Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Eclampsia 2362
Uploaded by
Edgar Gonzalez RomeroCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Eclampsia 2362
Uploaded by
Edgar Gonzalez RomeroCopyright:
Available Formats
www.doctor.
sd
www.doctor.sd
Pre- eclampsia
Impending
Eclampsia
It is a disease of pregnancy characterized
by
BP 140/ 90 or more.
After 20 week gestational age.
In previous normotensive pt.
Reading taken twice at interval 6 hours.
Exclude other causes of 2.ry hypertension
(ACDEPR)
www.doctor.sd
A
C
D
E
P
R
alcho
lcoarctation of
aorta
drugs
Endocrine
disease
PIH
renal disease
www.doctor.sd
But diagnosis can be
by:
DBP110 or more
Increase in SBP by 30 mmHg
Increase in DBP by 15mmHg
2 read of MABP 105 or more OR increase by 20
This condition is associated with significant
protienuria
www.doctor.sd
Aetiology:
???
Not related to the fetus or uterus
Failure of placentation
Abnormal lipid metabolism
Decrease Ca++ in diet
All pathogenesis due to vasospasm & endothelial
dysfunction
www.doctor.sd
Risk facctors:
Primigravida
age
Past history
Change the
husband
Condition in which
placenta enlarge
Pre-existing
disease
Low socioeconomic
Risk factor
decrease :
Smokers
Prolong exposure to
paternal antigen
www.doctor.sd
SYSTEMIC EFFECTS
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
CVS
Blood
Renal system
Liver
CNS
www.doctor.sd
INCIDENCE & EPIDEMIOLOGY
Occur in 5-10% pregnancy
Death about 2% in UK
Death increase in Eclampsia which
occur in intrapartum &post partum
due to:
-Relax of observation during these period
-Increase in release of pathogenic factor
www.doctor.sd
PRE-ECLAMPSIA
Symptoms: may be
Asymptomatic
Headache
Visual disturbance
Epigastric pain
oedema
Sign: may be
High BP
Fluid retension
Brisk reflexs
Fundel level less
than date
www.doctor.sd
Symptoms:
Headache
Visual disturbance
Epigastric pain
Nausea
Restlessness
Swelling
Poor urine output
signs:
Agitation
Hyperreflexia
Facial &peripheral
oedema
Rt upper quadrant
tendernes
www.doctor.sd
Eclampsia
www.doctor.sd
CLINICAL FEATURE
it is grand mal convulsion which pass
through stages of:
1. Tonic contraction
2. Clonic
3. Coma
Usually take about 60-90 seconds.
www.doctor.sd
EDENS CRITERIA OF SEVERITY
Coma take 6 hours or more
SBP reach 200 mmHg
Tm 39 or more
Pulse rate 120/min
RR 40/min
2 fits or more
All this can end in maternal brain
death
www.doctor.sd
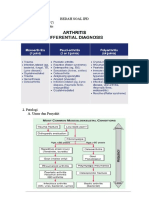
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
1.
2.
3.
4.
Epilepsy
CVA
SOL
Drugs reaction
www.doctor.sd
MANAGMENTS
Aim of it :
1-maintain patent airways
2-prevents the fits
3-terminate the pregnancy
www.doctor.sd
1.
2.
3.
Usually unnecessary to try to stop the
initial convulsion which usually last
about 60-90 seconds
IV Diazepam slowly 5mg over 1 min
3. Roll the patient on his left side to
avoid maternal injury
www.doctor.sd
4. Apply Suction to the secretion from her mouth
5. Adequate Oxygen should be maintained by face
mask & airways to prevent swallowing of tongue
6. Prevent further convulsions by MgSO4 by IV
bolus of 4 6 g over 15 min. If convulsion recur
further bolus of 2g.
7. Acidosis should be corrected if necessary by IV
NaHCO3
8. SBP 170 mmHg or more, DBP 110 mmHg is risk
factor for CVA so should be lowered by either
Nifedipine 10 20 mg SL. Or Hydrallazine 5mg
followed by infusion.
www.doctor.sd
1.Insert canula size 10
2.Send blood to Lab for Hb, blood
group, Platelet count, RFT, LFT, Uric
acid concentration, coagulation
study, RBS
3.Urine catheter (to urine output &
protein)
www.doctor.sd
1.Assessment of state of fetus (U/S,
Doppler CTG)
2.either : - Deliver the baby regardless
of the gestational age
intense monitoring maternal health in
hope of improvement fetal
outcome by increase gestational
age.
