Professional Documents
Culture Documents
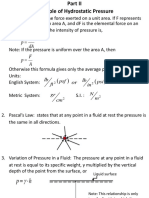
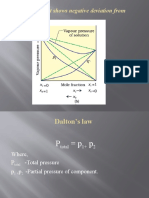
Where, P - Total Pressure P, P - Partial Pressure of Component
Uploaded by
PRAVIN0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views9 pagesERTYJKL
Original Title
Tt Ttttt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentERTYJKL
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views9 pagesWhere, P - Total Pressure P, P - Partial Pressure of Component
Uploaded by
PRAVINERTYJKL
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
Where,
Ptotal -Total pressure
p1 ,p2 -Partial pressure of component.
Fugacity: It is derived from Latin, expressed as
fleetness or escaping tendency. It is used
to study extensively phase and chemical reaction
equilibrium.
G = RT ln f +
- Is an constant depends on temperature and nature
of gas.
fugacity has same units as pressure for an ideal gas.
Fugacity coefficient () :
Fugacity coefficient is defined as the ratio of fugacity
of component to its pressure.
=f/P
- Is the measure of non ideal behavior of the gas.
Activity(a):
It is defined as the fugacity of the existing condition
to the standard state fugacity
a=f/ fo
Activity coefficient :
It measure the extent to which real solution depart from
ideality.
ln=bx
ln=bx
Wohls three suffix equation
Margules activity coefficient (UNIFAC) method
Using slope of ln curves
Using data at mid point
Redlich kister method
Using the coexistence equation
Using partial pressure data
Thank You
You might also like
- Fe Chemical EngineeringDocument5 pagesFe Chemical EngineeringJudith LugoNo ratings yet
- Working Guide to Vapor-Liquid Phase Equilibria CalculationsFrom EverandWorking Guide to Vapor-Liquid Phase Equilibria CalculationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Principles of Hydrostatic PressureDocument48 pagesPrinciples of Hydrostatic PressureChristian Duenas100% (2)
- Thermodynamic Models for Chemical Engineering: Design, Develop, Analyse and OptimizeFrom EverandThermodynamic Models for Chemical Engineering: Design, Develop, Analyse and OptimizeNo ratings yet
- Raoult's Law, Fugacity, Activity Coefficients, and Methods for Calculating Activity CoefficientsDocument14 pagesRaoult's Law, Fugacity, Activity Coefficients, and Methods for Calculating Activity CoefficientsPRAVINNo ratings yet
- Fugacity and Activity Coefficients in Phase EquilibriumDocument14 pagesFugacity and Activity Coefficients in Phase EquilibriumPRAVINNo ratings yet
- Composition in Gaseous Phase:: y P X P (I 1,2,3 ..N)Document8 pagesComposition in Gaseous Phase:: y P X P (I 1,2,3 ..N)PRAVINNo ratings yet
- Fugacity and Activity Coefficients in Gas MixturesDocument10 pagesFugacity and Activity Coefficients in Gas MixturesPRAVINNo ratings yet
- Vle 4Document15 pagesVle 4PRAVINNo ratings yet
- Vapour Liquid EquilibriumDocument15 pagesVapour Liquid EquilibriumPRAVINNo ratings yet
- Vap EquilibriumDocument14 pagesVap EquilibriumPRAVINNo ratings yet
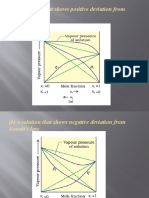
- (A) A Solution That Shows Positive Deviation From Raoult's LawDocument7 pages(A) A Solution That Shows Positive Deviation From Raoult's LawPRAVINNo ratings yet
- Effect of Pressure On VLE The High Pressure Diagrams Are Above Low PressureDocument7 pagesEffect of Pressure On VLE The High Pressure Diagrams Are Above Low PressurePRAVINNo ratings yet
- (B) A Solution That Shows Negative Deviation From Raoult's LawDocument9 pages(B) A Solution That Shows Negative Deviation From Raoult's LawPRAVINNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer Lecture 2: Thermodynamics and EquilibriumDocument2 pagesMass Transfer Lecture 2: Thermodynamics and EquilibriumRinaldi SaputraNo ratings yet
