Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dr. Jufri Latief (Compartment Syndromes)
Uploaded by
shinta0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
52 views11 pagesnnnn
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentnnnn
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
52 views11 pagesDr. Jufri Latief (Compartment Syndromes)
Uploaded by
shintannnn
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
COMPARTMENT
SYNDROMES
dr. Jufri Latief, Sp.B., Sp.OT
Bagian Ortopedi & Traumatologi
Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Hasanuddin
Makassar, 2006
DEFINITION
Increase pressure within a comfined space
(osteofascial space) that leads to
microvasculary compromise and ultimately
to cell death or tissue death
ETIOLOGY
1. Trauma 3. Coagulopathies
Fracture Genetic / hemophilia
Hematoma Iathrogenic
Gunshot (stab wounds) Acquired coagulopathies
Animal/Insect bites/Snack
bites
4. Others
Post ischemic swelling External compression / most
Crush injuries trousers, cast, thight dressings)
Vascular damage Thight closure of fascial defects
Electric injuries Burn-hypo / hiperthermia /
2. Edema related combustio
Nephrotic syndrome Lost of conciousness (drug
Frosbite (trauma dingin) overdose resulting in lying on
Burns limb four hours)
Over use injuries (over Infected : clostridiu perfringeus /
training) walchii (gas ganggren)
Prolonged tourniquet
Mast trousers (celana
ketat)
ANATOMICAL LOCATION
Forearm
The most common site
Anterior compartment of the leg
Abdominal compartment syndrome
Hand and wrist compartment
syndrome
Thigh compartment syndrome
Foot compartment syndrome
PATOPHYSIOLOGY
Vascular congestion capillary
beds occludedmuscle & nerve
ischemiatransudation of colloid
plasma into the surrounding tissues
increase of tissue pressurearterial
impaired (ellipsoid theory)
CLINICAL PRESENTATION
Pain (pain out of proportion)
Paresthesias / anesthesia (dont pin prick test,
because fibers smallerst, use two point
discrimination test)
Passive strestch severe pain
Pressure tenderness
PulsessnesThis is least releable of the
examination are frequently not affective (a
disorders microvasculature, major vessel)
DIAGNOSIS
Clinical presentation
Measurement
Whick catheter technique
Slit catheter technique
Stic catheter technique
Continous infusion technique
Needle manometer technique
Normal pressure = 20-30 mmHg
>30 mmHg need fasciotomy
Necrosis of the muscle happened 8 hours in 30 mmHg intra compartement
pressure
Lab
CPK, B.U.N., creatinin, aldolase, SGOT, LDH
Urine
Myoglobinuria, oliguria
EMG
SSEP
PROPER INITIAL
MANAGEMENT
Constrictive dressing should be removed or splint
Circumferential cast should be valued
Limb should be placed at the level of the heart
DEFINITIVE TREATMENT
Fasciotomy = skin & fascia are left open on > 30
mmHg pressure
Prophylactic fasciotomy should be performed on
Tibial osteotomy
Leg lenghtening
Arterial repair
Open tibial fracture
Genereous fluids (IVFD)
Alkalization urine by : bicarbonates or
acetazolamide
Antibiotic
COMPLICATION
Local
ischemic contracture
General
Renal failure
Cardiac arrest
Septicemia / septic shock
Death
Patophysiology and cause death of compartment
syndromes
Trauma / injury
Swelling / increases pressure in osteofascial
space
Microcirculation cuts off
Hypoxia Sistemic complication
Fasciotomy Cell / tissue death Infection
Pressure released K+ Release from cell Septicemia
Referfussion Hyper kalemia Septic shock
Myoglobulin in the muscle
released Cardiac arrest
Precitates in the renal tubule
Renal Failure
You might also like
