Professional Documents
Culture Documents
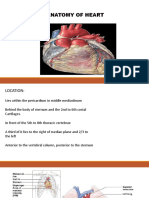
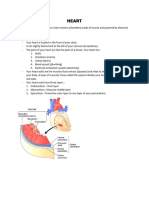
Mammalian Heart
Uploaded by
nickmirad2Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mammalian Heart
Uploaded by
nickmirad2Copyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 9
The Mamalian
Heart
Structure
Shape:
Cone (apex pointed left)
Size:
Fist
Mass:
300-500g
Location:
Thoracic cavity (left) *except Dextrocardia
Enveloped in pericardium
Muscle:
Myocardium (Cardiac muscle) joined by intercalated discs
for rapid nerve Impulse transmission. Mamalian heart Notes.doc
Myogenic Self-excitable (Contract and relax naturally
without nerve stimulation)
Structure
Left atrium
Chambers:
2 atrium - receives blood from vein
2 ventricles - pumps blood out of the
heart into arteries
Left
ventricle
Right atrium
Septum
Right ventricle
Atria wall
Ventricle wall
Reason
Thinner
Thicker
Ventricle pumps blood out of heart to lungs
and whole body.
Atria pumps to ventricles.
Right ventricle
Thinner
Left
ventricle
Thicker
Left ventricle- pumps to whole body
Right ventricle pumps to lungs only
Structure
Aorta
Vena Cava
(Superior)
Semilunar
valve
Tricuspid
valve
Valves:
Pulmonary artery
Pulmonary vein
Bicuspid
valve
Semilunar
valve
Atrio-ventricular valve-i) Tricuspid
ii) Bicuspid
(Mitral)
Semilunar valves- i) at Aorta entrance
(Aortic valve)
ii) at Pulmonary
artery entrance
(Pulmonary valve)
Function: One direction flow from..to,
prevent backflow
Vessels:
Vena Cava
Vena Cava
(Inferior)
Pulmonary artery
Pulmonary vein
Aorta
Circulations:
i)
Pulmonary circulation
ii) Systemic circulation
Carotid arteries:
- surface
- nutrients for myocardium
Cardiac Cycle
Sequence of events that makes one heart beat
1) Atrial systole
- Atria wall contract
- Atrial pressure high, forces blood
through AV valves into ventricles
- SL valve closes dub
2) Ventricular systole
- After 0.1 second, last for 0.3seconds
- Ventricles contract
- Ventricular pressure much
higher, forces blood through SL valves
out of the ventricles
- AV valves close lup
3) Ventricular diastole
- Atria and ventricles relax
- Heart pressure drops
- SL valves close
- Blood from vena cava fills atrium
1: AV valve close
3: SL valve close
2: SL valve open
4: AV valve open
Control of the Heart Beat
Pacemakers:
Specialized cardiac muscle cells that initiate
and coordinates rhythmic heart beat.
i)
SAN (Sinoatrial Node)
ii)
AVN (atrioventricular Node)
iii)
Purkyne Tissues (Bundle of Hiss,branches)
Non-conductive fibres between AV
Purkyne tissues
-rapid transmission between septum
outwards upwards ventricle walls
Heart beat rate: 70 times per minute
(average) =>pulse
Heart sound
- Ventricles contract bottom up
Electrocardiogram
Graph of electrical potential generated and
recorded against time Electrocardiograph
http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/animate/flash-electrical.swf
http://www.practicalclinicalskills.com/ekg-lesson.aspx?coursecaseorder=6&courseid=301
P: Atria contraction (depolarization)
Q, R, S: Ventricular contraction
Atria relaxation (repolarization)
T: Ventricular relaxation
Electrodes 10
http://www.aboutkidshealth.ca/En/HowTheBodyWorks/IntroductiontotheHeart/TheHeartbeat/Pages/Electroca
rdiogramECG.aspx
You might also like
- Heart and Neck VesselsDocument3 pagesHeart and Neck VesselsMark ElbenNo ratings yet
- Thorax: Selfi HandayaniDocument73 pagesThorax: Selfi HandayanisasmintooNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of HeartDocument30 pagesAnatomy of HeartLeno BennyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy, Coverings, Walls of HeartDocument8 pagesAnatomy, Coverings, Walls of HeartDeniebev'z OrillosNo ratings yet
- Anatomi JantungDocument54 pagesAnatomi JantungsaifudinNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Word Circulatory SystemDocument26 pagesUnit 4 Word Circulatory SystemChandan Shah100% (2)
- Circulatory SDocument110 pagesCirculatory SMohammed HabibNo ratings yet
- Parts and Function of Heart: Group 5 9 - ActsDocument47 pagesParts and Function of Heart: Group 5 9 - ActsJasmin GarciaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Circulatory SystemDocument157 pagesUnit 4 Circulatory SystemChandan ShahNo ratings yet
