Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Digestive System
Uploaded by
bjbitscs210 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
50 views36 pagesppt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentppt
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
50 views36 pagesDigestive System
Uploaded by
bjbitscs21ppt
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 36
1
The Digestive System
2
Digestion
Processing of food
Types
Mechanical (physical)
Chew
Tear
Grind
Mash
Mix
Chemical
Catabolic reactions
Enzymatic hydrolysis
Carbohydrate
Protein
Lipid
3
Digestion
Phases
Ingestion
Movement
Digestion
Absorption
Further digestion
4
Digestive System Organization
Gastrointestinal (Gl) tract (Alimentary canal)
Tube within a tube
Direct link/path between organs
Structures
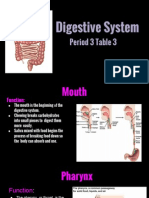
Mouth
Oral Cavity
Pharynx
Esophagus
Stomach
Duedenum
Jejenum
kIleum
Cecum
Ascending colon
Transverse colon
5
Digestive System Organization
Descending colon
Sigmoid colon
Rectum
Anus
Accessory structures
Not in tube path
Organs
Teeth
Tongue
Salivary glands
Liver
Gall bladder
Pancreas
6
Anatomy of the Mouth and
Throat
7
Human Deciduous and
Permanent Teeth
8
Dorsal Surface of the Tongue
9
The Major Salivary Glands
10
Deglutition (swallowing)
Sequence
Voluntary stage
Push food to back of
mouth
Pharyngeal stage
Raise
Soft palate
Larynx + hyoid
Tongue to soft palate
Esophageal stage
Contract pharyngeal
muscles
Open esophagus
Start peristalsis
11
Deglutition (swallowing)
Control
Nerves
Glossopharyngeal
Vagus
Accessory
Brain stem
Deglutition center
Medulla oblongata
Pons
Disorders
Dysphagia
Aphagia
12
Esophagus
Usually collapsed (closed)
3 constrictions
Aortic arch
Left primary bronchus
Diaphragm
Surrounded by
SNS plexus
Blood vessels
Functions
Secrete mucous
Transport food
13
Peristalsis and Segmentation
14
Esophagus
Sphincters
Upper
Lower
Abnormalities
Achalasia
Atresia
Hernia
Barrets esophagus
Esophageal varices
15
Stomach
Usually J shaped
Left side, anterior to the spleen
Mucous membrane
G cells make gastrin
Goblet cells make mucous
Gastric pit Oxyntic gland Parietal cells Make
HCl
Chief cells Zymogenic cells
Pepsin
Gastric lipase
16
Anatomy of the Stomach
17
Stomach
3 muscle layers
Oblique
Circular
Longitudinal
Regions
Cardiac sphincter
Fundus
Antrum (pylorus)
Pyloric sphincter
Vascular
Inner surface thrown into
folds Rugae
Contains enzymes that work
best at pH 1-2
18
Stomach
Functions
Mix food
Reservoir
Start digestion of
Protein
Nucleic acids
Fats
Activates some enzymes
Destroy some bacteria
Makes intrinsic factor B
12 absorption
Destroys some bacteria
Absorbs
Alcohol
Water
Lipophilic acid
B 12
19
Small Intestine
Extends from pyloric
sphincter ileocecal
valve
Regions
Duodenum
Jejenum
Ileum
Movements
Segmentation
Peristalsis
20
Small Intestine
Histology
Intestinal glands Intestinal enzymes
Duodenal glands Alkaline mucous
Paneth cells Lysozyme
Microvilli
Lacteals
Plica circularis
Smooth muscle
Lymphatic tissue GALT
Vascular
21
Small Intestine
Absorbs
80% ingested water
Electrolytes
Vitamins
Minerals
Carbonates
Active/facilitated
transport
Monosaccharides
Proteins
Di-/tripeptides
Amino acids
Lipids
Monoglycerides
Fatty acids
Micelles
Chylomicrons
22
Structure of the Villi in the
Small Intestine
23
Small Intestine
Secretes digestive
enzymes
Peptidases
Amino-
Di-
Tri-
Sucrases
Maltase
Lactase
Saccharidases
Di-
Tri-
Lipase
Nucleases
24
Small Intestine
Control
Requires pancreatic
enzymes & bile to
complete digestion
25
Large Intestine
Extends from ileocecal valve to anus
Regions
Cecum Appendix
Colon
Ascending
Transverse
Descending
Rectum
Anal canal
26
Anatomy of the Large Intestine
27
Large Intestine
Histology
No villi
No permanent circular folds
Smooth muscle
Taeniae coli
Haustra
Epiploic appendages
Otherwise like rest of Gl tract
28
Large Intestine
Functions
Mechanical digestion
Haustral churning
Peristalsis
Reflexes
Gastroileal
Gastrocolic
Chemical digestion
Bacterial digestion
Ferment carbohydrates
Protein/amino acid
breakdown
Absorbs
More water
Vitamins
B
K
Concentrate/eliminate
wastes
29
Feces Formation and Defecation
Chyme dehydrated to
form feces
Feces composition
Water
Inorganic salts
Epithelial cells
Bacteria
Byproducts of digestion
Defecation
Peristalsis pushes feces
into rectum
Rectal walls stretch
Control
Parasympathetic
Voluntary
30
Liver
Location
R. Hypochondrium
Epigastric region
4 Lobes
Left
Quadrate
Caudate
Right
Each lobe has lobules Contains hepatocytes
Surround sinusoids Feed into central vein
31
Liver
Functions
Makes bile
Detergent emulsifies
fats
Release promoted by:
Vagus n.
