Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Asystemfor Teaching Mis Andmbastudents To Depl Oy A S Calable Database-D Riv en Web Architecturefor B2Ce-Com Mer Ce
Uploaded by
gudunOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Asystemfor Teaching Mis Andmbastudents To Depl Oy A S Calable Database-D Riv en Web Architecturefor B2Ce-Com Mer Ce
Uploaded by
gudunCopyright:
Available Formats
A SY STE M F OR T EA CHIN G
MIS AND MB A ST UD ENT S
TO DEPL OY A S CALABLE
DATABASE-D RIV EN WEB
ARCHIT EC TUR E F OR B 2C E-
COM MER CE
Alexander Y. Yap, Ph.D.
Elon University, North Carolina
Claudia Loebbecke, Ph.D.
University of Cologne, Germany
Yap, Elon University, N. Carolina
Background
IS Environment: Five Years Teaching in two Business School
Environments (MIS & MBA students)
A variety of B2C E-commerce systems solutions are available for
different business needs …
But deciding on a particular systems solution can be a
challenging process
Putting things in perspective for students
• Choosing the appropriate IS strategy for Business Objectives
• Looking at Business Processes behind E-commerce systems
• Assessing how different solutions and systems address short
term vs. long term strategies
Yap, Elon University, N. Carolina
Objective
Show students different solution paths
We came up with four generic solutions models
Show different architecture scalability
Demonstrate the role of database in e-commerce
Show how a web application server (middleware) shuttles
data between the database and browser
Discuss the importance of web interface and its usability
(front-end design)
Develop and Deploy an E-commerce application (one
project for each student)
Yap, Elon University, N. Carolina
Business Process Optimization,
Outsourcing, & Content Development
Yap, Elon University, N. Carolina
Stand Alone Model
(Two-tier Architecture)
Yap, Elon University, N. Carolina
E-Commerce
Integrated with E-Business Systems
(Model 4 – Three-tier & Multi-tier Architecture)
Yap, Elon University, N. Carolina
Web Architectures
Two-tier Architecture Three-tier Architecture Multi-tier Architecture
Client Client Client
Computer Computer Computer
(Web Browser) (Web Browser) (Web Browser)
Web Server
+ Web Server Web Server
Stand Alone
Database
(Access)
Database Server
Database
Server Email Server
(Oracle,
SQL Server) File Server
Video Server
Yap, Elon University, N. Carolina
E-Commerce: A Two Component
Course (Teaching the Business &
Technology Components)
Students taking MIS (Graduate Level) – needed 2 semesters to cover
the business component (1) and the technology component (1)
• Three-tier architecture
• Oracle and SQL programming
• Customize the Application with a lot of hand coding
• Setting up the Application Server & Web/HTTP Server
MBA students learning E-commerce were limited to a one semester.
Business component (half a semester) and technology component
(half a semester)
• Two-tier architecture
• MS Access
• Use Rapid Application Development Methods for Coding
(Wizards, Drag and Drop coding, reuse of existing
components – shopping cart)
• No Server set up required
Yap, Elon University, N. Carolina
Student Feedback
MBA students with no database background were more
suited to learning Model 3 (just to see how technology
manages the electronic process)
MIS students preferred Model 4, because they know that
high-end relational database management systems (like
Oracle) work with other enterprise applications
MBA students were able to see how different systems
could be integrated with e-commerce systems, enabling
them to make technology acquisition decisions (Model 4)
MIS students were able to set-up customized e-
commerce applications with their own coding logic, their
choice of database, and operating system (Linux)
Yap, Elon University, N. Carolina
Application
Development Environment
Client Software Middleware Parsing Codes
(Home Installed) (University E-commerce Server) Embedded in Tags
Web WEB/HTTP SERVER
FLASH
Page (Microsoft IIS)
Animation
(Nested in html codes) COLD FUSION
Process HTML tags
APPLICATION HTML
SERVER Tags
Processes Web pages Cold Fusion Tags
with with SQL scripts are
HOMESITE +
CF tags passed on to
Generates Cold Fusion database
Enabled Cold