- 2 Lecture CardioDocument46 pages2 Lecture Cardiodr_mohanad100% (1)
- Cardiovascular NotesDocument16 pagesCardiovascular NotesPRAGATI RAINo ratings yet
- Chapter 20-Cardiovascular System The HeartDocument44 pagesChapter 20-Cardiovascular System The HeartleoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lec.6Document5 pagesAnatomy Lec.6aminqasm111No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument26 pagesCardiovascular SystemdumbledoreaaaaNo ratings yet
- Cardio Vascular SystemDocument56 pagesCardio Vascular SystemtazebNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument26 pagesCardiovascular SystemumerjicNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Heart Made Easy Part 1Document22 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Heart Made Easy Part 1adedayodavid860No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: Dr. Mohanad R. AlwanDocument46 pagesCardiovascular System: Dr. Mohanad R. Alwanmohanad11No ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Cardiovascular System 1Document54 pagesLecture 3 Cardiovascular System 1hafiz patah100% (1)
- HeartDocument105 pagesHeartkiranNo ratings yet
- 08 Human Physiology The HeartDocument107 pages08 Human Physiology The HeartsuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 Heart Marie BDocument29 pagesChapter 19 Heart Marie BomarNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi Cardiovaskular and Anestesi: Boby Suryawan, S.Ked Fadilla Octovini, S.KedDocument28 pagesFisiologi Cardiovaskular and Anestesi: Boby Suryawan, S.Ked Fadilla Octovini, S.KedBobby S PromondoNo ratings yet
- 3 CVS HeartDocument49 pages3 CVS HeartSepo CaciousNo ratings yet
- 8.cardiovascular SystemDocument13 pages8.cardiovascular Systempodki gurungNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 GcsDocument14 pagesCHAPTER 3 GcsNurse NotesNo ratings yet
- HeartDocument8 pagesHeartCitra Idtu ChiperNo ratings yet
- 10 - Heart & Great Vessels (FF)Document72 pages10 - Heart & Great Vessels (FF)checkmateNo ratings yet
- Lec 4 HeartDocument42 pagesLec 4 HeartEntesarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 - Introduction To The Cardiovascular System: Away From To BetweenDocument6 pagesChapter 20 - Introduction To The Cardiovascular System: Away From To Betweentomorrow.today.yesterday .yesterdayNo ratings yet
- Pedrajeta-Heart and Neck Vessels AssessmentDocument4 pagesPedrajeta-Heart and Neck Vessels AssessmentAndrei PedrajetaNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument114 pagesThe Circulatory SystemKhant Si ThuNo ratings yet
- Aims and Objectives: To Identify The Cross-Sectional Anatomy of The Following StructuresDocument23 pagesAims and Objectives: To Identify The Cross-Sectional Anatomy of The Following StructuresRoro91No ratings yet
- 5-Structure and Function of The Body Systems 2Document29 pages5-Structure and Function of The Body Systems 2uxdan154No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Cardiovascular System Functions of The HeartDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Cardiovascular System Functions of The HeartPeej ReyesNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument21 pagesCardiovascular System Anatomy and PhysiologyKBD100% (3)
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument34 pagesCardiovascular SystemAyesha SaleemNo ratings yet
- The Equine Cardiovascular SystemDocument5 pagesThe Equine Cardiovascular SystemSavannah Simone PetrachenkoNo ratings yet
- Ch22 HeartDocument65 pagesCh22 HeartC Bala Diwakesh100% (4)
- Human Anatomy,: First Edition Mckinley & O'LoughlinDocument65 pagesHuman Anatomy,: First Edition Mckinley & O'LoughlintommyakasiaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System NotesDocument3 pagesCirculatory System Notesapi-317705375No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System - Heart IntroDocument6 pagesCardiovascular System - Heart IntroKate Angeline TanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology of Heart: BY: Mr. Anurag Lecturer College of Nursing DMC & H, LudhianaDocument56 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of Heart: BY: Mr. Anurag Lecturer College of Nursing DMC & H, Ludhianapreet kaurNo ratings yet
