Professional Documents
Culture Documents
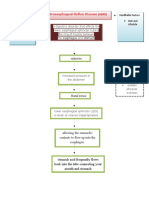
Crohn's Disease
Uploaded by
venzmartinez100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
712 views14 pagesAnatomy and Pathophysiology
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAnatomy and Pathophysiology
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
712 views14 pagesCrohn's Disease
Uploaded by
venzmartinezAnatomy and Pathophysiology
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
CROHNS DISEASE
Anatomy and Physiology
&
Pathophysiology
Definition
Crohns disease, also known as crohn syndrome
and regional entiritis, is a type of inflammation
bowel disease that may affect an part of the
gastrointestinal tract from mouth to anus,
causing a wide variety of symptoms, It primarily
causes abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting or
weight loss, but may also cause complication
outside the gastrointestinal tract such as
anemia, skin rashes, arthritis, inflammation of
the eye ,tiredness and lack of concentration
Anatomy and Physiology of GI Tract
Mucosal Lining of the GI Tract
Pathophysiology
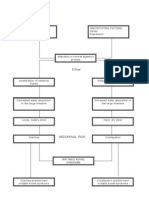
Predisposing Factors
Age
Race/Ethnicity
Genetic
Environmental (Smoking, Diet, Lifestyle
Precipitating Factors
Microbes
Immune/Inflammatory Response
NSAIDS
Appendectomy
Abnormal epithelial/mucosal barriers
Increased ANTIGENS
Uncontrolled Mucosal Inflammation
Activation of Inflammatory Helper T Cells
Release of Cytokinens
TNF (Tumor Necrosis Factor) alpha
Ulceration and Tissue/Bowel Injury
Ileocolitis
Diarrhea & cramping/pain
of abdomen
Weight loss
Ileitis
Diarrhea & cramping/pain
of abdomen
Weight loss
Gastroduodenal
crohns disease
Loss of appetite
Weight loss
Nausea & vomiting
Jejunoileitis
Mild to intense
abdominal pain & cramps
Diarrhea
Crohns
(granulomatous) colitis
Diarrhea
Rectal bleeding
Skin lesions
Joint pains
COMPLICATIONS
Malabsorption of nutrients, Intestinal bleeding, Disease of Anus (Abscess ,fistula, ulcers), Bowel Obstruction,
Perforation of Colon, massive distention/dilatation of colon, erythema, ulcerating skin, visual difficulties, uveitis,
Increased risk of cancer
Inflamed Mucosal Lining of
Intestine
Cobblestones
Assessment
Patients history and presenting sign
and symptoms:
26 yrs old woman
Abdominal pain Nausea
Constipation alternating with periods of
diarrhea.
Pain in her joints
skin lessions
Tiredness
Depression
Dietary history
Eating fried foods and some fruits
and vegetables worsen her
condition.
Nursing Diagnosis:
1. Imbalance Nutrition less than
body requirement related to
restricted nutrient intake
2. Acute pain related to increase
peristalsis.
3. Anxiety to crisis situation and
changes in health status.
4.Diarrhea related to effect of
inflammatory changes of the bowel.
Planning
Nutrition imbalance
Acute pain
In I week of nursing care
patient able to
demonstrate lifestyle
changes to regain and
maintain appropriate
weight.
In 1 week of nursing care
patient able to
demonstrate effective
coping and able to
participate the diet
therapy.
Anxiety to crisis situation
and changes in health
status.
Diarrhea
In 1 week of nursing care
patient able to determine
the benefits of the diet
therapy
In 1 week of nursing care
patient able to tell the
changes of her health
status based on restricted
food intake.
In 1 week of nursing care
patient will report of
reduction of frequency of
stool.
Nursing intervention
Weight daily
Encourage bedrest
Recommended rest before meal
Provide oral hygiene
Serve food in well-ventilated,
pleasant surrounding, with
unhurried atmosphere, congenital
company.
Avoid limit foods that can cause abdominal
pain.e.g milk product, high in fiber or fat and
etc.
Record intake and changes in symptomatology
Promote patient participation in dietary
planning as possible
Resume/advance diet as indicated, e.g., clear
liquids progressing to bland diet.