Web pages (*.cfm) Fusion
Tags
DATABASE
ORACLE or
MS ACCESS
(interprets SQL scripts)
Database
(University Server)
Yap, Elon University, N. Carolina
TECHNOLOGIES USED
SOFTWARE TOOLS
• Macromedia Homesite+ & Dreamweaver (editors
for coding)
• Cold Fusion Server (Application Server -
middleware)
• MS Access Database or Oracle (relational
database; back-end)
• Macromedia Flash MX (animation)
• Others (Fireworks, Photoshop, Graphic editors)
Yap, Elon University, N. Carolina
Application Features
When we decided to use CF
(2000-2001)
Features Cold Fusion (CF) Active Server Pages (ASP)
Multi-Platform Windows, HP Unix, Solaris, Windows only
(Interoperability) Linux
Native RDBMS Drivers (i.e. Yes No
Oracle drivers)
Simplified One Tag XML Yes No
Parser
Clustering and Software Load Yes No
Balancing
Security Sandboxes Yes No
CORBA / COM / Native support for all three Only COM is native to ASP
JAVA Support
Rapid Deployment (Rapid Drag and Drop coding, custom No
Application Development) tags, automated scripting
with SQL Builder,
Template Wizards
Yap, Elon University, N. Carolina
RDBMS/Database Connectivity
Yap, Elon University, N. Carolina
Cold Fusion Studio
(now Macromedia
Homesite +) – RAD
Features
You can link the tables:
‘click and drag’ the
primary key to the foreign
key
Then, double click on the
fields and they will
appear automatically
SQL Script appears
automatically
You can sort the order
by a chosen field (e.g.
date)
Yap, Elon University, N. Carolina
RAD Tools:
Drag and Drop Query Codes
(Cold Fusion Studio -> Homesite Plus)
Yap, Elon University, N. Carolina
RAP - Using Wizards to create
Form and Action Templates
Yap, Elon University, N. Carolina
Select Table and Fields
that you want to include in form
Yap, Elon University, N. Carolina
Form & Action Template Created
(product_entryform.cfm, product_entryaction.cfm)
Yap, Elon University, N. Carolina
Form Template
Design & Code
Yap, Elon University, N. Carolina
Action Template
(CFINSERT)
Validation/Confirmation that data
Yap, Elon has been
University, inputted into the database
N. Carolina
First Step: Create Database
Data Data Data Data Content
to be Provided Content to be Collected (Samples)
Product Categories Product Categories (i.e. Client Information Name, Address, E-Mail,
(Catalog) cars, computers) (upon ordering) Phone
Products Product Name, Product Payment Information Credit Card Number,
(Catalog) Description (short & (upon ordering) Billing Address
long), Price, Images
(small & large)
Product Inventory Stock Available (quantity), Order Information Products Ordered,
(Catalog) Back Orders, Date of (upon ordering) Quantity, Order
Delivery Date
Order Invoice Order No., Item No., Items Customer Services Complaints and
(after Ordering) Ordered, Total (after ordering) Comments, Item
and Order Tracking
Yap, Elon University, N. Carolina
Second Step: Show students how their data is
connected to the Server
“Creating the ‘data source’ using student’s name”
Yap, Elon University, N. Carolina
Data source
MSAccess – set
up the path of
the database file
in the server
Oracle – create
a schema name
for each student
(using Oracle’s
userid and
password)
Yap, Elon University, N. Carolina
Third Step:
Creating the E-commerce Application:
Separating Content and Web Design
Yap, Elon University, N. Carolina
The
Shopping Cart
Yap, Elon University, N. Carolina
Handling Session Variables
(Passing Data from Catalog to
Shopping Cart to Database)
Yap, Elon University, N. Carolina
Passing Data Variables
(Using different web templates)
Product Online Capture
Shopping
Table Product Order Info
Cart
Info Catalog In Database
Yap, Elon University, N. Carolina
Form Variables
Inserted into the Customer Table
Yap, Elon University, N. Carolina
Fourth Step:
Flash Animation
SPLASH PAGE
Create layers
Separate animated
objects for each layer
Different animation
effects
Timeline of the animated
objects
NAVIGATION BUTTONS
(optional)
Yap, Elon University, N. Carolina
Embedding Sound
Drag the sound clip to the object
If you successfully dragged the sound, it will
appear on the frame
Yap, Elon University, N. Carolina
Conclusion
Students taking MIS at the Graduate level, with background in SQL
and Oracle, handled the three-tier architecture system very well.
