Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Differential Feeder Protection Explained
Uploaded by
muaz_aminu1422100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
410 views10 pagesDifferential Feeder Protection overcomes application difficulties of simple overcurrent relays when applied to complex networks i.e. Co-ordination problems and excessive fault clearance times. Can be instantaneous in operation > Biased Differential Protection Merz-Price Differential Or Unit Protection Protected Circuit Or Plant boundaries of protection coverage accurately defined.
Original Description:
Original Title
2 Biased Differential Protection.ppt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDifferential Feeder Protection overcomes application difficulties of simple overcurrent relays when applied to complex networks i.e. Co-ordination problems and excessive fault clearance times. Can be instantaneous in operation > Biased Differential Protection Merz-Price Differential Or Unit Protection Protected Circuit Or Plant boundaries of protection coverage accurately defined.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
410 views10 pagesDifferential Feeder Protection Explained
Uploaded by
muaz_aminu1422Differential Feeder Protection overcomes application difficulties of simple overcurrent relays when applied to complex networks i.e. Co-ordination problems and excessive fault clearance times. Can be instantaneous in operation > Biased Differential Protection Merz-Price Differential Or Unit Protection Protected Circuit Or Plant boundaries of protection coverage accurately defined.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 10
Differential Feeder Protection
Why Needed?
Overcomes application difficulties of simple overcurrent
relays when applied to complex networks i.e. co-ordination
problems and excessive fault clearance times
Basic Principle
Involves measurement of current at each end of feeder
And transmission of information between each end of feeder
Protection should operate for faults inside the protected zone
(i.e. the feeder) but must remain stable for faults outside the
protected zone
Thus can be instantaneous in operation
> Biased Differential Protection
Merz-Price Differential Or Unit Protection
Protected
Circuit Or Plant
Boundaries of protection coverage accurately defined
Protection responds only to faults in protected zone
> Biased Differential Protection
Two Types of Scheme
End A
End B
Relay
Circulating Current System
End A
End B
Relay
Balanced Voltage System
Basic Mertz-Price principle applies well where CT
secondary circuit can be kept short e.g. protection of
transformers, busbars, machines
For feeder protection where boundaries of protection are
a distance apart a communication channel is required
> Biased Differential Protection
Unit Protection Involving Distance Between
Circuit Breakers (1)
A
Relayin
g
Point
R
Trip
B
Trip
A
Simple Local Differential Protection
4
> Biased Differential Protection
Unit Protection Involving Distance Between
Circuit Breakers (2)
A
B
Communication
Channel
Relayin
g
Point
Trip A
Trip B
Unit Protection Involving Distance
Between Circuits
5
Relayin
g
Point
> Biased Differential Protection
Early Merz-Price Balanced Voltage
Systems For Feeders
2 Problems:
1) Mal-operation due to unequal open circuit secondary
voltages of the two transformers for thro fault currents
2) High output voltages of CTs cause capacitance currents
to flow through relay Since capacitive currents are
proportional to pilot length, relay insensitive for all but
very short lines
> Biased Differential Protection
Early Merz-Price Circulating Current
System For Feeders
End Y
End X
a
c
Relay
EY
Relay
EX
b
a
EX
> Biased Differential Protection
Relay
X
Voltage Level
of Relay Pilot
Zero Voltage
Across Centre
of Outer Pilots
Relay
Y
d
EY
c
Voltage Diagram
for External Fault
Non-Biased Relay & Biased Relay
