Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Clouds
Uploaded by
Dean Jezer0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views17 pagespower point
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentpower point
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views17 pagesClouds
Uploaded by
Dean Jezerpower point
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 17
Clouds
Clouds in Humid Regions
Overcast daytime skies during the
rainy season.
Clouds in Dry Land like
Desert
The sky will be clear without clouds
We can see that the number of cloud
s depends on the air temperature
Summer (hot temperature)
Night (cold temperature)
Winter (cold temperature)
Landforms
Each land can absorb and release
infrared radiation differently accordin
g to landforms.
Light colored areas
Better at reflecting than absorbing infrared
radiation. (red-soil areas)
Dark-colored areas
Better at absorbing than reflecting
infrared radiation
Water Surfaces
Slowly absorb but keep heat energy
longer than the land (ocean, sea and
lake)
Thick Forest
Reduce or obstruct sunlight from
permeating the soil. The soil receives less h
eat resulting in cold air
Big Cities
Receive a large quantity of heat energy
affecting the air temperature to be very
high specially during the day.
Air Humidity
Humidity- when vapor from evaporation and
transpiration will diffuse into the air.
Evaporation- when the liquid turns to gas or
vapor because of heat
Transpiration- the plants reduce heat through
releasing water from eaves in the form of vapor.
Low humidity- has a high temperature and
the amount of vapor is high.
High humidity- has a low temperature and
the amount of vapor is low.
Air Density
Is defined as mass of the air per unit
volume of the air.
Characteristics of Air Density
1. At sea level air density is greatest at 1.2
kg per cubic meter.
2. The amount of air close to the Earths
surface is greater than that at a higher
level.
3. In areas of different temperatures, the
density of the air is different.
4. Cold areas is more dense than in hot
areas.
Atmospheric Pressure
The force of the atmosphere above a unit area
at a certain height from the Earths surface.
Properties of air pressure:
1. Different places- different air pressure
2. Low altitude-low pressure (diving underwater)
3. Same height- same pressure
4. Pressure depends on temperature (cold-high
pressure, hot- low pressure)
5. Pressure depends on humidity (wet humidity-
low pressure, and dry humid- high pressure)
Tools for Measuring Air
Pressure
Mercury
Barometer
A mercury barometer
balances the weight of
mercury in a glass tub
e against the atmosph
eric pressure above a r
eservoir of mercury at
its base to provide a m
easurement of atmosp
heric pressure.
Barograph
Is an instrument used
to make a
continuous recording
of atmospheric press
ure. ... The pen trace
s a record of pressur
e versus time on a c
hart, which is mount
ed on a drum rotate
d by a clockwork.
Altimeter
Altitude can be determined based on
the measurement of atmospheric pre
ssure. The greater the altitude, the lo
wer the pressure.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Blank Score SheetDocument1 pageBlank Score SheetDean JezerNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Meiosis QuizDocument4 pagesMitosis Meiosis QuizDean JezerNo ratings yet
- CloudsDocument17 pagesCloudsDean JezerNo ratings yet
- Earth's AtmosphereDocument31 pagesEarth's AtmosphereDean JezerNo ratings yet
- English ProgramDocument1 pageEnglish ProgramDean JezerNo ratings yet
- Come Ye Thankful People SampleDocument3 pagesCome Ye Thankful People SampleDean JezerNo ratings yet
- Compositions and Classifications of The AtmosphereDocument15 pagesCompositions and Classifications of The AtmosphereDean JezerNo ratings yet
- Seatwork Activities for Periods 1, 3, 4, 6, and 8 - Math Textbook TasksDocument1 pageSeatwork Activities for Periods 1, 3, 4, 6, and 8 - Math Textbook TasksDean JezerNo ratings yet
- Lung ModelDocument1 pageLung ModelDean JezerNo ratings yet
- Menstrual CycleDocument17 pagesMenstrual CycleDean JezerNo ratings yet
- Kalabasa SoupDocument1 pageKalabasa SoupDean JezerNo ratings yet
- Mixture ExperimentsDocument2 pagesMixture ExperimentsDean JezerNo ratings yet
- Texture Triangle Worksheet-1Document3 pagesTexture Triangle Worksheet-1Dean JezerNo ratings yet
- Alvary S RY: Written byDocument15 pagesAlvary S RY: Written byDean JezerNo ratings yet
- Letter e Lab - HDocument2 pagesLetter e Lab - HDean JezerNo ratings yet
- Dietary Fibre and Water (Foundation)Document21 pagesDietary Fibre and Water (Foundation)Dean JezerNo ratings yet
- Antonyms Are OppositesDocument2 pagesAntonyms Are OppositesJust LeeNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Compound Light MIcroscopeDocument11 pagesParts of The Compound Light MIcroscopeDean Jezer100% (1)
- Skimming and Scanning WorksheetsDocument3 pagesSkimming and Scanning WorksheetsDean JezerNo ratings yet
