Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EDP Accounting - Chapter 1 Lecture.B
Uploaded by
hassanjamil123Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EDP Accounting - Chapter 1 Lecture.B
Uploaded by
hassanjamil123Copyright:
Available Formats
Accounting
Information
Systems: An
Overview
The Users of Accounting Information
A. External Users of Accounting Information
B. Internal Users of Accounting Information
C. Mandatory vs. Discretionary Information
External Users of Accounting Information
Investors
Creditors
Stockholders
Customers and Vendors
Government Agencies
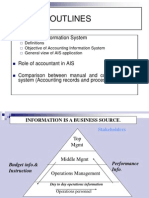
Internal Users of Accounting Information
Lower Level
Managers
Middle
Managers
Top-Level
Managers
Information Operational
Control
Management
Control
Strategic
Planning
Source Largely
internal
External
Level
Detailed
Aggregate
Time Horizon Historical Future
Required
Accuracy
High
Low
Mandatory vs. Discretionary Information
Mandatory Information
Certain types of
information must be
generated regardless
of the cost:
Government reports
Payroll
Basic bookkeeping
Evaluation Criteria
For mandatory
information, the primary
concern is minimization
of cost.
In contrast,
discretionary information
should provide greater
benefits than the cost of
generating it.
Information Systems
Accounting Information Systems (AIS)
The term information system suggests the use of
computer technology in an organization
Hardware
Software
Information
System
Data
Information for
Decision Making
Electronic Data Processing
(EDP) or Data Processing (DP)
Use of computer
technology to perform
an organizations
transaction-oriented
data processing. DP
systems serve routine,
recurring, general
information needs.
Accounting Information Systems
(AIS)
A computer-based
system designed to
transform accounting
data into information.
Can also include
transactions
processing cycles, the
use of information
technology, and the
development of
information systems.
Transaction Processing Cycles
A. Revenue Cycle
B. Expenditure Cycle
C. Production Cycle
D. Finance Cycle
E. Financial Reporting Cycle
The transaction processing
cycles provide a means of
viewing the activities of a
business.
A. Revenue Cycle
Events related to the
distribution of goods
and services to other
entities and the
collection of related
payments
Expenditure Cycle
Events related to the
acquisition of goods
and services from
other entities and the
settlement of related
obligations.
Production Cycle
Events related to the
transformation of
resources into goods
and services.
Finance Cycle
Events related to the
acquisition and
management of capital
funds, including cash.
The treasurer is
responsible for the
finances of the
business.
Financial Reporting Cycle
Not an operating cycle
This cycle obtains
accounting and operating
data from other cycles and
processes this data so that
financial reports can be
prepared.
A controller is in charge
of the accounting
function.
The Internal Control Process
A. Definition of Internal Control
B. The Five Elements of the Internal Control
Process
C. Segregation of Accounting Functions
D. The Internal Audit Function
Since management is far removed from the scene of
operations in a large organization, personal
supervision of employees is often replaced with
various control techniques.
Definition of Internal Control
Internal control is a process
designed to provide reasonable
assurance regarding the
achievement of objectives
relating to:
Reliability of financial
reporting
Effectiveness and efficiency of
operations
Compliance with applicable
laws and regulations
The concept of internal control structure is based on two major
premises: managements responsibility and reasonable assurance.
Five Elements of the Internal
Control Process
Control environment Overall values and integrity of
organization.
Risk assessment Identification and evaluation of risks
(Potential loss x Probability = Exposure).
Control activities Activities undertaken to reduce
probability of loss due to significant risks.
Information and communication Communicating
information about the control environment and control
activities.
Monitoring Keeping watch over and changing
internal controls so that they function effectively and
efficiently.
Segregation of Accounting
Functions
Segregate the following
duties:
Authorization
Record keeping
Custody of assets
I kept the
records and
the cash.
Internal Audit Function
Internal auditing is an
independent appraisal
function charged with
monitoring and
assessing compliance
with organizational
policies and
procedures.
Organization Interaction With
Information Systems
A. The Steering Committee
B. End-User Computing
C. Quick-Response Technology
The Steering Committee
A committee advising the
Chief Information
Officer that is
composed of high-level
members of user
functions such as
manufacturing and
marketing. The
committee provides a
means by which
managers from other
areas can influence the
information services
process.
End-User Computing (EUC)
Functional end users do
their own information
processing activities
through an EUC
application such as a
database that uses a
query language feature
to generate specific
information needed by
the end user to make
decisions.
Inadequate system
development May solve
wrong problem or have
poor documentation.
Ineffective use of resources
Underutilized equipment
or inefficient design.
Data integrity and security
problems Inadvertent
alteration of data or
failure to implement
security controls.