Differential
Current
External
Operate
Fault
Restrain
Through Current
Non-Biased Relay
Operate
Differential
Current
Restrain
Through Current
Biased Relay
8
> Biased Differential Protection
Basic Pilot Wire Schemes with Bias (1)
OP
OP
Circulating Current
> Biased Differential Protection
Basic Pilot Wire Schemes with Bias (2)
OP
OP
Balanced Voltage
10
> Biased Differential Protection
You might also like
- VSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsFrom EverandVSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsNo ratings yet
- 400kv Transmission Lines ProtectionDocument17 pages400kv Transmission Lines ProtectionbillymcrealNo ratings yet
- Protective Relays in Substations: Types and ApplicationsDocument46 pagesProtective Relays in Substations: Types and ApplicationsLee Boon HongNo ratings yet
- 6837X 12bDocument42 pages6837X 12bJorge A. Perez YebraNo ratings yet
- Busbar Differential ProtectionDocument19 pagesBusbar Differential ProtectionVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Transformer Setting Calculation Main-021Document38 pagesTransformer Setting Calculation Main-021Zahidul zahid100% (1)
- Capacitance Voltage Transforme1Document4 pagesCapacitance Voltage Transforme1ayushNo ratings yet
- Types and Applications of Overcurrent RelayDocument10 pagesTypes and Applications of Overcurrent Relayhasbi fadliNo ratings yet
- Differential Protection Explained - Principles, Design & ConsiderationsDocument3 pagesDifferential Protection Explained - Principles, Design & Considerationsjagadeesh_kumar_20No ratings yet
- Transformer Protection MethodsDocument63 pagesTransformer Protection MethodsAscerZayan100% (1)
- Trafo Differential & Distance Prot. RelaysDocument16 pagesTrafo Differential & Distance Prot. RelaysTheresa WestNo ratings yet
- Transformer Protection SchemesDocument5 pagesTransformer Protection SchemesIppiNo ratings yet
- Different Types of RelaysDocument34 pagesDifferent Types of RelayssupriyarakshitNo ratings yet
- 12 - Transformer ProtectionDocument40 pages12 - Transformer ProtectionSarthak Vats100% (2)
- Capediem Tech-Protection REF Relay Working PrincipleDocument4 pagesCapediem Tech-Protection REF Relay Working PrincipleEnpak ArsalanNo ratings yet
- LINEREV ProtectionDocument92 pagesLINEREV Protectionhafiz_hazreen100% (2)
- 1 4 Part 2 Feeder OC EF ProtectionDocument33 pages1 4 Part 2 Feeder OC EF ProtectionEpsp MedNo ratings yet
- MCQs Protection Engineering Booklet 2Document25 pagesMCQs Protection Engineering Booklet 2arsalanhamid100% (4)
- Ee1302 Protection and SwitchgearDocument12 pagesEe1302 Protection and SwitchgearMukesh Kumar0% (1)
- Magnetizing CurrentDocument4 pagesMagnetizing CurrentSureshraja9977No ratings yet
- Distance Relay Principle: Suppose Relay Is Designed To Operate WhenDocument40 pagesDistance Relay Principle: Suppose Relay Is Designed To Operate WhenAnonymous 9VcxlFErfNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line ProtectionDocument38 pagesTransmission Line ProtectionE.AvinashNo ratings yet
- 220kv Busbar Report Mahabub NagarDocument34 pages220kv Busbar Report Mahabub NagarKarthiKeyanNo ratings yet
- Grounding Resistance MeasurementsDocument13 pagesGrounding Resistance MeasurementskishansaiNo ratings yet
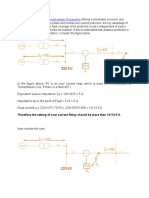
- Non-Unit System of Protection: Therefore The Setting of Over Current Relay Should Be More Than 14113.5 ADocument6 pagesNon-Unit System of Protection: Therefore The Setting of Over Current Relay Should Be More Than 14113.5 AyethweNo ratings yet
- TransformerStabilityTestDocument4 pagesTransformerStabilityTestHosam JabrallahNo ratings yet
- II.2 AS-shate-Jalawiyyah Line Protn Set - 2Document5 pagesII.2 AS-shate-Jalawiyyah Line Protn Set - 2Jay WinNo ratings yet
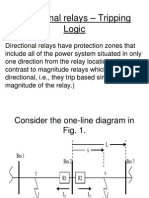
- Directional Relays Tripping Logic Based on Fault Current AngleDocument19 pagesDirectional Relays Tripping Logic Based on Fault Current AnglesahiiiiNo ratings yet