- Subject Verb Agreement Compound SubjectDocument3 pagesSubject Verb Agreement Compound SubjectDean Jezer0% (1)
- With All My Heart PDFDocument7 pagesWith All My Heart PDFDean JezerNo ratings yet
- 2016 2017 Spelling Bee Study Lists 4th 8th Grades PDFDocument16 pages2016 2017 Spelling Bee Study Lists 4th 8th Grades PDFDean Jezer100% (1)
- Investigatory ProjectDocument5 pagesInvestigatory ProjectDean Jezer100% (2)
- HMH School Publishers Spelling Bee Word ListDocument10 pagesHMH School Publishers Spelling Bee Word ListAdeniyi AleseNo ratings yet
- How Microscopes Work LabDocument6 pagesHow Microscopes Work LabDean JezerNo ratings yet
- May The Lord Find Us FaithfulDocument9 pagesMay The Lord Find Us FaithfulDean Jezer0% (1)
- Quiet UnderstandingDocument1 pageQuiet UnderstandingDean JezerNo ratings yet
- 2016 2017 Spelling Bee Study Lists 4th 8th Grades PDFDocument16 pages2016 2017 Spelling Bee Study Lists 4th 8th Grades PDFDean Jezer100% (1)
- p3 Prepositions of Time at in OnDocument11 pagesp3 Prepositions of Time at in OnDean JezerNo ratings yet
- The SensesDocument46 pagesThe SensesDean JezerNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Testing of Water Retaining StructuresDocument4 pagesTesting of Water Retaining StructuresIm ChinithNo ratings yet
- Basic Groundwater Hydrology and Evaluation Procedures Training ManualDocument134 pagesBasic Groundwater Hydrology and Evaluation Procedures Training Manualخليل العقوريNo ratings yet
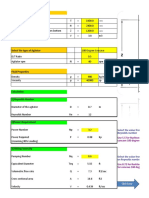
- Fluid Mechanics: 200 MM 0.0225 500 M 0.2 M /s 9.81 M/sDocument57 pagesFluid Mechanics: 200 MM 0.0225 500 M 0.2 M /s 9.81 M/sRamesh MundaNo ratings yet
- Lean Oil Absorption 02Document14 pagesLean Oil Absorption 02Shri JrNo ratings yet
- Jurnal CTAS MarlitaDocument8 pagesJurnal CTAS MarlitamarlitaNo ratings yet
- Past ExamDocument16 pagesPast ExamAlex ChungNo ratings yet
- Modules 1 and 2bridge Hydrology and HydraulicsDocument36 pagesModules 1 and 2bridge Hydrology and HydraulicsEdelyn Lindero Ambos100% (1)
- Spectra PureDocument49 pagesSpectra PurethermickNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Simulation of Multi-Effect Evaporators PDFDocument10 pagesDynamic Simulation of Multi-Effect Evaporators PDFdesai sanketNo ratings yet
- AICIP-ISI Exam CalculationsDocument4 pagesAICIP-ISI Exam CalculationsJomon MathewNo ratings yet
- UTP - Fluid Mechanics Course - September 2012 Semester - Chap 3 Bernoulli EquationsDocument35 pagesUTP - Fluid Mechanics Course - September 2012 Semester - Chap 3 Bernoulli EquationswhateveroilNo ratings yet
- Agitator Power Requirement & Mixing Intensity CalculationDocument26 pagesAgitator Power Requirement & Mixing Intensity CalculationYusuf DabhiyaNo ratings yet
- What Is A Water Treatment Plant OperatorDocument4 pagesWhat Is A Water Treatment Plant OperatorWaleed EmaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - PrecipitationDocument63 pagesChapter 2 - Precipitationneha1685No ratings yet
- SoilDocument5 pagesSoilJason AgbotNo ratings yet
- Condensate Oxygen Control in A Combined Cycle SystemDocument8 pagesCondensate Oxygen Control in A Combined Cycle SystemghezelasheghiNo ratings yet
- Psychrometry ProblemsDocument33 pagesPsychrometry Problems19R21A0334 MATTA SHASHANKNo ratings yet
- Quiz Bootcamp10collaborativegaslawsgasstoichiometryfa18 1Document5 pagesQuiz Bootcamp10collaborativegaslawsgasstoichiometryfa18 1api-233552637No ratings yet
- Viscosity: A Fluid's Resistance to FlowDocument17 pagesViscosity: A Fluid's Resistance to Flowkumar100% (1)
- Pre-Exam 2Document8 pagesPre-Exam 21A20 CHAN HIU MINGNo ratings yet
- Rbe All Fluids Modular Couplings Staubli - enDocument28 pagesRbe All Fluids Modular Couplings Staubli - enPaul WoodwardNo ratings yet
- Hysys CurvesDocument32 pagesHysys CurvespradheepNo ratings yet
- Pa-Shun Hawkins PhET - States of Matter - Lab 3 (1) - 2Document8 pagesPa-Shun Hawkins PhET - States of Matter - Lab 3 (1) - 2Parris HawkinsNo ratings yet
- Sublimation and Melting Point DeterminationDocument3 pagesSublimation and Melting Point DeterminationRhone RoqueNo ratings yet
- Donaldson Compressed Air Dryer Operating InstructionsDocument46 pagesDonaldson Compressed Air Dryer Operating InstructionsClaudiuNo ratings yet
- SEO Irrigation Efficiency CalculationsDocument6 pagesSEO Irrigation Efficiency CalculationsBeza Getachew100% (3)
- Datasheet For Booster PumpDocument1 pageDatasheet For Booster PumpLe Anh DangNo ratings yet
- Safe Oxygen Production Large Safe Hydrogen FacilitiyDocument5 pagesSafe Oxygen Production Large Safe Hydrogen FacilitiyTS WongNo ratings yet
- Principles of Hydrostatic Pressures - Advance Engineering Mathematics ReviewDocument2 pagesPrinciples of Hydrostatic Pressures - Advance Engineering Mathematics ReviewimrancenakkNo ratings yet
- The 4 Key Gas Laws ExplainedDocument20 pagesThe 4 Key Gas Laws Explaineddavid jenil nabua100% (1)