Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Deep Excavation
Uploaded by
bandhuarushiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Deep Excavation
Uploaded by
bandhuarushiCopyright:
Available Formats
DEEP EXCAVATIONS
NAME- ARUSHI BANDHU
ROLL NO. 5
THIRD YEAR A
TYPES OF DEEP EXCAVATION
TERMINOLOGY
EXCAVATION means to loosen and .take out materials leaving space
above or below ground. It is the process of moving earth, rock or other
materials with tools, equipment or explosives. It includes earthwork,
trenching, wall shafts, tunneling and underground.
METHODS
SLOPE EXCAVATION
PILE WALLS (CONTIGUOUS AND SECANT)
DIAPHRAGM WALL
TOP-DOWN CONSTRUCTION
BOTTOM-UP CONSTRUCTION
CUT AND COVER TECHNIQUE
TRENCH - An excavation that is longer than wide. In general, the
depth is greater than the width but the width measured at the bottom
of the trench is not greater than 15 feet.
CAVE-IN -The separation of a mass of soil or rock from the face
of an excavation into an excavation
SLOPING- A method of inclining the face of an excavation to
minimize the risk of a cave-in. The maximum allowable slope varies
with soil type, environment, and work done at the excavation site
BENCHING - A method of sloping the sides of an excavation by
forming a series of steps.
PROTECTIVE SYSTEM - Method of protecting employees from
cave-ins, from material that could fall or roll from an excavation face
or into an excavation, and from the collapse of adjacent structures.
Protective systems include support systems, sloping and benching
systems, shield systems, and other systems that provide the necessary
protection.
NEED OF DEEP EXCAVATION o Deep excavation has become more a necessity of better
utilization of space as the population of the world
increased.
SLOPING AND BENCHING
o Heavy traffic and lack of adequate space has compelled
Civil engineers to excavate deeper into the ground to
create additional floor space to meet increasing space
requirements for amenities, parking and for housing of
building utilities.
NAME- ARUSHI BANDHU
ROLL NO. 5
PILE
WALLS
( CONTIGUOUS
AND SECANT)
In-situ pile retaining walls are very popular due to their availability and
practicability. There are two types of pile walls :-
CONTIGUOUS PILE WALL
SECANT PILE WALL
In contiguous (intermittent) bored pile
construction, spacing between the piles is
greater than the diameter of piles.
DIFFERENCE B/W CONTIGUOUS
AND SECANT PILE WALLS
Spacing is decided based on type of soil
and level of design moments but it should
not be too large, otherwise pieces of
lumps etc. drop and extra precautions are
needed.
It is designed in such a way that it resists the
lateral earth pressure of retained soil.
Width of gap between piles varies between
50 and 500mm according to ground
conditions.
Typical depth of excavation supported by this
system is 5 to 10m without tie back anchors.
The soil between two piles is stabilized by shotcreting.
TYPICAL DEPTH OF EXCAVATION SUPPORTED BY THIS
SYSTEM IS 5-10M WITHOUT TIE BACK ANCHORS.
Secant bored pile walls are formed by
keeping spacing of piles less than
diameter.
D
S<D
In this technique
primary piles (PCC)
are installed first
with secondary piles
(RCC) constructed in
b/w primary piles
when it gained some
strength as shown.
NAME- ARUSHI BANDHU
ROLL NO. 5
DIAPHRAGM WALL
A diaphragm wall is constructed using a narrow trench excavated
in ground and supported by an engineered fluid (typically a
bentonite mud) until the mud is replaced by the permanent
material.
Generally diaphragm walls are made from reinforced concrete,
though unreinforced walls can also be used.
Walls generally range in thickness from 500mm to 1500mm and
can be excavated to depths of 50m or more.
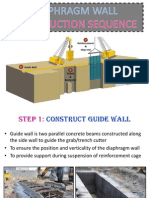
CONSTRUCTION SEQUENCE
CLAMSHELL USE TO
EXCAVATE THE TRENCH
TO FORM A DIAPHRAGM
WALL PANEL
BENTONITE SLURRY TO
PROTECT THE TRENCH
FROM COLLAPSE
These reinforced concrete diaphragm (continuous) walls
are also called slurry trench walls due to the reference
given to the construction technique where excavation of
wall is made possible by filling and keeping the wall
cavity full with bentonite water mixture during
excavation to prevent collapse of the excavated vertical
surfaces.
