Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To HCI201314
Uploaded by
Abdullah SalemOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction To HCI201314
Uploaded by
Abdullah SalemCopyright:
Available Formats
Interface Technology and Design
Human-Computer Interaction
Lectures:
1. Introduction to HCI
2. PACT analysis
3. Screen elements
4. Images
5. Screen layout
HCI Definitions
...a discipline concerned with the design,
evaluation and implementation of interactive
computing systems and with the study of
major phenomena surrounding them. (ACM
SIGCHI, 1992)
...the study of people, computer technology
and the ways these influence each other.
...making computer technology more usable
by people.
Development of HCI
2nd WW Weapons research
1950s Early computers: large,
expensive, used by experts
1980 PCs: small, cheap, ubiquitous
onward
A multidisciplinary subject
Cognitive
Psychology
Social &
Organisational
Psychology
Ergonomics
Engineering
Design
Social
Sciences
Linguistics
Computer
Science
Artificial
Intelligence
HCI
Adapted from Preece p38
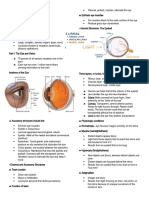
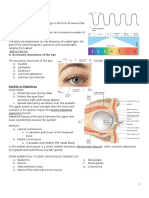
The eye
Light reflected from objects
Cornea and lens focus light onto retina
Image focused upside down
Receptors transform image into
electrical signals which are passed to
the brain
Blind spot where optic nerve enters eye
Photoreceptors
Rods:
highly sensitive to light
unable to resolve fine detail
subject to light saturation
120m rods per eye
situated towards edges of retina
Photoreceptors
Cones:
less sensitive, can tolerate more light
3 types >> colour vision
6m cones per eye
situated around fovea
Ganglion cells
X cells:
around fovea
pattern detection
Y cells
widely distributed
movement detection
http://animation.about.com/od/flashanimati
ontutorials/qt/nonflashwebsite.htm
Premises:
The system should be designed to
match user requirements - people
should not have to change to fit in with
the system
People should be able to concentrate
on their activities rather than on how to
use the system
Expectations
How do you turn the lights on?
What is this?
Usability
Definition:
the capability in human functional terms to
be used easily and effectively by the
specified range of users, given specified
training and user support, to fulfil the
specified range of tasks within the specified
range of environment scenarios.
(Shackel, 1979)
Usability
Usable technology is:
acceptable to the people
appropriate for the activities
suitable for the context
4 Factors:
People (Users)
Activities (Tasks)
Context (Environment)
Technology
Organisational
and Social Context
People
Technology
Activities
Physical
Environment
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Covaru Cover Sheeter SheetDocument1 pageCovaru Cover Sheeter SheetAbdullah SalemNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- 1FedExFinal Report-RevDocument44 pages1FedExFinal Report-RevTabish Ahmad100% (2)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Environment:: (PESTEL)Document36 pagesThe Environment:: (PESTEL)Abdullah SalemNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Analysis of Strategic PositionDocument9 pagesAnalysis of Strategic PositionAbdullah SalemNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Customer Perceived Value Satisfaction and Loyalty-The Role of Switching CostsDocument24 pagesCustomer Perceived Value Satisfaction and Loyalty-The Role of Switching CostsAraviinda Yereseeme0% (1)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Business Plan TemplateDocument9 pagesBusiness Plan TemplatebrendosNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- MBA PT Time-Table Feb16-Apr16Document1 pageMBA PT Time-Table Feb16-Apr16Abdullah SalemNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- MPD Coursework Component 2Document4 pagesMPD Coursework Component 2Abdullah SalemNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Portfolio SpecificationDocument2 pagesPortfolio SpecificationAbdullah SalemNo ratings yet
- IPOM (B)Document11 pagesIPOM (B)Abdullah SalemNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Dividend PolicyDocument11 pagesDividend PolicyAbdullah SalemNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- BIFDocument16 pagesBIFAbdullah SalemNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- 2014 GM Annual ReportDocument136 pages2014 GM Annual ReportAbdullah SalemNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Project Monitoring Form RP2Document1 pageProject Monitoring Form RP2Abdullah SalemNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Law Assignment PartDocument5 pagesLaw Assignment PartAbdullah SalemNo ratings yet
- Lab Task - Week 2&3Document2 pagesLab Task - Week 2&3Abdullah SalemNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Performance Metrics What Are We Trying To Measure? : O (&) &says¬hing&about&the&actual&cost&of&using&a&given&Document4 pagesPerformance Metrics What Are We Trying To Measure? : O (&) &says¬hing&about&the&actual&cost&of&using&a&given&Abdullah SalemNo ratings yet