- EE1402 Power System Protection and SwitchgearDocument8 pagesEE1402 Power System Protection and Switchgearmoonsoon_j100% (1)
- Differential Relay SlopeDocument6 pagesDifferential Relay SlopeNADEEM KHANNo ratings yet
- CT Burden, Knee Point Voltage, Core Saturation - Details of Current Transformer CharacteristicsDocument6 pagesCT Burden, Knee Point Voltage, Core Saturation - Details of Current Transformer Characteristicsmarkigldmm918No ratings yet
- Setting The Resistive Reach of Quadrilateral Characteristics o F Distance RelaysDocument5 pagesSetting The Resistive Reach of Quadrilateral Characteristics o F Distance RelaysSalvador ArcosNo ratings yet
- XS2 - Negative Sequence Relay: Original Technical Manual XS2 (Revision B)Document20 pagesXS2 - Negative Sequence Relay: Original Technical Manual XS2 (Revision B)Catrina FedericoNo ratings yet
- TKIS Relay Setting NewDocument34 pagesTKIS Relay Setting NewsalmanNo ratings yet
- Restricted Earth Fault Protection of Transformer - REF ProtectionDocument4 pagesRestricted Earth Fault Protection of Transformer - REF Protectionpoornak47No ratings yet
- Power System Protection (Distance) RelaysDocument6 pagesPower System Protection (Distance) RelaysAisamuddin SubaniNo ratings yet
- P10Document16 pagesP10Lynskey1973100% (1)
- Unbalance Protection of Fuseless, Split-Wye, Grounded, Shunt Capacitor BanksDocument4 pagesUnbalance Protection of Fuseless, Split-Wye, Grounded, Shunt Capacitor BanksgustavopaloNo ratings yet
- Exercise - Setting An SEL-751A To Replace An Existing Electromechanical RelayDocument8 pagesExercise - Setting An SEL-751A To Replace An Existing Electromechanical RelayDavidNo ratings yet
- Testing Directional Overcurrent ProtectionDocument2 pagesTesting Directional Overcurrent ProtectionZokiNo ratings yet
- Directional OverDocument28 pagesDirectional OverEdinson Milton Gaona BarbozaNo ratings yet
- Circuit Breaker Technical SpecificationsDocument24 pagesCircuit Breaker Technical SpecificationssanjayNo ratings yet
- Lec-3 Effect of Fault Resistance and Pre-Fault Power Flow On The Performance of Distance RelayDocument5 pagesLec-3 Effect of Fault Resistance and Pre-Fault Power Flow On The Performance of Distance RelayTamjidNo ratings yet
- Polarised Mho RelayDocument11 pagesPolarised Mho RelayPavan Gowda100% (2)
- Emtp PDFDocument34 pagesEmtp PDFagkacdm1163100% (1)
- Differential Protection Principles Applications Internal Faults DifficultiesDocument19 pagesDifferential Protection Principles Applications Internal Faults DifficultiesvthiyagainNo ratings yet
- Transformer REFDocument4 pagesTransformer REFs_banerjeeNo ratings yet
- Connections and applications of overcurrent and earth fault relaysDocument4 pagesConnections and applications of overcurrent and earth fault relaysMahmoud AlshairNo ratings yet
- Standby & Restricted Earth FaultDocument7 pagesStandby & Restricted Earth FaultanjnaNo ratings yet
- Protection Settings For 66kV Line - Rev00 - STERLINGDocument11 pagesProtection Settings For 66kV Line - Rev00 - STERLINGsgshekar30100% (1)
- Easun Reyrolle: Figure 11. Star Connected Bank, Two Limbs Per PhaseDocument20 pagesEasun Reyrolle: Figure 11. Star Connected Bank, Two Limbs Per PhaseE.AvinashNo ratings yet
- OLTC FailureDocument18 pagesOLTC FailurevtpsNo ratings yet
- IEC61850 Based Process Bus Protection SolutionDocument12 pagesIEC61850 Based Process Bus Protection Solutionraghavendran raghuNo ratings yet
- Protection Basic (Traditional) - IDAHO PowerDocument93 pagesProtection Basic (Traditional) - IDAHO PowerLiang CheNo ratings yet
- İnstruction To System ProtectionDocument91 pagesİnstruction To System ProtectionSuat KaracanNo ratings yet
- Basic Protection and Relaying SchemesDocument58 pagesBasic Protection and Relaying SchemesBattinapati Shiva100% (1)