PLACING OR FIXING CAGE FOR
REINFORCEMENT
NAME- ARUSHI BANDHU
ROLL NO. 5
TOP DOWN CONSTRUCTION
METHOD
Top Down Construction are commonly used in congested areas. These can be
installed in close proximity to existing structure with minimal loss of support to
existing foundations.
Top Down Construction are practically suited in the construction of deep basements ,
Metro Railway Projects.
The Top Down method of construction is designated to enable above ground
construction work to be carried out simultaneously with the excavation of the
basement resulting in significant saving of time on a project.
ADVANTAGES
Use of diaphragm wall as the side
support for the earth
Construction progress upwards and
downwards at the same time.
Savings in construction time
Schematics and pictures give ideas on
ongoing activities during construction
DISADVANTAGES
WHY IS IT
REQUIRED?
Distance between Boundary wall of Adjacent Existing Building and Building Line
for New Building is too close and the depth of excavation is more than 6 meter and
possibility of collapse the soil is higher during excavation.
Using Top Down Construction more Building and Basement Area can use. Suitable
for two or more basement.
The first base slab level slab will act in such area as a strut member and the
Retaining wall panels will not allow collapse of soil.
Water table is too high and difficult to cast Retaining wall, Diaphragm wall or
Continuous Pile can use as a Retaining wall.
Higher cost (due to the construction of pile
foundation)
Since the construction period of the basement
is lengthened, the lateral displacement of
retaining wall or ground settlement may
possible increase due to the influence of creep
if the soil layers are encountered.
It requires highly skilled supervision and
labour force
NAME- ARUSHI BANDHU
ROLL NO. 5
BOTTOM
UP
CONSTRUCTION
Excavation & Soil Stabilization
Construction of Base slab, Concourse
slab & Roof slab.
Construction of Columns and
Retaining wall.
Waterproofing of structure
Filling Operations
The construction of retaining wall,
followed by open cut excavation to certain
Installation of the strutting system to
support the basement walls during
excavation and
Ground is excavated to bottom level of
foundation.
THE CUT AND COVER CONSTRUCTION
PROCESS
The cut and cover method consists of excavating an open cut by
applying, practically, technical means identical to the traditional
excavation process and by constructing a single or twin tunnel lining
under ordinary building engineering conditions.
Once the cast-in-place concrete structure finished and particular
waterproofing and drainage measures taken, fill operations are carried
out, usually, up to the initial ground level.
Caution at the compaction process during the construction of the first
inferior soil layers is necessary, since heavy vibrating rollers risk
provoking distress to the tunnel structure.
Utilities and local transportation network are subsequently restored and
multiple environmental rehabilitation actions are performed
NAME- ARUSHI BANDHU
ROLL NO. 5
You might also like
- SSNDocument1,377 pagesSSNBrymo Suarez100% (9)
- Gas Chromatography - COLIN F. POOLE 2012 PDFDocument743 pagesGas Chromatography - COLIN F. POOLE 2012 PDFVo Manh Tien100% (1)
- Diaphragm Wall Construction SequenceDocument10 pagesDiaphragm Wall Construction Sequencedanzy89100% (2)
- Top Down Construction PresentationDocument11 pagesTop Down Construction PresentationGagan GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Socket H PileDocument9 pagesSocket H PilejoeliNo ratings yet