- 5 - Circulation GraysDocument33 pages5 - Circulation GraysdrmanojkulNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Anatomy and Physiology - Study Guide For NursesDocument34 pagesCardiovascular System Anatomy and Physiology - Study Guide For NursesMarie ParksNo ratings yet
- Q32.Heart Development, Anatomy, Topography, Function. Valves and Fibrous Skeleton of The HeartDocument10 pagesQ32.Heart Development, Anatomy, Topography, Function. Valves and Fibrous Skeleton of The HeartMohammed RamzyNo ratings yet
- Circulatory (2) (Autosaved)Document37 pagesCirculatory (2) (Autosaved)Tesfanew SeteNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument20 pagesCardiovascular SystemYna MacatangayNo ratings yet
- HEARTDocument3 pagesHEARTShan ShanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 - The Heart Study Guide: Save Date: Wednesday, March 25, 2009 4:18:00 PMDocument7 pagesChapter 18 - The Heart Study Guide: Save Date: Wednesday, March 25, 2009 4:18:00 PMBettina RosuNo ratings yet
- HeartDocument33 pagesHeartYesh kumarNo ratings yet
- The Stucture of The HeartDocument3 pagesThe Stucture of The Heartkamran imtiazNo ratings yet
- TH e Circulatory System: HeartDocument68 pagesTH e Circulatory System: HeartMica BernardoNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument53 pagesThe Circulatory SystemVera June RañesesNo ratings yet
- Mc1 Reviewer (Cardiovascular System) - MidtermsDocument2 pagesMc1 Reviewer (Cardiovascular System) - MidtermsFrancine Dominique CollantesNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The HeartDocument2 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The HeartPTV SportsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - HeartDocument5 pagesChapter 13 - Heartbussniesm05No ratings yet
- Anatomy of The HeartDocument7 pagesAnatomy of The HeartJanice ScatesNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 CH 4.05 The HeartDocument12 pagesGrade 7 CH 4.05 The HeartMunmun AfnanNo ratings yet
- IC3 Medicine Cardiac - General 2019Document2 pagesIC3 Medicine Cardiac - General 2019nickmirad2No ratings yet
- GI ExamDocument5 pagesGI Examnickmirad2No ratings yet
- 1B Hip ExaminationDocument13 pages1B Hip Examinationnickmirad2No ratings yet
- MCHT Leading and Managing Your Organisation Musculoskeletal Education IC3Document49 pagesMCHT Leading and Managing Your Organisation Musculoskeletal Education IC3nickmirad2No ratings yet
- www.Fullstuff.net.txtDocument1 pagewww.Fullstuff.net.txtnickmirad2No ratings yet
- Benign Bone Tumours Lecture - PpsDocument11 pagesBenign Bone Tumours Lecture - Ppsnickmirad2No ratings yet
- InstructionsDocument1 pageInstructionsnickmirad2No ratings yet
- Genetic Fingerprinting (A2)Document8 pagesGenetic Fingerprinting (A2)nickmirad2No ratings yet
- Clinical RelevanceDocument2 pagesClinical Relevancenickmirad2No ratings yet
- Neuro ExaminationDocument3 pagesNeuro Examinationnickmirad2No ratings yet
- Posterior Compartment of ForearmDocument60 pagesPosterior Compartment of Forearmnickmirad2No ratings yet
- Ns SyllabusDocument2 pagesNs Syllabusnickmirad2No ratings yet
- MMsyllabusDocument1 pageMMsyllabusnickmirad2No ratings yet
- CRRM1.11 Slides 2016-17Document36 pagesCRRM1.11 Slides 2016-17nickmirad2No ratings yet
- M1 - May June 2007 (9709-04)Document4 pagesM1 - May June 2007 (9709-04)nickmirad2No ratings yet
- 9701 s03 QP 6Document8 pages9701 s03 QP 6arghNo ratings yet
- American Spelling British SpellingDocument1 pageAmerican Spelling British Spellingnickmirad2No ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument8 pagesChemistrynickmirad2No ratings yet
- s1 (Set 1) SolutionsDocument5 pagess1 (Set 1) Solutionsnickmirad2No ratings yet
- The 6 Traits of Writing - English Speaking Course Lucknow (CDI)Document14 pagesThe 6 Traits of Writing - English Speaking Course Lucknow (CDI)SelfhelNo ratings yet
- 9701 Chemistry June 2003Document15 pages9701 Chemistry June 2003deeyamullaNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Enzyme (A2)Document11 pagesFactors Affecting Enzyme (A2)nickmirad2No ratings yet
- 5 As Forces PypDocument7 pages5 As Forces Pypnickmirad2No ratings yet
- CHEM SPM Periodic Table BWDocument1 pageCHEM SPM Periodic Table BWangie081250% (2)
- 10.1.10.SHM - Hookes LAW. Spring Practice Problems - KeyDocument3 pages10.1.10.SHM - Hookes LAW. Spring Practice Problems - KeyJose Barrera GaleraNo ratings yet
