Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Line Sizing Slides
Uploaded by
mat333r0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views22 pagesline sizing
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentline sizing
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views22 pagesLine Sizing Slides
Uploaded by
mat333rline sizing
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 22
31% of large property damage
losses are caused by failures in
piping systems.
Some lines reach 60 inches in
diameter - larger than many
equipment items.
MB & EB balances must include:
Normal mass balance - base case.
Start-up, shut down or upset
devn.
Recycle of off-spec products.
Equipment bypass conditions.
MB for flare, fire water, sewers,
steam, condensate and CTW
headers.
Limiting line velocities not
known or ignored.
Velocity greater than 15 fps in CS
pipe can cause erosion.
Low velocities (< 3 fps) can cause
entrained solids to settle and plug
lines.
Poor record keeping during Phase 3
prevents detailed follow-up in
Phase 4 design stage.
PSV lines need to be checked in
Phase 4.
Pump lines need to be checked in
Phase 4.
Corrosiveness of fluid unknown.
At high temps, degradation may
produce acidic components. (La.
HumbleTherm example).
Pipe not suitable for unexpected
cold temperatures.
Pipe not suitable for unexpected
extreme high temperatures.
Compressible fluid flow not well
understood by process engineers.
Flows at Mach 1 (Sonic Flow) can
be destructive.
Two Phase Flow not well
understood by process engineers.
Horizontal Flow - Baker Chart.
Vertical Down Flow.
Vertical Up Flow.
Siphons may form readily
May have damaging pulsating
flow
May have damaging pulsating
flow
4 ft. dia. Cooling tower inlet pipe
experiences severe vibration, fails
& floods plant
Two phase flow pressure drops
may be higher than expected and
thereby limit performance.
Flashing liquids often not
considered during process
design.
Two phase flow can be a
complex, transient problem.
PSVs are usually sized for single
phase flow.
Two phase flow can occur when
vessels operated above maximum
fill limit.
Two phase flow can occur when
flows are higher than expected.
Draining water from KO Pot to
open sewer during rain storm.
Flammable vapor entrained due
to formation of liquid vortex.
Lightning strikes near plant ISBL.
Sewer explodes, wrecks cold box
in Ammonia Plant.
One operator killed.
Flow in reactor manifolds.
Flows in branched piping.
Flows in shell-side of exchangers.
System or vessel design pressures
exceeded when EBV suddenly
stops flow.
EO transfer example.
See computer spreadsheet design
program.
Which flow regime should you
avoid for horizontal, two phase
flow?
If a liquid vortex forms on draining
from a vessel, what safety problems
can this create?
When can a PSV which is sized for
single phase flow experience two
phase flow?
You might also like
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Spec FurnaceOil SPL 1437546379Document1 pageSpec FurnaceOil SPL 1437546379mat333rNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Solvent CP and LamdaDocument28 pagesSolvent CP and Lamdamat333rNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
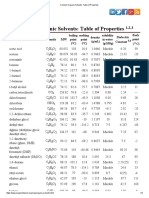
- Common Organic Solvents - Table of PropertiesDocument2 pagesCommon Organic Solvents - Table of Propertiesmat333rNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Product Latent Heat of Evaporation: (KJ/KG) (Btu/lb) - HDocument4 pagesProduct Latent Heat of Evaporation: (KJ/KG) (Btu/lb) - Hmat333rNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Dioctyl PhthalateDocument3 pagesDioctyl Phthalatemat333rNo ratings yet
- Thermal PhysicsDocument10 pagesThermal PhysicsharshanauocNo ratings yet