- Method Statement FOR Construction of Diaphragm Walls (With BAUER BC Trench Cutter System)Document24 pagesMethod Statement FOR Construction of Diaphragm Walls (With BAUER BC Trench Cutter System)sagar badheNo ratings yet
- Micro TunnelingDocument18 pagesMicro Tunnelingronison78No ratings yet
- Main Presentation Ground Anchors and Anchor SystemsDocument31 pagesMain Presentation Ground Anchors and Anchor SystemsMirza Waqar BaigNo ratings yet
- Toa Ngma FinalDocument7 pagesToa Ngma FinalbandhuarushiNo ratings yet
- BWT Septron Line 31-61 Rev01!08!05-18 Opm enDocument56 pagesBWT Septron Line 31-61 Rev01!08!05-18 Opm enDavide Grioni100% (1)
- Deep ExcavationsDocument29 pagesDeep ExcavationsBatu GajahNo ratings yet
- Retaining WallDocument20 pagesRetaining WallCharlesNo ratings yet
- FOUNDATION DESIGN & CONSTRUCTION IN HONG KONG - PRESENT & BEYOND, Daman Lee HK-Taiwan 2005Document28 pagesFOUNDATION DESIGN & CONSTRUCTION IN HONG KONG - PRESENT & BEYOND, Daman Lee HK-Taiwan 2005M Mushanif MuktiNo ratings yet
- Deep ExcavationDocument34 pagesDeep ExcavationsafrasacmNo ratings yet
- Soil NailingDocument21 pagesSoil NailingRizwana RpNo ratings yet
- Ground Improvement TechniquesDocument20 pagesGround Improvement TechniquesRajesh Prasad ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Design and Construction For Deep ExcavationDocument69 pagesDesign and Construction For Deep ExcavationSiPp.T0% (1)
- Plant & Guide Wall ConstructionDocument10 pagesPlant & Guide Wall ConstructionAnonymous S7Cq7ZDgPNo ratings yet
- Deep Excavation and Earth RetentionDocument71 pagesDeep Excavation and Earth RetentionESAM ALHASHEDINo ratings yet
- The New Bugis Station and Associated Tunnels For The Singapore MRTDocument8 pagesThe New Bugis Station and Associated Tunnels For The Singapore MRThutuguoNo ratings yet
- Deep Excavation ProcedureDocument26 pagesDeep Excavation ProcedureHuzaifa ZafarNo ratings yet
- Grouting Methods and Applications in Tunnel ConstructionDocument11 pagesGrouting Methods and Applications in Tunnel Constructionpurple agmjNo ratings yet
- Pipe Jacking in HKDocument6 pagesPipe Jacking in HKRead Do WanNo ratings yet
- Wellpoint DewateringDocument3 pagesWellpoint DewateringlearnafrenNo ratings yet
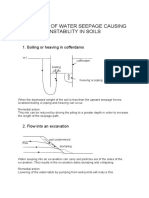
- Boiling or Heaving in CofferdamsDocument2 pagesBoiling or Heaving in Cofferdamsslawek780303No ratings yet
- GEOTECHNIC 2 - Site InvestigationDocument14 pagesGEOTECHNIC 2 - Site InvestigationMohd Farhan Syazwan100% (1)
- Penta-Ocean-Kier JV diaphragm wall constructionDocument9 pagesPenta-Ocean-Kier JV diaphragm wall constructionGary LoNo ratings yet
- Two Case Histories of Basement Excavation With Influence On Groundwater-Kl - 02Document19 pagesTwo Case Histories of Basement Excavation With Influence On Groundwater-Kl - 02Hoo Yen How100% (1)
- Top Down Construction Presentation.Document13 pagesTop Down Construction Presentation.Gagan Goswami100% (1)
- Eurocode in Geotechnical Engineering: Ground Investigation & Deep Foundation DesignDocument76 pagesEurocode in Geotechnical Engineering: Ground Investigation & Deep Foundation DesignLordM00nNo ratings yet
- Soil Nailing and Rock Anchors ExplainedDocument21 pagesSoil Nailing and Rock Anchors ExplainedMark Anthony Agnes AmoresNo ratings yet
- Req 4 Diaphragm WallsDocument72 pagesReq 4 Diaphragm WallsMohamed ElfawalNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Excavations and Excavation SupportsDocument15 pagesLesson 5 Excavations and Excavation SupportsRsjBugtong100% (1)