- Vapiquid IbriumDocument15 pagesVapiquid IbriumPRAVINNo ratings yet
- Fugacity - An Effective Pressure for Real GasesDocument47 pagesFugacity - An Effective Pressure for Real GasesShivani ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Project: TOPIC: Fugacity of Pure SubstancesDocument6 pagesThermodynamics Project: TOPIC: Fugacity of Pure SubstancesRaman K. BediNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics -II(2150503) Fugacity & Fugacity CoefficientDocument21 pagesChemical Engineering Thermodynamics -II(2150503) Fugacity & Fugacity CoefficientLaiba JanjuaNo ratings yet
- Vapour LiquidDocument5 pagesVapour LiquidPRAVINNo ratings yet
- Pure Component VLE in Terms of Fugacity: LiquidsDocument8 pagesPure Component VLE in Terms of Fugacity: Liquidsahad_shiraziNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Project-I: TopicDocument11 pagesChemical Engineering Thermodynamics Project-I: TopicRohit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Fugacity, Activity, and Standard StatesDocument5 pagesFugacity, Activity, and Standard Stateszion_buddha1253No ratings yet
- Vle 9Document10 pagesVle 9PRAVINNo ratings yet
- Fugacity ExplainedDocument9 pagesFugacity ExplainedKhawajaAsadNo ratings yet
- Non IdealDocument29 pagesNon IdealAmin SyazrinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2b KineticsDocument11 pagesChapter 2b KineticsSankar SasmalNo ratings yet
- Flash CalculationDocument12 pagesFlash CalculationHamidreza HasaniNo ratings yet
- SynopsisDocument13 pagesSynopsisShirish MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 4Document3 pagesChemistry 4Nothing is ImpossibleNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Lecture SummaryDocument26 pagesThermodynamics Lecture SummaryHan VendiolaNo ratings yet
- Prausnitz Thermodynamics Notes 26Document38 pagesPrausnitz Thermodynamics Notes 26Ramakrishna KoushikNo ratings yet
- Vapor-Liquid EquilibriumDocument2 pagesVapor-Liquid EquilibriumCornelius YudhaNo ratings yet
- Vle For DummiesDocument8 pagesVle For Dummiesira_rancicNo ratings yet
- Vapour Liquid EquilibriumDocument11 pagesVapour Liquid EquilibriumPRAVINNo ratings yet
- Chbe 346 Lecture 23 ReviewDocument72 pagesChbe 346 Lecture 23 ReviewJamie SamuelNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics IIIIIIIIDocument14 pagesChemical Engineering Thermodynamics IIIIIIIIDarnell HendersonNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry: Chemical EngineeringDocument11 pagesPhysical Chemistry: Chemical EngineeringEd Ryan RualesNo ratings yet
- Fugacity PDFDocument5 pagesFugacity PDFHannah TalindaNo ratings yet
- Activity CoefficientsDocument25 pagesActivity CoefficientsRajeev ReddyNo ratings yet
- Modeling Species Transport and Finite-Rate ChemistryDocument64 pagesModeling Species Transport and Finite-Rate ChemistryAzharuddin Ehtesham Farooqui100% (1)
- Kinetic Methods of Analysis: Chapter 15 - 1Document9 pagesKinetic Methods of Analysis: Chapter 15 - 1natsdorfNo ratings yet
- CRE 1 Materials - Unit 4 and 5Document69 pagesCRE 1 Materials - Unit 4 and 5Shivam SinghNo ratings yet
- 1st Law: Conservation of EnergyDocument85 pages1st Law: Conservation of EnergyAyu MilineaNo ratings yet
- Chemical-Reactor Design and EquilibriumDocument6 pagesChemical-Reactor Design and Equilibriumramesh pokhrelNo ratings yet
- CH.6 Fugacities in Liquid Mixtures: Excess Functions: 6.1 The Ideal SolutionDocument76 pagesCH.6 Fugacities in Liquid Mixtures: Excess Functions: 6.1 The Ideal SolutionSebastian BonanniNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Functions of SolutionsDocument2 pagesThermodynamic Functions of SolutionsBRENDA VIVIANA ARANDA JURADONo ratings yet
- An Overview of The Hamilton-Jacobi Equation - 21Document21 pagesAn Overview of The Hamilton-Jacobi Equation - 21John BirdNo ratings yet