CCK
Secretin
Contains
Water
Bile salts
Bile pigments
Electrolytes
Cholesterol
Lecithin
32
Liver
Detoxifies/removes
Drugs
Alcohol
Stores
Gycolgen
Vitamins (A, D, E, K)
Fe and other minerals
Cholesterol
Activates vitamin D
Fetal RBC production
Phagocytosis
Metabolizes absorbed food
molecules
Carbohydrates
Proteins
Lipids
33
Liver
Dual blood supply
Hepatic portal vein
Direct input from small
intestine
Hepatic artery/vein
Direct links to heart
34
The Duodenum and Related
Organs
35
The Organs and Positions in the
Abdominal Cavity
36
Structures of the Alimentary
Canal
You might also like
- Honda Wave Parts Manual enDocument61 pagesHonda Wave Parts Manual enMurat Kaykun86% (94)
- Digestive SystemDocument15 pagesDigestive SystemchinchuNo ratings yet
- Campbell & Reece Chapter 42 Circulatory System OverviewDocument23 pagesCampbell & Reece Chapter 42 Circulatory System OverviewAlexandra LigpitNo ratings yet
- Hindustan Motors Case StudyDocument50 pagesHindustan Motors Case Studyashitshekhar100% (4)
- Human Digestive SystemDocument39 pagesHuman Digestive SystemSha KhinaNo ratings yet
- Digestive System PowerpointDocument19 pagesDigestive System Powerpointapi-277974939No ratings yet
- Digestive System GuideDocument20 pagesDigestive System Guiderocky2219No ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument10 pagesCirculatory SystemKent Clark VillaNo ratings yet
- Digestive Systems of Vertebrates and InvertebratesDocument7 pagesDigestive Systems of Vertebrates and InvertebratesClexandrea Dela Luz CorpuzNo ratings yet
- The Cell Structure, Functions of The CellDocument76 pagesThe Cell Structure, Functions of The CellCharles SsekawuNo ratings yet
- Female Reproduction Female Reproductive Parts and Functions II. Oogenesis and OvulationDocument4 pagesFemale Reproduction Female Reproductive Parts and Functions II. Oogenesis and OvulationLana GalloNo ratings yet
- The Digestive SystemDocument2 pagesThe Digestive SystemAnonymous X3pqnliPjNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity No. 9: The Frog Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesLaboratory Activity No. 9: The Frog Respiratory SystemMaricris GuillermoNo ratings yet
- On Biological Science of Mark Mina and Krichelle Jane LopezDocument5 pagesOn Biological Science of Mark Mina and Krichelle Jane LopezMark MinaNo ratings yet
- HomeostasisDocument16 pagesHomeostasisDr M K GuptaNo ratings yet
- Effects of Exercise and Training On Human Excretory System: Rahul Arya Amit Singh Rishi Chaubey Vishal ThakranDocument13 pagesEffects of Exercise and Training On Human Excretory System: Rahul Arya Amit Singh Rishi Chaubey Vishal ThakranAnonymous Dx0S9QlNo ratings yet
- Lymph SystemDocument7 pagesLymph SystemghaiathNo ratings yet
- Support and Transport in PlantsDocument37 pagesSupport and Transport in PlantsGuruKPO100% (1)
- Circulatory System Sci 6Document26 pagesCirculatory System Sci 6Regin BaguioNo ratings yet
- Digestive System in HumanDocument20 pagesDigestive System in Humanapi-400692183No ratings yet
- Powerpoint #5: Honors BiologyDocument19 pagesPowerpoint #5: Honors BiologyNylan AnyerNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument67 pagesDigestive SystemShacquille Suelto Bautista0% (1)
- Organs of the Respiratory System ExplainedDocument12 pagesOrgans of the Respiratory System ExplainedSeptian PutraNo ratings yet
- How Species Evolve Over TimeDocument33 pagesHow Species Evolve Over TimeYoussef DiabNo ratings yet
- Nutrition (Digestive System)Document57 pagesNutrition (Digestive System)anglie feNo ratings yet