- Relay Protection of Distribution Networks Eugeniusz Rosołowski Protection and Control of Distributed Energy ResourcesDocument88 pagesRelay Protection of Distribution Networks Eugeniusz Rosołowski Protection and Control of Distributed Energy Resourcesahvaz1392bNo ratings yet
- Report On Radial Feeder ProtectionDocument20 pagesReport On Radial Feeder ProtectionSubhamGangdeb78% (9)
- Lecture 7 Relay CoordinationDocument30 pagesLecture 7 Relay Coordinationmuaz_aminu1422No ratings yet
- Level 3 Power System Protection Qualification Summary: Units Ref. No. Unit Tittle Remarks CLHDocument31 pagesLevel 3 Power System Protection Qualification Summary: Units Ref. No. Unit Tittle Remarks CLHmuaz_aminu1422No ratings yet
- Lecture 1. INTRODUCTION TO BASIC PROTECTION AND RELAYING SCHEMES PDFDocument57 pagesLecture 1. INTRODUCTION TO BASIC PROTECTION AND RELAYING SCHEMES PDFData-Aja TCNNo ratings yet
- Short Circuit2011-2Document65 pagesShort Circuit2011-2muaz_aminu1422No ratings yet
- Control Circuit FundamentalsDocument11 pagesControl Circuit Fundamentalsmuaz_aminu1422No ratings yet
- UNIT 11 Condition Monitoring On Hydro TurbineDocument4 pagesUNIT 11 Condition Monitoring On Hydro Turbinemuaz_aminu1422100% (1)
- Lecture 9 BASIC-LINE-PROTECTIONDocument46 pagesLecture 9 BASIC-LINE-PROTECTIONmuaz_aminu1422No ratings yet
- Distribution Transformer TestingDocument52 pagesDistribution Transformer TestingVIKRAM DESAI100% (1)
- Lecture 18 System StabilityDocument33 pagesLecture 18 System StabilityTEMIDAYONo ratings yet
- UNIT 4 Maintenance of Stuffing Box For Hydro TurbineIILDocument4 pagesUNIT 4 Maintenance of Stuffing Box For Hydro TurbineIILmuaz_aminu1422No ratings yet
- Lecture 4a. Instrument TransformerDocument85 pagesLecture 4a. Instrument Transformermuaz_aminu1422No ratings yet
- Control Circuits and Device NumbersDocument27 pagesControl Circuits and Device Numbersmuaz_aminu1422No ratings yet
- Egyptian Electricity Transmission Co. Network Training Center Substation Training DepartmentDocument30 pagesEgyptian Electricity Transmission Co. Network Training Center Substation Training DepartmentsherifmoussaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3.2 Control Circuits With Single Line DiagramDocument42 pagesLecture 3.2 Control Circuits With Single Line Diagrammuaz_aminu1422No ratings yet
- UNIT 1 Routine Maintenance Check On Gas TurbineIIIDocument3 pagesUNIT 1 Routine Maintenance Check On Gas TurbineIIImuaz_aminu1422No ratings yet
- Nos Classification Level 1Document22 pagesNos Classification Level 1muaz_aminu1422No ratings yet
- Haniftransfofrmer Protection 2015 PDFDocument113 pagesHaniftransfofrmer Protection 2015 PDFmuaz_aminu1422No ratings yet
- Nos Classification Level2Document25 pagesNos Classification Level2muaz_aminu1422No ratings yet
- Basic Power Protection Relaying Manual PDFDocument407 pagesBasic Power Protection Relaying Manual PDFmuaz_aminu1422No ratings yet
- DIFFERENTIAL PROTECTION APPLICATIONSDocument33 pagesDIFFERENTIAL PROTECTION APPLICATIONSmuaz_aminu1422No ratings yet
- Philosophy On Transformer ProtectionDocument30 pagesPhilosophy On Transformer Protectiongeddam06108825No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Distance Protection and Transmission LinesDocument111 pagesFundamentals of Distance Protection and Transmission Linesmuaz_aminu1422100% (1)
- Instrument Transformers: Reducing Voltages & CurrentsDocument95 pagesInstrument Transformers: Reducing Voltages & Currentsmuaz_aminu1422No ratings yet
- Power System Grounding MethodsDocument43 pagesPower System Grounding Methodsmuaz_aminu1422No ratings yet
- Protective Relay Testing and CommissioningDocument59 pagesProtective Relay Testing and Commissioningmuaz_aminu1422No ratings yet
- CT VT Basics SonnenbergDocument71 pagesCT VT Basics SonnenbergAnonymous OCDJg17Z67% (3)
- Electrical Fuse Types and CharacteristicsDocument26 pagesElectrical Fuse Types and Characteristicsmuaz_aminu142280% (5)
