Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Air Dan Larutan
Uploaded by
SitiNorashimahCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Air Dan Larutan
Uploaded by
SitiNorashimahCopyright:
Available Formats
Air dan larutan
Sifat fizikal air
Cecair tidak berwarna
Tidak berbau
Tidak mempunyai rasa
Takat beku 0C
Takat lebur 0C
Takat didih 100C
Teori kinetik jirim
Teori kinetik jirim menerangkan tentang daya
antara zarah dan pergerakkan zarah di dlm
pergerakan zarah di dlm jirim yang berbeza tidak
sama, bergantung kepada suhu dan daya tarikkan
antara zarah-zarah.
tenaga kinetik meningkat sekiranya suhu
meningkat.
The movement of particles in matter
Solids
Liquids
The particles
are held closely
together by very
strong forces.
The particles are
further apart and
vibrate but not in
fixed positions.
They can only
vibrate from
side to side and
spin around
their.
They move
randomly and the
collision between
these particles
take place
frequently.
Gases
The particle are
widely space and
move randomly in all
directions at high
speed.
Collisions between
gas particles take
place more
frequently than
collision particles of
liquids.
Takat didih: Suhu di mana air berubah menjadi
stim (gas)
Takat beku: Suhu di mana air berubah menjadi ais
Takat lebur: Suhu di mana ais berubah menjadi
air
Perubahan keadaan bagi air
HOW MATTER CAN CHANGE FROM ONE STATE TO ANOTHER
STATE?
SOLID
LIQUID
MATTER CHANGE FROM ONE STATE TO
ANOTHER :
IF HEAT IS ABSORBED
OR RELEASED FROM IT
FREEZING
SUBLIMATION
SOLID
MELTING
SUBLIMATION
EVAPORATION
LIQUID
BOILING
GAS
CONDENSATION
RELEASED ENERGY
ABSORB ENERGY
INTER-CONVERSION OF THE STATE OF MATTER
MELTING= The process solid to liquid upon
heating
BOILING= The process liquid to gas upon
heating
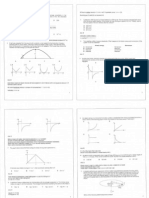
HEATING CURVES
Involves boiling and melting
the process where the energy is absorbed
HEATING CURVE
AB
Temperature increase as heat energy is absorbed
The particles gain kinetic energy and vibrate
vigorously
The substances exist in solid state
BC
Temperature constant
The heat supplied absorbed is use to overcome the
forces of attraction that hold the particles in their
positions.
Melting occur, the structure of solid breaks down
and turn to liquid.
The substances exist in solid and liquid state.
Temperature which solid convert to liquid known as
melting point.
CD
The particles gain more kinetic energy and move
faster as they absorb heat energy.
Temperature increases.
The substances exist in liquid state
COOLING CURVE
TU
Temperature decrease as heat energy is released to
surroundings
The particles lose kinetic energy and move closer
together
The substances exist in liquid state
UV
Temperature constant
As heat supplied released to surroundings is
balanced by the energy liberated to attract the
particles
Freezing occur, liquid turns to solid
The substances exist in solid and liquid state.
Temperature which liquid convert to solid known as
freezing point.
VW
The particles move slower as the lose heat energy
Temperature decrease.