- Syllabus For EMT BasicDocument10 pagesSyllabus For EMT BasicMichael B. San Juan100% (1)
- Paediatric Guidelines 2013-2014Document251 pagesPaediatric Guidelines 2013-2014Emad Adel100% (2)
- Burns in PaediatricDocument62 pagesBurns in PaediatricMusa yohana75% (4)
- CH 46 Complications of AnaesthesiaDocument29 pagesCH 46 Complications of AnaesthesiaChristian LeepoNo ratings yet
- Carcinoma Rectum - Janak - NEWDocument74 pagesCarcinoma Rectum - Janak - NEWTowhidulIslamNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia For The Pet Practitioner 2009 2 PDFDocument154 pagesAnesthesia For The Pet Practitioner 2009 2 PDFabibullaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular ExamDocument11 pagesCardiovascular ExamDonndulf Tizon Maningas100% (1)
- Acute Coronary Syndrome 052014Document91 pagesAcute Coronary Syndrome 052014Fatahillah NazarNo ratings yet
- Intradialytic Hypotension: Arwedi ArwantoDocument17 pagesIntradialytic Hypotension: Arwedi ArwantopiusiNo ratings yet
- Amls Als Pretest Version 1.11Document10 pagesAmls Als Pretest Version 1.11ArlanosaurusNo ratings yet
- Aspek Medikolegal Abortus Flo22 BaruDocument21 pagesAspek Medikolegal Abortus Flo22 BaruPusparasmi Mas Ayu SuprabhaNo ratings yet
- Double Lumen Catheter Dr. Ahmad GhozaliDocument20 pagesDouble Lumen Catheter Dr. Ahmad GhozaliastarimediantoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 - Postoperative Nursing ManagementDocument17 pagesChapter 20 - Postoperative Nursing ManagementTeemara KingNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Therapy For Peritonitis: Treatment Overview, Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis, Secondary and Tertiary PeritonitisDocument7 pagesAntibiotic Therapy For Peritonitis: Treatment Overview, Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis, Secondary and Tertiary PeritonitisTias SubagioNo ratings yet
- ShockDocument30 pagesShockvinnu kalyanNo ratings yet
- UTF-8''diarrhea 13-11-13Document32 pagesUTF-8''diarrhea 13-11-13yoga yogafenkanoNo ratings yet
- Lees BurnDocument20 pagesLees BurnJennifer DixonNo ratings yet
- Hemangiomas, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHemangiomas, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Tenosynovitis: Dr. Diyar A. SalihDocument32 pagesTenosynovitis: Dr. Diyar A. SalihsultantraNo ratings yet
- Hernia: and Other Digestive Congenital DiseaseDocument14 pagesHernia: and Other Digestive Congenital DiseaseLingga GumelarNo ratings yet
- Compartment Syndrome: Zulqaidandy RahmanDocument18 pagesCompartment Syndrome: Zulqaidandy RahmanMuhammad Shiddiq DwisuryaNo ratings yet
- Compartment SyndromeDocument10 pagesCompartment SyndromerobbyNo ratings yet
- Cervical Spine InjuriesDocument18 pagesCervical Spine InjuriesAnnapurna DangetiNo ratings yet
- Torsio Testis2016Document6 pagesTorsio Testis2016Patrico Rillah SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Clabsi DR - RonaldDocument19 pagesClabsi DR - RonaldsilviNo ratings yet
- Operasi Monokular Recess Resect Dengan Teknik: Hangback Pada Exotropia Deviasi BesarDocument10 pagesOperasi Monokular Recess Resect Dengan Teknik: Hangback Pada Exotropia Deviasi BesarBlack Clover IdNo ratings yet
- Episkleritis N Skleritis EditDocument12 pagesEpiskleritis N Skleritis EditAnonymous HgX3mN1oNo ratings yet
- Headache: Section BreakDocument40 pagesHeadache: Section BreakNicolas SimangunsongNo ratings yet
- Lapkas Fournier GangreneDocument29 pagesLapkas Fournier GangreneDavid Rainer Irianto HutajuluNo ratings yet
- 17 Brain VascularizationDocument86 pages17 Brain VascularizationMuhammad RidwanNo ratings yet
