument4 pagesCompanies (Auditor's Report) Order, 2020: Companies Specifically Excluded From Its PurviewABINASHNo ratings yet
- EF2A2 HDT Budget Indirect Taxes GST PCB7 1661016598246Document44 pagesEF2A2 HDT Budget Indirect Taxes GST PCB7 1661016598246Sikha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Foreign ExchangeDocument25 pagesForeign ExchangeAngelica AllanicNo ratings yet
- Accenture IT Strategy Transformation ServicesDocument6 pagesAccenture IT Strategy Transformation Serviceserusfid100% (1)
- Making Decision 4Document22 pagesMaking Decision 4MORSHEDNo ratings yet
- Helmet Manufacturing Industry-293269 PDFDocument68 pagesHelmet Manufacturing Industry-293269 PDFJaydeep MoharanaNo ratings yet
- Project Closure PresentationDocument12 pagesProject Closure PresentationBilalNo ratings yet
- FIN WI 001 Image Marked PDFDocument10 pagesFIN WI 001 Image Marked PDFGregurius DaniswaraNo ratings yet
- Planning Commission and NITI AayogDocument5 pagesPlanning Commission and NITI AayogsuprithNo ratings yet
- Peta 4TH QTR Business-Simulation-Final-042522Document4 pagesPeta 4TH QTR Business-Simulation-Final-042522Kevin GuinsisanaNo ratings yet