Acute pain
Encourage patient to report pain
Assess report of abdominal cramping or pain
You might also like
- Chapter 017Document17 pagesChapter 017MuhTaswinTachir100% (1)
- GIT DisordersDocument171 pagesGIT DisordersKatrina PonceNo ratings yet
- Cushing's Disease: A Case Presentation of BSN 3YB-7Document69 pagesCushing's Disease: A Case Presentation of BSN 3YB-7MARIA STEPHANY DELA CRUZ100% (1)
- PEPTIC ULCER DISEASE 2018 EdittedDocument43 pagesPEPTIC ULCER DISEASE 2018 EdittedJumbe MohamedNo ratings yet
- Crohns DiseaseDocument72 pagesCrohns Diseasea1savedNo ratings yet
- Gastritis Definition: Gastritis Can Be An Acute orDocument46 pagesGastritis Definition: Gastritis Can Be An Acute orOdey BeekNo ratings yet
- Duodenal UlcerDocument4 pagesDuodenal UlcerLourenz BontiaNo ratings yet
- Gastritis Englis 2018Document115 pagesGastritis Englis 2018irinaNo ratings yet
- Ugib Case StudyDocument36 pagesUgib Case StudyRJ MarquezNo ratings yet
- 2 Acute CholecystitisDocument21 pages2 Acute CholecystitisEtteh MaryNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer DiseaseDocument20 pagesPeptic Ulcer DiseaseALNAKINo ratings yet
- Acute Cholecystitis: Pableo, Rachel MDocument47 pagesAcute Cholecystitis: Pableo, Rachel MLd Rachel PableoNo ratings yet
- By: Leila Floresca Esteban BSNIII-BDocument38 pagesBy: Leila Floresca Esteban BSNIII-BMonica Morales100% (2)
- Inflammatory Bowel DiseaseDocument19 pagesInflammatory Bowel DiseaseDakshayani Vijayan100% (1)
- CROHNSDocument2 pagesCROHNSAlvin Germo Pasuquin100% (1)
- Cancer of The ColonDocument8 pagesCancer of The Colonnot your medz duranNo ratings yet
- Crohn's DiseaseDocument52 pagesCrohn's DiseaseSnobbish KissNo ratings yet
- CP - Acute GastritisDocument25 pagesCP - Acute GastritisRichard John Casquejo BroaNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Irritable Bowel SyndromeDocument1 pagePa Tho Irritable Bowel Syndromekaye0403No ratings yet
- The Pathophysiology of Peptic UlcerDocument15 pagesThe Pathophysiology of Peptic UlcerKike Meneses100% (1)
- Choledo A4Document53 pagesCholedo A4Czarina ManinangNo ratings yet
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) : Non Modifiable Factors Age Pregnancy Modifiable Factors Diet and LifestyleDocument3 pagesGastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) : Non Modifiable Factors Age Pregnancy Modifiable Factors Diet and Lifestylejoyrena ochondraNo ratings yet
- Crohn's DiseaseDocument16 pagesCrohn's DiseaseAhmad KhaledNo ratings yet
- Liver AbscessDocument3 pagesLiver AbscessLyiuiu TranNo ratings yet
- Celiac DiseaseDocument14 pagesCeliac Diseaseapi-355698448100% (1)
- IBDDocument27 pagesIBDKatarina SilalahiNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument28 pagesChronic Renal FailuremarshmalouNo ratings yet
- 14.malabsorption SyndromesDocument5 pages14.malabsorption SyndromesPriyaNo ratings yet
- Primary AldosteronismDocument31 pagesPrimary AldosteronismSteph100% (1)
- Bleeding Peptic Ulcer Disease Case StudyDocument17 pagesBleeding Peptic Ulcer Disease Case StudyChino Dela Cruz100% (2)
- Casestudy Gastric CarcinomaDocument53 pagesCasestudy Gastric CarcinomaAngelaTrinidadNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management Pancreatic CancerDocument2 pagesNursing Management Pancreatic CancerKit NameKo100% (2)
- Abdominal Compartment SyndromeDocument24 pagesAbdominal Compartment SyndromePrateek Vaswani100% (1)
- Gastro Esophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)Document7 pagesGastro Esophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)MahaNo ratings yet
- CholelithiasisDocument3 pagesCholelithiasisMIlanSagittarius0% (1)
- Gastritis: Medical AffairDocument11 pagesGastritis: Medical AffairKomal KhanNo ratings yet
- Crohn's DiseaseDocument5 pagesCrohn's DiseaseMark CapillanesNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of DiverticulitisDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Diverticulitisjordan aguilar100% (1)
- Case Study Ugib.Document19 pagesCase Study Ugib.Mary Ann Garcia100% (1)
- PancreatitisDocument12 pagesPancreatitismardsz100% (5)
- CholelithiasisDocument6 pagesCholelithiasismarkzamNo ratings yet
- Chron's Disease 2Document3 pagesChron's Disease 2TarantadoNo ratings yet
- GASTRITISDocument5 pagesGASTRITISmaria magdalena sagalaNo ratings yet
- Liver CancerDocument1 pageLiver CancerTarantado67% (3)
- GastritisDocument23 pagesGastritisLisnawati Nur Farida100% (1)
- Crohn's Disease - CSDocument28 pagesCrohn's Disease - CSMASII100% (2)
- Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding.Document13 pagesUpper Gastrointestinal Bleeding.Gieselle Scott100% (1)