- Plan 2013 PDFDocument2 pagesPlan 2013 PDFAbdullah SalemNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Activity Log: SOFT30161 - Advanced Software EngineeringDocument1 pageActivity Log: SOFT30161 - Advanced Software EngineeringAbdullah SalemNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Testing (Verification and Validation)Document29 pagesLecture 5 Testing (Verification and Validation)Abdullah SalemNo ratings yet
- Odule Eport Tatistics Ssistant: M R S ADocument1 pageOdule Eport Tatistics Ssistant: M R S AAbdullah SalemNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- ASE Module SpecDocument4 pagesASE Module SpecAbdullah SalemNo ratings yet
- AIMedicine 03Document25 pagesAIMedicine 03Abdullah SalemNo ratings yet
- Meeting and Facilities QuestionnaireDocument2 pagesMeeting and Facilities QuestionnaireAbdullah SalemNo ratings yet
- Lab - 07 COMP30211 Coursework 2013 14 PDFDocument1 pageLab - 07 COMP30211 Coursework 2013 14 PDFAbdullah SalemNo ratings yet
- Storybord NEWDocument49 pagesStorybord NEWAbdullah SalemNo ratings yet
- 1 Minutes Sheet TemplateDocument3 pages1 Minutes Sheet TemplateAbdullah SalemNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Survey ConductedDocument11 pagesAnalysis of Survey ConductedAbdullah SalemNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Use Case Requirement ListsDocument4 pagesUse Case Requirement ListsAbdullah SalemNo ratings yet
- COMP30211 - Coursework 2013-14 PDFDocument4 pagesCOMP30211 - Coursework 2013-14 PDFAbdullah SalemNo ratings yet
- Special SensesDocument6 pagesSpecial SensesmasorNo ratings yet
- ML Undergraduate Research Symposium Presentation - Madison LuceDocument1 pageML Undergraduate Research Symposium Presentation - Madison LucenurjNo ratings yet
- Animal EyesDocument291 pagesAnimal EyesjesusNo ratings yet
- 1-60 Lectures HandoutsDocument159 pages1-60 Lectures HandoutslaibaNo ratings yet
- Sensory and Motor SystemDocument12 pagesSensory and Motor SystemrobertoNo ratings yet
- Seminar Outline On Bionic TechnologyDocument5 pagesSeminar Outline On Bionic TechnologyRizNo ratings yet
- Neuroscience For Kids - Vision Exp PDFDocument23 pagesNeuroscience For Kids - Vision Exp PDFAr Hitesh ParmarNo ratings yet
- Why Red Doesn't Sound Like A Bell - Understanding The Feel of Consciousness (PDFDrive)Document287 pagesWhy Red Doesn't Sound Like A Bell - Understanding The Feel of Consciousness (PDFDrive)Roger13No ratings yet
- Newton's Theory of Color: Module 1 OverviewDocument5 pagesNewton's Theory of Color: Module 1 OverviewLee Eun JiNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Eye Anatomy - Review 6Document7 pagesEye Anatomy - Review 6Vidini Kusuma AjiNo ratings yet
- Bio Module-02Document40 pagesBio Module-02XdxdNo ratings yet
- Fatima Meesen PDFDocument15 pagesFatima Meesen PDFSena FernandoNo ratings yet
- Human Physiology From Cells To Systems 9th Edition Sherwood Test Bank 1Document23 pagesHuman Physiology From Cells To Systems 9th Edition Sherwood Test Bank 1eddie100% (46)
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EyeDocument9 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The EyeJayricDepalobos100% (1)
- Outline: Sensation and PerceptionDocument31 pagesOutline: Sensation and PerceptionBint e Ashraf100% (1)
- Vias Magno y ParvoDocument17 pagesVias Magno y ParvoLeonardo LeytonNo ratings yet
- Waves Aranoco Ppt-Anatomy of The EyeDocument40 pagesWaves Aranoco Ppt-Anatomy of The EyeARNOLD ARANOCONo ratings yet
- PNS Exam Full Study GuideDocument25 pagesPNS Exam Full Study GuideJean-JeanGwoNo ratings yet
- Carlson (7E) : Powerpoint Lecture OutlineDocument26 pagesCarlson (7E) : Powerpoint Lecture Outlinechat gazaNo ratings yet
- OCT Atlas Adams enDocument23 pagesOCT Atlas Adams enAnonymous PYgnwOWK100% (3)
- Peripheral Vision LinkDocument13 pagesPeripheral Vision LinkBeghin BoseNo ratings yet
- M-9 Human Factors: Aviation Training HubDocument104 pagesM-9 Human Factors: Aviation Training HubMuhammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- 185 Nervous System MCQs by Monsef - KarkorDocument60 pages185 Nervous System MCQs by Monsef - KarkorMostafa Montaser100% (5)
- Anatomy of Vitreous and RetinaDocument43 pagesAnatomy of Vitreous and RetinatariqNo ratings yet
- Modeling Blue Shift in Moonlit Scenes by Rod Cone InteractionDocument5 pagesModeling Blue Shift in Moonlit Scenes by Rod Cone InteractionNASAdocumentsNo ratings yet
- CIE Position Statement - Proper Light at The Proper Time (2019) - 0Document4 pagesCIE Position Statement - Proper Light at The Proper Time (2019) - 0ferdecoNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument31 pagesSeminar ReportBitNo ratings yet
- Consenso Internacional de OCTDocument7 pagesConsenso Internacional de OCTMilthon Catacora ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Bio SignalDocument20 pagesBio SignalThiyagu RajanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Special SensesDocument5 pagesChapter 8 Special SensesEdralyn EgaelNo ratings yet