Potential EUC Problems
Quick-Response Technology
1. Just-In-Time
2. Web Commerce
3. Electronic Data Interchange
4. Extensible Business Reporting Language
5. Computer Integrated Manufacturing
6. Electronic Payment Systems
Just-in-Time
Purchase orders for
inventory items are
made on a demand-
pull basis rather than
a fixed interval push
basis to restock store
inventory levels.
Adds flexibility to
meet customer needs
and reduces product
rework.
Web Commerce
Provides worldwide
availability of
products on a single
computer.
Specially trained
CPAs offer the Web
Trust seal to sites that
meet certain security
and privacy criteria.
Electronic Data Interchange
Electronic data interchange (EDI) is the direct
computer-to-computer exchange of business
documents via a communications network. EDI
differs from e-mail in that EDI messages are created
and interpreted by computers without human
intervention. Also makes use of universal product
code (UPC) bar code.
Extensible Business Reporting Language
Extensible Business Reporting Language (XBRL) is
a language that facilitates the exchange over the
Internet of all kinds of business documents and
financial statements. The SEC permits companies
to file their financial reports electronically using
XBRL format.
Computer-Integrated
Manufacturing (CIM)
Components of CIM
typically include
computer-aided design
(CAD) workstations, real-
time production
monitoring and control
systems, and order
inventory and control
systems.
Makes use of scanner
technology and machine-
readable bar codes.
Electronic Payment Systems
Electronic funds transfer
(EFT) systems are
electronic payment
systems in which
processing and
communication are
primarily or totally
electronic.
You might also like
- TASK 2 - BSBMGT517 Manage Operational Plan TASK 2 - BSBMGT517 Manage Operational PlanDocument14 pagesTASK 2 - BSBMGT517 Manage Operational Plan TASK 2 - BSBMGT517 Manage Operational PlanVioleta Hoyos Lopez68% (19)
- Island Cruise Reflective PaperDocument4 pagesIsland Cruise Reflective PaperCarlos Carranza100% (1)
- Chapter 22 Auditing in A CIS Environment - pptx990626434Document25 pagesChapter 22 Auditing in A CIS Environment - pptx990626434Clar Aaron Bautista67% (3)
- Fulbright Personal Statements Guide and Sample EssaysDocument30 pagesFulbright Personal Statements Guide and Sample EssaysFaisal AminNo ratings yet
- HFM and RulesDocument30 pagesHFM and RulesBHASKAR SANKARNo ratings yet
- 02 - Use of Technology in AccountingDocument8 pages02 - Use of Technology in AccountingKhine Myo TintNo ratings yet
- Business Plan Pizza ShopDocument11 pagesBusiness Plan Pizza ShopPaulaBrinzeaNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting G1Document9 pagesFinancial Accounting G1Precious Anne ValderramaNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting Information SystemDocument9 pagesCost Accounting Information SystemFaiz KhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Traditional Accounting Information SystemsDocument12 pagesLecture 2 Traditional Accounting Information SystemsCrispus KimingichNo ratings yet
- Overview of AISDocument8 pagesOverview of AISBulelwa HarrisNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Accounting Information Systems 11th Edition by BodnarDocument22 pagesSolution Manual For Accounting Information Systems 11th Edition by Bodnarfuze.riddle.ghik9100% (43)
- Is Types and Controls301 CH 1Document39 pagesIs Types and Controls301 CH 1R RNo ratings yet
- Accounting Information Systems, 6: Edition James A. HallDocument41 pagesAccounting Information Systems, 6: Edition James A. HallJc BuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- Topic 3-Accounting Systems & ControlDocument42 pagesTopic 3-Accounting Systems & Controlنورلينا رزاليNo ratings yet
- Verview OF Omputerised Ccounting Ystem: O C A SDocument16 pagesVerview OF Omputerised Ccounting Ystem: O C A SswathiNo ratings yet
- Accounting Information Systems: AnDocument39 pagesAccounting Information Systems: AnGlennizze GalvezNo ratings yet
- The Relevance of Auditing in A Computerized Accounting SystemDocument5 pagesThe Relevance of Auditing in A Computerized Accounting SystemEmebet TesemaNo ratings yet
- II 1ComputerAidedAccounting and BusinessSystemsDocument2 pagesII 1ComputerAidedAccounting and BusinessSystemsAwais AfzalNo ratings yet
- t3 Acntng - FinalDocument7 pagest3 Acntng - FinalMukul SinhaNo ratings yet