- Human Excretory System Removes WasteDocument15 pagesHuman Excretory System Removes WasteJames AysonNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument30 pagesDigestive SystemImneil Jeanne Melendres-PerezNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument6 pagesDigestive SystemLeylaNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument6 pagesProkaryotes and Eukaryoteshussainm1234No ratings yet
- Prepared By: Lyle Alexandra MondaresDocument12 pagesPrepared By: Lyle Alexandra MondaresLyle Alexandra MondaresNo ratings yet
- Human Respiration HandoutDocument4 pagesHuman Respiration HandoutJulius GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Organs of The Digestive SystemDocument16 pagesOrgans of The Digestive SystemBrandon HunterNo ratings yet
- Chapter25 Urinary SystemDocument9 pagesChapter25 Urinary Systemkikajet23No ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Respiratory SystemDocument29 pagesLesson 5 - Respiratory Systemapi-307592530No ratings yet
- BiosphereDocument27 pagesBiosphereJamaika Sofia LetimNo ratings yet
- Diffusion LabDocument8 pagesDiffusion LabGioVanna GVNo ratings yet
- Study Guide 24 - Urinary SystemDocument19 pagesStudy Guide 24 - Urinary SystemcharlesNo ratings yet
- Reproductive SystemDocument6 pagesReproductive SystemDara BMNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Power PointDocument17 pagesDigestive System Power PointAlyssa Mae DapadapNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic CellsDocument2 pagesProkaryotic CellsBerch MelendezNo ratings yet
- Digestion: The Digestive SystemDocument66 pagesDigestion: The Digestive SystemTonique GordonNo ratings yet
- Bped 65 Urinary SystemDocument26 pagesBped 65 Urinary SystemDollie May Maestre-TejidorNo ratings yet
- Digestive System of FrogDocument28 pagesDigestive System of FrogPaolo Naguit100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology: The CellDocument8 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: The Celllourd nabNo ratings yet
- Plant TissuesDocument11 pagesPlant TissuesRudra Patel100% (1)
- Endocrine SystemDocument31 pagesEndocrine Systemsalmeohenzgabry100% (1)
- 7th Grade BiomesDocument19 pages7th Grade BiomesCristianNoriegaNo ratings yet
- The Digestive SystemDocument19 pagesThe Digestive Systemianpoblete13No ratings yet
- BIOLAB FROG Organ HistologyDocument7 pagesBIOLAB FROG Organ HistologyCloie Anne Rabinetas100% (1)
- How Your Digestive System WorksDocument11 pagesHow Your Digestive System WorkssethurajeswariNo ratings yet
- The Skeletal System: Functions and AnatomyDocument28 pagesThe Skeletal System: Functions and AnatomyDian O. Velasquez100% (1)
- Muscular System Quiz Study GuideDocument10 pagesMuscular System Quiz Study Guidejbradee100% (2)
- The Cardiac Cycle: Hina Karim NES InstructorDocument19 pagesThe Cardiac Cycle: Hina Karim NES InstructorshahinaNo ratings yet
- Membrane TransportDocument24 pagesMembrane Transportolawandeilo123No ratings yet
- Handouts - Digestive System Sp11Document6 pagesHandouts - Digestive System Sp11Kelly TrainorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Tissues, Glands, and MembranesDocument11 pagesChapter 4 Tissues, Glands, and MembranesMaria Angela Del Gallego100% (2)
- Anatomy of the Female BreastDocument18 pagesAnatomy of the Female Breasthabtsh habshaNo ratings yet
- Digestivesystem 2012Document36 pagesDigestivesystem 2012Anityo Nugroho100% (1)
- Digestivesystem 2Document38 pagesDigestivesystem 2Ahmad IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument36 pagesDigestive SystemAmbray Felyn JoyNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument36 pagesDigestive SystemTiffany WadaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Electric PotentialDocument42 pagesChapter 4 - Electric PotentialDebora Sanny TeohNo ratings yet
- Pointers To Structures: Struct IntDocument2 pagesPointers To Structures: Struct Intbjbitscs21No ratings yet