- Method Statement Installation of Sheet PileDocument9 pagesMethod Statement Installation of Sheet PileRonnie Jungco SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Secant Pile Wall Design For Deep ExcavationsDocument1 pageSecant Pile Wall Design For Deep ExcavationsHorace Prophetic DavisNo ratings yet
- Prediction of Ground Subsidence Associated With Construction of Greater Cairo Metro - Line 3Document21 pagesPrediction of Ground Subsidence Associated With Construction of Greater Cairo Metro - Line 3Sayed ElarabyNo ratings yet
- A Parametric Study of Wall Deflections in Deep Excavations With The Installation of Cross Walls PDFDocument11 pagesA Parametric Study of Wall Deflections in Deep Excavations With The Installation of Cross Walls PDFAhmed ArafaNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For Execution of Jet Grout Columns Works - 2nd CommentDocument3 pagesMethod Statement For Execution of Jet Grout Columns Works - 2nd Commenthessian123100% (1)
- Bored PilingDocument3 pagesBored PilingAdonis AlabiNo ratings yet
- 10th Anniversary Geotechnical Seminar - Common Services Tunnel DesignDocument2 pages10th Anniversary Geotechnical Seminar - Common Services Tunnel DesignKheng BoonNo ratings yet
- Deep FoundationDocument10 pagesDeep Foundationvinod_commentNo ratings yet
- Dewatring Method StatementDocument8 pagesDewatring Method Statementreachpunnya5538No ratings yet
- Method of Statement CPDocument23 pagesMethod of Statement CPRaiza Ishak100% (1)
- Bored PileDocument9 pagesBored PileMichael RootNo ratings yet
- Soil Investigation Report for Aljunied Road / Geylang East CentralDocument71 pagesSoil Investigation Report for Aljunied Road / Geylang East CentralVasaNo ratings yet
- South Beach Development-IstructE Conference Singapore 2012Document20 pagesSouth Beach Development-IstructE Conference Singapore 2012blithevincentNo ratings yet
- BAUER Spezialtiefbau GMBH - ImagebrochureDocument0 pagesBAUER Spezialtiefbau GMBH - ImagebrochureagwsNo ratings yet
- MS of Concrete FoundationDocument18 pagesMS of Concrete FoundationSainbayar SBNo ratings yet
- MicrotunnlingDocument24 pagesMicrotunnlingmanishvekariyaNo ratings yet
- 1103-Sun Construction of Pipe Roof and Support System in Proposed Outlet Drain Under Crossing North Buona Vista Road, SingaporeDocument8 pages1103-Sun Construction of Pipe Roof and Support System in Proposed Outlet Drain Under Crossing North Buona Vista Road, SingaporeCheng KimHuaNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For Pad FoundationDocument13 pagesMethod Statement For Pad FoundationAbdul Rahman Hilmi0% (1)
- Methods of Piles InstallationDocument5 pagesMethods of Piles InstallationAsif KhanNo ratings yet
- MS For BoredDocument18 pagesMS For BoredsinlekmNo ratings yet
- EFFECTIVE PREPARATION FOR DEVELOPMENT WORKSDocument89 pagesEFFECTIVE PREPARATION FOR DEVELOPMENT WORKSEthan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Basha Diaphragm WallDocument43 pagesBasha Diaphragm Wallletuananhb100% (4)
- 12.excavation and Basement ConstructionDocument22 pages12.excavation and Basement ConstructionNiluka Ekanayaka100% (1)
- BasementDocument11 pagesBasementVedita Bhat100% (1)
- Basement Construction Methods Explained in 40 CharactersDocument51 pagesBasement Construction Methods Explained in 40 CharactersMUHAMMAD IMAN ASYRAF AHMAD NIZANo ratings yet