- 2B C.R.O: 1) (2004 Nov.) 3) (2003 June)Document2 pages2B C.R.O: 1) (2004 Nov.) 3) (2003 June)nickmirad2No ratings yet
- Centroid SDocument2 pagesCentroid Snickmirad2No ratings yet
- Alg QuadraticApps SolutionsDocument6 pagesAlg QuadraticApps Solutionsnickmirad2No ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Circulatory SystemDocument21 pagesLesson 4 - Circulatory Systemapi-307592530No ratings yet
- Concepts of Preload and AfterloadDocument2 pagesConcepts of Preload and AfterloadShar RiveraNo ratings yet
- CardioDocument48 pagesCardiomalisalukmanNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 CirculatoryDocument32 pagesGrade 6 Circulatoryalvarez9654No ratings yet
- L-4ff - 2/BME Date: 17/04/2022: Section-ADocument13 pagesL-4ff - 2/BME Date: 17/04/2022: Section-AHumyra HossainNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Notes Ch18 Body Fluids and CirculationDocument6 pages11 Biology Notes Ch18 Body Fluids and CirculationKambaska Kumar BeheraNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) Topic Quiz Cardiovascular SystemDocument19 pagesMultiple Choice Questions (MCQ) Topic Quiz Cardiovascular SystemMarimuthu ANo ratings yet
- Final - Mrs. X - Case Study (Group 3-RR21)Document45 pagesFinal - Mrs. X - Case Study (Group 3-RR21)Gabriel Andrei C. RelayoNo ratings yet
- Cardiogenic Shock Workup (Medscape)Document8 pagesCardiogenic Shock Workup (Medscape)Tia WasrilNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Physiology, 10th EditionDocument305 pagesCardiovascular Physiology, 10th Editionirina22_aless90% (20)
- VSDDocument4 pagesVSDtikabdullahNo ratings yet
- Pocket Tutor ECG Interpretation PDFDocument165 pagesPocket Tutor ECG Interpretation PDFasri100% (4)
- Six Minute Walk Test A Simple and Useful Test To Evaluate Functional Capacity in Patients With Heart Failure.Document8 pagesSix Minute Walk Test A Simple and Useful Test To Evaluate Functional Capacity in Patients With Heart Failure.Carolina Millan SalfateNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science 1Document6 pagesLesson Plan in Science 1Yenny YenNo ratings yet
- TRANSPOSITION OF THE GREAT VESSELS PrintDocument8 pagesTRANSPOSITION OF THE GREAT VESSELS PrintAnandhu GNo ratings yet
- Mergedsu PDFDocument614 pagesMergedsu PDFbizzarobmNo ratings yet
- Heart Lung InteractionDocument29 pagesHeart Lung InteractionKARDIOLOGI STASE RSALNo ratings yet
- Through The Human HeartDocument14 pagesThrough The Human HeartAsemed AsemedNo ratings yet
- CARDIOVASCULAR ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY TestDocument6 pagesCARDIOVASCULAR ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY TestDevilsnareNo ratings yet
- Pokemon Learning League The HeartDocument26 pagesPokemon Learning League The HeartTimothy WhitfieldNo ratings yet
- Surgical Management of Congenital Heart Disease II: Viktor Hraška Peter MurínDocument312 pagesSurgical Management of Congenital Heart Disease II: Viktor Hraška Peter MurínCardiologia PediatricaNo ratings yet
- Free Online Mock Test For MHT-CET BIOLOGY PDFDocument28 pagesFree Online Mock Test For MHT-CET BIOLOGY PDFBiologyForMHTCET75% (8)
- Ope-101-Human Anatomy-ModuleDocument37 pagesOpe-101-Human Anatomy-ModuleAlbert MartinezNo ratings yet
- Gs PreparationDocument215 pagesGs PreparationSara Abdul Rahman0% (1)
- Clinical Applications of The Venous Excess Ultrasound (Vexus) Score: Conceptual Review and Case SeriesDocument10 pagesClinical Applications of The Venous Excess Ultrasound (Vexus) Score: Conceptual Review and Case SeriesPablo Sanchez MartinezNo ratings yet
- Let's Review CirculatoryDocument38 pagesLet's Review CirculatoryDaivey UgaddanNo ratings yet
- Sistem Kardiovaskular: Cardiac Output Dan Otot JantungDocument46 pagesSistem Kardiovaskular: Cardiac Output Dan Otot JantungSusanna Arie KNo ratings yet
- Subject Enrichment Activity For Term 2Document5 pagesSubject Enrichment Activity For Term 2AADITRYA JAINNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: Circulatory SystemDocument6 pagesStudent Exploration: Circulatory SystemZachariah HernandezNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Output: Prof. K. SivapalanDocument9 pagesCardiac Output: Prof. K. SivapalanjikookNo ratings yet