They all wanted to learn full scalability of the architecture (Model
4).
MIS students mostly combined hand-coding and RAD functions
MBA students learning E-commerce for the first time could handle
the two-tier architecture without a problem.
But they need to use RAD methods with minimal coding (drag &
drop, wizards, application server handled by someone else)
MBA students felt they could make technology-related decisions
better knowing the capabilities of web technologies to improve
business process.
Multi-tier architecture was only feasible if taught across several
courses (logistics limitations; cannot be compressed into 1 or 2
semesters)
Yap, Elon University, N. Carolina
CFGraph
Create query Pie Chart
Of
You can use
SUM to add Quantity Sold
Use an alias –
e.g “as totalsum”
for the sum of a
variable
Define the graph Horizontal bar
as shown Chart of
Sum (Quantity x Sales Amount
Price)
Yap, Elon University, N. Carolina
Dynamic Charts based on the
Database (Sales Table)
Yap, Elon University, N. Carolina
You might also like
- Dominic Da Silva: SummaryDocument7 pagesDominic Da Silva: SummarySunny DhananiNo ratings yet
- Lee, Ting Wei (Wilson) : Contact InformationDocument3 pagesLee, Ting Wei (Wilson) : Contact InformationXuetong YanNo ratings yet
- FreeLance ResumeDocument3 pagesFreeLance ResumeMashuq RahmanNo ratings yet
- EBX5 Architecture IntegrationDocument31 pagesEBX5 Architecture IntegrationGanesh SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Reference ResumeDocument4 pagesReference Resumenirmala goudNo ratings yet
- SoaDocument79 pagesSoaMeghanagraj MeghaNo ratings yet
- Enabling Web and Software Technologies: Electronic Commerce (WS-02/03) 3-1Document37 pagesEnabling Web and Software Technologies: Electronic Commerce (WS-02/03) 3-1Tuan DaoNo ratings yet
- Radek ResumeDocument8 pagesRadek ResumertgluchNo ratings yet
- Mikhail Toumarev: Executive SummaryDocument4 pagesMikhail Toumarev: Executive Summarykiran2710No ratings yet
- Sample USResumeDocument1 pageSample USResumeAllan Kelvin Mendes de SalesNo ratings yet
- HugoMikel Java Developer ResumeDocument9 pagesHugoMikel Java Developer ResumeJoshElliotNo ratings yet
- SR - Documentum Architect Resume North Chicago, IL - Hire IT People - We Get IT DoneDocument8 pagesSR - Documentum Architect Resume North Chicago, IL - Hire IT People - We Get IT DoneSuneet SharmaNo ratings yet
- Dell Boomi Developer Resume Charlotte - Hire IT People - We Get IT DoneDocument5 pagesDell Boomi Developer Resume Charlotte - Hire IT People - We Get IT DoneSowmya NagarajaNo ratings yet
- Java J2EE Companion Resume 1Document4 pagesJava J2EE Companion Resume 1api-26045667No ratings yet
- Service Oriented ArchitectureDocument86 pagesService Oriented ArchitectureAkshay BagdiNo ratings yet
- Alexander S. Trakhimenok: CV ofDocument4 pagesAlexander S. Trakhimenok: CV ofkittu_m30No ratings yet
- Websphere Interview QuestionsDocument5 pagesWebsphere Interview Questions@vjNo ratings yet
- ApplicationdesignDocument53 pagesApplicationdesignbirukNo ratings yet
- Applications and Middleware Application Using JAVA/J2EE Related TechnologiesDocument8 pagesApplications and Middleware Application Using JAVA/J2EE Related TechnologiesJoshElliotNo ratings yet
- J2ee Developer With 10 Years Experience ResumeDocument4 pagesJ2ee Developer With 10 Years Experience ResumedivaNo ratings yet
- Dice Profile Yan HuoDocument4 pagesDice Profile Yan HuoDave JonesNo ratings yet
- Sales Force Sample 1Document5 pagesSales Force Sample 1rami.windowsNo ratings yet
- Shashikant/Satyam/Sr. SW Engg.Document9 pagesShashikant/Satyam/Sr. SW Engg.riteshshuklaNo ratings yet
- Smita VarmaDocument4 pagesSmita VarmaashokNo ratings yet