- Waterproofing and retaining wall solutions for basementsDocument49 pagesWaterproofing and retaining wall solutions for basementsSakshi Rawat100% (1)
- Deep Basement ExcavationDocument4 pagesDeep Basement Excavationmypenta2008No ratings yet
- Single Basement Construction GuideDocument19 pagesSingle Basement Construction GuideParitosh JambhaleNo ratings yet
- Diaphragm WallsDocument13 pagesDiaphragm WallsSaheer karimbilNo ratings yet
- Diaphragm Wall Construction GuideDocument18 pagesDiaphragm Wall Construction Guide04BHANDIWAD SANJANANo ratings yet
- Building Construction & Materials Sem - V Unit-2 19.07.2021Document55 pagesBuilding Construction & Materials Sem - V Unit-2 19.07.2021hyperloop707 designNo ratings yet
- Bus Terminal Building AreasDocument3 pagesBus Terminal Building AreasRohit Kashyap100% (1)
- Bus Terminal Design Bachelor Thesis 2006Document1 pageBus Terminal Design Bachelor Thesis 2006bandhuarushiNo ratings yet
- National Capital Region Planning Board: Regional Rapid Transit SystemDocument37 pagesNational Capital Region Planning Board: Regional Rapid Transit SystembandhuarushiNo ratings yet
- EoI-ISBT 31 Mar 06 PDFDocument1 pageEoI-ISBT 31 Mar 06 PDFbandhuarushiNo ratings yet
- Ranchi ISBT Development EOIDocument1 pageRanchi ISBT Development EOIbandhuarushiNo ratings yet
- Isbt Kashmere Gate A Case StudyDocument38 pagesIsbt Kashmere Gate A Case StudybandhuarushiNo ratings yet
- Parking StructuresDocument48 pagesParking Structuresbruinsfan915100% (1)
- Delhi Master Plan 2021Document312 pagesDelhi Master Plan 2021Tanya DewaniNo ratings yet
- FlowDocument1 pageFlowbandhuarushiNo ratings yet
- Delhi's transportation hub at Anand ViharDocument17 pagesDelhi's transportation hub at Anand ViharshishirkrNo ratings yet
- Peak Hour and Peak Hour FactorDocument2 pagesPeak Hour and Peak Hour FactorbandhuarushiNo ratings yet
- Towards Systematic Design of Urban Bus Stations Reinforcing A Weak Link in A P PDFDocument13 pagesTowards Systematic Design of Urban Bus Stations Reinforcing A Weak Link in A P PDFbandhuarushiNo ratings yet
- NSCDocument2 pagesNSCbandhuarushiNo ratings yet
- GurgaonDocument11 pagesGurgaonbandhuarushiNo ratings yet
- RourkelaDocument63 pagesRourkelabandhuarushiNo ratings yet
- 46 Tier1 PDFDocument86 pages46 Tier1 PDFbandhuarushiNo ratings yet
- View TendDocument26 pagesView TendbandhuarushiNo ratings yet
- Bus Terminal Design Bachelor Thesis 2006Document1 pageBus Terminal Design Bachelor Thesis 2006bandhuarushiNo ratings yet
- Development & Construction of A State-Of-The-Art Inter-State Bus Terminal Equipped With All Modern Amenities On A Public Private Partnership BasisDocument1 pageDevelopment & Construction of A State-Of-The-Art Inter-State Bus Terminal Equipped With All Modern Amenities On A Public Private Partnership BasisbandhuarushiNo ratings yet
- ViewtenddocDocument286 pagesViewtenddocbandhuarushiNo ratings yet
- Bus Terminal Building AreasDocument3 pagesBus Terminal Building AreasRohit Kashyap100% (1)
- ISBT Library Study - Planning and Design of Bus TerminalsDocument17 pagesISBT Library Study - Planning and Design of Bus TerminalsbandhuarushiNo ratings yet
- Built Environment Spatial Culture: Lecture 8, 21-03-2014Document20 pagesBuilt Environment Spatial Culture: Lecture 8, 21-03-2014bandhuarushiNo ratings yet
- Campus Sustainability Best PracticesDocument21 pagesCampus Sustainability Best PracticesU8x58No ratings yet
- LAJPAT BHAWAN SITE DETAILSDocument3 pagesLAJPAT BHAWAN SITE DETAILSbandhuarushiNo ratings yet