- 194 Surgical Cases PDFDocument160 pages194 Surgical Cases PDFkint100% (4)
- MALARIADocument34 pagesMALARIALisyah FadillahNo ratings yet
- Refreshing DHFDocument13 pagesRefreshing DHFNia Nurhayati ZakiahNo ratings yet
- An Approach To A Child With OedemaDocument14 pagesAn Approach To A Child With OedemaAdlina PutriantiNo ratings yet
- HERNIORRAPHY (Hernioplasty)Document37 pagesHERNIORRAPHY (Hernioplasty)Aldo AtjehNo ratings yet
- Taping OA Genu Dr. SIsca Susantio, Sp. KFRDocument11 pagesTaping OA Genu Dr. SIsca Susantio, Sp. KFRDsk IndryNo ratings yet
- Referat Kulit KakayDocument26 pagesReferat Kulit KakayRezky Dwiputra FellanysNo ratings yet
- Buttonhole DislocationDocument13 pagesButtonhole DislocationHanif Andhika WardhanaNo ratings yet
- ROZERPLASTYDocument13 pagesROZERPLASTYSaraya AmajidaNo ratings yet
- RozerplastyDocument4 pagesRozerplastyLutfi Aulia RahmanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Kasus: AppendisitisDocument50 pagesTutorial Kasus: Appendisitiseruza hiwatariNo ratings yet
- PPT Referat ADHD - Kevin LukitoDocument22 pagesPPT Referat ADHD - Kevin LukitonoviaNo ratings yet
- Hirschsprung DiseaseDocument20 pagesHirschsprung DiseaseIyan AsianaNo ratings yet
- Guildelines For Hiv Testing NacoDocument165 pagesGuildelines For Hiv Testing NacoNagendra Singh BeniwalNo ratings yet
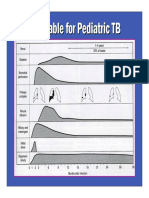
- Timetable For Pediatric TBDocument2 pagesTimetable For Pediatric TBAnnsh Hadji EliasNo ratings yet
- Pembahasan UKDI CLINIC 3 Batch Mei 2016Document662 pagesPembahasan UKDI CLINIC 3 Batch Mei 2016widi kusumaNo ratings yet
- K4. Diagnosis Holistik - EngDocument21 pagesK4. Diagnosis Holistik - EngBevila KorspoilvilNo ratings yet
- HipospadiaDocument66 pagesHipospadiaDichaNo ratings yet
- CombinedDocument3 pagesCombinedSolape Akin-WilliamsNo ratings yet
- CHOLANGIOCARCINOMADocument26 pagesCHOLANGIOCARCINOMAPremaKurnia100% (3)
- Pembahasan CBT COMBO 3Document802 pagesPembahasan CBT COMBO 3Sari Dewi WiratsihNo ratings yet
- Journal Reading Kista BartolinDocument16 pagesJournal Reading Kista BartolinAnnisa SaragiNo ratings yet
- Retinopati DiabetikDocument5 pagesRetinopati DiabetikMuhammad Afriadi HamdanNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Cancer Diagnosis and ManagementDocument45 pagesThyroid Cancer Diagnosis and Managementapi-3704562100% (1)
- Cme Acs 2. Stemi (Izzah)Document36 pagesCme Acs 2. Stemi (Izzah)Hakimah K. SuhaimiNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Toxoplasmosis: Diagnosis & ManagementDocument32 pagesCerebral Toxoplasmosis: Diagnosis & ManagementShinta DianNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Saraf PeriferDocument57 pagesAnatomi Saraf PeriferErreli K. KhusumawerdanieNo ratings yet
- Emergensi Urologi UiiDocument83 pagesEmergensi Urologi UiitrianaamaliaNo ratings yet
- Cholangiocarcinoma: R.KarthikeyanDocument49 pagesCholangiocarcinoma: R.KarthikeyanKarthikeyan R100% (2)
- 2 DHF InternaDocument59 pages2 DHF Internasaladass 2No ratings yet
- Epista Ks IsDocument27 pagesEpista Ks IsCynthia MelindaNo ratings yet
- Malignant Soft Tissue TumorsDocument21 pagesMalignant Soft Tissue TumorsEva GustianiNo ratings yet
- GestosisDocument12 pagesGestosisravannofanizzaNo ratings yet
- Referat Tumor OtakDocument29 pagesReferat Tumor OtakConsita Victoria100% (1)
- Sefalgia Kronik Dan Hemiparese Sinistra E.C. Space Occupying LesionDocument5 pagesSefalgia Kronik Dan Hemiparese Sinistra E.C. Space Occupying LesionrivienaNo ratings yet
- CLARA SKIN Who PDFDocument154 pagesCLARA SKIN Who PDFhasnul ramadhaniNo ratings yet