- Nagi SFDC ResumeDocument5 pagesNagi SFDC Resumebharath i5techNo ratings yet
- Michael R. E. Dixon: SummaryDocument5 pagesMichael R. E. Dixon: SummarySibananda MahantaNo ratings yet
- Yourfirstname Lastname Java Websphere SBC VlsDocument3 pagesYourfirstname Lastname Java Websphere SBC Vlsraj.bollimuntha100% (1)
- Cobol Modem ArchitectureDocument55 pagesCobol Modem ArchitecturesuryaNo ratings yet
- Sample US ResumeDocument1 pageSample US ResumeMarcoGarcíaNo ratings yet
- Ds ResumesDocument38 pagesDs Resumesknani9090No ratings yet
- +91-9XXXXX5. Career ObjectiveDocument4 pages+91-9XXXXX5. Career ObjectiveSuseela SivaramanNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Oracle Portal and Identity ManagementDocument33 pagesMechanics of Oracle Portal and Identity Managementsagar.biswas.079983No ratings yet
- Aashlesh - AEM ArchitectDocument5 pagesAashlesh - AEM ArchitectMadhav GarikapatiNo ratings yet
- Lecture4+ +Service+Oriented+ArchitectureDocument75 pagesLecture4+ +Service+Oriented+ArchitectureAmontos Edjie KentNo ratings yet
- Sample Resume 1Document8 pagesSample Resume 1Rohit WadhwaniNo ratings yet
- R01 1Document6 pagesR01 1vitig2No ratings yet
- Basic Technology ManualDocument33 pagesBasic Technology ManualSushil KumarNo ratings yet
- Ahmad R. ABUARJADocument3 pagesAhmad R. ABUARJAabuarja100% (1)
- SalesforceDocument8 pagesSalesforce19-12B1 SRIKANTHNo ratings yet
- John P Berry Resume 2Document2 pagesJohn P Berry Resume 2api-251291236No ratings yet
- IWS Training ArchitectureDocument64 pagesIWS Training ArchitectureRobert Pérez MartinezNo ratings yet
- Resumes EgDocument90 pagesResumes EgdheerajassudaniNo ratings yet
- Rony John Phone: 9850975603 Profile Summary: UBS Market Risk IT: Jan 2019 - PresentDocument4 pagesRony John Phone: 9850975603 Profile Summary: UBS Market Risk IT: Jan 2019 - PresentShreyas MishraNo ratings yet
- CV of Tim Clark (April 2008)Document3 pagesCV of Tim Clark (April 2008)timothyjcNo ratings yet
- 22 Years of It and Java Experience ResumeDocument4 pages22 Years of It and Java Experience ResumedivaNo ratings yet
- Sruthi Datastage ResumeDocument7 pagesSruthi Datastage Resumeabreddy2003No ratings yet
- J2EE Patterns: Seminar OnDocument22 pagesJ2EE Patterns: Seminar OnPrince ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- 11 - Install Patch MaintainDocument3 pages11 - Install Patch MaintainNabileNassimNo ratings yet
- Haritha - Salesforce Vlocity - DeveloperDocument11 pagesHaritha - Salesforce Vlocity - DeveloperMadhav GarikapatiNo ratings yet
- Trends in Enterprise Architectures From Client ToDocument19 pagesTrends in Enterprise Architectures From Client Toapi-24051001No ratings yet
- E-Business Suite 11iDocument50 pagesE-Business Suite 11iashi_25145591099No ratings yet
- aCSC VASDVC DFVDS FQWFWEACDocument6 pagesaCSC VASDVC DFVDS FQWFWEACashish ojhaNo ratings yet
- Database Modernization - Object Creation and AccessDocument42 pagesDatabase Modernization - Object Creation and AccessJesus MaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Sridhar RapalaDocument3 pagesSridhar RapalaPraveen MadupuNo ratings yet
- Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition 12c - Second EditionFrom EverandOracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition 12c - Second EditionNo ratings yet
- IBM WebSphere Portal 8: Web Experience Factory and the CloudFrom EverandIBM WebSphere Portal 8: Web Experience Factory and the CloudNo ratings yet
- Java / J2EE Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedFrom EverandJava / J2EE Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedNo ratings yet