- Anorexia NervosaDocument11 pagesAnorexia NervosaSashMalikNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument46 pagesChronic Renal Failurestepharry08100% (1)
- Case Study CholecystitisDocument13 pagesCase Study Cholecystitissanthyakunjumon100% (1)
- Acute GastritisDocument14 pagesAcute GastritisMenchie Vivas-AlotNo ratings yet
- Gastritis FinalDocument6 pagesGastritis Finalapi-371817450% (2)
- IA. Background of The StudyDocument49 pagesIA. Background of The Studyraffakervin50% (2)
- Gastrointestinal Health: The Self-Help Nutritional Program That Can Change the Lives of 80 Million AmericansFrom EverandGastrointestinal Health: The Self-Help Nutritional Program That Can Change the Lives of 80 Million AmericansNo ratings yet
- Medical Nutrition Therap y For Gastroenterohepatology DisordersDocument61 pagesMedical Nutrition Therap y For Gastroenterohepatology DisordersFeby Tegar KsatriaNo ratings yet
- Case Study Presentation - CGDocument37 pagesCase Study Presentation - CGapi-290866384No ratings yet
- Assessing AbdomenDocument115 pagesAssessing AbdomenKris TinaNo ratings yet
- Mentor: Sukron, S.Kep., NS., MNS: Cancer ColorectalDocument16 pagesMentor: Sukron, S.Kep., NS., MNS: Cancer Colorectalnurul hidayahNo ratings yet
- Gastritis Is An Inflammation of The Gastric MucosaDocument6 pagesGastritis Is An Inflammation of The Gastric MucosaJanineLingayoCasilenNo ratings yet
- Resources DistributionDocument10 pagesResources DistributionDarshan KanganeNo ratings yet
- Solowiej2016 - Processed Cheese AnaloguesDocument9 pagesSolowiej2016 - Processed Cheese AnaloguesDinoNo ratings yet
- CVDocument2 pagesCVJohn AttahNo ratings yet
- Number: 77-725 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 MinDocument40 pagesNumber: 77-725 Passing Score: 800 Time Limit: 120 MinArnold KanyindaNo ratings yet
- Multidisciplinary Action Project Report: "TO AT Trupti Snacks, Gandevi. Submitte ToDocument43 pagesMultidisciplinary Action Project Report: "TO AT Trupti Snacks, Gandevi. Submitte ToRahul LakhaniNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Milk Adulteration Using MID-IR SpectrosDocument6 pagesAnalysis of Milk Adulteration Using MID-IR SpectrosEditor IJRITCCNo ratings yet
- Boley - 1980 - Determination of Foods Synthetic Colours Using HPLCDocument11 pagesBoley - 1980 - Determination of Foods Synthetic Colours Using HPLCrnd labNo ratings yet
- Menu DietDocument11 pagesMenu DietKrisnaNo ratings yet
- E12P9Document7 pagesE12P9Nguyễn Thu TrangNo ratings yet
- Rules of Subject Verb Agreement Are All You NeedDocument8 pagesRules of Subject Verb Agreement Are All You Needalexandra jacobNo ratings yet
- Butterfly PDFDocument3 pagesButterfly PDFAmarjot KaurNo ratings yet
- Test Wider 4 2ADocument1 pageTest Wider 4 2AНаталья ОвчаренкоNo ratings yet
- Holder WebDocument4 pagesHolder Webapi-559148596No ratings yet
- Sith Kop 004Document16 pagesSith Kop 004musabNo ratings yet
- Ln-4 The Skeletal and Muscular SystemDocument2 pagesLn-4 The Skeletal and Muscular SystemAnnie GraceNo ratings yet
- Christians, Let Us Love One AnotherDocument2 pagesChristians, Let Us Love One AnotherGillie Caparas100% (1)
- Commercial GeographyDocument2 pagesCommercial GeographyAhsan IqbalNo ratings yet
- Design and Fabrication of Paddy Cleaning MachineDocument5 pagesDesign and Fabrication of Paddy Cleaning MachineDave RoneNo ratings yet
- Travefy Free Itinerary TemplateDocument5 pagesTravefy Free Itinerary TemplateAman kumarNo ratings yet
- Grand Soya Oil 2Document15 pagesGrand Soya Oil 2Yusuf HamidNo ratings yet
- Mark Twain's Essay On - The BeeDocument3 pagesMark Twain's Essay On - The BeetupelohuneyNo ratings yet
- THC 2 Module 1 - Risk Management Concept & PrinciplesDocument4 pagesTHC 2 Module 1 - Risk Management Concept & PrinciplesRyan ZarcoNo ratings yet
- QuestionnaireDocument8 pagesQuestionnaireMelvin HonorioNo ratings yet
- Itl Public School Sector - 9, Dwarka: SESSION 2014 - 2015Document3 pagesItl Public School Sector - 9, Dwarka: SESSION 2014 - 2015ik62299No ratings yet
- Phrasal Verbs - Make and DoDocument6 pagesPhrasal Verbs - Make and DoCarolina AndreaNo ratings yet
- Tanay Rizal Day Tour Itinerary and Tips - Tara Lets AnywhereDocument1 pageTanay Rizal Day Tour Itinerary and Tips - Tara Lets AnywhereShiela Marie MalanoNo ratings yet
- Shelf Life StudiesDocument24 pagesShelf Life Studieslod2008No ratings yet
- Star ThugsDocument160 pagesStar ThugsGlyn PulmanNo ratings yet
- Periodical Test English 6Document3 pagesPeriodical Test English 6Clifton MillerNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Rice TechnologyDocument2 pagesHybrid Rice TechnologyrscordovaNo ratings yet