- Electrolux Esf 2410Document16 pagesElectrolux Esf 2410michalis5255No ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- 01.unit 1 - Specification & Specification WritingDocument26 pages01.unit 1 - Specification & Specification WritingDhineshNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Gripple FencingDocument12 pagesGripple FencingronNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- DME Model QuesDocument3 pagesDME Model QuesSiva RamanNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Lesson 13 - Material Selection Process - Rev. 0Document21 pagesLesson 13 - Material Selection Process - Rev. 0Naufal RafifNo ratings yet
- Mcode and Mname Commercial and Alternate Designations: Material - Cross - IndexDocument33 pagesMcode and Mname Commercial and Alternate Designations: Material - Cross - IndexMohamedNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- B.6 Drainage - BQDocument5 pagesB.6 Drainage - BQSHARVINDRANADAN A/L SATHANANDHAN A18KA0153No ratings yet
- Driscoplex 6500 Pe2708 / (Pe2406) Pipe: Pipe & Fittings Data SheetDocument2 pagesDriscoplex 6500 Pe2708 / (Pe2406) Pipe: Pipe & Fittings Data SheetmariannyNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Features and Benefits: Model CB 15-100 HP BoilersDocument5 pagesFeatures and Benefits: Model CB 15-100 HP BoilerssebaversaNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Cost Estimating Guide Uniformat II 1Document9 pagesCost Estimating Guide Uniformat II 1Edson Lozano LafforeNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Part HF Requirements For Boilers Constructed of Wrought MaterialsDocument21 pagesPart HF Requirements For Boilers Constructed of Wrought MaterialsKarthikeyan ParthasarathyNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- West Bengal Schedule Rates of Sanitary & Plumbing Works 2015Document125 pagesWest Bengal Schedule Rates of Sanitary & Plumbing Works 2015Arunashish Mazumdar100% (11)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Coal SlagDocument4 pagesCoal SlagSivaratnam NavatharanNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- OSHA Slings 1910.184Document15 pagesOSHA Slings 1910.184Binoy GopinathanNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Characterization of Natural Fibre Polymer Composites For Structural ApplicationDocument159 pagesCharacterization of Natural Fibre Polymer Composites For Structural ApplicationAsia YahyaNo ratings yet
- Leaf SpringDocument3 pagesLeaf SpringChilsonHangadZerdaNo ratings yet
- Powder Production Techniques: AtomizationDocument13 pagesPowder Production Techniques: AtomizationVasantha SudasinghaNo ratings yet
- Dry Pack GroutDocument1 pageDry Pack Groutpravi3434No ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Drawing PDFDocument54 pagesCivil Engineering Drawing PDFgeos100189% (9)
- ACO Drain S100K ChannelDocument2 pagesACO Drain S100K ChannelMatt GhanaviNo ratings yet
- API Standard 600: Steel Gate Valves-Flanged and Butt-Welding Ends, Bolted BonnetsDocument3 pagesAPI Standard 600: Steel Gate Valves-Flanged and Butt-Welding Ends, Bolted BonnetsPasquale CutriNo ratings yet
- Jute Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Composites: A Comprehensive ReviewDocument21 pagesJute Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Composites: A Comprehensive ReviewbiniyamNo ratings yet
- Asce 7-22 CH 03com - For PCDocument16 pagesAsce 7-22 CH 03com - For PCsharethefilesNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Bridge EngineeringDocument16 pagesBridge EngineeringJoson Anquillano Villegas100% (1)
- Cozy ClassicDocument89 pagesCozy ClassicSerban MarinNo ratings yet
- PHB2 PVDocument5 pagesPHB2 PVMarusan Petpookaew0% (1)
- 04.utilization of Bamboo Ash To Enhance Cement Strength in Well Cementing OperationsDocument7 pages04.utilization of Bamboo Ash To Enhance Cement Strength in Well Cementing OperationsHerry SuhartomoNo ratings yet
- Frame Fixing - Nylon and Metal Anchors For FramesDocument22 pagesFrame Fixing - Nylon and Metal Anchors For FramesjulianNo ratings yet
- Shell Gadus S2 V220 0 TDSDocument2 pagesShell Gadus S2 V220 0 TDSsvntamil_159541837No ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)