- The Real MCTS SQL Server 2008 Exam 70-433 Prep Kit: Database DesignFrom EverandThe Real MCTS SQL Server 2008 Exam 70-433 Prep Kit: Database DesignRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Mastering IBM i: The Complete Resource for Today's IBM i SystemFrom EverandMastering IBM i: The Complete Resource for Today's IBM i SystemRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Decision Support Systems: Real World ApplicationsDocument27 pagesDecision Support Systems: Real World ApplicationsgudunNo ratings yet
- Ua Mis ProgramDocument17 pagesUa Mis ProgramgudunNo ratings yet
- PPC Chapter 1 WebDocument41 pagesPPC Chapter 1 Webanon-598027No ratings yet
- Strategic Planning ModelDocument55 pagesStrategic Planning Modelapi-3705877100% (1)
- Decision Support Systems: Real World ApplicationsDocument27 pagesDecision Support Systems: Real World ApplicationsgudunNo ratings yet
- Decision Support Systems: Real World ApplicationsDocument27 pagesDecision Support Systems: Real World ApplicationsgudunNo ratings yet
- Mayer Fund: Class of 2009 Recruiting PresentationDocument15 pagesMayer Fund: Class of 2009 Recruiting PresentationgudunNo ratings yet
- ADocument21 pagesAgudunNo ratings yet
- MBA Essentials: Information Technology For Strategic, Competitive AdvantageDocument59 pagesMBA Essentials: Information Technology For Strategic, Competitive AdvantagegudunNo ratings yet
- Internet Shoppingmall: (Lgeshop)Document33 pagesInternet Shoppingmall: (Lgeshop)gudunNo ratings yet
- Efficient InnovationDocument20 pagesEfficient InnovationgudunNo ratings yet
- Finance: Solvay Business School Université Libre de Bruxelles Fall 2006Document21 pagesFinance: Solvay Business School Université Libre de Bruxelles Fall 2006gudunNo ratings yet
- Opportunities For Strategic Alliances Between US and European Business SchoolsDocument21 pagesOpportunities For Strategic Alliances Between US and European Business SchoolsgudunNo ratings yet
- Introduction To AccountingDocument159 pagesIntroduction To Accountingsashank7No ratings yet
- Production-Planning Systems: Aggregate Planning and Master Production SchedulingDocument59 pagesProduction-Planning Systems: Aggregate Planning and Master Production SchedulinggudunNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of A Decision Support System For Environmental Effects MonitoringDocument15 pagesDesign and Implementation of A Decision Support System For Environmental Effects MonitoringgudunNo ratings yet
- Corporate Finance: Everything .. R SrinivasanDocument18 pagesCorporate Finance: Everything .. R SrinivasangudunNo ratings yet
- Operations Consulting and Reengineering: ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004Document29 pagesOperations Consulting and Reengineering: ©the Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2004gudunNo ratings yet
- Pursuing Innovation: Challenges and Opportunities: AACSB International 2005 Deans ConferenceDocument18 pagesPursuing Innovation: Challenges and Opportunities: AACSB International 2005 Deans ConferencegudunNo ratings yet
- EmpowermentDocument13 pagesEmpowermentmayur_23No ratings yet
- Working Capital ManagementDocument37 pagesWorking Capital ManagementgudunNo ratings yet
- Iona College Operations Management MBA-540Document57 pagesIona College Operations Management MBA-540Yang Seung HeonNo ratings yet
- Working Capital ManagementDocument37 pagesWorking Capital ManagementgudunNo ratings yet
- Production and Operations Management (POM) : An IntroductionDocument28 pagesProduction and Operations Management (POM) : An IntroductiongudunNo ratings yet
- Decision Support SystemsDocument33 pagesDecision Support SystemsJacton OpiyoNo ratings yet
- Decision Support SystemsDocument33 pagesDecision Support SystemsJacton OpiyoNo ratings yet
- AccountingDocument151 pagesAccountingOwais FarooquiNo ratings yet