- Comp4 (Accounting Information System)Document8 pagesComp4 (Accounting Information System)Ren Flores ViluanNo ratings yet
- BEC 4 Outline - 2015 Becker CPA ReviewDocument6 pagesBEC 4 Outline - 2015 Becker CPA ReviewGabrielNo ratings yet
- t3 AcntngDocument7 pagest3 AcntngMukul SinhaNo ratings yet
- Audit of A Computerized Accounting System 2Document27 pagesAudit of A Computerized Accounting System 2t4fgmwcb2kNo ratings yet
- AC 571 - Final Exam (Study Guide)Document14 pagesAC 571 - Final Exam (Study Guide)Natasha Declan100% (1)
- Accountancyc 12Document7 pagesAccountancyc 12Arif ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Audit in CIS - IntroductionDocument3 pagesAudit in CIS - IntroductionOrtiz, Trisha Mae S.No ratings yet
- Apu 276Document27 pagesApu 276Aliul ApuNo ratings yet
- Accounting Info - 1st SemDocument17 pagesAccounting Info - 1st SemPixie CanaveralNo ratings yet
- The Information System: An Accountant's PerspectiveDocument33 pagesThe Information System: An Accountant's PerspectiveLUIS ALFONSO DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1.PDF IIIDocument48 pagesChapter 1.PDF IIIChera HabebawNo ratings yet
- Introduction Is AuditDocument35 pagesIntroduction Is AuditSepti SaraswatiNo ratings yet
- Group 1 - Narrative Report - APAEDocument15 pagesGroup 1 - Narrative Report - APAEKeene Chester HabladoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer Audit PDFDocument28 pagesIntroduction To Computer Audit PDFmunguti kamandiNo ratings yet
- Management Information System (MIS) : Relationship of IT With ManagementDocument4 pagesManagement Information System (MIS) : Relationship of IT With ManagementSana MalikNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 12 - Applications of Computer in AccountingDocument9 pagesImportant Questions For Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 12 - Applications of Computer in AccountingABHISHEK SINGHNo ratings yet
- A20 MIDTERM NotesDocument10 pagesA20 MIDTERM NotesAguilan, Alondra JaneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7: Risk Exposures and The Internal Control StructureDocument35 pagesChapter 7: Risk Exposures and The Internal Control StructureFx Hadisumarta NNo ratings yet
- Topic ThirteenDocument37 pagesTopic ThirteenGordar BuberwaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 ReviewerDocument16 pagesChapter 1 Revieweranon_879788236No ratings yet
- AIS SummaryDocument5 pagesAIS SummaryKimboy Elizalde PanaguitonNo ratings yet
- Verview OF Omputerised Ccounting Ystem: O C A SDocument16 pagesVerview OF Omputerised Ccounting Ystem: O C A SssNo ratings yet
- 81.what Is Financial Audit?Document3 pages81.what Is Financial Audit?Huidrom SharatNo ratings yet
- Administrative EfficiencyDocument6 pagesAdministrative Efficiencyritesh MishraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction To AISDocument29 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To AISFatiha YusofNo ratings yet
- Set Up and Operate A Computerized Accounting SystemDocument10 pagesSet Up and Operate A Computerized Accounting Systemabebe kumelaNo ratings yet
- AIS Group 8 Report Chapter 17 Hand-OutDocument8 pagesAIS Group 8 Report Chapter 17 Hand-OutPoy GuintoNo ratings yet
- 11.what Are The Typical Business Processes?: MarketingDocument5 pages11.what Are The Typical Business Processes?: MarketingHuidrom SharatNo ratings yet
- Auditing Extra Notes1Document9 pagesAuditing Extra Notes1Hassan TariqNo ratings yet
- What Do You Mean by Computerized Accounting SystemDocument29 pagesWhat Do You Mean by Computerized Accounting SystemDivya DixitNo ratings yet
- Accounting Information SystemDocument5 pagesAccounting Information Systemaccajay230% (1)
- MIS Unit-4Document6 pagesMIS Unit-4suganyaselva06No ratings yet
- Accounting Information System Chapter 1Document28 pagesAccounting Information System Chapter 1Cassie100% (1)
- Sistem Information AccountingDocument9 pagesSistem Information AccountingNicole Daniella JinggaNo ratings yet
- Accounting Information SystemDocument4 pagesAccounting Information SystemtheateeqNo ratings yet
- Accounting 1Document5 pagesAccounting 1Dương Nguyễn ThuỳNo ratings yet
- Ais Chapter 1 and 2 QuizletDocument63 pagesAis Chapter 1 and 2 QuizletVenice Espinoza100% (1)
- Accounting Information Systems, 10th Edition: James A. HallDocument35 pagesAccounting Information Systems, 10th Edition: James A. HallAlexis Kaye DayagNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Pa IDocument11 pagesUnit 5 Pa IHussen AbdulkadirNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Computer AccountingDocument5 pagesIntroduction of Computer AccountingASHISH SAININo ratings yet