www.doctor.sd
It is attention to fluid balance , BP , Renal
& Hepatic function & CNS
1.More aggressive control of BP
2.MgSO4 maintained for 48 hrs at 1g/hr iv
3.Subcutaneous heparin prophylaxis
www.doctor.sd
1.During the fit
tounge bitting
head trauma
bone #
Aspiration
2.permanent CNS damage
3.Intracranial haemorrhage
4.Renal failure
5.Death
www.doctor.sd
1.Prematurity
2.placenta infarction
3.IUGR
4.Abruptio placentae
5.Fetal hypoxia
www.doctor.sd
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- 8C Microbes and DiseaseDocument31 pages8C Microbes and DiseaseyididiyayibNo ratings yet
- Health & Safety Policy QEB Standards 13Document2 pagesHealth & Safety Policy QEB Standards 13QBE European Operations Risk ManagementNo ratings yet
- Care Plan for Intranatal CareDocument11 pagesCare Plan for Intranatal CareBhumi ChouhanNo ratings yet
- CerebrolysinDocument3 pagesCerebrolysinMelissa Fatima Laurente Dosdos100% (2)
- Shock TraumaDocument37 pagesShock TraumaMaica LectanaNo ratings yet
- Causes of Mortality and MorbidityDocument8 pagesCauses of Mortality and MorbiditypurletpunkNo ratings yet
- Chemical Handling and ManagementDocument22 pagesChemical Handling and Managementrizwan chNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care For Patients With Endocrine DisordersDocument4 pagesNursing Care For Patients With Endocrine DisordersMark Russel Sean LealNo ratings yet
- Bio Research ProjectDocument12 pagesBio Research Projectapi-428108720No ratings yet
- FNCP List of 1st Level AssessmentDocument6 pagesFNCP List of 1st Level AssessmentReignallienn Inocencio MartinNo ratings yet
- 10 WinterDocument48 pages10 WintercontinentdriftNo ratings yet
- 2013 Sample Psychology Cover LettersDocument2 pages2013 Sample Psychology Cover LettersLavander Meggie100% (1)
- Philips issues urgent field safety notice for ventilator touchscreensDocument3 pagesPhilips issues urgent field safety notice for ventilator touchscreensChris SilerNo ratings yet
- Karya Ilmiah Akhir NersDocument27 pagesKarya Ilmiah Akhir NersSyaputri ChairulNo ratings yet
- Epididymo OrchitisDocument20 pagesEpididymo OrchitisDurai Raj Kumar100% (2)
- When A Child Dies LeafletDocument2 pagesWhen A Child Dies LeafletCruseBexleyNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Free Standing FP Clinic DOHDocument15 pagesGuidelines For Free Standing FP Clinic DOHAnthony Napalit TaneoNo ratings yet
- Ihme ResumeDocument1 pageIhme Resumeapi-339690559No ratings yet
- Task+3+ +threadwormsDocument2 pagesTask+3+ +threadwormsVin MenesesNo ratings yet
- "Extreme" Cosmetic Surgery: A Retrospective Study of Morbidity in Patients Undergoing Combined ProceduresDocument5 pages"Extreme" Cosmetic Surgery: A Retrospective Study of Morbidity in Patients Undergoing Combined ProceduresDakirdaNo ratings yet
- Talkshow #5Document11 pagesTalkshow #540Thiên TrangB2No ratings yet
- Managing The Health Insurance PortfolioDocument3 pagesManaging The Health Insurance PortfolioShantanuNo ratings yet
- 2014 Windsor University Commencement Ceremony PROOFDocument28 pages2014 Windsor University Commencement Ceremony PROOFKeidren LewiNo ratings yet
- Filipino BrillianceDocument6 pagesFilipino BrillianceEnerio EbisaNo ratings yet
- Sepsis Fact SheetDocument4 pagesSepsis Fact SheetJoana MoreiraNo ratings yet
- Product and Company Identification: Safety Data SheetDocument6 pagesProduct and Company Identification: Safety Data SheetSarlocoNo ratings yet
- Bedah Soal IpdDocument5 pagesBedah Soal Ipddfghjk lkjhgNo ratings yet
- Colorado Family Resilience Theory Focuses on RegulationDocument23 pagesColorado Family Resilience Theory Focuses on Regulationvbdfg5No ratings yet
- Nursing Student Cover LetterDocument8 pagesNursing Student Cover Letterafmrpaxgfqdkor100% (1)
- Aorn Laser SafetyDocument16 pagesAorn Laser SafetyAmanda RapaNo ratings yet