The substances exist in solid state
You might also like
- Latih TubiDocument11 pagesLatih TubiSitiNorashimahNo ratings yet
- Latih TubiDocument8 pagesLatih TubiSitiNorashimahNo ratings yet
- Latih TubiDocument8 pagesLatih TubiSitiNorashimahNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 4Document662 pagesChemistry Form 4SitiNorashimahNo ratings yet
- Summary of Manufacture in Industry, Sulphuric AcidDocument12 pagesSummary of Manufacture in Industry, Sulphuric AcidSitiNorashimahNo ratings yet
- Summary of Manufacture in Industry, Sulphuric AcidDocument12 pagesSummary of Manufacture in Industry, Sulphuric AcidSitiNorashimahNo ratings yet
- Paper 1Document15 pagesPaper 1SitiNorashimahNo ratings yet
- 3.6 Chemical Equation MeaningDocument33 pages3.6 Chemical Equation MeaningSitiNorashimahNo ratings yet
- Ostwald ProcessDocument7 pagesOstwald ProcessSitiNorashimahNo ratings yet
- Paper 1Document15 pagesPaper 1SitiNorashimahNo ratings yet
- 07 JPNT Kim f4 Modul1Document9 pages07 JPNT Kim f4 Modul1Mastura IsmailNo ratings yet
- Rate of Reaction (Kadar Tindak Balas)Document32 pagesRate of Reaction (Kadar Tindak Balas)SitiNorashimahNo ratings yet
- CrackingDocument3 pagesCrackingSitiNorashimahNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Solutions To The 8 Homework: Eece2530 ElectromagneticsDocument12 pagesSolutions To The 8 Homework: Eece2530 ElectromagneticsNutsoBoardNo ratings yet
- Timoshenko Beam ElementDocument11 pagesTimoshenko Beam ElementMahmoud M.S. DwaikatNo ratings yet
- Smoham CVDocument8 pagesSmoham CVOmid Kazemzadeh KhoeeNo ratings yet
- Davydov's SolitonDocument67 pagesDavydov's SolitonJayNo ratings yet
- Phys2 Ch3 Firstlawthermo NewDocument54 pagesPhys2 Ch3 Firstlawthermo NewQuỳnh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Turnitin Originality ReportDocument26 pagesTurnitin Originality Reportrabia.malikNo ratings yet
- Yield Line Analysis Analysis of Slab (Handout)Document5 pagesYield Line Analysis Analysis of Slab (Handout)Gabriel JamesNo ratings yet
- Seismic Force Resisting Systems and Response of Concrete BuildingDocument30 pagesSeismic Force Resisting Systems and Response of Concrete BuildingtaosyeNo ratings yet
- CJC Prelim Paper 1 AnsDocument8 pagesCJC Prelim Paper 1 Ansnewtonian_physicsNo ratings yet
- Sample Chemical Eng QuestionsDocument2 pagesSample Chemical Eng QuestionsEd Ryan RualesNo ratings yet
- Seismic Design of Timber StructuresDocument60 pagesSeismic Design of Timber StructuresSairam Venkat100% (1)
- MR647027EN - 1.0.0 Manitou PG115Document76 pagesMR647027EN - 1.0.0 Manitou PG115Fauan SNo ratings yet
- 3.2 DeformationDocument8 pages3.2 DeformationSalmanNo ratings yet
- UTA016 Engineering Design Project-IDocument6 pagesUTA016 Engineering Design Project-IVishal SinghNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 - Basic Trajectory Planning With MatlabDocument10 pagesLab 3 - Basic Trajectory Planning With MatlabazrarajanNo ratings yet
- Hydrodynamics: Basics: 4.1 General ConceptsDocument6 pagesHydrodynamics: Basics: 4.1 General ConceptsbennyNo ratings yet
- 2004 Asymmetric Buildings ASCE PDFDocument8 pages2004 Asymmetric Buildings ASCE PDFप्रतीक राज पण्डितNo ratings yet
- Solving The Schrödinger Equation Has Everything Been TriedDocument375 pagesSolving The Schrödinger Equation Has Everything Been Triedexfmln100% (3)
- Design of Seismic-Resistant Steel Building Structures: 1. Introduction and Basic PrinciplesDocument107 pagesDesign of Seismic-Resistant Steel Building Structures: 1. Introduction and Basic PrinciplessamNo ratings yet
- Moment Distribution MethodDocument13 pagesMoment Distribution MethodMD. SHUVO RAHMANNo ratings yet
- Mechanical WavesDocument23 pagesMechanical WavesAgus SetyawanNo ratings yet
- 1.6 Surface Tension and Capillarity - CE 309-CE22S2 - Fluid MechanicsDocument4 pages1.6 Surface Tension and Capillarity - CE 309-CE22S2 - Fluid MechanicsRusselNo ratings yet
- Dampers - A Configuration of Seismic Energy Dissipation System For Still StructuresDocument8 pagesDampers - A Configuration of Seismic Energy Dissipation System For Still Structurespepess2010No ratings yet
- 2018 - Hybrid CFD ModelDocument29 pages2018 - Hybrid CFD ModelSateesh kumar SNo ratings yet
- Spacecraft Dynamics Homework 1Document6 pagesSpacecraft Dynamics Homework 1TrevorNo ratings yet
- Modeling of Fillets in Thin-Walled Beams Using Shell/Plate and Beam Finite ElementsDocument16 pagesModeling of Fillets in Thin-Walled Beams Using Shell/Plate and Beam Finite Elementsacar1No ratings yet
- Norton University Department of Civil EngineeringDocument35 pagesNorton University Department of Civil EngineeringmaysheangNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Week 4Document4 pagesPhysical Science Week 4Alona Cello ParagesNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 Gas FulDocument20 pagesLab 3 Gas FulMarouane AdamNo ratings yet
- EXP 9 AC MainsDocument5 pagesEXP 9 AC MainsRude BøyNo ratings yet