- Relay Trip CircuitDocument32 pagesRelay Trip Circuitmuaz_aminu142250% (2)
- Transformer Protection 20Document121 pagesTransformer Protection 20muaz_aminu142283% (6)
- Protective Relay Testing and CommissioningDocument59 pagesProtective Relay Testing and Commissioningmuaz_aminu1422No ratings yet
- Intro To FmdtoolsDocument38 pagesIntro To FmdtoolsSmurf Account1No ratings yet
- Python Library ReferenceDocument92 pagesPython Library ReferenceaawaakNo ratings yet
- Maintenance of Electrical Equipment For FM Personnel: E-LearningDocument1 pageMaintenance of Electrical Equipment For FM Personnel: E-LearningNigel AngNo ratings yet
- Cover Letter DellDocument2 pagesCover Letter DellRavi SharmaNo ratings yet
- SEM Workshop Presentation 3Document28 pagesSEM Workshop Presentation 3felixkern1991No ratings yet
- EN 15232 - BMS For Eficiency of HVAC Buildings PDFDocument87 pagesEN 15232 - BMS For Eficiency of HVAC Buildings PDFStroe George100% (1)
- SD Exit Exm Tuto SoLDocument55 pagesSD Exit Exm Tuto SoLTadesse MegersaNo ratings yet
- Model Railway Turnout Control Circuit Uses Triacs and Logic Level InputDocument1 pageModel Railway Turnout Control Circuit Uses Triacs and Logic Level InputSantiago DiosdadoNo ratings yet
- 2019 Book DataScienceAndBigDataAnalyticsDocument418 pages2019 Book DataScienceAndBigDataAnalyticsfrmalthus100% (6)
- 0152 - Interational Confrence On 1200kV National Test StationDocument346 pages0152 - Interational Confrence On 1200kV National Test StationsreejitvpNo ratings yet
- REVO-II & REVO-E ComparisionDocument3 pagesREVO-II & REVO-E ComparisionPaul Abi najemNo ratings yet
- Software Engineering Unit 3Document103 pagesSoftware Engineering Unit 3navaneethNo ratings yet
- CareerPath SupplyChainDocument27 pagesCareerPath SupplyChainShobhit PareekNo ratings yet
- Design of Engine Cylinder Block : M NareshDocument4 pagesDesign of Engine Cylinder Block : M NareshMudavath NareshNo ratings yet
- Bugs Fixed in Each 19.0.0.0.0 Grid Infrastructure Release UpdateDocument56 pagesBugs Fixed in Each 19.0.0.0.0 Grid Infrastructure Release UpdateAuttapol TunwilaiNo ratings yet
- The Unified Kill ChainDocument19 pagesThe Unified Kill ChainManuNo ratings yet
- Calculate volume and number of tilesDocument8 pagesCalculate volume and number of tilesRichard Antoni GosnoNo ratings yet
- Ciena DTM-100G2 - DS PDFDocument2 pagesCiena DTM-100G2 - DS PDFrobert adamsNo ratings yet
- Payback2 CHEATus - LuaDocument41 pagesPayback2 CHEATus - LuaDoanh ĐặngNo ratings yet
- Cigré2016 Experiencesandinnovationsinpowertransformershort Circuitcurrentwithstandtesting A2 304Document11 pagesCigré2016 Experiencesandinnovationsinpowertransformershort Circuitcurrentwithstandtesting A2 304cisnatelNo ratings yet
- Alarms and Error Codes 88 SeriesDocument40 pagesAlarms and Error Codes 88 SeriesOzgyur MehmedovNo ratings yet
- Gill - Stealth Racer - W017 - Instruction Manual - enDocument27 pagesGill - Stealth Racer - W017 - Instruction Manual - enalmoghaddamNo ratings yet
- Ti Sns50-Hba0-S01 1034097Document8 pagesTi Sns50-Hba0-S01 1034097zaleksNo ratings yet
- Happy Plugs Air 1 ManualDocument1 pageHappy Plugs Air 1 ManualHalley JiménezNo ratings yet
- Yealink W52P V73 - 27 User GuideDocument98 pagesYealink W52P V73 - 27 User GuideAleksey MarmiloNo ratings yet
- Telefone IP 8002 - 80012Document3 pagesTelefone IP 8002 - 80012Ronaldo JoseNo ratings yet
- Structure Charts: Agenda: - Use of Structure Charts - Symbols - How To CreateDocument12 pagesStructure Charts: Agenda: - Use of Structure Charts - Symbols - How To CreateSujata RoyNo ratings yet
- Build a better internet together with Cloudflare partnersDocument19 pagesBuild a better internet together with Cloudflare partnersVicky MahiNo ratings yet
- Petrel ShaleDocument4 pagesPetrel ShaleAnderson Portilla BenavidesNo ratings yet
- Panasonic Ptae700 Service ManualDocument215 pagesPanasonic Ptae700 Service ManualTarra Ramakrishna RaoNo ratings yet