- Ujian Snake Bite RusmitaDocument33 pagesUjian Snake Bite RusmitaArina TsusayyaNo ratings yet
- Timebomb:The Global Epidemic of Multi-Drug Resistant TuberculosisFrom EverandTimebomb:The Global Epidemic of Multi-Drug Resistant TuberculosisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Sss Orthopedicemergencies 2012 Final Samuel-WongDocument38 pagesSss Orthopedicemergencies 2012 Final Samuel-WongMuhammad Irham FananiNo ratings yet
- Complicationsoffractures 120127084025 Phpapp02Document62 pagesComplicationsoffractures 120127084025 Phpapp02Aaliyah ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Complications of Multiple FracturesDocument35 pagesComplications of Multiple Fractureshello from the other sideNo ratings yet
- Chalkboard Background by SlidesgoDocument51 pagesChalkboard Background by SlidesgoshintaNo ratings yet
- DAFTAR PUSTAKA BaruDocument2 pagesDAFTAR PUSTAKA BarushintaNo ratings yet
- Dr. Jufri Latief (Penyembuhan Tulang, Tendo Dan Saraf)Document20 pagesDr. Jufri Latief (Penyembuhan Tulang, Tendo Dan Saraf)shintaNo ratings yet
- Outcome of Surgical Treatment of Pelvic Osteosarcoma: Hospital University Sains Malaysia ExperienceDocument3 pagesOutcome of Surgical Treatment of Pelvic Osteosarcoma: Hospital University Sains Malaysia ExperienceshintaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Nursing Thesis TopicsDocument4 pagesPediatric Nursing Thesis Topicsmonicacartergrandrapids100% (2)
- Norcet Notes PDFDocument4 pagesNorcet Notes PDFmonishaNo ratings yet
- Oct Dec 09Document112 pagesOct Dec 09G VenkateshNo ratings yet
- PresentationDocument13 pagesPresentationLohcchana MoganNo ratings yet
- Surgical Critical Care ReviewDocument70 pagesSurgical Critical Care ReviewSteven GodelmanNo ratings yet
- NCP Gouty ArthritisDocument21 pagesNCP Gouty ArthritisSeanmarie CabralesNo ratings yet
- DR Paul Harijanto - WS MALARIA-PIN PAPDI-19 PDFDocument33 pagesDR Paul Harijanto - WS MALARIA-PIN PAPDI-19 PDFMukhammadBurhanuddinNo ratings yet
- St. John Ambulance Malaysia: ShockDocument20 pagesSt. John Ambulance Malaysia: ShockJus KhooNo ratings yet
- MS CA and EN Ans KeyDocument15 pagesMS CA and EN Ans KeyAydh Dim-Mac RsclNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument15 pagesUntitledMayla De Vela RiveraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Thesis Sample PhilippinesDocument6 pagesNursing Thesis Sample Philippinesdngw6ed6100% (2)
- NCM 106 ReviewDocument21 pagesNCM 106 ReviewChristine PatriarcaNo ratings yet
- Dr. Nur Samsu, SPPD-KGH, FINASIM - ICD Pengenalan Dini Sepsis Di Layanan PrimerDocument37 pagesDr. Nur Samsu, SPPD-KGH, FINASIM - ICD Pengenalan Dini Sepsis Di Layanan PrimerWahyu PurnamaNo ratings yet
- Hemodynamic PathologyDocument9 pagesHemodynamic PathologyjoeNo ratings yet
- 2023 Management of Heart Failure RelatedCardiogenic ShockDocument7 pages2023 Management of Heart Failure RelatedCardiogenic ShockOscar AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Case Study... 22Document8 pagesNursing Case Study... 22Benjamin KelwonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Manag BURNDocument34 pagesNursing Manag BURNumi margi rahayuNo ratings yet
- Slemani Pediatric Teaching Hospital GuidelinesDocument93 pagesSlemani Pediatric Teaching Hospital GuidelinesHeersh RaofNo ratings yet
- Cebu Doctors' University College of Nursing Mandaue City, Cebu NCM 109 Theory Postnatal ComplicationsDocument47 pagesCebu Doctors' University College of Nursing Mandaue City, Cebu NCM 109 Theory Postnatal ComplicationsJanica Rose Maloloy-onNo ratings yet