- Micro-Insurance: Principles Characteristics Opportunities ChallengesDocument9 pagesMicro-Insurance: Principles Characteristics Opportunities ChallengesgudunNo ratings yet
- Decision Support SystemsDocument33 pagesDecision Support SystemsJacton OpiyoNo ratings yet
- Error From OAFDocument17 pagesError From OAFUnknown1879No ratings yet
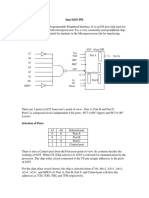
- Traffic Light ControllerDocument3 pagesTraffic Light ControllerSyed Muzahir AliNo ratings yet
- 3D-Computer Animation: Dhole Patil College of Engineering, Pune Department of Computer EngineeringDocument22 pages3D-Computer Animation: Dhole Patil College of Engineering, Pune Department of Computer EngineeringPraveen AnimatorNo ratings yet
- Desktop Auditoría de SoftwareDocument377 pagesDesktop Auditoría de SoftwareSantos May Cante SantosNo ratings yet
- Step-by-Step - Configuring A 2-Node Multi-Site Cluster On Windows Server 2008 R2 - Part 3 - Clustering For Mere MortalsDocument64 pagesStep-by-Step - Configuring A 2-Node Multi-Site Cluster On Windows Server 2008 R2 - Part 3 - Clustering For Mere Mortalssatya28No ratings yet
- Sce 031 100 FC Programming s7 1200 r1709 enDocument54 pagesSce 031 100 FC Programming s7 1200 r1709 enandersonNo ratings yet
- Python in 30 Minutes! : Fariz DarariDocument64 pagesPython in 30 Minutes! : Fariz DarariJuan DominguezNo ratings yet
- Malware Analysis Nicolas BrulezDocument27 pagesMalware Analysis Nicolas BrulezFranck DernoncourtNo ratings yet
- Firewall and Ips Design GuideDocument106 pagesFirewall and Ips Design GuideBerrezeg MahieddineNo ratings yet
- SRX For BeginnersDocument6 pagesSRX For BeginnersSon Tran Hong NamNo ratings yet
- WWW Thewindowsclub Com Disable Superfetch Prefetch SSDDocument11 pagesWWW Thewindowsclub Com Disable Superfetch Prefetch SSD4t3tt43No ratings yet
- Er & RMDocument26 pagesEr & RMEftekher Ahmed AqibNo ratings yet
- Viva Questions With Answers Internet Fundamental Lab (IT-253E)Document8 pagesViva Questions With Answers Internet Fundamental Lab (IT-253E)Jaat Pankaj BurraNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of 600va Ups Based 0n 89c51Document5 pagesDesign and Implementation of 600va Ups Based 0n 89c51setsindiaNo ratings yet
- Computer Software: 1 Neha Asthana, IT LecturerDocument8 pagesComputer Software: 1 Neha Asthana, IT Lecturernehaasthana18No ratings yet
- Source Code Analysis of GstumblerDocument23 pagesSource Code Analysis of GstumblerFrankNo ratings yet
- Presentation - Exadata Storage LayoutDocument34 pagesPresentation - Exadata Storage Layoutkinan_kazuki104No ratings yet
- OOD Ooking: Mid-Term Project Report (Jan-May 2011)Document39 pagesOOD Ooking: Mid-Term Project Report (Jan-May 2011)b1b11b111b1111No ratings yet
- 8255 Ppi ExamplesDocument10 pages8255 Ppi Examplesvenky258100% (1)
- 1Document123 pages1zayazssNo ratings yet
- LogRhythm PowerTech Interact DatasheetDocument2 pagesLogRhythm PowerTech Interact DatasheetjordagroNo ratings yet
- Bio Perl TutorialDocument34 pagesBio Perl TutorialPatel BansariNo ratings yet
- Pengenalan MikroTik MTCNADocument126 pagesPengenalan MikroTik MTCNAAung Zaw LinNo ratings yet
- Understanding Harbour GTDocument23 pagesUnderstanding Harbour GToskisanNo ratings yet
- Types of SimulationDocument2 pagesTypes of SimulationRudelsa Agcolicol LangamanNo ratings yet
- Master ChiefDocument15 pagesMaster ChiefBhanunjay Kumar ChaurasiaNo ratings yet
- DFo 4 2 ProjectDocument10 pagesDFo 4 2 ProjectMilanAdzic75% (4)
- Tib Ems Users GuideDocument641 pagesTib Ems Users GuidejanofassNo ratings yet
- Vala TutorialDocument56 pagesVala TutorialFelipe Borges50% (2)
- Hyper-V ESXI Server MigrationDocument16 pagesHyper-V ESXI Server MigrationKrishanThiseraNo ratings yet