- AFIS AssignmentDocument3 pagesAFIS Assignmentbsaf2147266No ratings yet
- Functions of An Accounting Information SystemDocument2 pagesFunctions of An Accounting Information SystemHannah YnciertoNo ratings yet
- Ais M1-Quiz No. 1: B. Automating All Decision Making C. Allocating Organizational ResourcesDocument12 pagesAis M1-Quiz No. 1: B. Automating All Decision Making C. Allocating Organizational ResourcesJenny Ann ManaladNo ratings yet
- Start And Grow Your Own Consulting Business From Zero: Artificial Intelligence in Accounting Practical Applications Odoo 17: odoo consultations, #1.1From EverandStart And Grow Your Own Consulting Business From Zero: Artificial Intelligence in Accounting Practical Applications Odoo 17: odoo consultations, #1.1No ratings yet
- 531 CV Format Internship Summer 2013Document1 page531 CV Format Internship Summer 2013hassanjamil123No ratings yet
- Setting An Audit StrategyDocument14 pagesSetting An Audit Strategyhassanjamil123No ratings yet
- Transactions Recording Chapter2 BDocument19 pagesTransactions Recording Chapter2 Bhassanjamil123No ratings yet
- 2013 May Skpi-TesttubeDocument370 pages2013 May Skpi-TesttubeAngelica Sta. MariaNo ratings yet
- Vascon Engineers LTD Financial Results and PriceDocument1 pageVascon Engineers LTD Financial Results and PricePillu The DogNo ratings yet
- Huimfisllfia: 18 July - August 2006 Aba Bank MarkehngDocument8 pagesHuimfisllfia: 18 July - August 2006 Aba Bank MarkehngGhumonto SafiurNo ratings yet
- Asset Issuance SlipDocument105 pagesAsset Issuance SlipMuneer HussainNo ratings yet
- Nash EquilibriumDocument5 pagesNash EquilibriumNiyati44100% (1)
- The Commercial Dispatch EEdition 5-13-14Document16 pagesThe Commercial Dispatch EEdition 5-13-14The DispatchNo ratings yet
- Intellectual Property Prelim NotesDocument5 pagesIntellectual Property Prelim NotesGretchen CanedoNo ratings yet
- Approved Employers - LahoreDocument15 pagesApproved Employers - Lahoreraheel97No ratings yet
- Bam 040 Demand and Supply PT.2Document14 pagesBam 040 Demand and Supply PT.2Vkyla BataoelNo ratings yet
- Job Order Contract Ground MowingDocument2 pagesJob Order Contract Ground MowingLiza BacudoNo ratings yet
- Assessing ROI On CloudDocument6 pagesAssessing ROI On CloudLeninNairNo ratings yet
- Od 126044903266212000Document1 pageOd 126044903266212000ABHINAV VELAGANo ratings yet
- Q4 2010 Financial Reports - EnglishDocument364 pagesQ4 2010 Financial Reports - Englishalexa_libraNo ratings yet
- 1 CISSP 1er Dummy Examen Respuestas y Explicaciones - QADocument58 pages1 CISSP 1er Dummy Examen Respuestas y Explicaciones - QAIvan MartinezNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 and 4Document42 pagesCHAPTER 3 and 4Josua PranataNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Engro PakistanDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Engro Pakistanasfand yar waliNo ratings yet
- Report On Business LetterDocument28 pagesReport On Business LetterAnum SheikhNo ratings yet
- SBI ProjectDocument82 pagesSBI Projectchandan sharmaNo ratings yet
- Nullification Crisis and States Rights L2Document16 pagesNullification Crisis and States Rights L2mjohnsonhistory100% (1)
- Gepco Inspection Certificate STG18-35Document3 pagesGepco Inspection Certificate STG18-35Farhan IlyasNo ratings yet
- Ellis CAMPBELL, JR., Director of Internal Revenue For The Second Collection District of Texas, v. William A. SAILER and Wife, Patricia O'Leary SailerDocument4 pagesEllis CAMPBELL, JR., Director of Internal Revenue For The Second Collection District of Texas, v. William A. SAILER and Wife, Patricia O'Leary SailerScribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Mosque DetailsDocument21 pagesMosque DetailsdavinciNo ratings yet
- IND AS 103 - Bhavik Chokshi - FR ShieldDocument26 pagesIND AS 103 - Bhavik Chokshi - FR ShieldSoham Upadhyay100% (1)
- Cost Analysis and Control Hyundai Motors India Limited (HMIL) 2014Document94 pagesCost Analysis and Control Hyundai Motors India Limited (HMIL) 2014ravikumarreddyt100% (2)
- Leading Through Digital Disruption AmazonDocument13 pagesLeading Through Digital Disruption AmazonMaham Tariq0% (1)
- PDFFFFFDocument7 pagesPDFFFFFkyla manaloNo ratings yet
- Cost AccountingDocument57 pagesCost AccountingM.K. TongNo ratings yet