- Physical Education Guidelines Sample Question PaperDocument1 pagePhysical Education Guidelines Sample Question PaperkagomekikioNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System: By: Mrs. BourlandDocument26 pagesThe Digestive System: By: Mrs. Bourlandbjbitscs21No ratings yet
- Portfolio by Harshit Dhameliya-1Document85 pagesPortfolio by Harshit Dhameliya-1Aniket DhameliyaNo ratings yet
- GlastonburyDocument4 pagesGlastonburyfatimazahrarahmani02No ratings yet
- Axe Case Study - Call Me NowDocument6 pagesAxe Case Study - Call Me NowvirgoashishNo ratings yet
- Catalogoclevite PDFDocument6 pagesCatalogoclevite PDFDomingo YañezNo ratings yet
- LM1011 Global ReverseLogDocument4 pagesLM1011 Global ReverseLogJustinus HerdianNo ratings yet
- Non Circumvention Non Disclosure Agreement (TERENCE) SGDocument7 pagesNon Circumvention Non Disclosure Agreement (TERENCE) SGLin ChrisNo ratings yet
- Exercises 6 Workshops 9001 - WBP1Document1 pageExercises 6 Workshops 9001 - WBP1rameshqcNo ratings yet
- India Today 11-02-2019 PDFDocument85 pagesIndia Today 11-02-2019 PDFGNo ratings yet
- Coffee Table Book Design With Community ParticipationDocument12 pagesCoffee Table Book Design With Community ParticipationAJHSSR JournalNo ratings yet
- DNA Gel Electrophoresis Lab Solves MysteryDocument8 pagesDNA Gel Electrophoresis Lab Solves MysteryAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- HCW22 PDFDocument4 pagesHCW22 PDFJerryPNo ratings yet
- Jfif 1.02Document9 pagesJfif 1.02Berry Hoekstra100% (1)
- Liebert PSP: Quick-Start Guide - 500VA/650VA, 230VDocument2 pagesLiebert PSP: Quick-Start Guide - 500VA/650VA, 230VsinoNo ratings yet
- Rtsa 2012Document7 pagesRtsa 2012Justin RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Engineering Comprehensive Board Exam Reviewer: Agricultural Processing, Structures, and Allied SubjectsDocument84 pagesAgricultural Engineering Comprehensive Board Exam Reviewer: Agricultural Processing, Structures, and Allied SubjectsRachel vNo ratings yet
- John Titor TIME MACHINEDocument21 pagesJohn Titor TIME MACHINEKevin Carey100% (1)
- Unit 3 Computer ScienceDocument3 pagesUnit 3 Computer ScienceradNo ratings yet
- Olympics Notes by Yousuf Jalal - PDF Version 1Document13 pagesOlympics Notes by Yousuf Jalal - PDF Version 1saad jahangirNo ratings yet
- Budgetary ControlsDocument2 pagesBudgetary Controlssiva_lordNo ratings yet
- 4 Wheel ThunderDocument9 pages4 Wheel ThunderOlga Lucia Zapata SavaresseNo ratings yet
- August 03 2017 Recalls Mls (Ascpi)Document6 pagesAugust 03 2017 Recalls Mls (Ascpi)Joanna Carel Lopez100% (3)
- Free Radical TheoryDocument2 pagesFree Radical TheoryMIA ALVAREZNo ratings yet
- GIS Multi-Criteria Analysis by Ordered Weighted Averaging (OWA) : Toward An Integrated Citrus Management StrategyDocument17 pagesGIS Multi-Criteria Analysis by Ordered Weighted Averaging (OWA) : Toward An Integrated Citrus Management StrategyJames DeanNo ratings yet
- Neuropsychological Deficits in Disordered Screen Use Behaviours - A Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisDocument32 pagesNeuropsychological Deficits in Disordered Screen Use Behaviours - A Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisBang Pedro HattrickmerchNo ratings yet
- Account Statement From 30 Jul 2018 To 30 Jan 2019Document8 pagesAccount Statement From 30 Jul 2018 To 30 Jan 2019Bojpuri OfficialNo ratings yet
- Sarvali On DigbalaDocument14 pagesSarvali On DigbalapiyushNo ratings yet
- Antenna VisualizationDocument4 pagesAntenna Visualizationashok_patil_1No ratings yet
- Oxford Digital Marketing Programme ProspectusDocument12 pagesOxford Digital Marketing Programme ProspectusLeonard AbellaNo ratings yet