- Chem Module Heat of ReactionDocument5 pagesChem Module Heat of ReactionSIR Arjay PerezNo ratings yet
- Fugacity and Phase RuleDocument17 pagesFugacity and Phase RuleHafsa IqbalNo ratings yet
- LIGSflashpointDocument2 pagesLIGSflashpointjonabelNo ratings yet
- Actual Molecular Mass Empirical Molecular Mass: Che 102 Chemistry For Engineers ReviewDocument8 pagesActual Molecular Mass Empirical Molecular Mass: Che 102 Chemistry For Engineers ReviewTariq Ceniza RasulNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering - Section of The FE - Chemical Engineering - Section of The FE Supplied-Reference Handbook - NCEESDocument5 pagesChemical Engineering - Section of The FE - Chemical Engineering - Section of The FE Supplied-Reference Handbook - NCEESjazz fraire bernalNo ratings yet
- What Is Equilibrium?Document12 pagesWhat Is Equilibrium?PRAVINNo ratings yet
- Review of Phase Equilibria - NEWDocument19 pagesReview of Phase Equilibria - NEWkarmawii taqatqaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering 301 Lecture Notes Chapters 13. Chemical-Reaction EquilibriaDocument5 pagesChemical Engineering 301 Lecture Notes Chapters 13. Chemical-Reaction EquilibriaJavier Moreno TapiaNo ratings yet
- Schmitz Lente Concepts KineticsDocument7 pagesSchmitz Lente Concepts Kineticsjesus castorenaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Properties Chart CorrelationsDocument44 pagesThermodynamic Properties Chart CorrelationsDavid RomeroNo ratings yet
- Thermometric Titrimetry: International Series of Monographs in Analytical ChemistryFrom EverandThermometric Titrimetry: International Series of Monographs in Analytical ChemistryNo ratings yet
- EconomicsDocument1 pageEconomicsPRAVINNo ratings yet
- DDDDocument2 pagesDDDPRAVINNo ratings yet
- CCCCDocument2 pagesCCCCPRAVINNo ratings yet
- B BBBBBBDocument3 pagesB BBBBBBPRAVINNo ratings yet
- OIUHGFDXZDocument5 pagesOIUHGFDXZPRAVINNo ratings yet
- Where, P - Total Pressure P, P - Partial Pressure of ComponentDocument3 pagesWhere, P - Total Pressure P, P - Partial Pressure of ComponentPRAVINNo ratings yet
- Yip=Xiγip (I= 1,2,…..,N) : Where Γi = Activity CoefficientDocument2 pagesYip=Xiγip (I= 1,2,…..,N) : Where Γi = Activity CoefficientPRAVINNo ratings yet
- Effect of Pressure On VLE The High Pressure Diagrams Are Above Low PressureDocument7 pagesEffect of Pressure On VLE The High Pressure Diagrams Are Above Low PressurePRAVINNo ratings yet
- ViumDocument11 pagesViumPRAVINNo ratings yet
- Ptotal and Partial Pressures in Gas MixturesDocument12 pagesPtotal and Partial Pressures in Gas MixturesPRAVINNo ratings yet
- SssssssDocument1 pageSssssssPRAVINNo ratings yet
- Asdfgh ERFLKLJHGFDGNjDocument2 pagesAsdfgh ERFLKLJHGFDGNjPRAVINNo ratings yet
- Vapiquid IbriumDocument15 pagesVapiquid IbriumPRAVINNo ratings yet
- Activity (A) :: It Is Defined As The Fugacity of The Existing Condition To The Standard State FugacityDocument4 pagesActivity (A) :: It Is Defined As The Fugacity of The Existing Condition To The Standard State FugacityPRAVINNo ratings yet
- SDFGHJDocument6 pagesSDFGHJPRAVINNo ratings yet
- RGHJDocument17 pagesRGHJPRAVINNo ratings yet
- ViumDocument11 pagesViumPRAVINNo ratings yet
- Vapiquid IbriumDocument15 pagesVapiquid IbriumPRAVINNo ratings yet
- Vapiquid IbriumDocument15 pagesVapiquid IbriumPRAVINNo ratings yet
- SDFGHJDocument6 pagesSDFGHJPRAVINNo ratings yet
- ViumDocument11 pagesViumPRAVINNo ratings yet
- Activity (A) :: It Is Defined As The Fugacity of The Existing Condition To The Standard State FugacityDocument4 pagesActivity (A) :: It Is Defined As The Fugacity of The Existing Condition To The Standard State FugacityPRAVINNo ratings yet
- ViumDocument11 pagesViumPRAVINNo ratings yet