- Griha Booklet FullDocument92 pagesGriha Booklet FullpatentfilerNo ratings yet
- Terrace GardenDocument5 pagesTerrace GardenbandhuarushiNo ratings yet
- Airconditioning Capacity - The TonDocument1 pageAirconditioning Capacity - The TonbandhuarushiNo ratings yet
- Operating Instructions: Blu-Ray Disc™ / DVD Player BDP-S470Document39 pagesOperating Instructions: Blu-Ray Disc™ / DVD Player BDP-S470JhamNo ratings yet
- Amo Plan 2014Document4 pagesAmo Plan 2014kaps2385No ratings yet
- Cuplock Scaffold 18mPHx1.6mx2.5m SafetyDocument1 pageCuplock Scaffold 18mPHx1.6mx2.5m SafetyDIGITAL SIRNo ratings yet
- KG ResearchDocument257 pagesKG ResearchMuhammad HusseinNo ratings yet
- Principles of Marketing Eighth Edition Philip Kotler and Gary ArmstrongDocument17 pagesPrinciples of Marketing Eighth Edition Philip Kotler and Gary ArmstrongJunaid KhalidNo ratings yet
- Checklist For Mold RemediationDocument2 pagesChecklist For Mold Remediation631052No ratings yet
- Sheet (1) : An Iron Ring Has A Cross-Sectional Area of 3 CMDocument2 pagesSheet (1) : An Iron Ring Has A Cross-Sectional Area of 3 CMKhalifa MohamedNo ratings yet
- Questions - TrasportationDocument13 pagesQuestions - TrasportationAbhijeet GholapNo ratings yet
- Badminton Lesson 1 4 - 5 Grade: TH THDocument31 pagesBadminton Lesson 1 4 - 5 Grade: TH THLoxcey LopezNo ratings yet
- Arcelor Mittal - Bridges PDFDocument52 pagesArcelor Mittal - Bridges PDFShamaNo ratings yet
- CM Template For Flora and FaunaDocument3 pagesCM Template For Flora and FaunaJonathan Renier Verzosa0% (1)
- Destroyed Inventory Deduction ProceduresDocument7 pagesDestroyed Inventory Deduction ProceduresCliff DaquioagNo ratings yet
- Developmen of Chick EmbryoDocument20 pagesDevelopmen of Chick Embryoabd6486733No ratings yet
- Lay Out New PL Press QltyDocument68 pagesLay Out New PL Press QltyDadan Hendra KurniawanNo ratings yet
- C++ Programmierung (Benjamin Buch, Wikibooks - Org)Document257 pagesC++ Programmierung (Benjamin Buch, Wikibooks - Org)stefano rossiNo ratings yet
- Verification of First Law V-SonometerDocument3 pagesVerification of First Law V-SonometerRick astley's microphoneNo ratings yet
- Impression Techniques in Complete Denture Patients: A ReviewDocument6 pagesImpression Techniques in Complete Denture Patients: A ReviewRoja AllampallyNo ratings yet
- Cs On RH IncompatibilityDocument17 pagesCs On RH IncompatibilityRupali Arora100% (2)
- Programming Language II CSE-215: Dr. Mohammad Abu Yousuf Yousuf@juniv - EduDocument34 pagesProgramming Language II CSE-215: Dr. Mohammad Abu Yousuf Yousuf@juniv - EduNaruto DragneelNo ratings yet
- ĐỀ CƯƠNG ANH 9 - CK2 (23-24)Document7 pagesĐỀ CƯƠNG ANH 9 - CK2 (23-24)thuyhagl2710No ratings yet
- 2019 BioscienceJDocument14 pages2019 BioscienceJPatrícia Lima D'AbadiaNo ratings yet
- Manuais - 727312 - manuais-Raios-X AXR - 77000001249Document72 pagesManuais - 727312 - manuais-Raios-X AXR - 77000001249Hosam Ahmed HashimNo ratings yet
- APLI - Annual Report - 2016Document122 pagesAPLI - Annual Report - 2016tugas noviaindraNo ratings yet
- WCM - March 2017-Final Version PDF - 4731677 - 01Document211 pagesWCM - March 2017-Final Version PDF - 4731677 - 01Antonio VargasNo ratings yet
- ACM JournalDocument5 pagesACM JournalThesisNo ratings yet
- Roll Covering Letter LathiaDocument6 pagesRoll Covering Letter LathiaPankaj PandeyNo ratings yet
- B+V ELEVATOR SIDE DOOR Collar Type VS09 A4Document19 pagesB+V ELEVATOR SIDE DOOR Collar Type VS09 A4Игорь ШиренинNo ratings yet